
1267
.pdfText 2
1. Просмотрите текст и постарайтесь понять, о чем идет речь.
TRANSISTORS
In 1948 a revolutionary concept was introduced to the electronics world: the invention of the transistor, a crystal which amplified, was announced. Nothing like this had happend in electronics since the discovery of the triode vacuum tube in 1907; some years later radio tubes replaced the crystal detectors of the wireless era.
Now a crystal amplifier, the transistor, challenges the vacuum tube because transistors are smaller, simpler, more efficient, more rugged and longer lived. Already transistors have replaced tubes in hearing aids, with unheard-of battery economy. Moreover, many transistor circuits have fewer components than the vacuum tube circuits, such as multi-vibrators. For example, in switching circuits, such as multi-vibrators, one point-contact transistor will do the work of two triode tubes.
The transistor is a current-operated device, whereas the vacuum tube is a voltage-operated device. The transistor seems destined to become a relatively high current, low-voltage device, although the vacuum tube is a high-voltage, low current device. Transistors, because of their desirable properties, shortly may replace electron tubes to a large extent in communication equipment, computers, radio and television receivers.
2. Прочтите и выучите:
amplify – усиливать, расширять unheard-of – неслыханный
rugged – неровный, твердый, стойкий challenge – бросать вызов
aid – помощь, пособие, средство
switch – переключать, переключатель, выключатель, коммутатор point-contact transistor – точечный транзистор
the transistor seems destined to become – транзистору, кажется, суждено стать
receiver – приемник, резервуар
3. Задайте общие вопросы к следующим предложениям и дайте краткие ответы:
1. The beginnings of all science lie far back near the dawn of human history. 2. The transformer grew out of the experiment of Faraday. 3. Both
23
elements differ in their chemical and phisical properties. 4. This mixture is placed into a test tube. 5. The rotor of a steam turbine consists of many-bladed fanlike wheels. 6. The resistivity of semiconductors will depend upon the direction of the current flow. 7. The signal can be amplified, recorded, or modified by an electric circuit.
4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на перевод because и because of.
1.Energy resources of our country are very large because of the great power potential in Siberia. 2. World energy resources are practically unlimited because we have studied only a small part of the mineral wealth of the earth.
3.Electronocs is useful to industry and science because a physical condition – temperature, weight, viscosity and thickness – can be converted into an electric signal. 4. All electric effects are really electronic, because all electric currents result from the movement of electrons, and all electric charges appear because of accumulation of electrons.
5.Прочтите текст повторно и ответьте на следующие вопросы:
1. When were transistors invented? 2. When was the triode vacuum tube discovered? 3. What is the difference? 4. Why does the transistor challenge the vacuum tube? 5. What can you say about the destiny of transistors?
6. Подготовьте резюме (аннотацию) текста.
Text 3
1. Переведите текст на русский язык в письменной форме.
SEMICONDUCTORS
A transistor is an active semiconductor device with three or more electrodes. By active we mean that the transistor is capable of current gain, voltage, amplification and power gain. A transistor is an electron device in which electronic conduction takes place within a semiconductor.
A semiconductor is an electric conductor with resistivity in the range between metals and insulators, in which the electrical charge carrier concentration increases with increasing temperature over some temperature range.
24
The resistivities of semiconductors and insulators decrease rapidly with rising temperatures, while those of metals increase relatively slowly. Unlike metals and insulators, the resistivity of semiconductors depends upon the direction of current flow. The direction of easiest current flow of lowest resistivity is called the forward direction, the direction of restricted current flow or highest resistivity is known as the reverse or back direction.
Semiconductors, such as the elements germanium and silicon, possess two types of current carries, namely, negative electrons and positive holes. A hole is a mobile vacancy in the electronic valence structure of a semiconductor which acts like a positive electronic charge with a positive mass.
2. Прочтите и выучите:
voltage – напряжение germanium – германий silicon – кремний valence – валентность
3. |
Закончите следующие предложения, используя текст: |
|
1. |
A transistor is an electron --------------------------------------------- |
. |
2. |
The resistivity of semiconductors depends on --------------------- |
. |
3. |
The forward direction is ---------------------------------------------- |
. |
4. |
The riverse or back direction is -------------------------------------- |
. |
5. |
Semiconductors possess ---------------------------------------------- |
. |
4. Дайте краткие утвердительные или отрицательные ответы на следующие вопросы:
1.Is a semiconductor defined as an electric conductor? 2. Do semiconductors vary greatly in appearance? 3. May transistors replace vacuum tubes?
