
- •About the Authors
- •Contents at a Glance
- •Contents
- •Introduction
- •Goal of the Book
- •How to Use this Book
- •Introduction to the .NET Framework
- •Common Language Runtime (CLR)
- •Class Library
- •Assembly
- •Versioning
- •Exceptions
- •Threads
- •Delegates
- •Summary
- •Introduction to C#
- •Variables
- •Initializing Variables
- •Variable Modifiers
- •Variable Data Types
- •Types of Variables
- •Variable Scope
- •Types of Data Type Casting
- •Arrays
- •Strings
- •Initializing Strings
- •Working with Strings
- •Statements and Expressions
- •Types of Statements
- •Expressions
- •Summary
- •Classes
- •Declaring Classes
- •Inheritance
- •Constructors
- •Destructors
- •Methods
- •Declaring a Method
- •Calling a Method
- •Passing Parameters to Methods
- •Method Modifiers
- •Overloading a Method
- •Namespaces
- •Declaring Namespaces
- •Aliases
- •Structs
- •Enumerations
- •Interfaces
- •Writing, Compiling, and Executing
- •Writing a C# Program
- •Compiling a C# Program
- •Executing a C# Program
- •Summary
- •Arrays
- •Single-Dimensional Arrays
- •Multidimensional Arrays
- •Methods in Arrays
- •Collections
- •Creating Collections
- •Working with Collections
- •Indexers
- •Boxing and Unboxing
- •Preprocessor Directives
- •Summary
- •Attributes
- •Declaring Attributes
- •Attribute Class
- •Attribute Parameters
- •Default Attributes
- •Properties
- •Declaring Properties
- •Accessors
- •Types of Properties
- •Summary
- •Introduction to Threads
- •Creating Threads
- •Aborting Threads
- •Joining Threads
- •Suspending Threads
- •Making Threads Sleep
- •Thread States
- •Thread Priorities
- •Synchronization
- •Summary
- •Case Study
- •Project Life Cycle
- •Analyzing Requirements
- •High-Level Design
- •Primary and Foreign Keys
- •Referential Integrity
- •Normalization
- •Designing a Database
- •Low-Level Design
- •Construction
- •Integration and Testing
- •User Acceptance Testing
- •Implementation
- •Operations and Maintenance
- •Summary
- •Creating a New Project
- •Console Application
- •Windows Applications
- •Creating a Windows Application for the Customer Maintenance Project
- •Creating an Interface for Form1
- •Creating an Interface for WorkerForm
- •Creating an Interface for CustomerForm
- •Creating an Interface for ReportsForm
- •Creating an Interface for JobDetailsForm
- •Summary
- •Performing Validations
- •Identifying the Validation Mechanism
- •Using the ErrorProvider Control
- •Handling Exceptions
- •Using the try and catch Statements
- •Using the Debug and Trace Classes
- •Using the Debugging Features of Visual Studio .NET
- •Using the Task List
- •Summary
- •Creating Form1
- •Connecting WorkerForm to the Workers Table
- •Connecting CustomerForm to the tblCustomer Table
- •Connecting the JobDetails Form
- •to the tblJobDetails Table
- •Summary
- •Introduction to the Crystal Reports Designer Tool
- •Creating the Reports Form
- •Creating Crystal Reports
- •Creating the Windows Forms Viewer Control
- •Creating the Monthly Worker Report
- •Summary
- •Introduction to Deploying a Windows Application
- •Deployment Projects Available in Visual Studio .NET
- •Deployment Project Editors
- •Summary
- •Case Study
- •Project Life Cycle
- •Analyzing Requirements
- •High-Level Design
- •Low-Level Design
- •Summary
- •Populating the TreeView Control
- •Displaying Employee Codes in the TreeView Control
- •Event Handling
- •Displaying Employee Details in the ListView Control
- •Summary
- •Case Study
- •Project Life Cycle
- •Analyzing Requirements
- •High-Level Design
- •Low-Level Design
- •Summary
