
- •Part I. Overview of the petroleum industry text 1. Basic refinery processes: description and history
- •Tasks on the text
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms.
- •Look through the text and say what (in the left column) is / are done /produced /removed, etc. By what (in the right column).
- •Translate the sentences paying attention to the meanings and pronunciation of the word subject. Define the functions it performs in the sentences.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Look through the text and answer the questions given.
- •Translate the following passages into English.
- •Text 2. Basics of crude oil
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Look through the text and find equivalents to the word combinations given.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list below.
- •A) Study the ways of translating the … the … construction.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions.
- •Translate the following sentences into English.
- •Read the text The api gravity and prepare to discuss the following.
- •Explain the meaning of the words given using your own words.
- •Translate the given passages into Russian.
- •Approximate characteristics and properties of various crudes
- •Text 3. Principal groups of hydrocarbon compounds
- •Tasks on the text
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Figure 3.1 typical paraffins and aromatics
- •Figure 3.2 typical naphthenes and alkenes
- •Figure 3.3 typical diolefins and alkynes
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Combine the names of different hydrocarbon compounds (given in the left column) with their structural definitions (in the right column).
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words and their derivatives belong to. Write out and memorize those that are new for you.
- •Read the meanings of the word alternate and its synonymic derivatives and translate the given sentences. State what part of speech they belong to.
- •Do you know the difference between the words principal and principle? Read the following and answer the question.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Explain the ideas expressed in the phrases using the words of your own.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Study the Figures 3.1–3.3 and name hydrocarbons having formulas c4h10, c10h8, c6h12, c4h8, c2h2.Practice their reading according to the patterns given.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •Explain the difference between alkanes (алканы), alkenes (алкены) and alkynes (алкины). They are pronounced as [ˈælkeınz], [ˈælkiːnz] and [ˈælkaınz] respectively.
- •Read the text and find out what other names are in use for paraffins, aromatics, naphthenes, alkenes, dienes and alkynes.
- •Iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Study 3d models of the simplest representatives (представители) of different hydrocarbon series given below and define their names.
- •Text 4. Nonhydrocarbons
- •Tasks on the text
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Practise the pronunciation of the words given. Make sure you remember their meanings.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list below.
- •Find the pairs of antonyms in the list below.
- •Translate the phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Match the names of chemical compounds with their English translations.
- •Read the text again and answer the questions given.
- •Translate the following passages into English.
- •A) Practice reading the following numbers and equations.
- •Solve the given arithmetical problems.
- •Text 5. Major refinery products
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Look through the text and find synonyms to the words given in the list.
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the terms given.
- •Read the text again and discuss the following.
- •Explain the difference between the words commercial, military, domestic.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •Translate the following abstract into Russian.
- •Translate the text into English. Классификация товарных нефтепродуктов
- •Make up a report about the basic refinery products using the scheme given.
- •Text 6. Petroleum refining operations
- •Tasks on the text
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Memorize the meanings that are new for you.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list given below.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention to the different meanings of the word involve (вовлекать, касаться, затрагивать):
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Read the text again and speak on the following.
- •Find the suitable definition for each of the refinery processes listed.
- •Translate the following sentences into English paying attention to the use of modal verbs can, could, must, should with Passive Infinitive.
- •Part II. Fractionation and conversion processes and health and safety considerations text 7. Crude oil pretreatment (desalting)
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •Translate the words given and practise their pronunciation.
- •Read, translate and define what parts of speech the words, their derivatives and related words belong to. Consult the dictionary, write out the meanings that are new for you and memorize them.
- •Find the pairs of synonyms in the list given below.
- •Find the pairs of antonyms in the list given below.
- •Translate the given phrases paying attention to the prepositions.
- •Explain the meaning of: adjust, dehydrate, emulsify, filter; moisten; suspend.
- •Read the text gain and answer the questions given.
- •State whether the statements are true or false. Prove your point of view.
- •Find the sentences with the Participle I / II having attributive function.
- •Translate the following sentences paying attention the Participle II.
- •Translate the following sentences into English paying attention to the words (be) due to, fail, failure, involve, separate, should.
- •Translate the following abstracts into English.
- •Describe the method of electrostatic crude oil-desalting using the picture of cross-sectional view of Electrostatic crude oil desalter and the information you learnt from the text.
Read the text again and answer the questions given.
What is IUPAC nomenclature and its basic principle?
What are saturated hydrocarbons?
What are unsaturated hydrocarbons?
What are cycloalkanes and aromatics?
