
- •1. Основные понятия и положения 11
- •2. Центральное растяжение и сжатие стержня 17
- •3. Геометрические характеристики плоских сечений 42
- •4. Кручение 49
- •5. Изгиб стержней 57
- •Introduction 173
- •1. Basic concepts and principles 175
- •2. Tension and compression of a bar 181
- •3. Geometric characteristics of cross sections 202
- •4. Torsion 208
- •5. Bending of bars 216
- •Index 405 введение
- •1. Основные понятия и положения
- •1.1. Задачи сопротивления материалов, основные гипотезы и допущения
- •1.2. Типы нагрузок и деформаций
- •1.3. Определение внутренних усилий методом сечений. Напряжения
- •2. Центральное растяжение и сжатие стержня
- •2.1. Напряжения и продольная деформация при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.2. Закон Гука при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.3. Поперечная деформация при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.4. Диаграмма растяжения низкоуглеродистой стали
- •2.5. Потенциальная энергия деформации при растяжении
- •2.6. Расчеты на прочность при растяжении и сжатии
- •2.7. Статически неопределимые задачи
- •2.8. Напряжения в наклонных сечениях при растяжении (сжатии) в одном направлении
- •2.9. Закон парности касательных напряжений
- •2.10. Определение напряжений в наклонных сечениях при растяжении (сжатии) в двух направлениях
- •2.11. Определение главных напряжений и положения главных площадок
- •2.12. Зависимость между деформациями и напряжениями при плоском и объемном напряженных состояниях (обобщенный закон Гука)
- •2.13. Работа внешних и внутренних сил при растяжении (сжатии). Потенциальная энергия деформации
- •3. Геометрические характеристики плоских сечений
- •3.1. Статический момент площади
- •3.2. Полярный момент инерции
- •3.3. Осевой момент инерции
- •3.4. Момент инерции при параллельном переносе осей
- •3.5. Главные оси и главные моменты инерции
- •4. Кручение
- •4.1. Определение крутящего момента
- •4.2. Определение напряжений в стержнях круглого сечения
- •4.3. Деформации и перемещения при кручении валов
- •4.4. Потенциальная энергия при кручении
- •5. Изгиб стержней
- •5.1. Типы опор балок
- •5.2. Определение опорных реакций
- •5.3. Определение внутренних усилий при изгибе
- •5.4. Правило знаков для изгибающих моментов и поперечных сил
- •5.5. Дифференциальные зависимости при изгибе
- •5.6. Построение эпюр изгибающих моментов и поперечных сил
- •5.7. Определение нормальных напряжений
- •5.8. Условия прочности по нормальным напряжениям
- •5.9. Потенциальная энергия деформации при изгибе
- •5.10. Теорема о взаимности работ. Теорема о взаимности перемещений
- •5.11. Определение перемещений методом Мора
- •6. Теории прочности
- •6.1. Назначение гипотез прочности
- •6.2. Первая гипотеза прочности
- •6.3. Вторая и третья гипотезы прочности
- •6.4. Энергетические гипотезы прочности
- •7. Сложное сопротивление
- •7.1. Изгиб в двух плоскостях (косой изгиб)
- •7.2. Изгиб с растяжением (сжатием)
- •7.3. Внецентренное сжатие (растяжение)
- •7.4. Кручение с изгибом
- •7.5. Кручение с растяжением (сжатием)
- •7.6. Пример расчета вала на изгиб с кручением
- •8. Расчет тонкостенных сосудов
- •9. Расчет сжатых стержней на устойчивость (продольный изгиб)
- •9.1. Устойчивые и неустойчивые формы равновесия
- •9.2. Формула Эйлера для критической силы
- •9.3. Влияние способа закрепления концов стержня на критическую силу
- •9.4. Пределы применимости формулы Эйлера
- •9.5. Эмпирические формулы для определения критических напряжений
- •9.6. Практическая формула для расчета на устойчивость
- •10. Динамическое действие нагрузок
- •10.1. Динамические нагрузки
- •10.2. Вычисление напряжений при равноускоренном движении
- •10.3. Определение перемещений и напряжений при ударе
- •11. Расчет на прочность при напряжениях, циклически изменяющихся во времени (расчет на усталость)
- •11.1. Основные определения
- •11.2. Кривая усталости при симметричном цикле. Предел выносливости
- •11.3. Диаграммы предельных напряжений и амплитуд цикла
- •11.4. Факторы, влияющие на предел выносливости
- •11.5. Определение коэффициента запаса прочности при симметричном цикле
- •11.6. Определение коэффициента запаса прочности при асимметричном цикле напряжений
- •Предположим, что при увеличении нагрузки на деталь отношение Такое нагружение называется простым.
