
- •Hematuria II: causes and investigation
- •Hematospermia
- •Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)
- •Nocturia and nocturnal polyuria
- •Flank pain
- •Urinary incontinence in adults
- •Genital symptoms
- •Abdominal examination in urological disease
- •Digital rectal examination (DRE)
- •Lumps in the groin
- •Lumps in the scrotum
- •2 Urological investigations
- •Urine examination
- •Urine cytology
- •Radiological imaging of the urinary tract
- •Uses of plain abdominal radiography (KUB X-ray—kidneys, ureters, bladder)
- •Intravenous pyelography (IVP)
- •Other urological contrast studies
- •Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- •Radioisotope imaging
- •Post-void residual urine volume measurement
- •3 Bladder outlet obstruction
- •Regulation of prostate growth and development of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- •Pathophysiology and causes of bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) and BPH
- •Benign prostatic obstruction (BPO): symptoms and signs
- •Diagnostic tests in men with LUTS thought to be due to BPH
- •Why do men seek treatment for their symptoms?
- •Watchful waiting for uncomplicated BPH
- •Medical management of BPH: combination therapy
- •Medical management of BPH: alternative drug therapy
- •Minimally invasive management of BPH: surgical alternatives to TURP
- •Invasive surgical alternatives to TURP
- •TURP and open prostatectomy
- •Indications for and technique of urethral catheterization
- •Indications for and technique of suprapubic catheterization
- •Management of nocturia and nocturnal polyuria
- •High-pressure chronic retention (HPCR)
- •Bladder outlet obstruction and retention in women
- •Urethral stricture disease
- •4 Incontinence
- •Causes and pathophysiology
- •Evaluation
- •Treatment of sphincter weakness incontinence: injection therapy
- •Treatment of sphincter weakness incontinence: retropubic suspension
- •Treatment of sphincter weakness incontinence: pubovaginal slings
- •Overactive bladder: conventional treatment
- •Overactive bladder: options for failed conventional therapy
- •“Mixed” incontinence
- •Post-prostatectomy incontinence
- •Incontinence in the elderly patient
- •Urinary tract infection: microbiology
- •Lower urinary tract infection
- •Recurrent urinary tract infection
- •Urinary tract infection: treatment
- •Acute pyelonephritis
- •Pyonephrosis and perinephric abscess
- •Other forms of pyelonephritis
- •Chronic pyelonephritis
- •Septicemia and urosepsis
- •Fournier gangrene
- •Epididymitis and orchitis
- •Periurethral abscess
- •Prostatitis: presentation, evaluation, and treatment
- •Other prostate infections
- •Interstitial cystitis
- •Tuberculosis
- •Parasitic infections
- •HIV in urological surgery
- •6 Urological neoplasia
- •Pathology and molecular biology
- •Prostate cancer: epidemiology and etiology
- •Prostate cancer: incidence, prevalence, and mortality
- •Prostate cancer pathology: premalignant lesions
- •Counseling before prostate cancer screening
- •Prostate cancer: clinical presentation
- •PSA and prostate cancer
- •PSA derivatives: free-to-total ratio, density, and velocity
- •Prostate cancer: transrectal ultrasonography and biopsies
- •Prostate cancer staging
- •Prostate cancer grading
- •General principles of management of localized prostate cancer
- •Management of localized prostate cancer: watchful waiting and active surveillance
- •Management of localized prostate cancer: radical prostatectomy
- •Postoperative course after radical prostatectomy
- •Prostate cancer control with radical prostatectomy
- •Management of localized prostate cancer: radical external beam radiotherapy (EBRT)
- •Management of localized prostate cancer: brachytherapy (BT)
- •Management of localized and radiorecurrent prostate cancer: cryotherapy and HIFU
- •Management of locally advanced nonmetastatic prostate cancer (T3–4 N0M0)
- •Management of advanced prostate cancer: hormone therapy I
- •Management of advanced prostate cancer: hormone therapy II
- •Management of advanced prostate cancer: hormone therapy III
- •Management of advanced prostate cancer: androgen-independent/ castration-resistant disease
