- •А.Д. Музафарова а.Г. Ковалева
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Our guide to cleaning and maintaining your keyboard.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •1. Communication between the primary storage unit and the arithmetic-logical and control units
- •2. Arithmetic-logical unit functional diagram
- •3. Control unit functional diagram
- •Vocabulary quiz.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Windows 2000
- •People and computers: information society
- •Input devices
- •Data processing
- •Output devices
- •Data storage
- •Operating systems
- •Список использованной литературы
Vocabulary practice section 2
1. Here is a list of typical tasks performed by an operating system. In each case the main verb has been omitted. Fill in the blanks from the words given (sometimes more than one may apply).
|
execute monitor format diagnose |
A typical operating system will:
|
1. …… input and output devices. 2. …… the status of hardware devices. 3. …… hardware interrupts. 4. …… new disks. 5. …… disk directories. 6. …… disk reading and writing operations. 7. …… disk errors. 8. …… disk commands relating to the deletion, copying, renaming, and dumping of files. |
|
2. Match these common DOS commands with the appropriate explanation.
|
1. BACKUP |
a. searches for a specific string of text in a file. |
|
2. CHDIR or CD |
b. allows a text file from the current directory to be displayed on screen. |
|
3. CHKDSK |
c. allows the user to change the name of a file. |
|
4. CLS |
d. saves the contents of the hard disk to a floppy disk for security purposes. |
|
5. DEL |
e. is used when it is necessary to change the current directory. |
|
6. DIR:SORT |
f. clears data from the screen. |
|
7. REN |
g. alphabetically sorts and lists a disk directory. |
|
8. TYPE |
h. makes back-up copies of the contents of one disk to another. |
|
9. FIND |
i. deletes a specified file from the current directory, specified drive or path. |
|
10. DISKCOPY |
j. produces a status report of the currently logged-on disk, indicating the amount of disk space used, the available capacity (in bytes), and the number of files on disk.
|
3. Make two-word expressions by combining words from the two columns. Then match these expressions with the appropriate phrase.
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
1. Running several programs at the same time in an efficient manner.
2. A group of computer programs that help manage the computer's resources, acting as an interface between the computer and application programs.
3. Routine used to interface and manage a peripheral.
4. Small programs which improve a system's performance and help users.
5. The way people interact with computers.
6. Computer software that is designed for a particular use or user.
7. Planning particular tasks to be performed by a computer at particular time.
8. A type of computer system in which the computer does several jobs one after the other, without needing instructions between each job.
4. Complete the texts using the words in the boxes.
|
|
Operating systems
|
|
control functions MS-DOS software version Windows | |
|
MS-DOS is operating system 1 … developed by Microsoft that controls and co-ordinates the basic 2 … of your computer. If you are using Windows 95 or a later 3 … of |
Windows, the functions of MS-DOS have been integrated. If you are using Windows 3.1x or do not have 4…, then you are relying on 5… (or a similar product from IBM called PC-DOS) to 6… the computer.
|
commands icons Microsoft mouse multitasking user |
|
Windows is a 7 … graphical 8 … interface for the IBM PC developed by 9 … Corp. that is designed to be easy to use. Windows uses 10 … to represent files and devices and can be controlled using a 11 … , unlike MS-DOS which |
|
requires 12 … to be typed in.
|
filenames interface Internet memory networks processor |
Windows 95 provides support for long 13 …, an 14 … that's easier to use and better support for 15 … and the 16 … It does, however, require a faster 17 … and more 18 … to get good results - an absolute minimum of 8Mb and a fast 80486 are required.
|
communications configure enhanced features version |
Windows 98 is an 19 … 20 … of Microsoft's Windows 95 that provides more 21 … and internet 22 … and is easier to use and 23 … .
