
- •1. Основные понятия и положения 11
- •2. Центральное растяжение и сжатие стержня 17
- •3. Геометрические характеристики плоских сечений 42
- •4. Кручение 49
- •5. Изгиб стержней 57
- •Introduction 173
- •1. Basic concepts and principles 175
- •2. Tension and compression of a bar 181
- •3. Geometric characteristics of cross sections 202
- •4. Torsion 208
- •5. Bending of bars 216
- •Index 405 введение
- •1. Основные понятия и положения
- •1.1. Задачи сопротивления материалов, основные гипотезы и допущения
- •1.2. Типы нагрузок и деформаций
- •1.3. Определение внутренних усилий методом сечений. Напряжения
- •2. Центральное растяжение и сжатие стержня
- •2.1. Напряжения и продольная деформация при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.2. Закон Гука при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.3. Поперечная деформация при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.4. Диаграмма растяжения низкоуглеродистой стали
- •2.5. Потенциальная энергия деформации при растяжении
- •2.6. Расчеты на прочность при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.7. Статически неопределимые задачи
- •2.8. Напряжения в наклонных сечениях при растяжении (сжатии) в одном направлении
- •2.9. Закон парности касательных напряжений
- •2.10. Определение напряжений в наклонных сечениях при растяжении (сжатии) в двух направлениях
- •2.11. Определение главных напряжений и положения главных площадок
- •2.12. Зависимость между деформациями и напряжениями при плоском и объемном напряженных состояниях (обобщенный закон Гука)
- •2.13. Работа внешних и внутренних сил при растяжении (сжатии). Потенциальная энергия деформации
- •3. Геометрические характеристики плоских сечений
- •3.1. Статический момент площади
- •3.2. Полярный момент инерции
- •3.3. Осевой момент инерции
- •3.4. Момент инерции при параллельном переносе осей
- •3.5. Главные оси и главные моменты инерции
- •4. Кручение
- •4.1. Определение крутящего момента
- •4.2. Определение напряжений в стержнях круглого сечения
- •4.3. Деформации и перемещения при кручении валов
- •4.4. Потенциальная энергия при кручении
- •5. Изгиб стержней
- •5.1. Типы опор балок
- •5.2. Определение опорных реакций
- •5.3. Определение внутренних усилий при изгибе
- •5.4. Правило знаков для изгибающих моментов и поперечных сил
- •5.5. Дифференциальные зависимости при изгибе
- •5.6. Построение эпюр изгибающих моментов и поперечных сил
- •5.7. Определение нормальных напряжений
- •5.8. Условия прочности по нормальным напряжениям
- •5.9. Потенциальная энергия деформации при изгибе
- •5.10. Теорема о взаимности работ. Теорема о взаимности перемещений
- •5.11. Определение перемещений методом Мора
- •6. Теории прочности
- •6.1. Назначение гипотез прочности
- •6.2. Первая гипотеза прочности
- •6.3. Вторая и третья гипотезы прочности
- •6.4. Энергетические гипотезы прочности
- •7. Сложное сопротивление
- •7.1. Изгиб в двух плоскостях (косой изгиб)
- •7.2. Изгиб с растяжением (сжатием)
- •7.3. Внецентренное сжатие (растяжение)
- •7.4. Кручение с изгибом
- •7.5. Кручение с растяжением (сжатием)
- •7.6. Пример расчета вала на изгиб с кручением
- •8. Расчет тонкостенных сосудов
- •9. Расчет сжатых стержней на устойчивость (продольный изгиб)
- •9.1. Устойчивые и неустойчивые формы равновесия
- •9.2. Формула Эйлера для критической силы
- •9.3. Влияние способа закрепления концов стержня на критическую силу
- •9.4. Пределы применимости формулы Эйлера
- •9.5. Эмпирические формулы для определения критических напряжений
- •9.6. Практическая формула для расчета на устойчивость
- •10. Динамическое действие нагрузок
- •10.1. Динамические нагрузки
- •10.2. Вычисление напряжений при равноускоренном движении
- •10.3. Определение перемещений и напряжений при ударе
- •11. Расчет на прочность при напряжениях, циклически изменяющихся во времени (расчет на усталость)
- •11.1. Основные определения
- •11.2. Кривая усталости при симметричном цикле. Предел выносливости
- •11.3. Диаграммы предельных напряжений и амплитуд цикла
- •11.4. Факторы, влияющие на предел выносливости
- •11.5. Определение коэффициента запаса прочности при симметричном цикле
- •11.6. Определение коэффициента запаса прочности при асимметричном цикле напряжений
- •Предположим, что при увеличении нагрузки на деталь отношение Такое нагружение называется простым.