- •Palliative management of prostate cancer
- •Prostate cancer: prevention; complementary and alternative therapies
- •Bladder cancer: epidemiology and etiology
- •Bladder cancer: pathology and staging
- •Bladder cancer: presentation
- •Bladder cancer: diagnosis and staging
- •Muscle-invasive bladder cancer: surgical management of localized (pT2/3a) disease
- •Muscle-invasive bladder cancer: radical and palliative radiotherapy
- •Muscle-invasive bladder cancer: management of locally advanced and metastatic disease
- •Bladder cancer: urinary diversion after cystectomy
- •Transitional cell carcinoma (UC) of the renal pelvis and ureter
- •Radiological assessment of renal masses
- •Benign renal masses
- •Renal cell carcinoma: epidemiology and etiology
- •Renal cell carcinoma: pathology, staging, and prognosis
- •Renal cell carcinoma: presentation and investigations
- •Renal cell carcinoma: active surveillance
- •Renal cell carcinoma: surgical treatment I
- •Renal cell carcinoma: surgical treatment II
- •Renal cell carcinoma: management of metastatic disease
- •Testicular cancer: epidemiology and etiology
- •Testicular cancer: clinical presentation
- •Testicular cancer: serum markers
- •Testicular cancer: pathology and staging
- •Testicular cancer: prognostic staging system for metastatic germ cell cancer
- •Testicular cancer: management of non-seminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCT)
- •Testicular cancer: management of seminoma, IGCN, and lymphoma
- •Penile neoplasia: benign, viral-related, and premalignant lesions
- •Penile cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathology
- •Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: clinical management
- •Carcinoma of the scrotum
- •Tumors of the testicular adnexa
- •Urethral cancer
- •Wilms tumor and neuroblastoma
- •7 Miscellaneous urological diseases of the kidney
- •Cystic renal disease: simple cysts
- •Cystic renal disease: calyceal diverticulum
- •Cystic renal disease: medullary sponge kidney (MSK)
- •Acquired renal cystic disease (ARCD)
- •Autosomal dominant (adult) polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
- •Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction in adults
- •Anomalies of renal ascent and fusion: horseshoe kidney, pelvic kidney, malrotation
- •Renal duplications
- •8 Stone disease
- •Kidney stones: epidemiology
- •Kidney stones: types and predisposing factors
- •Kidney stones: mechanisms of formation
- •Evaluation of the stone former
- •Kidney stones: presentation and diagnosis
- •Kidney stone treatment options: watchful waiting
- •Stone fragmentation techniques: extracorporeal lithotripsy (ESWL)
- •Intracorporeal techniques of stone fragmentation (fragmentation within the body)
- •Kidney stone treatment: percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
- •Kidney stones: open stone surgery
- •Kidney stones: medical therapy (dissolution therapy)
- •Ureteric stones: presentation
- •Ureteric stones: diagnostic radiological imaging
- •Ureteric stones: acute management
- •Ureteric stones: indications for intervention to relieve obstruction and/or remove the stone
- •Ureteric stone treatment
- •Treatment options for ureteric stones
- •Prevention of calcium oxalate stone formation
- •Bladder stones
- •Management of ureteric stones in pregnancy
- •Hydronephrosis
- •Management of ureteric strictures (other than UPJ obstruction)
- •Pathophysiology of urinary tract obstruction
- •Ureter innervation
- •10 Trauma to the urinary tract and other urological emergencies
- •Renal trauma: clinical and radiological assessment
- •Renal trauma: treatment
- •Ureteral injuries: mechanisms and diagnosis
- •Ureteral injuries: management
- •Bladder and urethral injuries associated with pelvic fractures
- •Bladder injuries
- •Posterior urethral injuries in males and urethral injuries in females
- •Anterior urethral injuries
- •Testicular injuries
- •Penile injuries
- •Torsion of the testis and testicular appendages
- •Paraphimosis
- •Malignant ureteral obstruction
- •Spinal cord and cauda equina compression
- •11 Infertility
- •Male reproductive physiology
- •Etiology and evaluation of male infertility
