
Operators
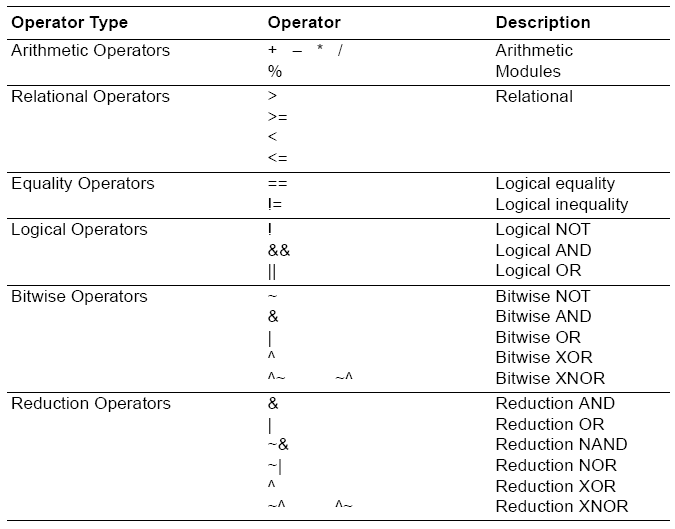

** ... Power Operator (i.e. 2**8 returns 256)
= = = .. Inputs Equal including X and Z (simulation only)
! = = .. Inputs Not Equal including X and Z (simulation only)
<<< ... Left shift and maintain sign bit
>>> ... Right shift and maintain sign bit

Operands
• Numbers


![]()
• Wires and registers (wire, reg)
- Bit-selects
wire [7:0] a,b,c;
assign c[0] = a[0] & b[0];
-
Part-selects
assign c[7:0] = a[7:0] & b[7:0]
• Function calls
Verilog allows you to call one function from inside an expression and use the return value from the called function as an operand.
assign error = legal(in1, in2);
Concatenation of Operands
wire [7:0] byte;
wire [3:0] nibble1, nibble2;
assign byte = {nibble1,nibble2};
Functional Descriptions
• Sequential Constructs
Sequential Statements
x = b;
if (y) x = x + a;
Equivalent Combinational Description
if (y) x = b + a; else x = b;
Function Declarations
A user defined function is a set of Verilog statements that can be called from elsewhere within the body of the code by an assignment. A funcion can have multiple inputs however can return only a single output. No timing information can be specified within a function.
• Input declarations
• Output from a function
• Register declarations
• Memory declarations
• Parameter declarations
• Integer declarations
function [<lower>:<upper>] <output_name> ;
input <name>;
begin
<statements>
end
endfunction
Example
function [9:0] gray_encode;
input [9:0] binary_input;
begin
gray_encode[9] = binary_input[9];
for (k=8; k>=0; k=k-1) begin
gray_encode[k] = binary_input[k+1] ^ binary_input[k];
end
end
endfunction
assign FIFO_ADDR = gray_encode(write_count);
Integer variables are local or global variables that hold numeric values. The syntax for an integer declaration is
integer identifier_list;
You can declare integer variables locally at the function level or globally at the module level. The default size for integers is 32 bits.
Function Statements
• Procedural assignments
Procedural assignments are assignment statements used inside a function. The left side of a procedural assignment can contain only reg variables and integers.
sum = a + b;
control[5] = (instruction == 8’h2e);
{carry_in, a[7:0]} = 9’h 120;
• RTL assignments
RTL Nonblocking Assignments
module rtl (clk, data, regc, regd);
input data, clk;
output regc, regd;
reg regc, regd;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
regc <= data;
regd <= regc;
end
endmodule

Blocking Assignment
module rtl (clk, data, rega, regb);
input data, clk;
output rega, regb;
reg rega, regb;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
rega = data;
regb = rega;
end
endmodule