4.Does the state of substances depend on temperature and pressure? 5. Will you study electronics this year? 6. Have many human activities played a part in scientific inventors? 7. Did the ancients know anything about electricity?
5.Используя текст, расскажите все, что вы узнали о полупроводниках. При ответе используйте следующие выражения:
the subject of the discussion is...; I know that..; it should be noted that...; the text deals with ...; as for the problem of ...; it is worth mentioning ...; it is wellknown fact ... .
25
Text 4
1. Прочтите текст, найдите в тексте предложения, в которых содержатся: а) основная информация; б) уточняющая информация.
THE DESTINY OF SEMICONDUCTORS
A semiconductor is often defined as an electric conductor that has a conductivity intermidiate between that of an insulator and that of a metal. The more important semiconductors are: boron, germanium, silicon, selenium, phosphorus, gray tin and others.
The mechanical properties of semiconductors vary greatly. However, in hardness, brittleness, and fracture strength, semiconducting crystals resemble insulating crystals more than they do metals. Besides their electric propertis, which in themselves may be of great variety, semiconductors vary in such physical qualities as magnetism, specific heat and thermal conductivity.
Simiconductors are widely used in electronics. They challenge vacuum tubes in many applications in the electronic industry. Engineers and physicists are going to solve many engineering problems by means of semiconductors.
2. Прочтите и выучите:
boron – бор selenium – селен phosphorus – фосфор tin – олово
vary – меняться, разниться brittleness – хрупкость, ломкость fracture – перелом, трещина
strength – сила, прочность, сопротивление resemble – походить, иметь сходство thermal – термический
3. Быстро просмотрите следующие слова и выпишите те из них, которые относятся к теме “Полупроводники”:
magnetism, diod, machinery, electricity, temperature, transistor, heat, current flow, aluminium, tin, motor, transformer, generator, subject,concept, engine, turbine, electrode, metal, brittle, wax, insulator, resistivity,direction, valence.
4. Прочтите еще раз тексты 3, 4 и сделайте их аннотацию на английском языке в письменной форме.
26
5. Задайте вопросы ко всем частям следующих предложений:
1. Semiconductors will replace vavuum tubes in many applications. 2. The more important semiconductors may be classified into three groups.
6. Переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на употребление страдательного залога:
1. When the molecules of even a good insulator are acted upon by an electric field, there is a motion of electrons due to this field. 2. the possibility of a breakdown of an insulator which is referred to in the above article is due to high voltage. 3. The exact operation of some devices cannot be much relied upon due to their being slightly influenced by the changes in the ambient temperature. 4. If the electron is allowed to go back to the atom the balance of ghargr is restored and the atom is again uncharged or neutral. 5. The conclusions which were arrived at by the experimenter fill the demands of the present state of technical development. 6. It should be noted that each control field is given a definite polarity. 7. When the microphone is being spoken into, the alternator does not produce a high frequency current of constant amplitude.
Text 5
1.Определите по формальным признакам, какой частью речи являются выделенные в тексте слова.
2.Найдите в ряду данных ниже слов антонимические пары.
Solid-state, receive, continue, reverse, stop, more, positive, unobvious, send, include, long, many, evident, static, negative, short, forward, conclude, less, apparent, liquid-state, dynamic.
3.Найдите в тексте сказуемые в различных грамматических формах и залогах, объясните их употребление.
4.Прочтите текст, постарайтесь понять его основное содержание
искажите, что вы знаете об устройствах, о которых идет речь в данном тексте. Помогли ли ваши знания об этих устройствах пониманию текста?
27
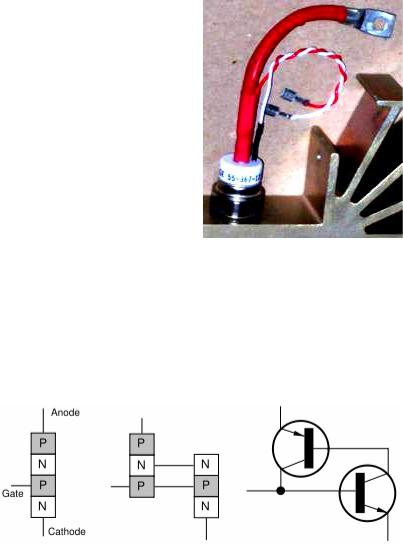
THYRISTORS
The thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as a switch, conducting when their gate receives a current pulse, and continue to conduct for as long as they are forward biased (that is, as long as the voltage across the device has not reversed).
Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous; others define SCRs as a subset of thyristors, along with gate turn-off thyristor (GTO), triode ac switch (triac), static induction transistor (SIT), static induction thyristor (SITH) and MOS-controlled thyristor (MCT). Among the latter, the International Electrotechnical Commission 60747-6 standard stands out.
Non-SCR thyristors include devices with more than four layers, such as triacs and DBGTOs.
The thyristor is a four-layer semiconducting device, with each layer consisting of alternately N-type or P-type material, for example P-N-P-N. The main terminals, labeled anode and cathode, are across the full four layers, and the control terminal, called the gate, is attached to p-type
material |
near |
to the |
Function |
cathode. |
(A |
variant |
|
called a |
SCS |
Silicon |
|
Controlled |
Switch |
|
|
brings all four |
layers |
|
|
out to terminals.) The operation of a thyristor can be understood in terms of a pair of
tightly coupled Bipolar Junction Transistors, arranged to cause the self-latching action.
Thyristors have three states:
Reverse blocking mode - Voltage is applied in the direction that would be blocked by a diode.
Forward blocking mode - Voltage is applied in the direction that would cause a diode to conduct, but the thyristor has not yet been triggered into conduction.
28
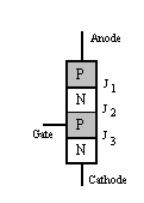
Forward conducting mode - The thyristor has been triggered into conduction and will remain conducting until the forward current drops below a threshold value known as the "holding current".
Function of the gate terminal
The thyristor has three p-n junctions (serially named J1, J2, J3 from the anode).
When the anode is at a positive potential Vak with respect to the cathode with no voltage applied at the gate, junctions J1 and J3 are forward biased, while junction J2 is reverse biased. As J2 is reverse biased, no conduction takes place (Off state). Now if Vak is increased beyond the breakdown voltage VBO of the thyristor, avalanche breakdown of J2 takes place and the thyristor starts conducting (On state).
If a positive potential VG is applied at the gate terminal with respect to the cathode, the breakdown of the junction J2 occurs at a lower value of Vak. By selecting an appropriate value of
VG, the thyristor can be switched into the on state immediately.
It should be noted that once avalanche breakdown has occurred, the thyristor continues to conduct, irrespective of the gate voltage, until either: a) the potential VG is removed or; b) the current through the device (anode−cathode) is less than the holding current specified by the manufacturer. Hence VG can be a voltage pulse, such as the voltage output from a unjunction transistor (UJT) relaxation oscillator.
These gate pulses are characterized in terms of gate trigger voltage (VGT) and gate trigger current (IGT). Gate trigger current varies inversely with gate pulse width in such a way that it is evident that there is a minimum gate charge required to trigger the thyristor.
5. Прочтите и выучите:
solid-state – твердое состояние
bias – смещение (с помощью подачи напряжения), подмагничивание; смещать/ся
subset – подгруппа
gate turn-off thyristor – запирающий тиристор
triode ac switch – симметричный триодный тиристор, симистор static induction transistor – неподвижныц индукционный транзистор static induction thyristor – неподвижный индукционный тиристор
MOS-controlled thyristor – МОП (металл – оксид – полупроводник) –
тиристор
tightly – наглухо, плотно
29
Silicon Controlled Switch – кремниевый тетродный тиристор holding current – ток удержания
gate terminal – вывод управляющего электрода (тиристора) UJT – однопереходный транзистор
relaxation oscillator – релаксационный генератор
DB-GTO – Distributed Buffer Gate Turn-Off thyristor reverse blocking – не проводящий в обратном направлении forward conducting – прямая проводимость
gate terminal – вывод затвора
6. Прочтите слова и словосочетания и назовите их эквиваленты в русском языке.
layer |
to conduct |
to define |
control terminal |
gate |
self-latching |
freshold value |
junction |
avalanche breakdown |
to occur |
irrespecnive |
|
hence |
gate trigger voltage |
gate trigger current |
|
7. Найдите в тексте слова, соответствующие данным ниже определениям (дефинициям):
1)a piece of equipment, a machine or tool used for a specific task;
2)the substance of which a thing is made or composed;
3)an electromotive force or potential difference expressed in volts;
4)a brittle metalloid element that exists in two allotropic forms; occurs principally in sand, quartz, granite, feldspar, and clay;
5)he condition of a person, thing, etc., with regard to main attributes;
6)the course or line along which a person or thing moves, points, or lies;
7)a flow of electric charge through a conductor;
8)the attribute of matter by which it responds to electromagnetic forces responsible for all electrical phenomena, existing in two forms to which the signs negative and positive are arbitrarily assigned;
9)the least possible amount, degree, or quantity;
10)the linear extent or measurement of something from side to side, usually being the shortest dimension or (for something fixed) the shortest horizontal dimension.