- •Lab investigation of male infertility
- •Oligospermia and azoospermia
- •Varicocele
- •Treatment options for male factor infertility
- •12 Disorders of erectile function, ejaculation, and seminal vesicles
- •Physiology of erection and ejaculation
- •Impotence: evaluation
- •Impotence: treatment
- •Retrograde ejaculation
- •Peyronie’s disease
- •Priapism
- •13 Neuropathic bladder
- •Innervation of the lower urinary tract (LUT)
- •Physiology of urine storage and micturition
- •Bladder and sphincter behavior in the patient with neurological disease
- •The neuropathic lower urinary tract: clinical consequences of storage and emptying problems
- •Bladder management techniques for the neuropathic patient
- •Catheters and sheaths and the neuropathic patient
- •Management of incontinence in the neuropathic patient
- •Management of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) in the neuropathic patient
- •Management of hydronephrosis in the neuropathic patient
- •Bladder dysfunction in multiple sclerosis, in Parkinson disease, after stroke, and in other neurological disease
- •Neuromodulation in lower urinary tract dysfunction
- •14 Urological problems in pregnancy
- •Physiological and anatomical changes in the urinary tract
- •Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- •Hydronephrosis
- •15 Pediatric urology
- •Embryology: urinary tract
- •Undescended testes
- •Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- •Ectopic ureter
- •Ureterocele
- •Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction
- •Hypospadias
- •Normal sexual differentiation
- •Abnormal sexual differentiation
- •Cystic kidney disease
- •Exstrophy
- •Epispadias
- •Posterior urethral valves
- •Non-neurogenic voiding dysfunction
- •Nocturnal enuresis
- •16 Urological surgery and equipment
- •Preparation of the patient for urological surgery
- •Antibiotic prophylaxis in urological surgery
- •Complications of surgery in general: DVT and PE
- •Fluid balance and management of shock in the surgical patient
- •Patient safety in the operating room
- •Transurethral resection (TUR) syndrome
- •Catheters and drains in urological surgery
- •Guide wires
- •JJ stents
- •Lasers in urological surgery
- •Diathermy
- •Sterilization of urological equipment
- •Telescopes and light sources in urological endoscopy
- •Consent: general principles
- •Cystoscopy
- •Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- •Transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
- •Optical urethrotomy
- •Circumcision
- •Hydrocele and epididymal cyst removal
- •Nesbit procedure
- •Vasectomy and vasovasostomy
- •Orchiectomy
- •Urological incisions
- •JJ stent insertion
- •Nephrectomy and nephroureterectomy
- •Radical prostatectomy
- •Radical cystectomy
- •Ileal conduit
- •Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
- •Ureteroscopes and ureteroscopy
- •Pyeloplasty
- •Laparoscopic surgery
- •Endoscopic cystolitholapaxy and (open) cystolithotomy
- •Scrotal exploration for torsion and orchiopexy
- •17 Basic science of relevance to urological practice
- •Physiology of bladder and urethra
- •Renal anatomy: renal blood flow and renal function
- •Renal physiology: regulation of water balance
- •Renal physiology: regulation of sodium and potassium excretion
- •Renal physiology: acid–base balance
- •18 Urological eponyms
- •Index
206 CHAPTER 6 Urological neoplasia
Prostate cancer staging
Tumor staging uses the most current 2002 TNM (tumor, nodes, malignancy) classification (see Table 6.2 and Fig. 6.3). As with all cancer, prostate cancer staging may be considered clinical (prefixed with c) or pathological (prefixed with p), dependent on available data. (Note: In 2010 the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) will begin to incorporate PSA and Gleason Score into the staging system for prostate cancer.)
Tstage
Tstage is assessed primarily by digital rectal examination (see Fig. 6.3). Current imaging resolution limits reliability in detection of focal and microscopic extraprostatic extension of disease by means of MRI or TRUS. Recent prostatic biopsy may also confuse the interpretation of MRI images, particularly regarding the seminal vesicles.