• begin...end block statements
begin : block_name
reg local_variable_1;
integer local_variable_2;
parameter local_variable_3;
... statements ...
end
• if...else statements
if ( e xpr )
begin ... statements ... end
else
begin ... statements ... end
• case, casex, and casez statements
case ( expr )
case_item1: begin ... statements ... end
case_item2: begin ... statements ... end
default: begin ... statements ... end
endcase
Example
case (<input>)
2'b00 : <output> <= 4'b0001;
2'b01 : <output> <= 4'b0010;
2'b10 : <output> <= 4'b0100;
2'b11 : <output> <= 4'b1000;
default : <output> <= 4'b0000;
endcase
• for loops
for (index = low_range; index < high_range; index = index + step)
for (index = high_range; index > low_range; index = index - step)
for (index = low_range; index <= high_range ;index = index + step)
for (index = high_range; index >= low_range ;index = index - step)
Ex: for ( i=0; i < 8; i=i+1 ) c[i] = a[i] & b[7-i];
• while loops
while (<condition>) begin <statement>; end
• forever loops
forever begin <statement>; end
• disable statements
disable <loop_identifier>;
• task Statements
Task statements are similar to functions, but task can have any number of inputs, outputs and inouts as well as contain timing information.
task <task_name>;
input <input_name>;
<more_inputs>
output <output_name>;
<more_outputs>
begin <statements>; end
endtask
<task_name>(<comma_seperated_inputs>, <comma_seperated_outputs>);
Only reg variables can receive output values from a task; wire variables cannot.
• always Blocks
An always block can imply latches or flip-flops, or it can specify purely combinational logic. An always block can contain logic triggered in response to a change in a level or the rising or falling edge of a signal.
always @ ( event-expression [or event-expression*] )
begin ... statements ... end
• A change in a specified value
always @ ( identifier ) begin ... statements ... end
• The rising/ falling edge of a clock
always @ ( posedge event ) begin ... statements ... end
always @ ( negedge event ) begin ... statements ... end
Accumulator
parameter ACC_SIZE=<accumulator_width>;
reg [ACC_SIZE-1:0] <accumulate_out>;
always @ (posedge <clock> or posedge <reset>)
if (<reset>)
<accumulate_out> <= 0;
else if (<clock_enable>)
<accumulate_out> <= <accumulate_out> + <accumulate_in>;
Adder
parameter ADDER_WIDTH = <adder_bit_width>;
wire [ADDER_WIDTH-1:0] <a_input>;
wire [ADDER_WIDTH-1:0] <b_input>;
wire [ADDER_WIDTH-1:0] <sum>;
assign <sum> = <a_input> + <b_input>;
Comparator
reg <output>;
always @(posedge <clock> or posedge <reset>)
if (<reset>)
<output> <= 1'b0;
else if (<input1> > <input2>)
<output> <= 1'b1;
else
<output> <= 1'b0;
Counter
reg [<upper>:0] <reg_name>;
always @(posedge <clock> or posedge <reset>)
if (<reset>)
<reg_name> <= 0;
else if (<clock_enable>)
if (<load_enable>)
<reg_name> <= <load_signal_or_value>;
if (<up_down>)
<reg_name> <= <reg_name> + 1;
else
<reg_name> <= <reg_name> - 1;
Decoder
reg [3:0] <output>;
<reg_or_wire> [1:0] <input>;
always @(posedge <clock> or posedge <reset>)
if (<reset>)
<output> <= 4'h0;
else
case (<input>)
2'b00 : <output> <= 4'b0001;
2'b01 : <output> <= 4'b0010;
2'b10 : <output> <= 4'b0100;
2'b11 : <output> <= 4'b1000;
default : <output> <= 4'b0000;
endcase
Encoder
reg [1:0] <output>;
<reg_or_wire> [3:0] <input>;
always @(posedge <clock> or posedge <reset>)
if (<reset>)
<output> <= 2'b00;
else
case (<input>)
4'b0001 : <output> <= 2'b00;
4'b0010 : <output> <= 2'b01;
4'b0100 : <output> <= 2'b10;
4'b1000 : <output> <= 2'b11;
default : <output> <= 2'b00;
endcase
Multiplexer
always @(<2-bit_select>, <input1>, <input2>, <input3>, <input4>)
case (<2-bit_select>)
2'b00: <output> = <input1>;
2'b01: <output> = <input2>;
2'b10: <output> = <input3>;
2'b11: <output> = <input4>;
endcase
Register
always @(posedge <clock> ) begin
if (!<reset>) begin
<reg> <= 1'b0;
end
else if (<clock_enable>) begin
<reg> <= <signal>;
end
Shift Register
parameter piso_shift = <shift_width>;
reg [piso_shift-2:0] <reg_name>;
reg <output>;
always @(posedge <clock> or negedge <reset>)
if (!<reset>) begin
<reg_name> <= 0;
<ouput> <= 1'b0;
end
else if (<load_signal>) begin
<reg_name> <= <input>[piso_shift-1:1];
<ouput> <= <input>[0];
end
else if (<clock_enable>) begin
<reg_name> <= {1'b0, <reg_name>[piso_shift-1:1]};
<output> <= <reg_name>[0];
end