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 3
The Graphical User Interface
|
|
|
|
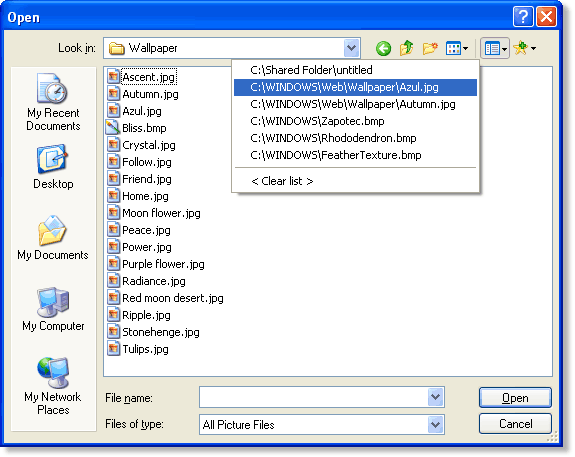
The term ‘user interface’ refers to the standard procedures the user follows to interact with a particular computer. A good user interface is important because when you buy a program you want to use it easily. A few years ago, the way in which users had access to a computer system was quite complex. They had to memorize and type a lot of commands just to see the content of a disk, to copy files or to respond to a single prompt. So, a user interface based on graphics and intuitive tools was designed with a single clear aim: to facilitate interaction with the computer.
Nowadays most computers have a Graphical User Interface (GUI).It is a type of user interface which allows people to interact with electronic devices such as computers; hand-held devices such as MP3 Players, Portable Media Players or Gaming devices; household appliances and office equipment.
A GUI makes use a WIMP environment: Windows, Icons, Menus and Pointer. This type of interface is user-friendly, where system functions are accessed by selecting self-explanatory icons and items from menus. A GUI offers graphical icons (graphic images (or intuitive symbols)representing programs, documents,an object or task), and visual indicators (as opposed to text-based interfaces), typed command labels or text navigation to fully represent the information and actions available to a user. Agraphical user interface saves a lot of time: you don't need to memorize commands in order to execute an application; you only have to point and click so that its content appears on the screen.
|
|
Command Line Interface - CLI Static, Direct, Recall. Graphical User Interface - GUI Responsive, Indirect, Recognition. Natural User Interface - NUI Evocative, Contextual, Intuition. |
Double-clicking an icon opens a window that lets you work with different tools and menus. A windowis a viewing area of the computer screen where you can see the contents of a folder, a file,
|
|
or a program. Some systems allow several windows on the screen at the same time and windows can overlap each other. The window on the top is the one which is "active", the one in use. By using different windows you can work on several documents or applications simultaneously. The actions are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements by the means of a drop-down menu, pop-up menu or pull-down menu (a list of options that appear below a menu bar when you click | |
|
on an item). The tool for these manipulations is the pointer. The pointer is the arrow, controlled by the mouse, which allows you to move around the screen and choose options from menus. You operate the menu by pressing and releasing one or more buttons on the mouse.Toolbar buttons are found at the top of a window, they take you to the Home folder and others. Thedockis a set of icons at |
| |
|
the bottom of the screen that give you instant access to the things you use most. When information has to be given to the user or input by the user, a window known as a dialog boxis often used. It can contain a variety of elements to gather information from the user including:text boxes,drop-down list boxes,checkboxesandcommand buttons. Afind dialog boxis used to gather information from the user about the files they wish to find.All these activities take place on a desktop (the background screen that displays icons, representing programs, files and folders-directoriesor containers for documents and applications). | ||
Today, the most innovative GUIs are the Macintosh, Microsoft Windows and IBM OS/2 Warp. These three platforms include similar features: a desktop with icons, windows and folders, a printer selector, a file finder, a control panel and various desk accessories. Double-clicking a folder opens a window which contains programs, documents or further nested folders. At any time within a folder, you can launch the desired program or document by double-clicking the icon, or you can drag it to another location. The three platforms differ in other areas such as device installation, network connectivity or compatibility with application programs.