Table 6.2 TNM (2002) staging of adenocarcinoma of the prostate
|
|
T0 |
No tumor (pT0 if no cancer found by histological examination) |
|
|
Tx |
T stage uncertain |
|
|
||
|
|
T1a |
Cancer nonpalpable on digital rectal examination (DRE), present |
|
|
|
in <5% of TURP specimens (in up to 18% of TURPs) |
|
|
T1b |
Cancer nonpalpable on DRE, present in >5% of TURP specimens |
|
|
T1c |
Cancer nonpalpable on DRE, present in needle biopsy taken |
|
|
|
because of elevated PSA |
|
|
T2a |
Palpable tumor, feels confined, in <half of one lobe on DRE |
|
|
T2b |
Palpable tumor, feels confined, in >half of one lobe on DRE |
|
|
T2c |
Palpable tumor, feels confined, in both lobes on DRE |
|
|
T3a |
Palpable tumor, locally advanced into periprostatic fat, unior |
|
|
|
bilateral and mobile on DRE |
|
|
T3b |
Palpable tumor, locally advanced into seminal vesicle(s) on DRE |
|
|
T4a |
Palpable tumor, locally advanced into adjacent structures, feels |
|
|
|
fixed on DRE |
|
|
T4b |
Palpable tumor, locally advanced into pelvic side-wall, feels fixed |
|
|
|
on DRE |
|
|
Nx |
Regional lymph not assessed |
|
|
N0 |
No regional lymph node metastasis |
|
|
N1 |
Tumor involves regional (pelvic) lymph nodes |
|
|
Mx |
Distant metastases not assessed |
|
|
M0 |
No distant metastasis |
|
|
M1a |
Nonregional lymph node metastasis |
|
|
M1b |
Tumor metastasis in bone |
|
|
M1c |
Tumor metastasis in other sites |
|
|
|
|

|
PROSTATE CANCER STAGING 207 |
Bladder |
T1 |
|
|
|
Early (non-palpable) prostate |
|
cancer only detectable under |
|
the microscope; found at |
|
TURP or by needle biopsy |
Urethra |
|
|
T2 |
|
Early (palpable) prostate |
|
cancer |
T3
Locally advanced prostate cancer—into peri-prostate fat or seminal vesicles
T4
Locally advanced prostate cancer—invades the bladder, rectum, penile urethra, or pelvic side wall
Figure 6.3 The T stages of prostate cancer. (2002 TNM System)
Nstage
Nstage is assessed by imaging (CT/MRI) or biopsy as necessary. Pelvic lymph node dissection is the gold-standard assessment of N stage. MRI or CT scanning may image enlarged nodes and most radiologists report nodes of >5 mm in maximal diameter.
However, nodes larger than this often contain no cancer, while micrometastases may be present in normal-sized nodes.

208 CHAPTER 6 Urological neoplasia
Mstage
Mstage is assessed by use of physical examination, imaging (MRI or isotope bone scan, chest radiology), and biochemical investigations (e.g., alkaline phosphatase).
Nomograms
Based on several thousand radical prostatectomies, these are used widely to predict pathological T and N stage by combining clinical T stage, PSA, and biopsy Gleason score. Nomograms, developed by Kattan and associates (www.nomograms.org), may be able to predict final pathological stage on the basis of preoperative parameters.
Higher pathological stage (i.e., pT3 disease) found at radical prostatectomy may also be predicted by the following:1
•Higher percentages (>66%) of positive biopsies
•Cancer invading adipose in the biopsies (there is no fat in the prostate)
•Possibly the presence of perineural cancer invasion within the prostate
Partin tables
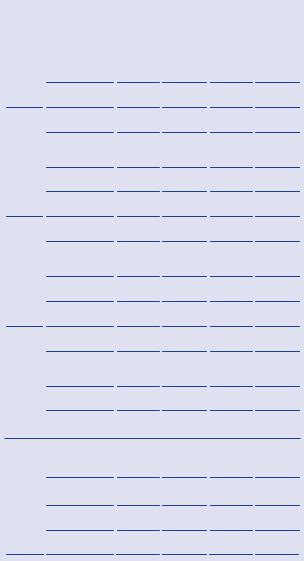
These tables are useful to predict the stage of prostate cancer treated by radical prostatectomy (Table 6.3). Table 6.3 reflects an updated version of the 2001 Partin tables with a contemporary patient cohort (5730 men treated with prostatectomy and no additional therapy from 2000 to 2005 at the Johns Hopkins Hospital). This cohort demonstrated trends in presentation and pathological stage for men diagnosed with clinically localized prostate cancer and was used to correct for the effects of stage migration.