- •11.7. Практические меры повышения сопротивления усталости
- •Практикум Лабораторная работа № 1
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Контрольные вопросы
- •Литература
- •Лабораторная работа № 2
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Контрольные вопросы
- •Литература
- •Лабораторная работа № 3
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Introduction
- •Basic concepts and principles
- •Tasks, main hypothesis and assumptions of the strength of materials
- •1.2. Types of loads and deformations
- •1.3. Determining the internal forces by the method of sections. Stresses
- •2. Tension and compression of a bar
- •2.1. Stresses and a longitudinal deformation in tension and compression
- •2.2. Hooke,s law in tension and compression
- •2.3. The transverse deformation in tension and compression
- •2.4. The tension diagram of the lowcarbon steel
- •2.5. The potential deformation energy in tension
- •2.6. Strength calculation in tension and compression
- •2.7. Statically indeterminate problems
- •2.8. Stresses at inclined sections under tension (compression) in one direction
- •2.9. Law of the shearing stresses couple
- •2.10. Determination of stresses at the inclined sections in tension (compression) in two directions
- •2.11. Determining the principal stresses and the principal planes position
- •2.12. The relation between the deformations and the stresses for the plane and general stresses (a general form of Hook’s law)
- •2.13. The work of the external and internal forces in tension (compression). Strain energy
- •3. Geometric characteristics of cross sections
- •3.1. First moment of an area
- •3.2. Polar moment of inertia
- •3.3. Axial moment of inertia
- •3.4. The moment of inertia at parallel displacement of axis
- •3.5. Principal axes and principal moment of inertia
- •4. Torsion
- •4.1. Determining the twisting moment
- •4.2. Determining the stresses in the round section bar
- •4.3. The deformations and displacements in the shaft torsion
- •4.4. Internal strain energy in torsion
- •5. Bending of bars
- •5.1. Types of the beam support
- •5.2. Determining the support reactions
- •5.3. Determining the internal stresses in bending
- •5.4. The sign rule for the bending moments and the shearing forces
- •5.5. The differential relationships in bending
- •I.E. The intensity of the distributed load is equal to the derivative of the shearing force with respect to the bar section abscissa.
- •I.E. The shearing force is equal to the derivative of the bending moment with respect to the bar section abscissa.
- •I.E. The second derivative of the bending moment with respect to the bar section abscissa is equal to the intensity of the distributed load.
- •5.6. Drawing bending moment and shearing force diagrams
- •5.7. Determining the normal stress
- •5.8. Strength conditions with normal stresses
- •5.9. Strain energy in bending
- •5.10. Betty’s reciprocal theorem. Reciprocal displacement theorem
- •5.11. Determining displacements by Mohr’s method
- •6. Strengtn theory
- •6.1. The purpose of strength hypotheses
- •6.2. The first strength hypothesis
- •6.3. The second and third strength hypotheses
- •6.4. The energy hypotheses of strength
- •7. Combined stress
- •7.1. Bending in two planes (non-uniplanar bending)
- •7.2. Combined axial tension (compression) and bending
- •7.3. Eceentrical tension (compression)
- •7.4. Combined torsion and bending
- •7.5. Combined torsion and compression
- •7.6. Example of the shaft calculation in bending with torsion
- •8. Calculation of the thin-walled vessels
- •9. Stability analysis of the bars in compression (buckling)
- •9.1. Stable and unstable equilibrium forms
- •9.2. Euler’s formula for the critical force
- •9.3. Influence of bar end conditions on the critical force
- •9.4. Applicability limits of of Euler’s formula
- •9.5. Empirical formula for determining the critical stresses
- •9.6. The practical formula for the stability analysis
- •10. Dynamic load action
- •10.1. Dynamic load
- •10.2. Calculating stresses under the uniformly accelerated motion
- •10.3. Determining displacements and stresses under the impact
- •11. Stress analysis under the stresses changing cyclically in time
- •11.1. Basic definitions
- •11.2. Fatigue (Wohler’s) curve under the symmetrical cycle. Fatigue strength
- •11.3. The limit stress diagram and the cycle amplitude
- •11.4. Factors influencing on the fatigue strength
- •11.5. Determining the factor of safety under the symmetrical cycle
- •11.6. Determining the factor of safety under the asymmetrical stress cycle
- •11.7. Practical measures to increase the fatigue strength
- •Practicum Laboratory work № 1
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Test specimens
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Laboratory work № 2
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Laboratory work № 3
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Individual task report
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Англо-русский терминологический словарь
- •Список фамилий ученых
- •Greek alphabet
- •Сокращения
- •Единицы измерения
- •Список наиболее употребительных знаков
- •Список использованной литературы
- •Алфавитный указатель
- •Сопротивление материалов
- •625000, Тюмень, ул. Володарского, 38.