- •11.7. Практические меры повышения сопротивления усталости
- •Практикум Лабораторная работа № 1
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Контрольные вопросы
- •Литература
- •Лабораторная работа № 2
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Контрольные вопросы
- •Литература
- •Лабораторная работа № 3
- •Введение
- •Установка
- •Порядок выполнения
- •Introduction
- •Basic concepts and principles
- •Tasks, main hypothesis and assumptions of the strength of materials
- •1.2. Types of loads and deformations
- •1.3. Determining the internal forces by the method of sections. Stresses
- •2. Tension and compression of a bar
- •2.1. Stresses and a longitudinal deformation in tension and compression
- •2.2. Hooke,s law in tension and compression
- •2.3. The transverse deformation in tension and compression
- •2.4. The tension diagram of the lowcarbon steel
- •2.5. The potential deformation energy in tension
- •2.6. Strength calculation in tension and compression
- •2.7. Statically indeterminate problems
- •2.8. Stresses at inclined sections under tension (compression) in one direction
- •2.9. Law of the shearing stresses couple
- •2.10. Determination of stresses at the inclined sections in tension (compression) in two directions
- •2.11. Determining the principal stresses and the principal planes position
- •2.12. The relation between the deformations and the stresses for the plane and general stresses (a general form of Hook’s law)
- •2.13. The work of the external and internal forces in tension (compression). Strain energy
- •3. Geometric characteristics of cross sections
- •3.1. First moment of an area
- •3.2. Polar moment of inertia
- •3.3. Axial moment of inertia
- •3.4. The moment of inertia at parallel displacement of axis
- •3.5. Principal axes and principal moment of inertia
- •4. Torsion
- •4.1. Determining the twisting moment
- •4.2. Determining the stresses in the round section bar
- •4.3. The deformations and displacements in the shaft torsion
- •4.4. Internal strain energy in torsion
- •5. Bending of bars
- •5.1. Types of the beam support
- •5.2. Determining the support reactions
- •5.3. Determining the internal stresses in bending
- •5.4. The sign rule for the bending moments and the shearing forces
- •5.5. The differential relationships in bending
- •I.E. The intensity of the distributed load is equal to the derivative of the shearing force with respect to the bar section abscissa.
- •I.E. The shearing force is equal to the derivative of the bending moment with respect to the bar section abscissa.
- •I.E. The second derivative of the bending moment with respect to the bar section abscissa is equal to the intensity of the distributed load.
- •5.6. Drawing bending moment and shearing force diagrams
- •5.7. Determining the normal stress
- •5.8. Strength conditions with normal stresses
- •5.9. Strain energy in bending
- •5.10. Betty’s reciprocal theorem. Reciprocal displacement theorem
- •5.11. Determining displacements by Mohr’s method
- •6. Strengtn theory
- •6.1. The purpose of strength hypotheses
- •6.2. The first strength hypothesis
- •6.3. The second and third strength hypotheses
- •6.4. The energy hypotheses of strength
- •7. Combined stress
- •7.1. Bending in two planes (non-uniplanar bending)
- •7.2. Combined axial tension (compression) and bending
- •7.3. Eceentrical tension (compression)
- •7.4. Combined torsion and bending
- •7.5. Combined torsion and compression
- •7.6. Example of the shaft calculation in bending with torsion
- •8. Calculation of the thin-walled vessels
- •9. Stability analysis of the bars in compression (buckling)
- •9.1. Stable and unstable equilibrium forms
- •9.2. Euler’s formula for the critical force
- •9.3. Influence of bar end conditions on the critical force
- •9.4. Applicability limits of of Euler’s formula
- •9.5. Empirical formula for determining the critical stresses
- •9.6. The practical formula for the stability analysis
- •10. Dynamic load action
- •10.1. Dynamic load
- •10.2. Calculating stresses under the uniformly accelerated motion
- •10.3. Determining displacements and stresses under the impact
- •11. Stress analysis under the stresses changing cyclically in time
- •11.1. Basic definitions
- •11.2. Fatigue (Wohler’s) curve under the symmetrical cycle. Fatigue strength
- •11.3. The limit stress diagram and the cycle amplitude
- •11.4. Factors influencing on the fatigue strength
- •11.5. Determining the factor of safety under the symmetrical cycle
- •11.6. Determining the factor of safety under the asymmetrical stress cycle
- •11.7. Practical measures to increase the fatigue strength
- •Practicum Laboratory work № 1
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Test specimens
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Laboratory work № 2
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Laboratory work № 3
- •Introduction
- •Installation
- •Individual task report
- •Test questions
- •Literature
- •Англо-русский терминологический словарь
- •Список фамилий ученых
- •Greek alphabet
- •Сокращения
- •Единицы измерения
- •Список наиболее употребительных знаков
- •Список использованной литературы
- •Алфавитный указатель
- •Сопротивление материалов
- •625000, Тюмень, ул. Володарского, 38.