Table 6.3 Partin tables
PSA |
Pathological |
Biopsy Gleason Score |
||
range |
stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(ng/mL) |
5–6 |
3 + 4=7 |
4 + 3 = 7 8–10 |
|
Clinical stage T1c (nonpalpable, PSA elevated) (n = 4419)
0–2.5 |
Organ confined |
93 (91–95) |
82 (76–87) |
73 (64–80) |
77 (65–85) |
|
(n = 226) |
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
6 (5–8) |
14 (10–18) |
20 (14–28) |
16 (11–24) |
|
extension |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 19) |
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle |
0 (0–1) |
2 (0–5) |
2 (0–5) |
3 (0–8) |
|
(+) (n = 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–1) |
2 (0–6) |
4 (1–12) |
3 (1–12) |
|
(n = 3) |
|
|
|
|
2.6–4.0 |
Organ confined |
88 (86–90) |
72 (67–76) |
61 (54–68) |
66 (57–74) |
|
(n = 619) |
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
11 (10–13) |
23 (19–27) |
33 (27–39) |
26 (19–34) |
|
extension (n = 92) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PROSTATE CANCER STAGING |
209 |
||||
|
Table 6.3 Continued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSA |
Pathological |
|
Biopsy Gleason Score |
|
|
|
|
|
|
range |
stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5–6 |
3 + 4=7 |
4 + 3 = 7 |
8–10 |
|
|
|||
|
(ng/mL) |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 (0–1) |
4 (2–7) |
5 (2–8) |
7 (3–13) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–0) |
1 (0–1) |
1 (0–3) |
1 (0–3) |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1–6.0 |
Organ confined |
83 (81–85) |
63 (59–67) |
51 (45–56) |
55 (46–64) |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 1266) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
16 (14–17) |
30 (26–33) |
40 (34–45) |
32 (25–40) |
|
|
|
|
|
extension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 297) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 (1–1) |
6 (4–8) |
7 (4–10) |
10 (6–15) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 37) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–0) |
2 (1–3) |
3 (1–6) |
3 (1–6) |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.1–10.0 |
Organ confined |
81 (79–83) |
59 (54–64) |
47 (41–53) |
51 (41–59) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
(n = 989) |
18 (16–19) |
32 (27–36) |
42 (36–47) |
34 (26–42) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Extraprostatic |
|
|
|||||
|
|
extension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 281) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 (1–2) |
8 (6–11) |
8 (5–12) |
12 (8–19) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 36) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–0) |
1 (1–3) |
3 (1–5) |
3 (1–5) |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>10.0 |
Organ confined |
70 (66–74) |
42 (37–48) |
30 (25–36) |
34 (26–42) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 324) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
27 (23–30) |
40 (35–45) |
48 (40–55) |
39 (31–48) |
|
|
|
|
|
extension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 165) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 2 (2–3) |
12(8–16) |
11 (7–17) |
17 (10–25) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 25) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
1 (0–1) |
6 (3–9) |
10 (5–17) |
9 (4–17) |
|
|
|
|
|
(n = 13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clinical stage T2a (palpable < ½ of one lobe) (n = 998)
0–2.5 Organ confined 88 (84–90) 70 (63–77) 58 (48–67) 63 (51–74)
(n = 156)
Extraprostatic |
12 (9–15) |
24 (18–30) |
32 (24–41) |
26 (18–36) |
|
extension (n = 18) |
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle |
0 (0–1) |
2 (0–6) |
3 |
(0–7) |
4 (0–10) |
(+) (n = 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–1) |
3 (1–9) |
7 |
(1–17) |
6 (1–16) |
(n = 1) |
|
|
|
|
|

210 |
CHAPTER 6 Urological neoplasia |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Table 6.3 Continued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSA |
Pathological |
|
Biopsy Gleason Score |
|
|
|
|
|
range |
stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5–6 |
3 + 4=7 |
4 + 3 = 7 |
8–10 |
|||
|
|
(ng/mL) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.6–4.0 |
Organ confined |
79 (75–82) |
57 (51–63) |
45 (38–52) |
50 (40–59) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 124) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
20 (17–24) |
37 (31–42) |
48 (40–55) |
40 (30–50) |
|
|
|
|
extension (n = 49) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 (0–1) |
5 (3–9) |
5 (3–10) |
8 (4–15) |
||
|
|
|
(n = 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–0) |
1 (0–2) |
2 (0–5) |
2 (0–4) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1–6.0 |
Organ confined |
71 (67–75) |
47 (41–52) |
34 (28–41) |
