
ECHO 2013 / Management Decisions in the ICU and ER The Role of the FOCUS Echo
.pdf
Management Decisions in the ICU
and ER: The Role of the FOCUS
Echo
Rebecca T. Hahn, MD, FACC, FASE
Director of Interventional Echocardiography
Columbia University
No Disclosures


11 core or primary emergency ultrasound applications
American College of Emergency Physicians. Emergency ultrasound guidelines 2008.
Available at: http://www.acep.org. Accessed November 1, 2009.

Mayo PH et al. CHEST 2009; 135:1050–1060

Critical Care Ultrasonography
(CCUS)
•Two categories
General critical care ultrasonography (GCCUS) [thoracic, abdominal, and vascular]
Echocardiography (basic and advanced)
•Advanced critical care echocardiography (CCE) is performed and
interpreted by the intensivist at the bedside to establish diagnoses and to guide therapy of pts with cardiopulmonary compromise
Basic CCE is performed as a goal-directed examination using
transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) or transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) 2D imaging to identify specific findings and to answer straightforward clinical questions.
Advanced CCE allows the intensivist to perform a comprehensive evaluation of cardiac anatomy and function including hemodynamic assessment using TTE or TEE 2D and Doppler echocardiography
Mayo PH et al. CHEST 2009; 135:1050–1060


Principal Role of FOCUS
•Time-sensitive assessment of the symptomatic patient.
Assessment for pericardial effusion
Evaluation of relative chamber size, global cardiac function
Assessment of patient volume status
•LV size and function
•IVC size and respirophasic variability
•Guide for emergent invasive procedures
Pericardiocentesis
Position of transvenous pacemaker placement
•All other pathologic findings may be suspected on a FOCUS
Require additional evaluation
•Comprehensive Echocardiography
•Cardiology consultation
Labovitz AJ et al. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010;23:1225-30.

Role of Comprehensive
Echocardiography
•Advanced hemodynamic assessment
Intracardiac pressures
Valvular function
Diastolic function
•Advanced Imaging Interpretation
Regional wall motion abnormalities
Specific cardiac diagnoses
•Myocardial disease (ie: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy)
•Intracardiac Masses
Labovitz AJ et al. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010;23:1225-30.
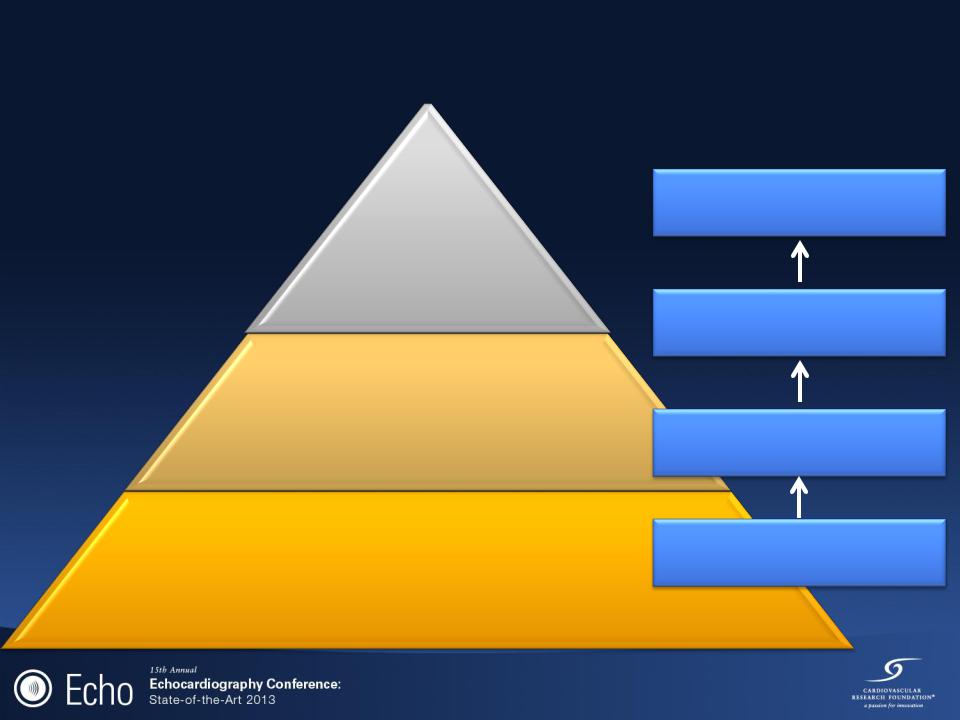
The „pyramid‟ of echocardiography skills in the
ICU
Full range of cardiac
Diagnosis & complete hemodynamic evaluation
Detect gross valvular dysfunction
Assessment of fluid responsiveness
Measure CO, PASP, and detect ACP
Quantitative assessment of LV function
Detect large pericardial effusion Recognize marked RV dilatation Measure inferior vena cava diameter
Recognize severely impaired LV function (twodimensional imaging only)
Trained operators, supervisors, teachers
Diagnostic level knowledge and skills
Good TTE knowledge and proficiency
Limited echo/pattern recognition
Orme et al. Br J Anaesth 2009; 102: 340–4

•Two hundred and fifty-eight echocardiograms were performed in 217 patients, of which 224 (86.8%) were performed by intensive care consultants.
•187 studies (72.4%) were TTEs
•71 (27.8%) were TEEs
•TTE provided diagnostic images in 91.3% of spontaneously breathing and 84.2% of mechanically ventilated patients.
•Management was changed directly as a result of information provided in 51.2% of studies.
•Changes included fluid administration, inotrope or drug therapy, and treatment limitation.
Orme et al. Br J Anaesth 2009; 102: 340–4
