
- •Informatics as a unity of science and technology.
- •Information, its types and properties.
- •Information representation options in the Computer
- •Von Neumann's principles, the control device, instruction sets and types of commands
- •Instruction counter
- •Input-output and interruptions.
- •Virtual memory.
- •Input-output devices.
- •Variables, expressions and assignment, the elementary input-output, operators of branching and iterated operators.
- •Models of operating systems
- •Video information output devices.
- •Internet services.
- •Laboratory work № 2. Formatting. Design of tables. Use of functions.
- •Laboratory work 3. Using the formulas in absolute and relative references. Linking worksheets.
- •Table 10 – Economic indicators for the implementation of company «dt»
- •Laboratory work №4. Graphic features of ms excel
- •Table 16 – Data on the volume of sales
- •11. Set the format of integers.
- •Laboratory work № 5. AutoComplete. AutoCompletion. Working with lists. Create custom lists. Using cell names in formulas.
- •Laboratory work №6. Using mathematical and statistical functions. Worksheet protection.
- •Laboratory work № 7 Using a spreadsheet as a database. Using the function Date and time
- •Laboratory work №8 Sort and list processing. AutoFilter and Advanced Filter.
- •Laboratory work № 9. Organization workbooks. List processing.
- •Laboratory work № 10
- •Laboratory work № 11 a hierarchical structure of the electronic table.
- •Laboratory work №12. Database in Excel. Processing data using forms. Data analysis
- •Laboratory work №13. Creation of schedules. Creation of function graphs with two conditions.
- •Laboratory work №14.
- •Laboratory work №15
- •Vba. User functions of a work sheet and procedure
- •Laboratory work №16 Automation of calculations
S. Seyfullin Kazakh AgroTechnical university
Methodical complex discipline "Informatics"
for students of economics
content
№ |
Name |
page |
Lectures |
||
2 |
Topic 1. The basic concepts of computer science. Informatics as a unity of science and technology. The structure of modern science. The place of informatics in the sciences. Social aspects of informatics. Law aspects of informatics. Ethical aspects of informatics. Information, its types and properties. Information representation options in the Computer. The continuous and discrete information. Data media. |
5 |
3 |
Topic 2. Bases of discrete mathematics. Relation and set functions. Bases of logic, logician of statements, logic sheaves, validity tables |
14 |
4 |
Topic 3. Main concepts of architecture of the computer. Review and history of computers architecture. Logic elements of the computer. Submission of numerical data and notation. Sign representations and representations in an additional code |
21 |
5 |
Topic 4. The machine organization. Von Neumann's principles, the control device, instruction sets and types of commands. Input-output and interruptions. Devices of storage of the computer. Memory hierarchy. The base memory and operation organization. Virtual storage. Input-output devices. The review of the modern hardware support |
31 |
6 |
Topic 5. Algorithmic solution of tasks, analysis of algorithmic complexity. Strategy of the solution of tasks. Algorithms and search of decisions. Concept and properties of algorithms. Strategy of realization of algorithms. Structures of data. Block diagrams as graphic realization of algorithms. Main computing algorithms. Analysis of algorithms: standard classes of complexity, an expense on memory size and time |
45 |
7 |
Topic 6. Acquaintance to programming languages. Review of programming languages. Main designs of programming. Variables, expressions and giving, the elementary input-output, operators of branching and iterative operators. Programming paradigms. Procedural programming. Object-oriented programming |
55 |
8 |
Topic 7. Bases of operating systems and networks. Review of the modern application software. Main concepts of operating systems. History of development of operating systems. Functioning of a typical operating system. Decomposition techniques of an operating system. Control of processes. Planning and dispatching. File systems. Utilities. Drivers. Networks and telecommunications. Network safety. |
64 |
9 |
Topic 8. Graphics and Internet. Hierarchy of the graphic software. Simple color models. Graphic systems. Systems of bitmap and vector graphics. Video information output devices. Graphic editors. Graphic communications. History and sources of Internet. Theoretical bases of the Internet. Internet services. Information security and its components. Archives. Anti-virus programs. |
80 |
Laboratory researches |
|
|
10 |
MS Excel. Organization workbooks. Organization of calculation |
94 |
11 |
MS Excel. Formatting. Design of tables. Use of functions |
97 |
12 |
MS Excel. Using the formulas in absolute and relative references. Linking worksheets. |
