
ECHO 2013 / Management Decisions in the ICU and ER The Role of the FOCUS Echo
.pdf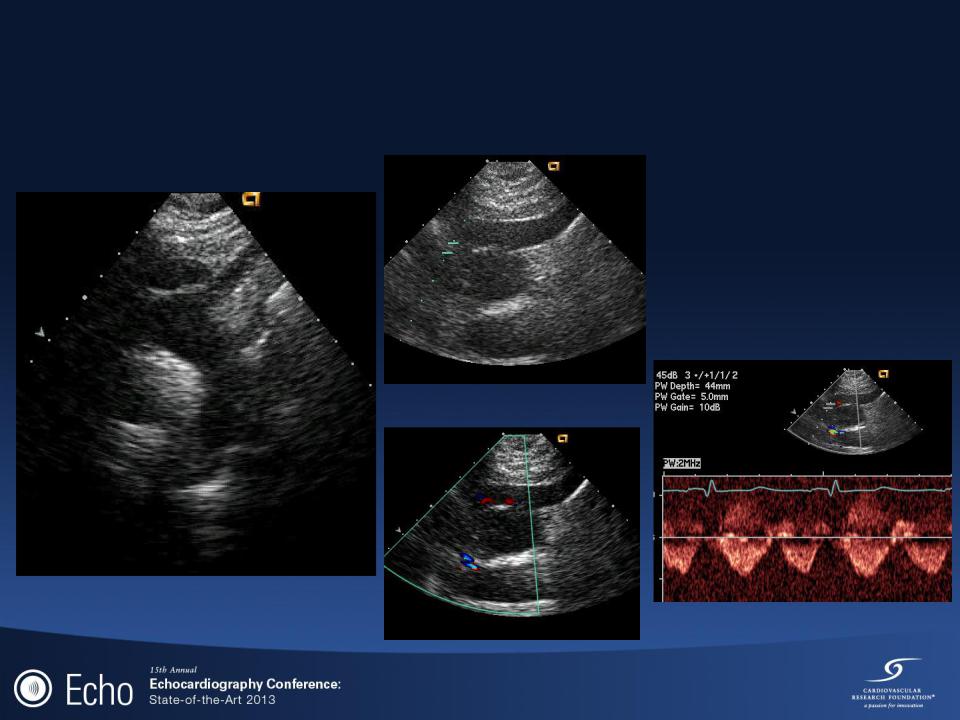
Comprehensive Echo Imaging the
Superior Vena Cava
Suprasternal Notch
View

TTE 11/26
Mitral Valve Inflow (33% respirophasic variability)
Lateral TDI (E’ = 8 cm/s)
TR (Vmax = 3.0 m/s)
Medial TDI (E’ ~12 cm/s)

PERICARDIOCENTESSIS
•Define the best trajectory for needle insertion by imaging the fluid collection from the most appropriate transthoracic window (commonly the subcostal)
•Subcostal/subxiphoid window
The probe is placed transversely at the left costal margin at the level of the subxiphoid process with the ultrasound beam aimed at the patient‟s left shoulder.
The structures closest to the probe will appear on top of the screen display with the liver being a landmark.
The liver borders the right ventricle of the heart.
The pericardial effusion (which is INFERIOR to the heart border) will appear as an anechoic area surrounding the heart.
Tibbles, CD and Porcaro W. Emerg Med Clin North
Am.2004;22(3):797-815.

Global Cardiac Systolic Function
•FOCUS is performed to assess global function and differentiates patients into „„normal‟‟ or minimally impaired function versus „„depressed‟‟ or significantly impaired function
•Indications:
Acute shortness of breath
Cardiac trauma
•Evaluation of segmental wall motion abnormalities and other causes of shortness of breath (e.g., valvular dysfunction) can be challenging and should be assessed by performing a comprehensive echocardiogram.
Labovitz AJ et al. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010;23:1225-30.

Normal

Abnormal
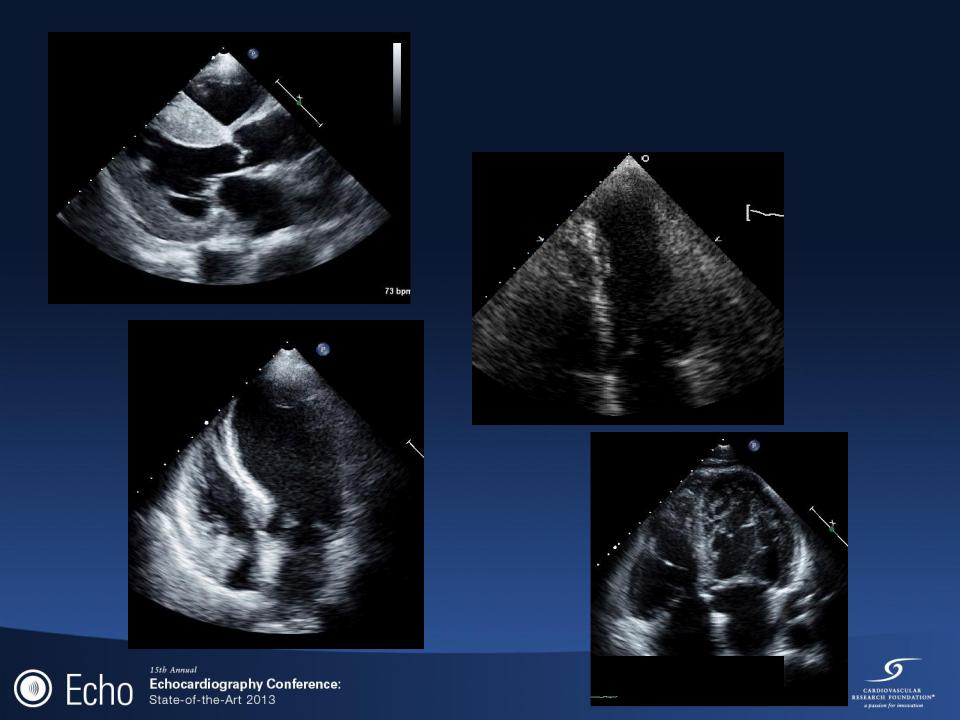
Amyloid
Apical
Aneurysm
Takotsubo
Left
Ventricle
Noncompaction

Right ventricular enlargement
•FOCUS is performed in patients with suspected pulmonary embolus is to prioritize further testing, alter differential diagnosis assessments, and assist with treatment decisions in the severely compromised patient
•Once the diagnosis is established, it is recommended to further assess the size and function of the RV using comprehensive echocardiography
•Pulmonary Embolus Echocardiographic Findings:
Right ventricular dilatation (>1:1 RV/LV ratio), Sn = 29%
Decreased right ventricular systolic function, Sn = 51%
•Both: Sn = 52-56%
Visualizing free-floating thrombus
Labovitz AJ et al. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010;23:1225-30.

Acute Pulmonary Embolus

Acute Pulmonary Embolus
Initial Study: Subcostal
