
Topic 3
.2.pdf
06/10/2012 |
©Elena G. Serova serovah@gmail.com |
1 |
|
|
|
ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION
Elena G. Serova,
PhD in Economics,
Associate professor
St. Petersburg State University of Economics and Finance
serovah@gmail.com

06/10/2012 |
©Elena G. Serova serovah@gmail.com |
Страница 2 |
|
|
|
Course content and structure
Course introduction
Topic 1. Economics and Innovations
Basic definitions and concepts. People, organizations and innovation
Topic 2. Information and Knowledge Management
Information and decision making. Knowledge management in organizations.
Topic 3. Innovation Management in the Knowledge-driven Economy.
Managing Knowledge for Innovation. Business Innovation Models and Strategy.
Topic 4. ICT for Innovation Economics The Role ICT in the knowledge driven economy. Knowledge Management Systems.
Conclusion
06/10/2012 |
©Elena G. Serova serovah@gmail.com |
3 |
|
|
|
Topic 3. Innovation Management in the Knowledge-driven
Economy
•Theme 5. Managing knowledge for innovation. Innovation as an interactive process. Impact of knowledge on innovation dynamics. Open innovation. Innovation Management Techniques. Case-study.
•Theme 6. Business Innovation Models and Strategy.
Theoretical foundation of business models. Examples of business models. Business models as innovation. Business Models, business strategy, and competitive advantage. Open innovation and open business models.