101 |
13 |
MS Excel. Graphic features |
107 |
14 |
MS Excel. AutoComplete. Auto Completion. Working with lists. Create custom lists. Using cell names in formulas. |
112 |
15 |
MS Excel. Using mathematical and statistical functions. Worksheet protection. |
116 |
16 |
MS Excel. Using a spreadsheet as a database. Using the functions of category «Date and time» |
122 |
17 |
MS Excel. Sort and list processing. AutoFilter and Advanced Filter. |
125 |
18 |
MS Excel. Organization workbooks. List processing. |
127 |
19 |
MS Excel. Calculating totals. Data consolidation. |
130 |
20 |
MS Excel. A hierarchical structure of the electronic table. |
135 |
21 |
MS Excel. Database in Excel. Processing data using forms. Data analysis |
138 |
22 |
MS Excel. Creation of schedules. Creation of function graphs with two conditions |
143 |
23 |
MS Excel. Bit-by-bit addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of two massifs. Decision of system of the linear equations |
147 |
24 |
MS Excel. VBA. User functions of a work sheet and procedure |
153 |
25 |
MS Excel. Automation of calculations |
156 |
26 |
Independent work of the student № 1 |
159 |
27 |
Independent work of the student № 2 |
159 |
28 |
The used literature and sources |
160 |
29 |
Glossary |
162 |
Topic 1. The basic concepts of informatics.
Informatics as a unity of science and technology. The structure of modern science. The place of informatics in the sciences. Social aspects of informatics. Law aspects of informatics. Ethical aspects of informatics. Information, its types and properties. Different levels of presentation options about information. The continuous and discrete information. Data media. Operations with data.
Informatics as a unity of science and technology.
The matter, energy and information are the basic essence of nature; they are «three whales» upon which the universe is based. And if the matter and energy role in the existence of human society and the Universe as a whole was realized for many years ago, information role in the live and lifeless nature only just start to be understood.
The modern informatics is great on volume and it is very dynamic. The courses of mathematics, physics, chemistry, theoretical mechanics, theory of electric chains, chemistry and the majority of other disciplines studied in higher education institutions practically haven’t been changed for many years of training, this process of training in informatics is dynamic.
First of all, it is necessary to define what the subject «Informatics» is. The interpretation of the term «informatics» isn't established and it is not considered to be standard.
Informatics is a young scientific discipline studying questions connected with search, collecting, storage, transformation and information use in the most various fields of activity of the person.
Let's see the history of emergence and development of the first computers.
After the Second World War the cybernetics appeared and developed. Cybernetics is a science about the general regularities in management and communication in various systems – artificial, biological and social. The birth of cybernetics is connected with the publication of the book of American mathematician «Cybernetics: Or the Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine» in 1948. Developing at the same time with the computer development, the cybernetics passed to the general science about information transformation.
The attempt to define the meaning of modern informatics was made in 1978. The international congress on informatics – «The concept of informatics covers the areas connected with development, creation, use and material service of systems of processing of information, including cars, equipment, software, organizational aspects and also the complex of industrial, commercial, administrative and social influence»
The term «informatique» is entered in France in the 60-70th years of the last century. A little earlier in the USA there was a term «computer science» – information transformation on the basis of computer facilities. Now both terms are used on equal ground. In the USSR the term «informatics» was fixed in 1983 when in the Academy of Sciences of the USSR the office of informatics, computer facilities and automation was created. The modern meaning of the term «informatics» contains in the definition formulated by the international congress in Japan in 1978:
The informatics is a complex of the scientific and practical disciplines studying all aspects of receiving, storage, transformation, transfer and information use.
The informatics has two complementary aspects – scientific and technological. The scientific aspect is more settled, technological aspect is very mobile, though in a technological part there is quite created kernel which is a little subjected to changes.