- •Adding the Programming Logic to the Application
- •Adding Code to the Form Load() Method
- •Adding Code to the OK Button
- •Adding Code to the Exit Button
- •Summary
- •The Created Event
- •Adding Code to the Created Event
- •Overview of XML
- •The XmlReader Class
- •The XmlWriter Class
- •Displaying Data in an XML Document
- •Displaying an Error Message in the Event Log
- •Displaying Event Entries from Event Viewer
- •Displaying Data from the Summary.xml Document in a Message Box
- •Summary
- •Airline Profile
- •Role of a Business Manager
- •Role of a Network Administrator
- •Role of a Line-of-Business Executive
- •Project Requirements
- •Creation and Deletion of User Accounts
- •Addition of Flight Details
- •Reservations
- •Cancellations
- •Query of Status
- •Confirmation of Tickets
- •Creation of Reports
- •Launch of Frequent Flier Programs
- •Summarizing the Tasks
- •Project Design
- •Database Design
- •Web Forms Design
- •Enabling Security with the Directory Structure
- •Summary
- •Getting Started with ASP.NET
- •Prerequisites for ASP.NET Applications
- •New Features in ASP.NET
- •Types of ASP.NET Applications
- •Exploring ASP.NET Web Applications
- •Introducing Web Forms
- •Web Form Server Controls
- •Configuring ASP.NET Applications
- •Configuring Security for ASP.NET Applications
- •Deploying ASP.NET Applications
- •Creating a Sample ASP.NET Application
- •Creating a New Project
- •Adding Controls to the Project
- •Coding the Application
- •Summary
- •Creating the Database Schema
- •Creating Database Tables
- •Managing Primary Keys and Relationships
- •Viewing the Database Schema
- •Designing Application Forms
- •Standardizing the Interface of the Application
- •Common Forms in the Application
- •Forms for Network Administrators
- •Forms for Business Managers
- •Forms for Line-of-Business Executives
- •Summary
- •The Default.aspx Form
- •The Logoff.aspx Form
- •The ManageUsers.aspx Form
- •The ManageDatabases.aspx Form
- •The ChangePassword.aspx Form
- •Restricting Access to Web Forms
- •The AddFl.aspx Form
- •The RequestID.aspx Form
- •The Reports.aspx Form
- •The FreqFl.aspx Form
- •Coding the Forms for LOB Executives
- •The CreateRes.aspx Form
- •The CancelRes.aspx Form
- •The QueryStat.aspx Form
- •The ConfirmRes.aspx Form
- •Summary
- •Designing the Form
- •The View New Flights Option
- •The View Ticket Status Option
- •The View Flight Status Option
- •The Confirm Reservation Option
- •Testing the Application
- •Summary
- •Locating Errors in Programs
- •Watch Window
- •Locals Window
- •Call Stack Window
- •Autos Window
- •Command Window
- •Testing the Application
- •Summary
- •Managing the Databases
- •Backing Up the SkyShark Airlines Databases
- •Exporting Data from Databases
- •Examining Database Logs
- •Scheduling Database Maintenance Tasks
- •Managing Internet Information Server
- •Configuring IIS Error Pages
- •Managing Web Server Log Files
- •Summary
- •Authentication Mechanisms
- •Securing a Web Site with IIS and ASP.NET
- •Configuring IIS Authentication
- •Configuring Authentication in ASP.NET
- •Securing SQL Server
- •Summary
- •Deployment Scenarios
- •Deployment Editors
- •Creating a Deployment Project
- •Adding the Output of SkySharkDeploy to the Deployment Project
- •Deploying the Project to a Web Server on Another Computer
- •Summary
- •Organization Profile
- •Project Requirements
- •Querying for Information about All Books
- •Querying for Information about Books Based on Criteria
- •Ordering a Book on the Web Site
- •Project Design
- •Database Design
- •Database Schema
- •Web Forms Design
