
ECHO 2013 / Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
.pdf
HOCM
vs Hypertrophy of the Athlete
Palka et al. JACC 1997;30:760-8.

Fabry’s Disease
•X-linked recessive disorder
•Gene mutations results in a deficiency in the enzyme alpha - galactosidase
•Accumulation of glycosphingolipids
•Dx by laboratory test showing low levels of enzyme, genetic testing
•Endomyocardial biopsy shows inclusion bodies in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
•Responds to enzyme replacement therapy
HCM
Fabry’s

Metabolic Diseases Mimicking HCM
Glycogen storage disease II) Pompe’s disease
(Glycogen storage disease III (Forbes’ disease)
Carnitine deficiency
Phosphorylase B kinase deficiency
Infant of diabetic mother
AMP kinase (WPW, HCM, conduction disease)
Debrancher enzyme deficiency
Hurler’s syndrome
Hurler-Scheie disease
Hunter’s syndrome
Mannosidosis
Fucosidosis
Total lipodystrophy
Mitochondrial cytopathy

HCM
Pathophysiology
•LVOT obstruction
30% of the cases
Caused by outflow tract narrowing and abnormal elongation of the mitral leaflets
Static or dynamic (exercise, vasodilators)
False positive induced by inotropics (dobutamine)
Symptoms depend upon the timing of obstruction
In general, symptoms when peak gradient > 50 mmHg

Differential Diagnosis
Sub-valvular Membrane |
HOCM |

Imaging in Hypertrophic
Cardiomyopathy
•Diagnosis
•Evaluation of Symptoms
•Screening
•Therapy Guidance
Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
Relief of LVOT obstruction
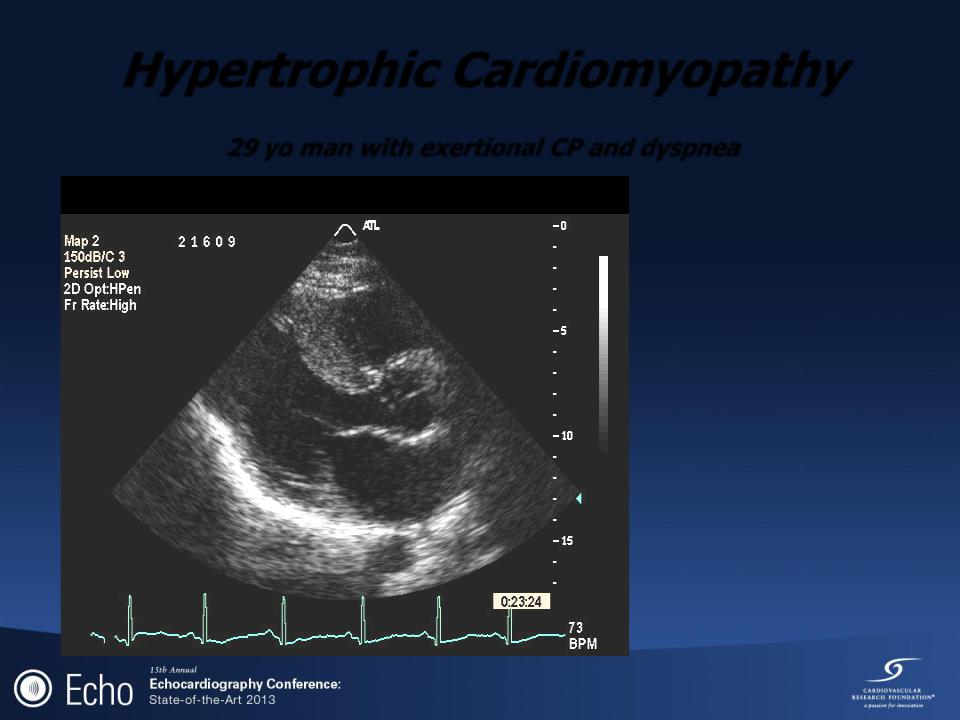
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
29 yo man with exertional CP and dyspnea
No Hx. of syncope
Adopted
LVH with strain
Frequent NSVT

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
29 yo man with exertional CP and dyspnea
No SAM or gradient at rest
Exercise treadmill test:
8.5 METS Chest pain
PVC’s
SAM with peak
dynamic gradient of 64mmHg 3+MR

HOCM
Determinants of symptoms
Wigle, Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1985;28:1

LV torsion and Diastolic Function
*Systolic Torsion is net sum of basal CW and apical CCW twist
Basal level
“LV torsion”
During systole
Apical level
Notomi Y, Circulation 2005