The informatics is the technical science systematizing receptions of creation, storage, reproduction, processing, and data transmission by means of computer aids, and also principles of functioning of these means and methods of their control. The informatics is a practical science. The informatics as a science develops on the basis of mathematics, cybernetics, physics, and equipment.
The concepts «informatics» and «cybernetics» are identified, but it is wrong. Cybernetics – science about the general regularities in management and communication in various systems.
Structure of modern informatics.
The main objective of informatics – ordering of receptions and work methods with hardware and software computer facilities
The subjects of informatics are the following:
• Hardware of computer aids
• Software of computer aids
• Interaction means of hardware and software aids
• Interaction of the person with hardware and software aids
The objects of appendices of informatics are the most various sciences and areas of practical activities.
The structures of informatics (constituents) are the following:
Theoretical informatics – the informatics section using mathematical methods for the general studying of processes of processing of information (the theory of algorithms and machine of Turing, information theory, the coding theory, the theory of languages and grammar, research operation, the theory of turns)
Computer facilities – the informatics section in which the general principles of construction computing systems (basic decisions at level of architecture of the computing systems defining structure, appointment, functionality and principles of interaction of devices are developed)
Programming – the section which is engaged in development of systems of the software (creation of the system software and creation of the applied software)
Information systems – the section of informatics connected with the solution of questions on the analysis of flows of information in various difficult systems, their optimization, structuring, storage and information search principles
Artificial intelligence – the section in which the most difficult problems connected with psychology, physiology, linguistics and other sciences are solved.
The place of informatics in the sciences.
Let's consider the place of science of informatics in the traditionally developed system of sciences (technical, natural, humanitarian etc.). In particular, it would allow finding the place of general educational course of informatics among other subjects.
Let's remind A. Ershov's definition of informatics – «a fundamental natural science». Academician B.N.Naumov defined informatics «as the natural science studying the general properties of information, processes, methods and means of its processing (collecting, storage, transformation, moving, delivery)».
Let's specify what the fundamental science is and what the natural science is. The fundamental sciences are the sciences with general scientific character, the sciences which are used in fundamental sciences and many kinds of activity. There is no doubt in the fundamental nature of so different sciences as mathematics and philosophy. Informatics has also general scientific importance as the concepts «information», «processes of processing of information» have general scientific meaning.
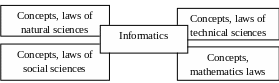
Fig.1.2 – The place of informatics in the sciences
However, many scientists emphasize that the informatics has characteristic features of other groups of sciences – technical and humanitarian (or public).
Informatics has such lines of technical sciences as the aspects connected with creation and functioning of machine systems of processing of information. Informatics has some lines of humanitarian (public) science that is caused by its contribution to the development and improvement of the social sphere. Thus, the informatics is complex, interdisciplinary branch of scientific knowledge as it is represented on fig. 1.2.
Social aspects of informatics
The term «social aspects» with reference to the most part of the sciences especially fundamental sounds strange. The phrase «Social aspects of mathematics» is not meaningful. However, informatics – not only a science.
Let's remember the definition quoted above: «... complex of industrial, commercial, administrative and social influence».
Indeed, not many factors make an influence on the social sphere of societies (certainly, only those factors which are in the condition of quiet development, without wars and cataclysms) as information.
Society’s information – process of penetration of information technologies to all spheres of life and society activity.
In XXI century’s information is one of the reasons of an overflow of people of the sphere of direct production of goods to the so-called, information sphere. There are many people known as «white collars» – the people creating material values directly; they are connected with the information processing. They are: teachers, bank employees, programmers and many other categories of workers. There were also new boundary specialties. Is it possible to recognize the programmer as a worker developing programs for machines with numerical programmed control? – According to number of parameters it is possible, however his work is not physical, it is intellectual.
It is difficult to live in the described above processes and to weigh what is more inside of them– positive or negative sides and there are no accurate criteria for this purpose. The hard physical activity in not too comfortable conditions, but with confidence that it will be a constant source of existence for you and your family, on the one hand, or intellectual work at comfortable office, but without confidence of tomorrow. What is better? Certainly, it is not necessary to assimilate yourself to the English workers breaking at the end of the XVIII century machines depriving them, but the government and society are obliged to remember negative social consequences of information and scientific and technical progress as a whole and to look for compensatory mechanisms.