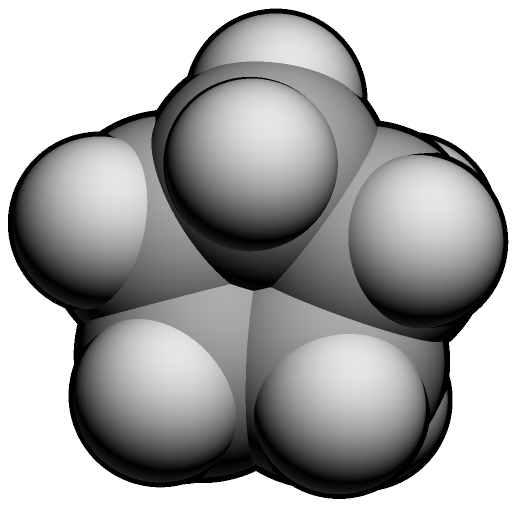
Study 3d models of the simplest representatives (представители) of different hydrocarbon series given below and define their names.
|
|
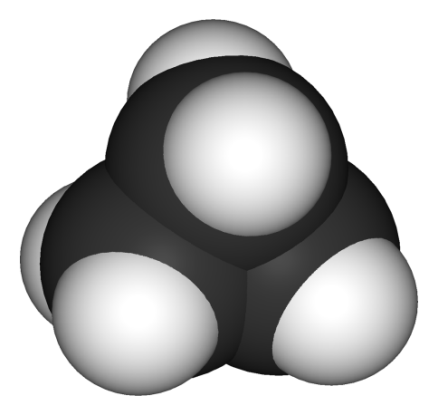
1. |
2. |
3 |

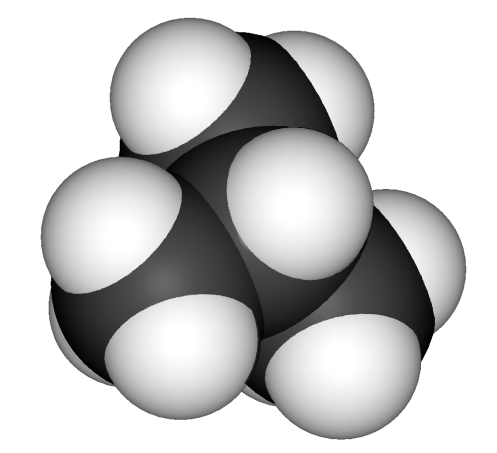
4 |
5. |
6. |
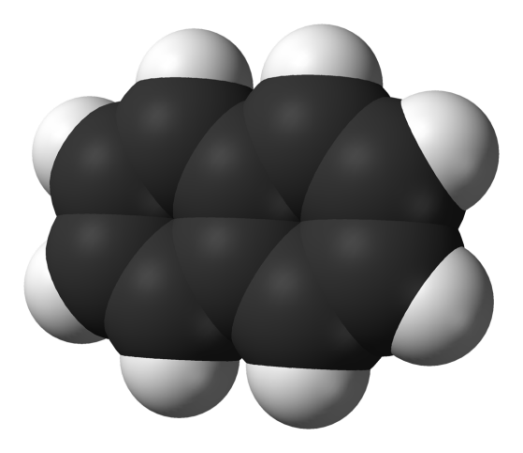
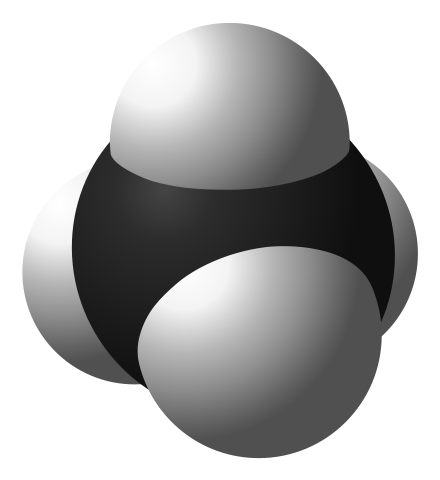
7 |
8. |
9. |
Text 4. Nonhydrocarbons
Sulfur Compounds. Sulfur may be present in crude oil as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), as compounds (e.g. mercaptans, sulfides, disulfides, thiophenes, etc.) or as elemental sulfur. Each crude oil has different amounts and types of sulfur compounds, but as a rule the proportion, stability, and complexity of the compounds are greater in heavier crude-oil fractions. Hydrogen sulfide is a primary contributor to corrosion in refinery processing units. Other corrosive substances are elemental sulfur and mercaptans. Moreover, the corrosive sulfur compounds have an obnoxious odor.