Def_Business Model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value.
In short, a business model defines the organizational and financial 'architecture' of a business (Chesbrough and
Rosenbloom, 2002). The business model makes implicit assumptions about the behavior of revenues and costs, the nature of user needs, and likely competitor behavior. It outlines the logic required to earn a profit, if a profit is available to be earned. Once adopted the business model defines the way the enterprise 'goes to market.
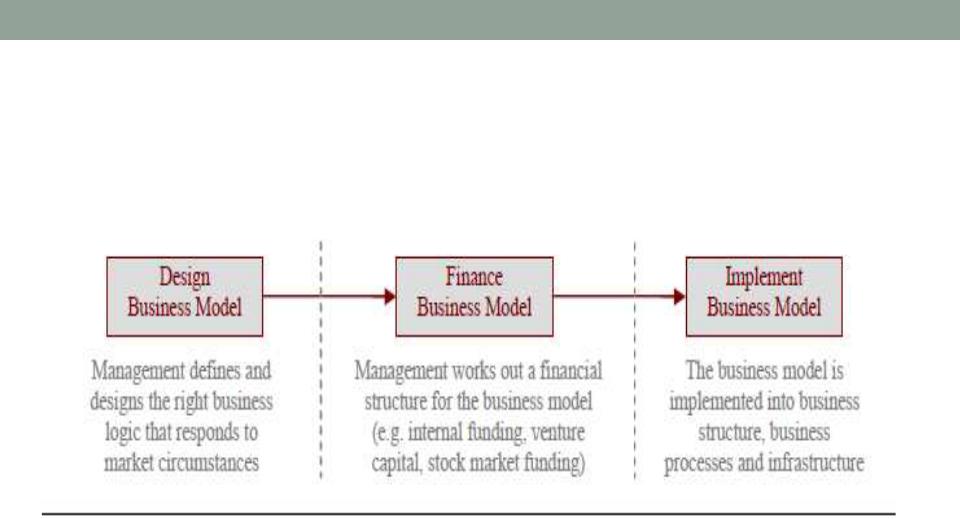
Business Model steps
(Alexander Osterwalder)
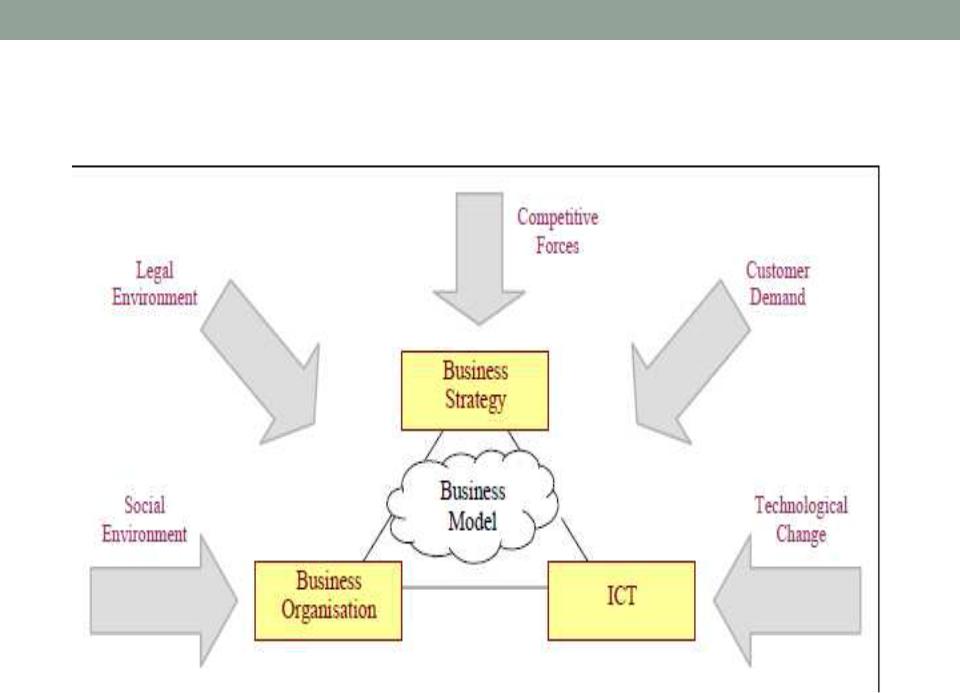
Environment, business model, strategy, process and information systems (Alexander Osterwalder)
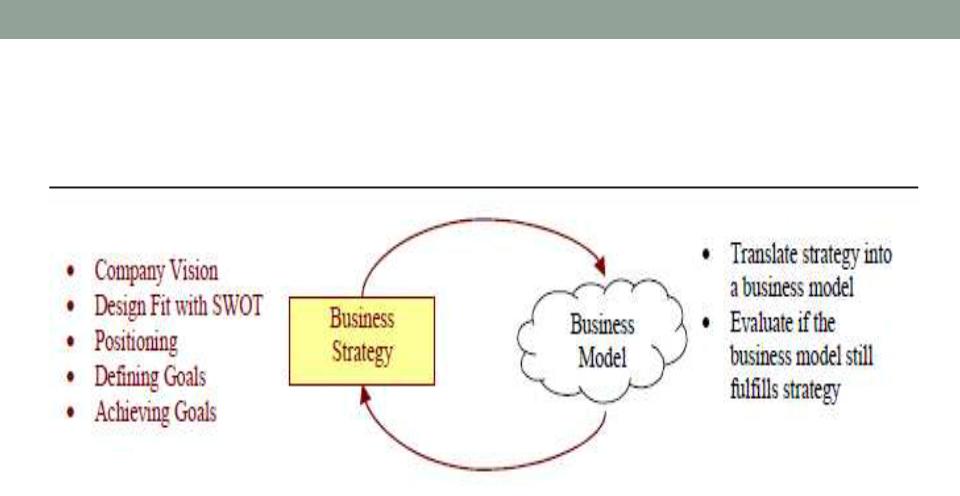
Business strategy and business model (Alexander Osterwalder)
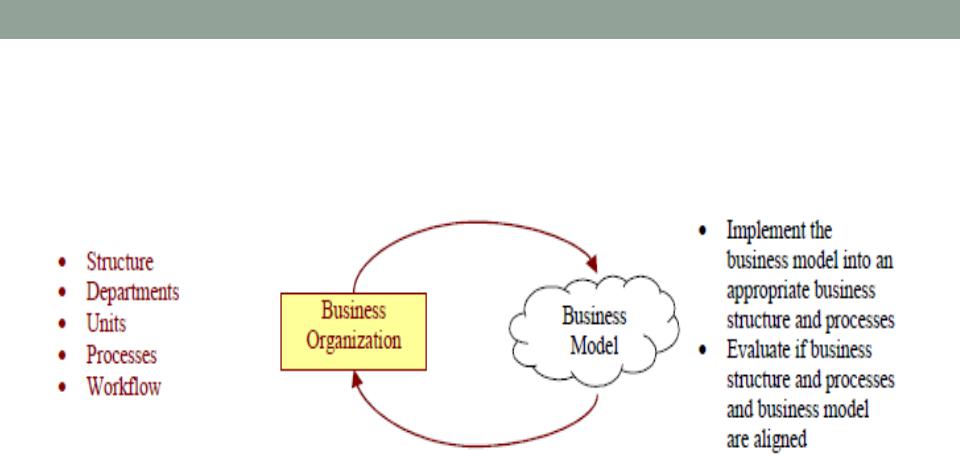
Business organization and business mode (Alexander Osterwalder)

ICT and business model (Alexander Osterwalder)

Business model design involves assessments with respect to determining (David J. Teece):
(1)the identity of market segments to be targeted;
(2)the benefit the enterprise will deliver to the customer;
(3)the technologies and features that are to be embedded in the product and service;
(4)how the revenue and cost structure of a business is to be 'designed' (and if necessary 'redesigned') to meet customer needs;
(5)the way in which technologies are to be assembled and offered to the customer; and
(6)the mechanisms and manner by which value is to be captured, and competitive advantage sustained.