8. Найдите в тексте синонимы к словам и составьте с ними предложения.
Рroducer, to take place, gadget, carry on, to form, case, to enlarge, acceptable, substance, to assign, to incorporate.
30
9. Найдите эквиваленты в русском языке для следующих выражений:
to act as…, along with…, can be understood in terms of…, arranged to cause…, to take place…, should be noted that.
10. Преобразуйте в предложениях страдательный залог в действительный и наоборот по следующей модели:
a) A triac can be triggered by either a positive or a negative voltage being applied to its gate electrode.
Either a positive or a negative voltage being applied to triac’s gate electrode can trigger it.
b) The Thyristor block implements a macromodel of the real thyristor.
A macromodel of the real thyristor is implemented in the Thyristoe block.
1.Low power TRIACs are used in many applications such as light dimmers, speed controls for electric fans and other electric motors.
2.However, when used with inductive loads such as electric fans, care must be taken to assure that the TRIAC will turn off correctly at the end of each half-cycle of the ac power.
3.The GTO can be turned-on by a gate signal, and can also be turned-off by a gate signal of negative polarity.
4.The turnoff time Tq represents the carrier recovery time: it is the time interval between the instant the anode current has decreased to 0 and the instant
when the thyristor is capable of withstanding positive voltage Vak without turning on again.
5.You must use a stiff integrator algorithm to simulate circuits containing thyristors.
6.When the output voltage of the supply rises above the zener voltage, the thyristor conducts, shorting the power supply output to ground.
7.The stabilized high voltage DC supply for the receiver was obtained by moving the switching point of the thyristor device up and down the falling slope of the positive going half of the AC supply input.
8.The precise switching point was determined by the load on the output DC supply as well fluctuations on the input AC supply.
9.Because thyristors can be triggered on by a high rate of rise of off-state voltage, in many applications this is prevented by connecting a resistor-capacitor (RC) snubber circuit between the anode and cathode terminals in order to limit the dV/dt (i.e., rate of change of voltage versus time).
11. Прочтите текст еще раз, подготовьте 10 специальных вопросов по содержанию и предложите своим одногруппникам ответить на них.
31
12.Выделите в тексте элементы, которые, на ваш взгляд, являются ключевыми, и на их основе составьте сокращенный вариант текста из 10–12 предложений.
13.Прочтите текст. Предложите свой вариант заголовка. Выполните письменный перевод на русский язык.
In a conventional thyristor, once it has been switched on by the gate terminal, the device remains latched in the on-state (i.e. does not need a continuous supply of gate current to conduct), providing the anode current has exceeded the latching current (IL). As long as the anode remains positively biased, it cannot be switched off until the anode current falls below the holding current (IH).
A thyristor can be switched off if the external circuit causes the anode to become negatively biased. In some applications this is done by switching a second thyristor to discharge a capacitor into the cathode of the first thyristor. This method is called forced commutation.
After a thyristor has been switched off by forced commutation, a finite time delay must have elapsed before the anode can be positively biased in the offstate. This minimum delay is called the circuit commutated turn off time (tQ). Attempting to positively bias the anode within this time causes the thyristor to be self-triggered by the remaining charge carriers (holes and electrons) that have not yet recombined.
For applications with frequencies higher than the domestic AC mains supply (e.g. 50 Hz or 60 Hz), thyristors with lower values of tQ are required. Such fast thyristors are made by diffusing into the silicon heavy metals ions such as gold or platinum which act as charge combination centres. Alternatively, fast thyristors may be made by neutron irradiation of the silicon.
14. Подготовьте сообщение на любую из предложенных ниже тем.
Asymmetrical SCR
Reverse Conducting Thyristor
Light Activated SCR, or LTT – Light Triggered Thyristor
Breakover Diode
Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
Modified Anode Gate Turn-Off thyristor
Distributed Buffer Gate Turn-Off thyristor
Base Resistance Controlled Thyristor
Static Induction Thyristor
Light Activated Semiconducting Switch
32