Pyrophoric iron sulfide results from the corrosive action of sulfur compounds on the iron and steel used in refinery process equipment, piping, and tanks. The combustion of petroleum products containing sulfur compounds produces undesirables such as sulfuric acid and sulfur dioxide. Catalytic hydrotreating processes such as hydrodesulfurization remove sulfur compounds from refinery product streams. Sweetening processes either remove the obnoxious sulfur compounds or convert them to odorless disulfides, as in the case of mercaptans.
Oxygen Compounds. Oxygen compounds such as phenols, ketones, and carboxylic acids occur in crude oils in varying amounts.
Nitrogen Compounds. Nitrogen is found in lighter fractions of crude oil as basic compounds, and more often in heavier fractions of crude oil as nonbasic compounds that may also include trace metals such as copper, vanadium, and/or nickel. Nitrogen oxides can form in process furnaces. The decomposition of nitrogen compounds in catalytic cracking and hydrocracking processes forms ammonia and cyanides that can cause corrosion.
Trace Metals. Metals, including nickel, iron, and vanadium are often found in crude oils in small quantities and are removed during the refining process. Burning heavy fuel oils in refinery furnaces and boilers can leave deposits of vanadium oxide and nickel oxide in furnace boxes, ducts, and tubes. It is also desirable to remove trace amounts of arsenic, vanadium, and nickel prior to processing as they can poison certain catalysts.
Salts. Crude oils often contain inorganic salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, and calcium chloride in suspension or dissolved in entrained water (brine). These salts must be removed or neutralized before processing to prevent catalyst poisoning, equipment corrosion, and fouling. Salt corrosion is caused by the hydrolysis of some metal chlorides to hydrogen chloride (HCl) and the subsequent formation of hydrochloric acid when crude is heated. Hydrogen chloride may also combine with ammonia to form ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), which causes fouling and corrosion.
Carbon Dioxide. Carbon dioxide may result from the decomposition of bicarbonates present in or added to crude, or from steam used in the distillation process.
Naphthenic Acids. Some crude oils contain naphthenic (organic) acids, which may become corrosive at temperatures above 450 °F when the acid value of the crude is above a certain level.

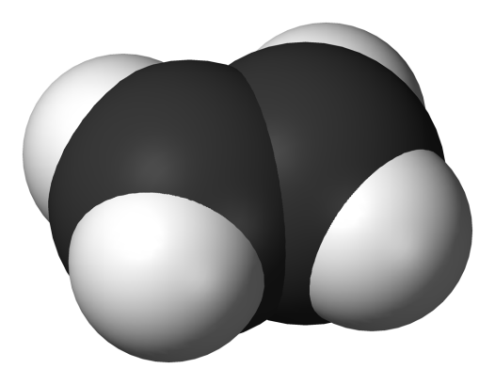 .
.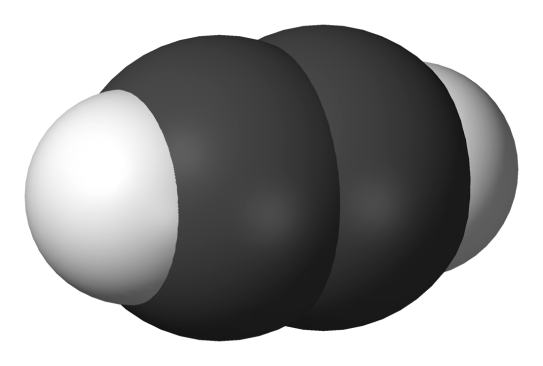 .
.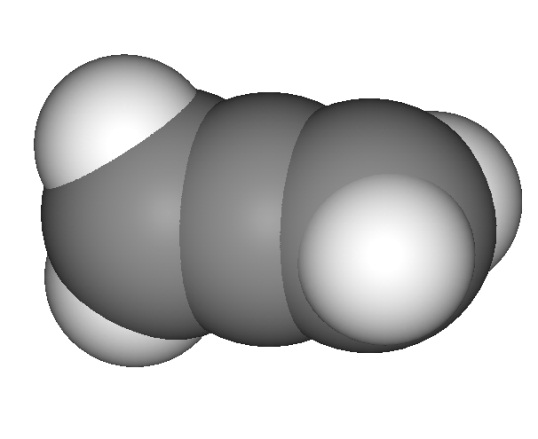 .
.