- •Contents
- •1. Pharmacokinetics
- •3. Practice Questions
- •2. Antiarrhythmic Drugs
- •3. Antihypertensive Drugs
- •3. Anticonvulsants
- •5. Opioid Analgesics
- •8. Drugs of Abuse
- •1. Antibacterial Agents
- •4. Antiprotozoal Agents
- •1. Histamine and Antihistamines
- •3. Drugs Acting on Serotonergic Systems
- •1. Drugs Used in Diabetes
- •2. Steroid Hormones
- •6. Endocrine Drug List
- •1. Anticancer Drugs
- •1. Immunopharmacology
- •1. Toxicology
- •2. Toxicology Practice Questions
- •Index

Histamine and Antihistamines |
1 |
HISTAMINE
•Histamine is an autacoid present at high levels in the lungs, skin, and the gastrointestinal tract and is released from mast cells and basophils bytype I hypersensitivity reactions, drugs, venoms, and trauma.
•Histamine receptors are ofthe serpentine family, with seven transmem brane-spanning domains with G-protein-coupled second messenger effectors.
-H1 activation
0 i capillary dilation (via NO) -7J, BP
0 i capillary permeability -7i edema
0 i bronchiolar smooth muscle contraction (via IP3 and DAG release)
0 i activation ofperipheral nociceptive receptors -7i pain and pruritus
0J, AV nodal conduction
-H2 activation
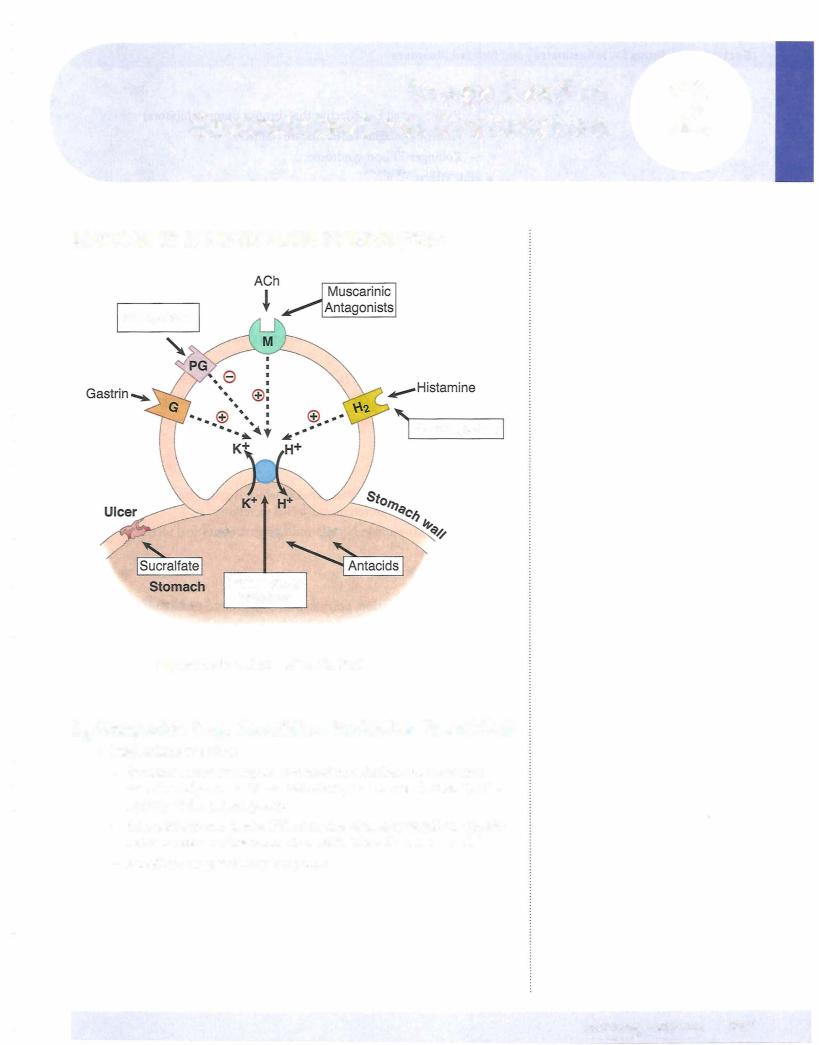
0i gastric acid secretion -7i gastrointestinal ulcers
0i SA nodal rate, positive inotropism, and automaticity
H1 ANTAGONISTS
•Mechanism of action:
-H1 antagonists act as competitive antagonists ofhistamine and there fore may be ineffective at high levels ofhistamine.
-Vary in terms ofboth pharmacologic and kinetic properties, but all require hepatic metabolism and most cross the placental barrier.
MEDICAL 217


Section VI • Drugs for Inflammatory and Related Disorders
•Uses:
-PUD (overall less effective than proton pump inhibitors)
-Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
-Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
•Side effects:
-Cimetidine is a major inhibitor of P450 isoforms drug interaction via i effects
-Cimetidine J, androgens gynecomastia and J, libido
Proton Pump Inhibitors
• Mechanism ofaction:
- Omeprazole and related"-prazoles" are irreversible, direct inhibitors ofthe proton pump (K+/H+ antiport) in the gastric parietal cell
•Uses:
-More effective than H2 blockers in peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
-Also effective in GERD and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
-Eradication regimen for H. pylori
Misoprostol
•Mechanism ofaction: PGE1 analog, which is cytoprotective i mucus and bicarbonate secretion and J, HCl secretion
•Uses: Selective use in NSAID-induced gastrointestinal ulcers
Sucralfate
•Mechanism of action: polymerizes on gastrointestinal luminal surface to form a protective gel-like coating ofulcer beds. Requires acid pH (antacids may interfere)
•Uses: i healing and J, ulcer recurrence
Bismuth Subsalicylate
•Mechanism ofaction: like sucralfate, binds selectively to ulcer, coating it, and protecting it from acid and pepsin
•Combined with metronidazole and tetracycline to eradicate H. pylori (BMT regimen)
220 MEDICAL