- •А.Д. Музафарова а.Г. Ковалева
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Our guide to cleaning and maintaining your keyboard.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •1. Communication between the primary storage unit and the arithmetic-logical and control units
- •2. Arithmetic-logical unit functional diagram
- •3. Control unit functional diagram
- •Vocabulary quiz.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Windows 2000
- •People and computers: information society
- •Input devices
- •Data processing
- •Output devices
- •Data storage
- •Operating systems
- •Список использованной литературы
Vocabulary practice section 2
1. Match the terms with the appropriate explanation or definition.
|
1. The brain of the computer. 2. Physical parts that make up a computer system. 3. Programs which can be used on a particular computer system. 4. The information which is presented to the computer. 5. Results produced by a computer 6. Hardware equipment attached to the CPU. 7. Visual display unit. 8. Small device used to store information. Same as 'diskette'. 9. Any socket or channel in a computer system into which an input/output device may be connected. 10. A device used to produce voice output and play back music. 11. A mechanism that reads and/or writes to optical discs 12. A device that converts data so that it can travel over the Internet |
a. software b. peripheral devices с. monitor d. floppy disk e. hardware f. input g. port h. output i. CPU j. CD/DVD drive k. speaker l. modem |
2. Read these slogans or quotations, and say what computer element they refer to.
|
1. a. 'Point and click here for power.' b. 'Obeys every impulse as if it were an extension of your hand.' 2. a. ‘Displays your ideas with perfect brilliance.’ b. ‘See the difference - sharp images and a fantastic colour range.’ 3. a. ‘I love this drive. It's quiet and fast.’ b. 'With this it's easy to back up your data before it's too late.' |
|
4. a. ‘Power and speed on the inside.’
b. ‘Let your computer's brain do the work.’
5. a. ‘…. a big impact on the production of text and graphics.'
b. ‘Your choice: a laser powerhouse.’
6. 'Accelerate your digital lifestyle by choosing a Pentium at 4.3 GHz.'
7. 'Right-click to display a context-sensitive menu.'
8. 'You will see vivid, detailed images on a 17" display.'
9. 'This will produce high-quality output, with sharp text and impressive graphics.'
10. 'Use it when you want to let the grandparents watch the new baby sleeping.'
11. 'Press any key to continue.'
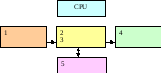
3. Match each component in column with its function and label the diagram of a computer system using these terms:
|
1. Storage device |
a. It displays the processed data |
|
2. Input device |
b. It holds the programs and data being used by the processor |
|
3. Output device |
с It does all the processing and controls the peripherals |
|
4. Main memory |
d. It allows data to be entered |
|
5. Processor |
e. It provides permanent storage for programs and data |
|
|
|
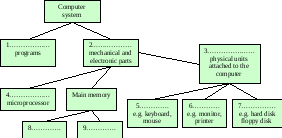
4. Label this diagram with the correct terms from the Key Information Section.
5. Look at these extracts from reviews on a consumer website. Which piece of hardware is each extract describing?
1. Available in 15” or 21” models, flat (LCD monitor/keyboard/webcam).
2. With both wired and wireless versions to choose from. (DVD drive/ mouse/ USB port)
3. (DVD drive/ printer/ USB port) … you can back up over 4GB of data in minutes.
4. … ,(CD/ webcam/ printer) and the pages per minute increases for black and white jobs.
5. (webcam/printer/keyboard) … surprisingly at this price, it even works in very low light conditions.