- •625039, Г. Тюмень, ул. Киевская, 52
1.2. Types of loads and deformations
In the process of work structural and machine elements are subjected to external load actions which can be subdivided into:
triaxial loads (they are distributed in the body volume, for example, own weights, inertness, magnetic field forces);
concentrated loads (those acting on a very small area);
distributed loads (distributed on the body surface);
static loads (the ones that increase slowly, conserve a maximum value in a long period of time and decrease slowly);
dynamic loads (those changing quickly on the value).
The external loads cause the change of the body dimensions and shapes i.e. bodies are deformed. The basic deformation types are as follows:
tension (dimensions increase in the action force direction);
compression (dimensions decrease under the force action);
shear (it is caused by the mutual displacement of the body parts which made up one whole in the opposite directions in one plane; it arises under cutting, stamping details from a sheet, while cutting by mechanical scissors);
torsion (it arises under loading by twisting moments which have the action plane perpendicular to the bar axis and the mutual turn of the cross section in this section plane);
bend (the bar axis turns into a curve and changes its curvature).
The external loads can cause two or three basic deformation types simultaneously.
1.3. Determining the internal forces by the method of sections. Stresses
The method of sections consists in that a body is cut by an imagining plane into two parts, one part is removed, and internal forces acting before the cutting are applied to the section of the remained part; the remaining portion of the body is considered as a separate body being in equilibrium under the external and internal forces applied to this section.
The method of sections is based on Newton’s third law.
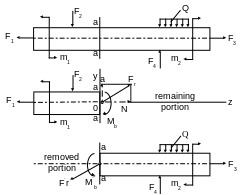
Fig. 1.1.
We can find the resultant of these forces by applying the equilibrium condition to the remaining body portion.
The bar is the basic calculating object in the strength of materials. Let us consider the static resultant of the internal forces in a bar cross section. Cut a bar by the cross section a-a and consider the equilibrium of its left portion (Fig.1.1).
The resultant force vector Fr applied in the centroid of the area and the resultant moment Mr = Mb (they balance the external force plane system applied to the remaining beam portion) are the static resultants of internal forces in the general case which act at the section a-a, if the external forces, applied to the bar, are in one plane.
Let us decompose the resultant force vector into the component N directed along the bar axis and the component Q perpendicular to this axis i.e. the axis lying at the cross-section plane.
These components of the resultant force vector and the resultant moment are called internal forces factors acting at a cross section of a bar. The component N is called the axial force, the component Q is called the shearing force and the couple forces with Mb are the bending moment.
Statics gives three eguations for the remaining bar portion to determine three pointed internal forces, namely:
![]()
(Z – is the axis always directed along the bar).
If the external forces acting at the bar do not lie in the same plane i.e. they form the spatial force system, then in the general case there arise six internal forces factors in the cross section. To determine these statics gives six equilibrium equations (Fig.1.2):
![]()

Fig. 1.2.
The six internal forces factors arising at the bar cross section in a most general case are given the following names: N is an axial force; Qx, Qy are shearing forces; Mt is a twisting moment; Mbx, Mby are bending moments.
There arise different internal forces factors at the bar cross section under different deformations. Consider the following special cases:
1. There is only an axial force N at the section. In this case we have a tension deformation (if the force is directed from the section) or a compression deformation (if the force is directed to the section).
2. There is only a shearing force Q, in this case we have a shear deformation.
3. There is only a twisting moment Mt. In this case we have a torsional deformation.
4. There is only a bending moment Mb. In this case we have a pure bending deformation. When a section has a simultaneous bending moment Mb and a simultaneous shearing force Q, the bend is called cross-bending.
5. When a section has some internal forces factors simultaneously (for example, a bending and a twisting moments or a bending moment and an axial force), then there is a combination of the basic deformations (combined stress).
The stress is one of basic concepts of the strength of materials.
The stress characterizes the intensity of internal forces acting over the section i.e. the load per a unit area.
Let us consider any arbitrary loading beam and apply to it the method of sections (Fig.1.3)
Let us
remove from the section an infinitely small element of the area dA.
Because the element is small, it can be assumed that within its
limits the internal forces applied in different points are equal to
the value and direction, hence, they form a system of parallel
forces. The resultant of this system is denoted by dF.
After dividing dF
into the element area dA
we can determine the internal forces intensity i.e. the stress p
at the points of the element area dA
and we get
![]() adm
adm
Thus, the stress is the internal force acting over a unit area of the section. The stress is the vector value.
The stress unit is:
![]() Newton
per square meter
=
Newton
per square meter
=
![]() = Pascal (Pa).
= Pascal (Pa).
Fig.1.3.
Since this stress unit is very small, we shall apply a bigger divisible unit, namely megapascal (MPa):
1 MPa =10 6 Pа = 1 N/mm2.
Let us decompose the stress vector P into two components: - perpendicular to the section plane and -lying at the section plane (see Fig.1.3). These components are called as follows: is the normal stress, is the shearing stress.
Since the angle between the normal and shearing stress is always 900, then the absolute value of the resultant stress p is determined by the formula
