
- •Block Reference
- •Commonly Used
- •Continuous
- •Discontinuities
- •Discrete
- •Logic and Bit Operations
- •Lookup Tables
- •Math Operations
- •Model Verification
- •Model-Wide Utilities
- •Ports & Subsystems
- •Signal Attributes
- •Signal Routing
- •Sinks
- •Sources
- •User-Defined Functions
- •Additional Math & Discrete
- •Additional Discrete
- •Additional Math: Increment — Decrement
- •Run on Target Hardware
- •Target for Use with Arduino Hardware
- •Target for Use with BeagleBoard Hardware
- •Target for Use with LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Hardware
- •Blocks — Alphabetical List
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Settings Pane
- •Measurements Pane
- •Signal Statistics Measurements
- •Settings Pane
- •Transitions Pane
- •Overshoots/Undershoots
- •Cycles
- •Settings Pane
- •Peaks Pane
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Command-Line Information
- •Function Reference
- •Model Construction
- •Simulation
- •Linearization and Trimming
- •Data Type
- •Examples
- •Main Toolbar
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Command-Line Alternative
- •Mask Icon Drawing Commands
- •Simulink Classes
- •Model Parameters
- •About Model Parameters
- •Examples of Setting Model Parameters
- •Common Block Parameters
- •About Common Block Parameters
- •Examples of Setting Block Parameters
- •Block-Specific Parameters
- •Mask Parameters
- •About Mask Parameters
- •Notes on Mask Parameter Storage
- •Simulink Identifier
- •Simulink Identifier
- •Model Advisor Checks
- •Simulink Checks
- •Simulink Check Overview
- •See Also
- •Identify unconnected lines, input ports, and output ports
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check root model Inport block specifications
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check optimization settings
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check for implicit signal resolution
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check for optimal bus virtuality
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •See Also
- •Identify disabled library links
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Identify parameterized library links
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Identify unresolved library links
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •See Also
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •See Also
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Capabilities and Limitations
- •See Also
- •Check usage of function-call connections
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check signal logging save format
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check data store block sample times for modeling errors
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check for potential ordering issues involving data store access
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check for partial structure parameter usage with bus signals
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check for calls to slDataTypeAndScale
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check for proper bus usage
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Action Results
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check for proper Merge block usage
- •Description
- •Input Parameters
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Action Results
- •See Also
- •Check for non-continuous signals driving derivative ports
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Runtime diagnostics for S-functions
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Check file for foreign characters
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check model for known block upgrade issues
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Action Results
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Action Results
- •See Also
- •Check that the model is saved in SLX format
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Check Model History properties
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Analyze model hierarchy for upgrade issues
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •Tips
- •See Also
- •Description
- •Results and Recommended Actions
- •See Also
- •Simulink Performance Advisor Checks
- •Simulink Performance Advisor Check Overview
- •See Also
- •Baseline
- •See Also
- •Check Preupdate Items
- •See Also
- •Checks that need Update Diagram
- •See Also
- •Checks that require simulation to run
- •See Also
- •Check Accelerator Settings
- •See Also
- •Create Baseline
- •See Also
- •Identify resource intensive diagnostic settings
- •See Also
- •Check optimization settings
- •See Also
- •Identify inefficient lookup table blocks
- •See Also
- •Identify Interpreted MATLAB Function blocks
- •See Also
- •Check MATLAB Function block debug settings
- •See Also
- •Check Stateflow block debug settings
- •See Also
- •Identify simulation target settings
- •See Also
- •Check model reference rebuild setting
- •See Also
- •Check Model Reference parallel build
- •See Also
- •Check solver type selection
- •See Also
- •Select normal or accelerator simulation mode
- •See Also
- •Simulink Limits
- •Maximum Size Limits of Simulink Models
- •Index
- •Filter Structures and Filter Coefficients
- •Valid Initial States
- •Number of Delay Elements (Filter States)
- •Frame-Based Processing
- •Sample-Based Processing
- •Valid Initial States
- •Frame-Based Processing
- •Sample-Based Processing
- •Model Parameters in Alphabetical Order
- •Common Block Parameters
- •Continuous Library Block Parameters
- •Discontinuities Library Block Parameters
- •Discrete Library Block Parameters
- •Logic and Bit Operations Library Block Parameters
- •Lookup Tables Block Parameters
- •Math Operations Library Block Parameters
- •Model Verification Library Block Parameters
- •Model-Wide Utilities Library Block Parameters
- •Ports & Subsystems Library Block Parameters
- •Signal Attributes Library Block Parameters
- •Signal Routing Library Block Parameters
- •Sinks Library Block Parameters
- •Sources Library Block Parameters
- •User-Defined Functions Library Block Parameters
- •Additional Discrete Block Library Parameters
- •Additional Math: Increment - Decrement Block Parameters
- •Mask Parameters
Time Scope
this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox slewrate function reference.