Law aspects of informatics
The activity of programmers and other experts working in the sphere of informatics, even more often represents itself as object of legal regulation. Some actions can be qualified as an offense (crime).
The legal consciousness as a whole and in the field of informatics especially, is in our society at a low level. Whether all know answers to the following questions:
• Whether it is possible without copying the bought program to give opportunity to use it to other person;
• Who possesses copyright of the program created by the student during implementation of the thesis?
• Whether it is possible to copy the bought program to have a backup copy;
• Whether it is possible to decompile the program to understand its details or to correct mistakes;
• What is the difference between an author's and property right.
There are many questions similar to these ones. Of course, the following answers are obvious: it is impossible to create viruses, it is impossible to misbehave in networks, it is impossible to start commercial information in noncommercial teleconferences, it is impossible to open and distort protected information in another's databases etc., i.e. to make acts which can be object of criminal prosecution. But the answers to many questions aren't so obvious and sometimes casuistic and confused and not only in our country.
It is necessary to note that regulation in the sphere connected with protection of information, programming etc., is essentially new for Kazakhstan legislation, it is still poorly developed direction. Now the criminal legislation of Kazakhstan not fully considers all possible computer crimes. In general, in legislative practice of many countries different types of computer crimes are noted and methods of fight against them are developed.
Computer crimes can be divided into two big categories (we will consider in detail it later):
1) Crimes connected with intervention in operation of computers;
2) Crimes using computers as necessary means.
The current state of legal regulation of the sphere concerning the informatics in Kazakhstan is connected with the questions of violation of copyright. The most part of the software used by certain programmers, users and the whole organizations is acquired as a result of illegal copying, i.e. plunder. The requirement to legalize ways of fight against this vicious practice appears, first of all, it concerns the development of informatics.
Ethical aspects of informatics
Not all rules regulating activity in the sphere of informatics can be known as rules of law. A lot of things are defined by observance of unwritten rules of behavior for those who are involved in the world of computers. However, in this regard the informatics doesn't differ at all from any other field of activity of the person in society.
As well as in any other big and branched-out sphere of human activity, in informatics there were certain moral ethical standards of behavior and activity.
Moral ethical standards in the environment software designer differ from ethics of an everyday life by little bigger openness and altruism. The majorities of present experts-informatics were created and acquired the knowledge and qualification thanks to disinterested consultations and assistance of other experts. It is obvious; therefore they are ready to render disinterested aid, to give advice or consultation, to provide the computer for performance of any manipulations with diskettes etc. A striking example of the psychological atmosphere in the environment software designer is an extending international movement of the programmers providing software created by them for free distribution.
These are positive aspects, but there are also negative ones. Let's pay attention to the language software designer. The slang software designer is constructed on the English-speaking terms distorted under our pronunciation and the abbreviations entered by foreign firms – developers of computers and the software in technical documentation. The slang words borrowed from Russian-Kazakh on the basis of analogies and associations on similarity and contiguity are formed. We have to reconcile with the fact that many special terms came to us from the USA. Nobody won't pass today from the term «printer» to similar «the automatic digital printer» (which was used not too long ago). The relative brevity makes influence on the use of similar words in domestic literature.
Ethical problems acquire a special sharpness in the process of operation in the wide area telecommunication networks. To open protection of another’s database – a criminal offense. And whether is it possible to afford obscene expressions or their transparent euphemisms? Commercial advertising in a noncommercial teleconference? The decent person won’t allow himself to do it in spite of the fact if the punishment is provided for it by the law or not.
Ethics – system of norms of moral behavior of the person. The decent person won't read contents of the diskette forgotten by the neighbor on a workplace, not because it threatens it with punishment but because it is an immoral act; he won't copy the program because of the absence of her master not because he can be brought to an action, but because these act will be condemned by his colleagues. Every time, when the person is going to make a doubtful act in the sphere of professional activity, he will reflect whether it meets the ethical standards developed in professional community.
