
Problems
1. Fill in Table 1. Assume a fixed cost of $50.
Table 1
|
Output |
Variable Cost |
AFC |
AVC |
ATC |
MC |
|
1 |
$20 |
50 |
20 |
70 |
20 |
|
2 |
35 |
25 |
17.5 |
42.5 |
15 |
|
3 |
55 |
17 |
27.5 |
44.5 |
20 |
|
4 |
80 |
12,5 |
20 |
52.5 |
25 |
-
In the short run, when the output is zero, total cost is always equal to_______
fixed cost__________________________________________________.
-
Please label the firm's break-even point, shutdown point, and short-run, and long-run supply curves in Figure 2.
avc atc mc shut
down

4. To sketch a firm's average fixed cost curve and explain why it has that shape.
5. As price rises, what happens to the quantity supplied in a market? What are the two reasons for this?
6. This problem should be done in three steps.
First: Fill in Table 2. Assume fixed cost is $100 and price is $54.
Table 2
|
Output |
Variable Cost |
AFC |
AVC |
ATC |
MC |
|
1 |
$30 |
100 |
30 |
130 |
30 |
|
2 |
50 |
50 |
25 |
75 |
20 |
|
3 |
80 |
33 |
40 |
73 |
30 |
|
4 |
125 |
25 |
31 |
56 |
45 |
|
5 |
190 |
20 |
38 |
58 |
65 |
|
6 |
280 |
16.6 |
46.6 |
63.2 |
90 |
Table 3
|
If the Price Were |
What Would the Firm Do in the |
How Much Would Output Be in The Short Run? |
|
|
Long Run? |
Short Run? |
||
|
$90 |
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
Second: Use the graph paper to draw a graph of the firm's demand, marginal revenue, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves. Be sure you label the graph correctly. On the graph, indicate the break-even and shutdown points and the firm's short-run and long-run supply curves.
Third: Calculate total profit in the space below, then answer questions a through c.
a. The minimum price the firm would accept in the short run would be $__
b. The minimum price the firm would accept in the long run would be $__
c. The output at which the firm would maximize profits would be____.
Supply and demand Multiple-Choice Questions
1. An increase in supply while demand remains unchanged will lead to
a. an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
b. a decrease in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
c. an increase in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
d. a decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
2. A decrease in demand while supply remains unchanged will lead to
a. an increase in equilibrium price and quantity
b. a decrease in equilibrium price and quantity
c. an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
d. a decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
3. As price rises,
a. quantity demanded and quantity supplied both rise
b. quantity demanded and quantity supplied both fall
c. quantity demanded rises and quantity supplied falls
d. quantity demanded falls and quantity supplied rises
Table 1
|
Price |
Quantity Demanded |
Quantity Supplied |
|
$12 |
10 |
15 |
|
11 |
14 |
10 |
|
10 |
20 |
5 |
Use Table 1 to answer questions 4 and 5.
4. The equilibrium price is about
a. $11.25
b. $11.40
c. $11.50
d. $11.60
e. $11.75
5. Equilibrium quantity is about
a. 12
b.12.3
c. 12.5
d. 12.8
e. 13
6. Demand for a good or service may be depicted in
a. a table, but not a graph
b. a graph, but not a table
c. both a graph and a table
d. neither a graph nor a table
7. When quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, there
a. is a shortage
b. is a surplus
c. may be either a shortage or a surplus
d. may be neither a shortage nor a surplus
8. When quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
a. price will fall to its equilibrium level
b. price will rise to its equilibrium level
c. price may rise, fall, or stay the same, depending on a variety of factors.
Use Figure 1 to answer questions 9 and 10.
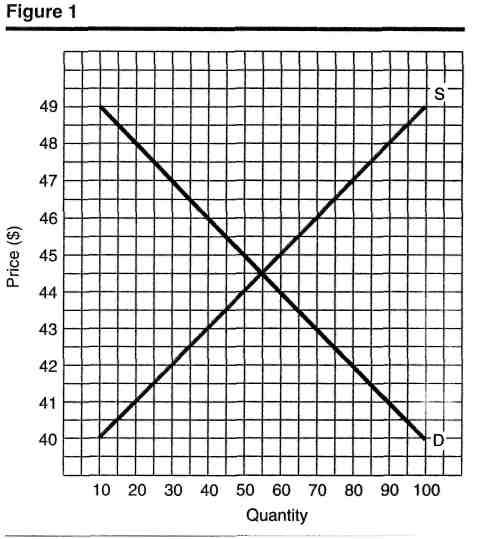
9. At a market price of $47, there is
a. a shortage
b. a surplus
c. both a shortage and a surplus
d. neither a shortage nor a surplus
10. At a market price of $42, there is
a. a shortage
b. a surplus
c. both a shortage and a surplus
d. neither a shortage nor a surplus
11. In Figure 2, an increase in demand and supply leads to
a. an increase in equilibrium price and quantity
b. a decrease in equilibrium price and quantity
c. an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
d. a decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity

12. In general, an increase in demand and supply will lead to
a. a definite increase in equilibrium quantity
b. a definite increase in equilibrium price
c. a definite increase in equilibrium price and quantity
d. a definite increase in neither equilibrium price nor quantity
