- •А.Д. Музафарова а.Г. Ковалева
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Our guide to cleaning and maintaining your keyboard.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
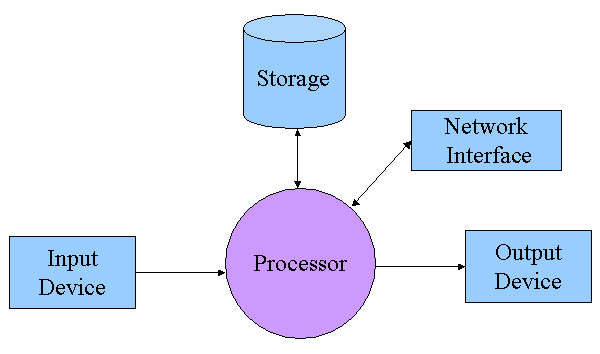
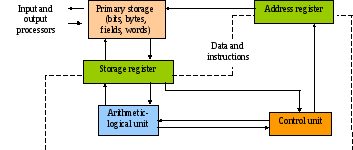
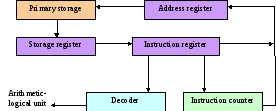
- •1. Communication between the primary storage unit and the arithmetic-logical and control units
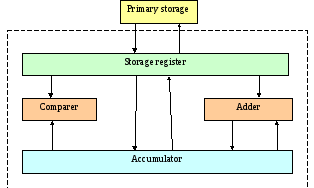
- •2. Arithmetic-logical unit functional diagram
- •3. Control unit functional diagram
- •Vocabulary quiz.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Windows 2000
- •People and computers: information society
- •Input devices
- •Data processing
- •Output devices
- •Data storage
- •Operating systems
- •Список использованной литературы
1. Communication between the primary storage unit and the arithmetic-logical and control units
2. Arithmetic-logical unit functional diagram
3. Control unit functional diagram
2. Make notes about the features of the computer that you would like to have and describe it.
CPU: Speed: Optical disk drives: Minimum/maximum RAM:
Monitor: Hard disk: Software:
Useful expressions:
|
It has got... It's very fast. It runs at... |
The standard RAM memory... and it is expandable . The hard disk can hold ... |
As for the Internet... I need a SuperVGA monitor because ... |
FUN AND GAMES SECTION
Vocabulary quiz.
1. In groups of three, write answers to these questions. The winners are the group that answers the most questions correctly in three minutes.
|
|
What is the ALU? What does it do?
How can we store data and programs permanently?
2. Solve the clues and complete the puzzle with words from the Key Information Section.
|
|
|
The ……. uses ROM to control the input/output of data.
The main printed circuit board is called the …….
Down:The brain of a computer
HUMOR SECTION
What does each of the cartoons imply? Why is it funny, in your opinion? Explain its humour.
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT DEVICES |
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 1
An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing to the outside world. The most common outputs are monitors, printers and speakers.
Display screens
|
|
|
|
The screen of a computer is often known as the monitor or display, orVDU (visual display unit). Itis a piece of electrical equipment which displays images generated from the video output of computers, without producing a permanent record. The monitor comprises the display device, simple circuitry to generate and format a picture from video sent by the signals source, and usually an enclosure. The monitor is controlled by a separate circuit board, known as thedisplay adaptor, which plugs into themotherboardof the computer and generates video in a format compatible with the monitor. Thevideo cardprocesses images and sends signals to the monitor. For example, theVGA (video graphics array) card has become a standard for colour monitors.
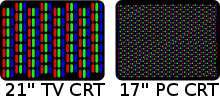
Older monitors are based around a cathode ray tube (CRT), similar to a traditional TV set. At the
|
back of the tube there is a negatively charged cathode andthree electron guns - each gun shoots out a beam of electrons for each of theprimary colours: red, green and blue. These electrons strike the inside of thechargedscreen which is coated with substances calledphosphors (there are different materials for each of the three colours) that glow when struck by electrons and create colours. |
|
Each cluster of three phosphor dots, one of each color, is one pixel. The electron beam scans the screen and turns on or off the pixels that make up the image. To create different colours, the intensity of each of the three electron beams is varied. There are two electromagnets around the collar of the tube which deflect the electron beam. The beam scans across the top of the monitor from left to right, is then blanked and moved back to the left-hand side slightly below the previous trace (on the next scan line), scans across the second line and so on until the bottom right of the screen is reached. It is again blanked, and moved back to the top left to start again. It scans the screen in a continuous sequence, similar to the movement of our eyes when we read, but much faster - this process draws a complete picture. This sequence is repeated 50-100 times per second,
|
|
depending on the system. If the rate of this repetition is low, we can perceive a flickering, unsteady screen, which can cause eye fatigue. CRTs are cheap, but they are heavy, can flicker and emit radiation. |
Most newer monitors typically consist of a TFT-LCD. ALiquid Crystal Display (LCD)is made from flat plates with a liquid crystal solution between them. The crystals block the light in different quantities to create the image.Active-matrixLCDs useTFT (thin film transistor)technology, in
|
which each pixel has its own transistor switch. TFT systems offer a wider angle of vision and high-quality images, they are flat and take up less space, use less power than CRTs, they are distortion-free while typical CRTs are curved, which may cause image distortion, so they are replacing CRTs. Users talk of benefits such as more desk space, how easy they are to adjust for tilt |
|
and height, crisper, clearer images and the total elimination of screen flicker. Manufacturers offer compatible flat screens including built-in stereo speakers, headphone connection, and a USB port. Some models can also be removed from the stand and mounted on the wall. They come with stylish designs for a variety of applications.
Plasma displayshave many advantages: high-contrast images and bright colours, generated by a plasma discharge which contains noble, non-harmful gases. Gas-plasma TVs allow for larger screens and wide viewing angles, perfect for movies.
Home cinemaenthusiasts set up systems with a DVD recorder, speakers forsurround sound, and arear projection TV, which has the video projector and the screen within a large TV box. It’s a real cinema experience.
Video projectorsare used when audiovisual presentations are on a laptop connected to a front-screen projector which displays the images on a distant screen or white wall.
Portable DLP projectorsare used for business presentations. This is adigital light-processingdevice which creates the image with millions of microscopic mirrors arranged on a silicon chip.
Sound output
|
|
Computer speakers, or multimedia speakers, are external speakers, commonly equipped with a low-power internal amplifier. The standard audio connection is a 3.5mm (1/8 inch) stereo jack plug often colour-coded lime green for computer |
sound cards. There are also USB speakers. More sophisticated computer speakers may have a 'subwoofer' unit to enhance bass output. Some computer displays have rather basic speakers built-in. Laptops come with integrated speakers. For some users, a lead connecting computer sound output to an existing stereo system is practical. This normally yields much better results than small low-cost computer speakers.
|
|
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeakers, or less commonly a single speaker, with a way of holding them close to a user's ears and a means of connecting them to a signal source. They are also known as earphones, earbuds, |
stereophones, headsets or, informally cans. In the context of telecommunication, the term headset is used to describe a combination of headphone and microphone used for two-way communication.