6. Label the pictures below with the correct terms relating to computer parts and essentials.
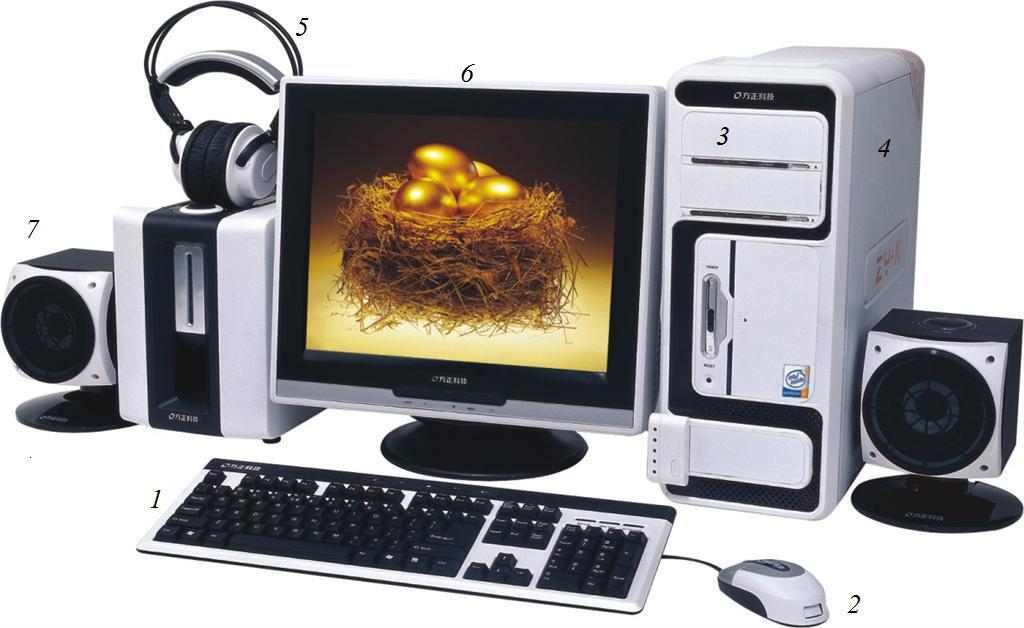
|
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
12,13
|
|
|
|
Have you got a computer at home? What kind is it?
How often do you use it? What do you use it for?
What are the main components and features (the configuration) of your computer system?
7. Complete the sentences below with the correct terms from the Key Information Section.
Computer ……. is the visible or audible result of data processing – information that can be read, printed or heard by the user.
The CPU will process data as instructed by the programs you're running. ……. includes functions like calculating, sorting, editing, drawing and searching.
DVDs are expected to replace CDs as ……. devices.
As a scanner, the Sigma-100 can be used to ……. photographs as well as ……. documents into the computer.
8. Complete this customer review from a website with the words from the box.
|
perform word processor online download digital built-in store personal monitor data |

The best professional laptop on the market
I bought a new MacBook Pro last month, and I’ve been very happy with it so far. The Intel Core 2 Duo processor is a real bonus, allowing the computer to 1……. tasks faster than earlier MacBook models; the 160GB hard drive is large enough to 2……. all of my music, photos and videos; and I didn’t even need to buy an external 3……. – the widescreen 17” display is easy to look at, even for long periods of time.
Another great feature is the 4……. iSight camera; it can be used for webchats, to make video podcasts, or even just to take 5……. photos. Software updates are easy, too: if you’re 6……. – just surfing the Web or checking email – and an update becomes available, a box appears asking if you want to 7……. the update. You just click OK, and it’s done. I don’t even have to worry about security either. Every time I transmit 8……. from my computer on the Internet, Apple’s Safari web browser protects my 9……. information, such as bank details and credit card numbers, using a firewall.
The only criticism I have is the lack of a good 10……. , such as Microsoft Word. I had to buy a copy of Microsoft Office 2008 in the end, which cost an extra £99.95 – and that’s with a student discount!
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 3
Types of computer systems
|
|
|
|
Computers can be divided into different types, depending on their size and power. There is an increasing variety of computers of different sizes and designed for different purposes.
|
|
Mainframecomputers are the largest and most powerful. They can handle large amounts of information very quickly supporting multiple users at the same time and can support more simultaneous processes than a PC. A terminal, consisting of a keyboard and a monitor, is used to input and output information on a mainframe. The central system is a large server connected to hundreds of terminals over a network. They usually fill a whole room and are sometimes referred to as mainframes or computer installations. Mainframes are large, powerful, expensive computers that are operated by a team of |
professionals and are used for large-scale computing purposes in banks, big companies and in large institutions like universities or government departments. The most powerful mainframes are called supercomputers.