- •Flowcharts for the Web Forms Modules
- •Summary
- •Introduction to ASP.NET Web Services
- •Web Service Architecture
- •Working of a Web Service
- •Technologies Used in Web Services
- •XML in a Web Service
- •WSDL in a Web Service
- •SOAP in a Web Service
- •UDDI in a Web Service
- •Web Services in the .NET Framework
- •The Default Code Generated for a Web Service
- •Testing the SampleWebService Web Service
- •Summary
- •Creating the SearchAll() Web Method
- •Creating the SrchISBN() Web Method
- •Creating the AcceptDetails() Web Method
- •Creating the GenerateOrder() Web Method
- •Testing the Web Service
- •Securing a Web Service
- •Summary
- •Creating the Web Forms for the Bookers Paradise Web Site
- •Adding Code to the Web Forms
- •Summary
- •Case Study
- •Project Life Cycle
- •Analyzing Requirements
- •High-Level Design
- •Low-Level Design
- •Summary
- •Overview of Mobile Applications
- •The Microsoft Mobile Internet Toolkit
- •Overview of WAP
- •The WAP Architecture
- •Overview of WML
- •The Mobile Web Form
- •The Design of the MobileTimeRetriever Application
- •Creating the Interface for the Mobile Web Forms
- •Adding Code to the MobileTimeRetriever Application
- •Summary
- •Creating the Forms Required for the MobileCallStatus Application
- •Creating the frmLogon Form
- •Creating the frmSelectOption Form
- •Creating the frmPending Form
- •Creating the frmUnattended Form
- •Adding Code to the Submit Button in the frmLogon Form
- •Adding Code to the Query Button in the frmSelectOption Form
- •Adding Code to the Mark checked as complete Button in the frmPending Form
- •Adding Code to the Back Button in the frmPending Form
- •Adding Code to the Accept checked call(s) Button in the frmUnattended Form
- •Adding Code to the Back Button in the frmUnattended Form
- •Summary
- •What Is COM?
- •Windows DNA
- •Microsoft Transaction Server (MTS)
- •.NET Interoperability
- •COM Interoperability
- •Messaging
- •Benefits of Message Queues
- •Limitations
- •Key Messaging Terms
- •Summary
- •Pointers
- •Declaring Pointers
- •Types of Code
- •Implementing Pointers
- •Using Pointers with Managed Code
- •Working with Pointers
- •Compiling Unsafe Code
- •Summary
- •Introduction to the Languages of Visual Studio .NET
- •Visual C# .NET
- •Visual Basic .NET
- •Visual C++ .NET
- •Overview of Visual Basic .NET
- •Abstraction
- •Encapsulation
- •Inheritance
- •Polymorphism
- •Components of Visual Basic .NET
- •Variables
- •Constants
- •Operators
- •Arrays
- •Collections
- •Procedures
- •Arguments
- •Functions
- •Adding Code to the Submit Button
- •Adding Code to the Exit Button
- •Summary
- •Introduction to Visual Studio .NET IDE
- •Menu Bar
- •Toolbars
- •Visual Studio .NET IDE Windows
- •Toolbox
- •The Task List Window
- •Managing Windows
- •Customizing Visual Studio .NET IDE
- •The Options Dialog Box
- •The Customize Dialog Box
- •Summary
- •Index
888 |
Part X |
APPENDIXES |
|
|
|
names of the servers that are currently being used. Figure C-9 shows the Server Explorer window.
|
Y |
L |
|
F |
|
M |
|
A |
|
E |
|
FIGURE C-9 The ServerTxplorer window
The Server Explorer window also allows you to add event logs, message queues, and performance counters to your project. A toolbar displaying the buttons for commonly used commands is displayed in the Server Explorer window.
Toolbox
The Toolbox contains various tools available in Visual Studio .NET. The Toolbox can be opened by clicking the Toolbox tab displayed on the left margin of the Visual Studio .NET IDE. You can also open the Toolbox by selecting the Toolbox command from the View menu.