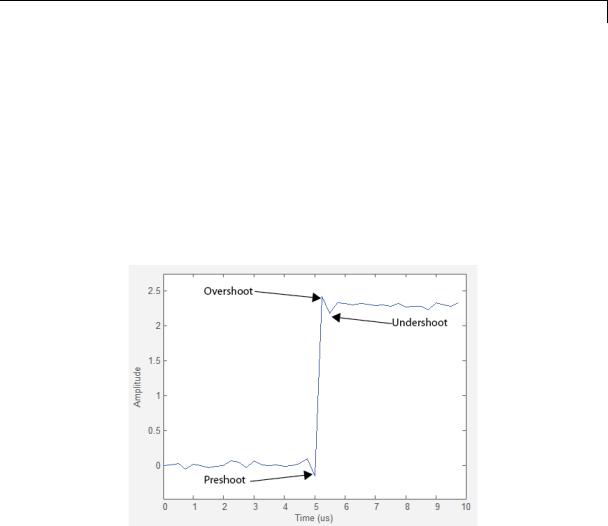
Overshoots/Undershoots
The Overshoots/Undershoots pane displays calculated measurements involving the distortion and damping of the input signal. Overshoot and undershoot refer to the amount that a signal respectively exceeds and falls below its final steady-state value. Preshoot refers to the amount prior to a transition that a signal varies from its initial steady-state value. This figure shows preshoot, overshoot, and undershoot for a rising-edge transition.
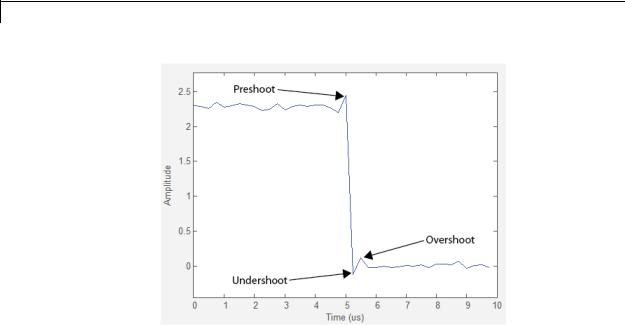
The next figure shows preshoot, overshoot, and undershoot for a falling-edge transition.
2-1781
Time Scope
•+ Preshoot — Average lowest aberration in the region immediately preceding each rising transition.
•+ Overshoot — Average highest aberration in the region immediately following each rising transition. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox overshoot function reference.
•+ Undershoot — Average lowest aberration in the region immediately following each rising transition. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox undershoot function reference.
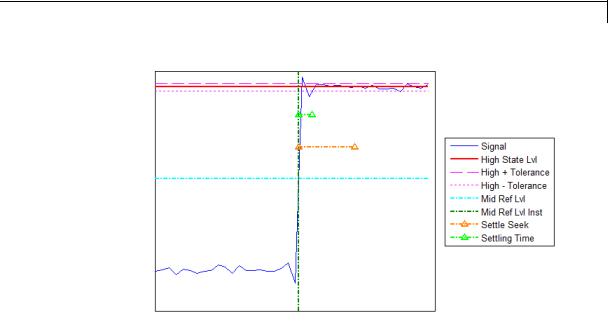
•+ Settling Time — Average time required for each rising edge to enter and remain within the tolerance of the high-state level for the remainder of the settle seek duration. The settling time is the time after the mid-reference level instant when the signal crosses into and remains in the tolerance region around the high-state level. This crossing is illustrated in the following figure.