39 (31–48) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 171) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
27 (23–31) |
44 (39–49) |
54 (47–60) |
46 (37–54) |
|
|
|
|
extension (n = 101) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 (1–2) |
7 (4–10) |
7 (4–11) |
11 (6–17) |
||
|
|
|
(n = 10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–1) |
2 (1–4) |
5 (2–8) |
4 (2–9) |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
(n = 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.1–10.0 |
Organ confined |
68 (64–72) |
43 (38–48) |
31 (26–37) |
36 (27–44) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 142) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
29 (26–33) |
46 (41–51) |
56 (49–62) |
47 (37–56) |
|
|
|
|
extension (n = 99) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 2 (1–3) |
9 (6–13) |
9 (5–14) |
13 (8–20) |
||
|
|
|
(n = 12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 (0–1) |
2 (1–4) |
4 (2–8) |
4 (1–8) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>10.0 |
Organ confined |
54 (49–60) |
28 (23–33) |
18 (14–23) |
21 (15–28) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 36) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
41 (35–46) |
52 (46–59) |
57 (48–66) |
49 (39–59) |
|
|
|
|
extension (n = 47) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 3 (2–5) |
12(7–18) |
11 (6–17) |
17 (9–25) |
||
|
|
|
(n = 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
1 (0–3) |
7 (3–14) |
13 (6–24) |
12 (5–22) |
|
|
|
|
(n = 7) |
|
|
|
|
|
Clinical stage T2b (palpable ½ of lobe) or T2c (palpable both lobes) (n = 313)
0–2.5 |
Organ confined |
84 |
(78–89) 59 |
(47–70) |
44 (31–58) |
49 (32–65) |
|
|
(n = 16) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
14 |
(9–19) |
24 |
(16–33) |
29 (19–42) |
24 (14–36) |
|
extension (n = 10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
PROSTATE CANCER STAGING |
211 |
||||
|
Table 6.3 Continued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSA |
Pathological |
|
|
|
Biopsy Gleason Score |
|
|
|
|
|
|
range |
stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5–6 |
3 + 4=7 |
4 + 3 = 7 |
8–10 |
|
|
|||||
|
(ng/mL) |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 1 |
(0–3) |
6 (0–14) |
6 (0–14) |
8 (0–21) |
|
|
|||
|
|
(n = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
1 |
(0–3) |
10(2–25) |
19 (4–40) |
17 (3–42) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.6–4.0 |
Organ confined |
|
74 (68–80) |
47 (39–56) |
36 (27–45) |
39 (28–50) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 28) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
|
23 (18–29) |
37 (28–45) |
46 (36–55) |
37 (27–48) |
|
|
||
|
|
extension (n = 15) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle |
2 |
(1–5) |
13(7–21) |
13 (7–22) |
19 (9–32) |
|
|
||
|
|
(+)(n = 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
0 |
(0–1) |
3 (0–7) |
5 (0–14) |
4 (0–13) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1–6.0 |
Organ confined |
|
66 (59–72) |
36 (29–43) |
25 (19–32) |
27 (19–37) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 46) |
|
30 (24–36) |
41 (33–47) |
47 (38–55) |
38 (28–48) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Extraprostatic |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
extension (n = 40) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle |
4 |
(2–6) |
16(10– 23) |
15 (9–23) |
22 (13–33) |
|
|
||
|
|
(+)(n = 7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
1 |
(0–2) |
7 (3–12) |
13 (6–21) |
11 (4–23) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.1–10.0 |
Organ confined |
|
62 (55–68) |
32 (26–38) |
22 (17–29) |
24 (17–33) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 53) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
|
32 (26–38) |
41 (33–49) |
47 (38–56) |
38 (29–48) |
|
|
||
|
|
extension (n = 28) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 5 |
(3–8) |
20 (13–28) |
19 (11–28) |
27 (16–39) |
|
|
|||
|
|
(n = 15) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
1 |
(0–2) |
6 (3–11) |
11 (5–19) |
10 (3–20) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>10.0 |
Organ confined |
|
46 (39–53) |
18 (13–24) |
11 (7–15) |
12 (7–18) |
|
|
|||
|
|
(n = 8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extraprostatic |
|
41 (34–50) |
40 (31–51) |
40 (30–52) |
33 (22–46) |
|
|
||
|
|
extension (n = 15) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seminal vesicle (+) 7 |
(4–12) |
23 (15–33) |
19 (10–29) |
28 (16–42) |
|
|
|||
|
|
(n = 10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymph node (+) |
5 |
(2–8) |
18(9–30) |
29(15–44) |
26 (12–44) |
|
|
||
|
|
(n = 8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reprinted with permission from Makarov DV, Trock BJ, Humphreys EB, et al. (2007). Urology 69(6):1095–1101.
