
- •Part I. Overview of the petroleum industry text 1. Basic refinery processes: description and history
- •Tasks on the text
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms.
- •Look through the text and say what (in the left column) is / are done /produced /removed, etc. By what (in the right column).
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to the meanings and pronunciation of the word subject. Define the functions it performs in the sentences.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Look through the text and answer the questions given.
- •Translate the following passages into English.
- •Text 2. Basics of crude oil
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Look through the text and find equivalents to the word combinations given.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list below.
- •A) Study the ways of translating the … the … construction.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions.
- •Translate the following sentences into English.
- •Read the text The api gravity and prepare to discuss the following.
- •Explain the meaning of the words given using your own words.
- •Translate the given passages into Russian.
- •Approximate characteristics and properties of various crudes
- •Text 3. Principal groups of hydrocarbon compounds
- •Tasks on the text
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Figure 3.1 typical paraffins and aromatics
- •Figure 3.2 typical naphthenes and alkenes
- •Figure 3.3 typical diolefins and alkynes
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Combine the names of different hydrocarbon compounds (given in the left column) with their structural definitions (in the right column).
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words and their derivatives belong to. Write out and memorize those that are new for you.
- •Read the meanings of the word alternate and its synonymic derivatives and translate the given sentences. State what part of speech they belong to.
- •Do you know the difference between the words principal and principle? Read the following and answer the question.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Explain the ideas expressed in the phrases using the words of your own.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Study the Figures 3.1–3.3 and name hydrocarbons having formulas c4h10, c10h8, c6h12, c4h8, c2h2.Practice their reading according to the patterns given.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •Explain the difference between alkanes (алканы), alkenes (алкены) and alkynes (алкины). They are pronounced as [ˈælkeınz], [ˈælkiːnz] and [ˈælkaınz] respectively.
- •Read the text and find out what other names are in use for paraffins, aromatics, naphthenes, alkenes, dienes and alkynes.
- •Iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Study 3d models of the simplest representatives (представители) of different hydrocarbon series given below and define their names.
- •Text 4. Nonhydrocarbons
- •Tasks on the text
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list below.
- •Find the pairs of antonyms in the list below.
- •Translate the phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Match the names of chemical compounds with their English translations.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Translate the following passages into English.
- •A) Practice reading the following numbers and equations.
- •Solve the given arithmetical problems.
- •Text 5. Major refinery products
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Look through the text and find synonyms to the words given in the list.
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Read the text again and discuss the following.
- •Explain the difference between the words commercial, military, domestic.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •Translate the following abstract into Russian.
- •Translate the text into English. Классификация товарных нефтепродуктов
- •Make up a report about the basic refinery products using the scheme given.
- •Text 6. Petroleum refining operations
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Memorize the meanings that are new for you.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list given below.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the different meanings of the word involve (вовлекать, касаться, затрагивать):
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Read the text again and speak on the following.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the refinery processes listed.
- •Translate the following sentences into English paying attention to the use of modal verbs can, could, must, should with Passive Infinitive.
- •Part II. Fractionation and conversion processes and health and safety considerations text 7. Crude oil pretreatment (desalting)
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list given below.
- •Find the pairs of antonyms in the list given below.
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Explain the meaning of: adjust, dehydrate, emulsify, filter; moisten; suspend.
- •Read the text gain and answer the questions given.
- •State whether the statements are true or false. Prove your point of view.
- •Find the sentences with the Participle I / II having attributive function.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention the Participle II.
- •Translate the following sentences into English paying attention to the words (be) due to, fail, failure, involve, separate, should.
- •Translate the following abstracts into English.
- •Describe the method of electrostatic crude oil-desalting using the picture of cross-sectional view of Electrostatic crude oil desalter and the information you learnt from the text.
Translate the following abstract into Russian.
Существует ряд химических веществ, широко применяемых в различных нефтеперерабатывающих процессах. Окислители (oxygenates) улучшают октановые числа бензина и сокращают выбросы (emissions) угарного газа. Каустики добавляются к обессоленной воде, чтобы нейтрализовать кислоты и уменьшить коррозию. Они также добавляются к обессоленной нефти, чтобы сократить количество вызывающих коррозию хлоридов в верхних погонах (the tower overheads). Они применяются в некоторых очистных процессах для удаления загрязнителей из углеводородных потоков. Серная кислота и фтористоводородная (hydrofluoric) кислота используются, как катализаторы в процессе алкилирования.
Translate the text into English. Классификация товарных нефтепродуктов
Нефтеперерабатывающая промышленность вырабатывает исключительно большой ассортимент (более 500 наименований) газообразных, жидких и твердых нефтепродуктов. Требования к ним весьма разнообразны и диктуются постоянно изменяющимися условиями применения или эксплуатации нефтепродуктов.
Поскольку требования, как к объему производства, так и к качеству товаров диктуют их потребители, то классифицируют нефтепродукты по их назначению.
В соответствии с этим различают следующие группы нефтепродуктов.
1. Моторные топлива в зависимости от принципа работы двигателей: 1) бензины (авиационные и автомобильные); 2) реактивные; 3) дизельные.