The most common type of computer is the microcomputer, sometimes calledpersonal computer.
It gets the name from the tiny electronic device, called the microprocessorthat does the actual processing. A PC is a computer designed to meet the needs of a single person. It is used by an individual, usually in an interactive mode. PCs are found in many businesses and are popular for home use.They are becoming as common as the television and the telephone in the household.
There is a wide variety of PCs but two common types are desktop computersandportables.
|
A desktop PChas its own processing unit (or CPU), monitor and keyboard. It is used as a personal computer in the home or as a workstation for group work. Desktops are small enough to sit on an office desk and are relatively cheap. Typical examples are the IBM PC and the Apple Macintosh. It's designed to be placed on your desk. Some models have a vertical case called atower. |
| |
|
|
A laptop(also called anotebook PC) is a lightweight computer that you can transport easily. It can work as fast as a desktop PC, with similar processors, memory capacity, and disk drives, but it is portable and has a smaller screen. Laptops are capable of the same tasks as adesktop computer, although they are typically less powerful for the same price. They contain components that are similar to their desktop counterparts and perform the same functions, but are | |
miniaturizedand optimized for mobile use and efficient power consumption. Modern notebooks have aTFT (Thin Film Transistor) screenthat produces very sharp images.
In addition to a built-in keyboard, they may utilize atouchpad(also known as atrackpad) - a sensitive pad that you can touch to move the pointer on the screen - or apointing stickfor input, though an external keyboard ormousecan usually be attached.
They offer a lot of connectivity options: USB (Universal Serial Bus)portsfor connecting peripherals, slots for memory cards, etc.
They come with battery packs, which let you use the computer when there are no electrical outlets available.
One of the reasons that notebook portables are popular is because their screens and keyboards are just big enough to use comfortably for word processing and they are even used for multimedia.
|
A tablet PC refers to a laptop or slate-shaped mobile computer, equipped with a touchscreen or graphics tablet/screen hybrid to operate the computer with a stylus or digital pen, or a fingertip, instead of a keyboard or mouse.It looks like a book, with an LCD screen which you can fold and rotate 180 degrees. Your handwriting can be recognized and converted into editable text. You can also type at the detached keyboard or usevoice recognition. It's mobile and |
|
versatile. The form factor offers a more mobile way to interact with a computer. Tablet PCs are often used where normal notebooks are impractical or do not provide the needed functionality.
|
|
A personal digital assistantorPDAis a tiny pocket-sized computer which can be held in one hand. The term PDA refers to a wide variety ofhandhelddevices,palmtops,smartphones andpocket PCs. For input, you type at a small keyboard or use a stylus - a special pen used with a touch screen to select items, draw pictures, etc. Some |
models incorporate handwriting recognition, which enables a PDA to recognize characters written by hand. Some PDAs recognize spoken words by using voice recognition software. Some include a virtual keyboard which pops up when you want to enter email text or a WAP address. They are also equipped with software to handle e-mail and surf the Webviawirelesstechnology, without cables. You can hear popular MP3 music or record your ideas through its built-in voice recorder. Once at home you can synchronise data with your desktop PC. PDAs support mobile computing, but almost never run any desktop software. They can be used as cellphones or as personal organizers for storing notes, reminders and addresses.
|
A wearable computerruns on batteries and is worn on the user's body, e.g. on a belt, backpack or vest; it is designed for mobile orhands-freeoperation, often incorporating a microphone and a head-mounted display. Some devices are equipped with a wireless modem, a keypad and a small screen; others are voice-activated, worn like a scarf and can access |
|
email or voice mail. Wearable computers are especially useful for applications that require computational support while the user's hands, voice, eyes or attention are actively engaged with the physical environment. Users of wearable technology consider themselves 'cyborgs'. This term comes from 'cybernetic organism', referring to a being that is part robot, part human.