- •625039, Г. Тюмень, ул. Киевская, 52
11. Stress analysis under the stresses changing cyclically in time
11.1. Basic definitions
A lot of machine details in their function time are repeatedly subjected to variable loads stresses in time.
For example, the carriage axle working in the bend and rotating together with the wheels suffer changing cyclically stresses although the external forces conserve their values and directions. The axle fibers are either in tension or in compression.
It is highly significant that under the action of the repeated changing loads the fracture occurs as the result of the gradual fracture development called the fatigue fracture. The term «fatigue» is obliged by its origin to the erroneous assumption of the first investigators of this nature about the fact that under the action of variable stresses the metal structure changes.
In the present it is established that the metal structure under the action of the periodical loads does not change. The fracture fatigue nature is conditioned by the peculiarity of the molecular and crystalline substance structure. Apparently, it is concluded in the heterogeneity of the material structure. The separate metal crystal has a different strength in different directions. Therefore, the plastic deformations arise in a separate crystal under certain stresses.
Under the repeated loads and unloadings the strain-hardness arises and the material brittleness increases. Finally, the material ability to the hardness is exhausted and the microcrack arises on one of the crystal sliding planes under the large number of the load reiteration. The appeared crack itself becomes the powerful concentration of stresses and becomes the place of final failure with the consideration of the increasing section weakening.
Two zones in the section where the failure takes place can be clearly differed: the zone with the smooth close-sitting surface (the zone of the gradual crack fatigue development) and the zone with the rough surface.
In Fig. 11.1 the photograph of the destroyed rail section is represented. It is visible that the smooth close-fitting surface arisin as the result of the gradual crack fatigue development around the internal crack which was left in the rail after its rolling; further there is a rough section surface where the final failure of the rail took place due to the large reduction of its section.
Fig. 11.1.
The defect of the internal material structure (the internal cracks, the slag inclusions and the like) and the defect of the detail surface treatment (scratches, traces from the chisel or the grinding stone and so on).
The process of the gradual material damage accumulations under the actions of the variable stresses leading to the property change, the crack formation, its development and failure is called the fatigue and the failure on account of the fatigue crack diffusion is called the fatigue failure.
The material property to resist to the fatigue is called the fatigue strength.
The researches show that the breakdown of the machine parts in the majority cases occurs because of the fatigue crack.
In a general case loads and the stresses can change in time under very complicated laws. The variable stresses can have the stationary and non-stationary modes.
Under the non-stationary mode the change law of stresses in time can be any.
Under the stationary mode the change stresses in time have a repeated (periodical) character. In a certain interval of time (period) the precise repetition of stresses takes place.
The total combination of the consequent stress values for one period of its change, under regular loading is called the stress cycle.
The curves of changing in time of normal and shear stresses in the motor bent axie at one revolution are presented in Fig. 11.2 a, b. As we see the stresses change by a very complicated law but they have a periodical (cyclic) character.
The influence of the stress change curve shape on the fatigue strength is studied insufficiently but this influence is small and the value of the maximum and minimum cycle stresses and their relation play a decisive role. Therefore in future we will suppose that the stress change in time arises accordingly to the law near to the sinusoid (Fig. 11.3 a).