2. Энергетические топлива:1) газотурбинные (gas-turbine); 2) котельные.
3. Нефтяные масла подразделяют на смазочные и несмазочные.
4. Углеродные и вяжущие (binding) материалы включают: 1) нефтяные коксы; 2) битумы; нефтяные пеки (petroleum pitch /tars).
5. Нефтехимическое сырье. К этой группе можно отнести следующие.
Ароматические углеводороды (бензол, толуол, ксилолы, нафталин, др.).
Сырье для пиролиза (нефтезаводские и попутные (associated) нефтяные газы, прямогонные (straight-run) бензиновые фракции, олефинсодержащие газы).
Парафины и церезины: жидкие (получаемые депарафинизацией нефтяных дистиллятов) и твердые (получаемые при депарафинизации масел).
6. Нефтепродукты специального назначения подразделяют на: 1) термогазойль; 2) консистентные смазки; 3) осветительный керосин; 4) присадки к топливам и маслам, деэмульгаторы; 5) элементная сера; 6) водород и др.
Make up a report about the basic refinery products using the scheme given.
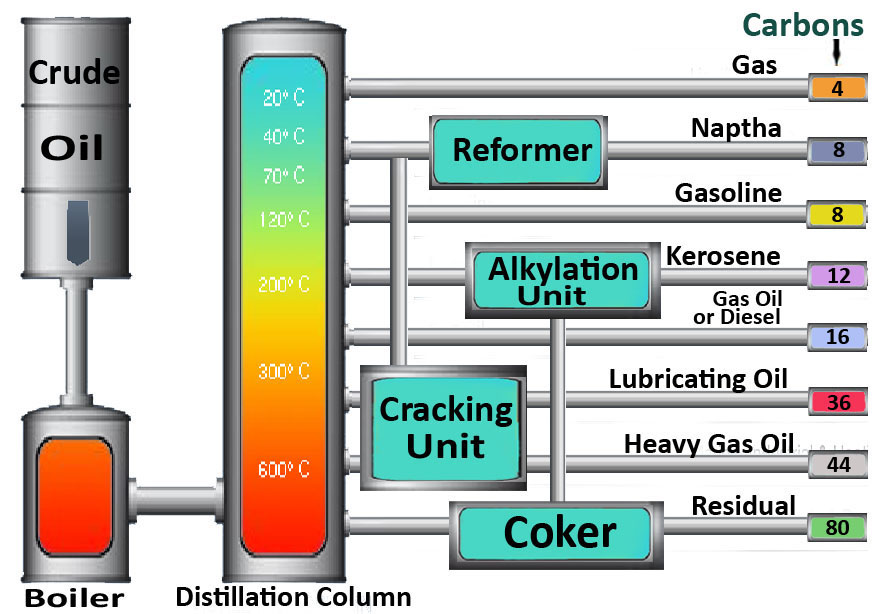
20 °C
40 °C
70 °C
120 °C
200 °C
300 °C
600 °C
Text 6. Petroleum refining operations
Petroleum refining begins with the distillation, or fractionation, of crude oils into separate hydrocarbon groups. The resultant products are directly related to the characteristics of the crude processed. Most distillation products are further converted into more usable products by changing the size and structure of the hydrocarbon molecules through cracking, reforming, and other conversion processes. These converted products are then subjected to various treatment and separation processes such as extraction, hydrotreating, and sweetening to remove undesirable constituents and improve product quality. Integrated refineries incorporate fractionation, conversion, treatment, and blending operations and may also include petrochemical processing. Refining processes and operations can be separated into five basic areas:
Fractionation (distillation) is the separation of crude oil in atmospheric and vacuum distillation towers into groups of hydrocarbon compounds of differing boiling-point ranges called "fractions" or "cuts."
Conversion processes change the size and/or structure of hydrocarbon molecules. These processes include:
Decomposition (dividing) by thermal and catalytic cracking;
Unification (combining) through alkylation and polymerization; and
Alteration (rearranging) with isomerization and catalytic reforming.
Treatment processes are intended to prepare hydrocarbon streams for additional processing and to prepare finished products. Treatment may include the removal or separation of aromatics and naphthenes as well as impurities and undesirable contaminants. Treatment may involve chemical or physical separation such as dissolving, absorption, or precipitation using a variety and combination of processes including desalting, drying, hydrodesulfurizing, solvent refining, sweetening, solvent extraction, and solvent dewaxing.
Formulating and Blending is the process of mixing and combining hydrocarbon fractions, additives, and other components to produce finished products with specific performance properties.
Other Refining Operations include: light-ends recovery; sour-water stripping; solid waste and wastewater treatment; process-water treatment and cooling; storage and handling; product movement; hydrogen production; acid and tail-gas treatment; and sulfur recovery.
Auxiliary operations and facilities include: steam and power generation; process and fire water systems; flares and relief systems; furnaces and heaters; pumps and valves; supply of steam, air, nitrogen, and other plant gases; alarms and sensors; noise and pollution controls; sampling, testing, and inspecting; and laboratory control room, maintenance, and administrative facilities.