2-1782
Time Scope
You can modify the settle seek duration parameter in the Settings pane. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox settlingtime function reference.
•– Preshoot — Average highest aberration in the region immediately preceding each falling transition.
•– Overshoot — Average highest aberration in the region immediately following each falling transition. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox overshoot function reference.
•– Undershoot — Average lowest aberration in the region immediately following each falling transition. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox undershoot function reference.
•– Settling Time — Average time required for each falling edge to enter and remain within the tolerance of the low-state level for the remainder of the settle seek duration. The settling time is the time after the mid-reference level instant when the signal crosses into and remains in the tolerance region around the low-state level. You can
2-1783
Time Scope
modify the settle seek duration parameter in the Settings pane. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox settlingtime function reference.
Cycles
The Cycles pane displays calculated measurements pertaining to repetitions or trends in the displayed portion of the input signal.
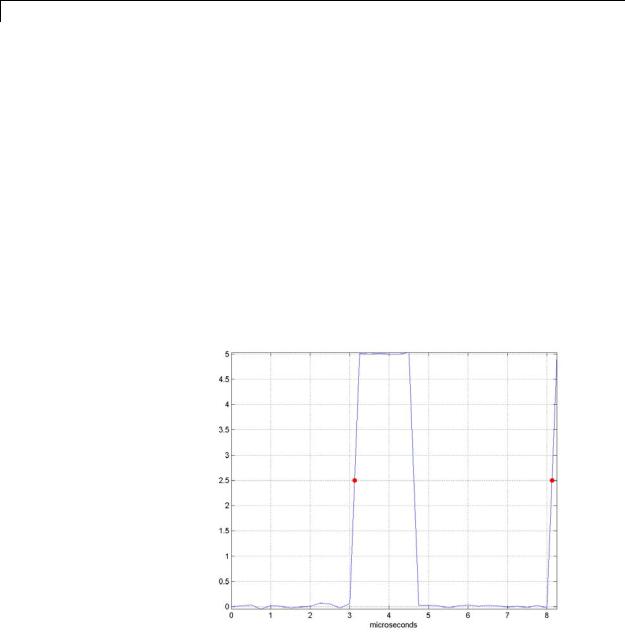
•Period — Average duration between adjacent edges of identical polarity within the displayed portion of the input signal. The Bilevel measurements panel calculates period as follows. It takes the difference between the mid-reference level instants of the initial transition of each positive-polarity pulse and the next positive-going transition. These mid-reference level instants appear as red dots in the following figure.
2-1784

Time Scope
For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox pulseperiod function reference.
•Frequency — Reciprocal of the average period. Whereas period is typically measured in some metric form of seconds, or seconds per cycle, frequency is typically measured in hertz or cycles per second.
•+ Pulses — Number of positive-polarity pulses counted.
•+ Width — Average duration between rising and falling edges of each positive-polarity pulse within the displayed portion of the input signal. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox pulsewidth function reference.
•+ Duty Cycle — Average ratio of pulse width to pulse period for each positive-polarity pulse within the displayed portion of the input signal. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox dutycycle function reference.
•– Pulses — Number of negative-polarity pulses counted.
•– Width — Average duration between rising and falling edges of each negative-polarity pulse within the displayed portion of the input signal. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox pulsewidth function reference.
•– Duty Cycle — Average ratio of pulse width to pulse period for each negative-polarity pulse within the displayed portion of the input signal. For more information on the algorithm this measurement uses, see the Signal Processing Toolbox dutycycle function reference.
When you use the zoom options in the Scope, the bilevel measurements automatically adjust to the time range shown in the display. In the Scope toolbar, click the Zoom In or Zoom X button to constrict the x-axis range of the display, and the statistics shown reflect this time range. For example, you can zoom in on one rising edge to make the Bilevel Measurements panel display information about only that
2-1785