The cycle of variable stresses is characterized:
1) by the
maximum algebraic stress value of the cycle
![]()
2) by the
minimum algebraic stress value of the cycle
![]()
3) by the average stress of the cycle
a)
b)
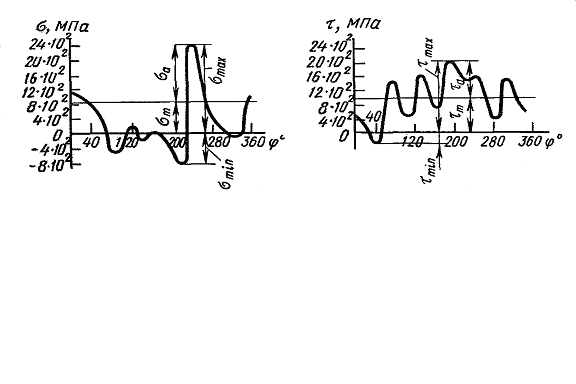
Fig. 11.2.
![]() (11.1)
(11.1)
The average stress of the cycle is the constant cycle component in time (positive or negative);
4) by the cycle stress amplitude
![]() (11.2)
(11.2)
the cycle stress amplitude is the maximum (positive) value of the stress cycle component;
5) by the coefficient of the cycle asymmetry of the stresses
![]() (11.3)
(11.3)
The cycles having the same value R are called similar.
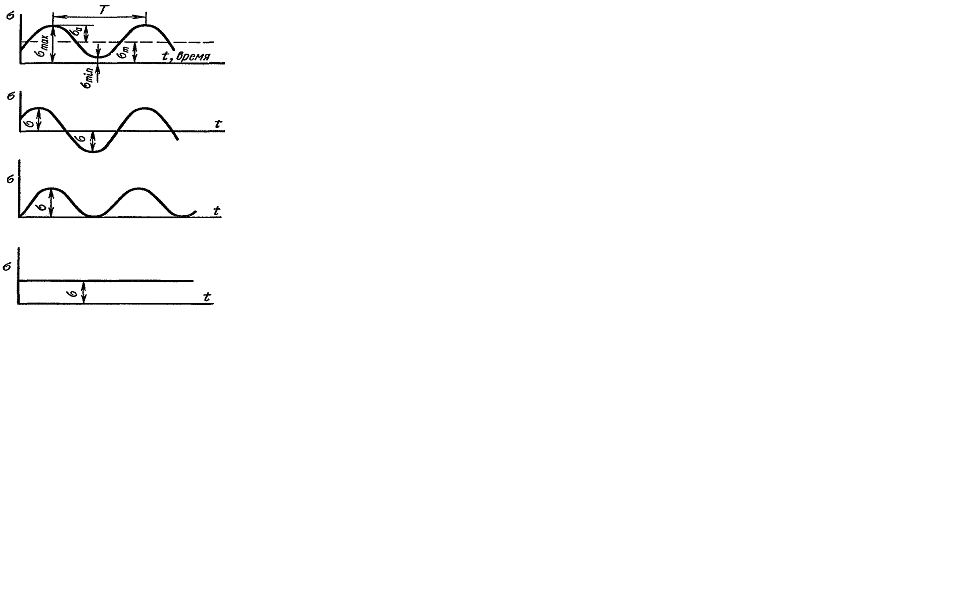
а)
b)
c)
d)
Fig. 11.3.
From the formulas (11.1), (11.2) and Fig. 11.3 we see that
![]() (11.4)
(11.4)
![]() (11.5)
(11.5)
In the case
if
![]() we have the symmetrical
stress cycle
(Fig. 11.3 b). Under that
we have the symmetrical
stress cycle
(Fig. 11.3 b). Under that
![]()
The stress cycle represented in Fig. 11.3 c is called pulsating.
For this case we have
![]()
![]()
The constant statically stress (Fig. 11.3 d) we can consider as a special case of a variable one with the characters
![]()
Any
symmetrical stress cycle can be represented by the sum of the
symmetrical cycle with the maximum stress which is equal to the
amplitude of the given cycle and the constant stress which is equal
to the middle stress of the given cycle (Fig. 11.3 a). All
given terms and relations after the replacement
![]() into
into
![]() remain in force for the case of the variable shearing stress.
remain in force for the case of the variable shearing stress.