The General and Clipboard Ring tabs are displayed by default. In addition, tools with specific functions are displayed in the toolbox. You can view all the tabs on the Toolbar by selecting the Show All Tabs option from the context menu.
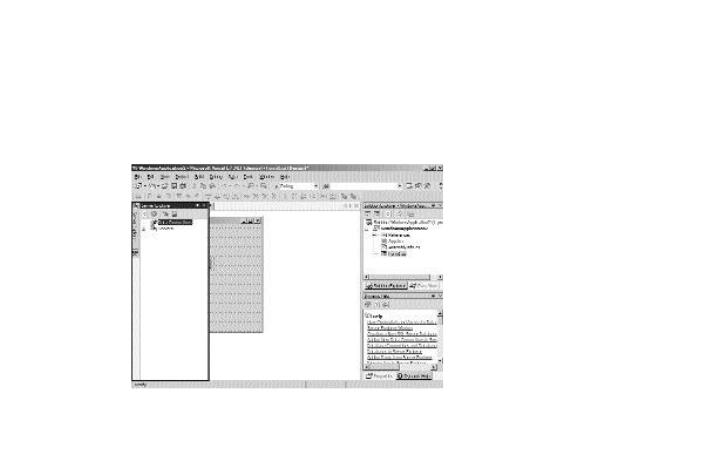
Some of the tabs available in the Toolbox are:
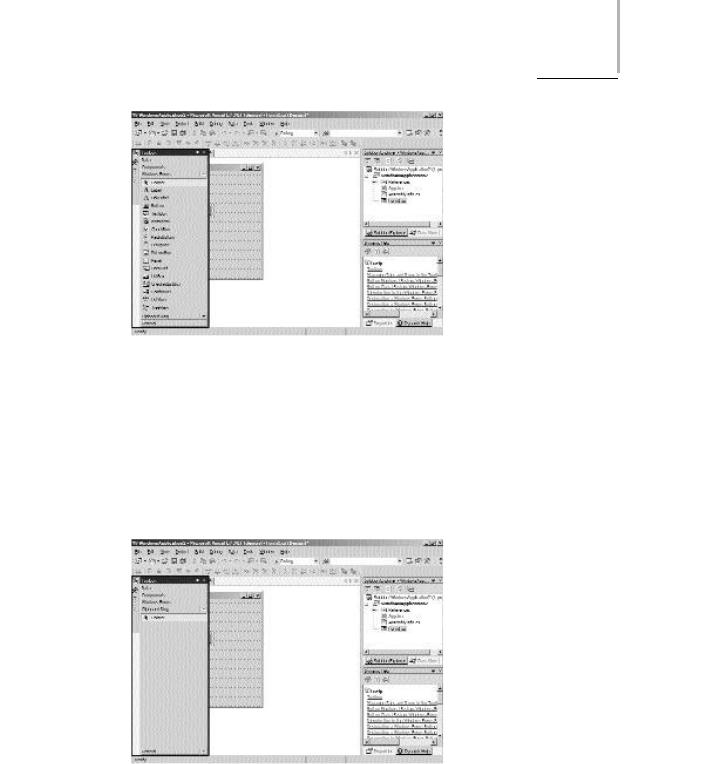
General tab. The General tab, by default, displays only the Pointer control. You can also add controls, such as custom controls, to the General tab. Custom controls refer to user-defined controls. Figure C-10 shows the General tab of the Toolbox.
Team-Fly®
VISUAL STUDIO .NET IDE Appendix C 889
FIGURE C-10 The General tab of the Toolbox
Clipboard Ring tab. The Clipboard Ring tab also displays only the Pointer control by default. The Clipboard Ring tab displays the last 12 items that are added to the clipboard. The clipboard is basically a memory cache maintained by the Microsoft Windows operating system. The Clipboard Ring tab of the Toolbox is shown in Figure C-11.
FIGURE C-11 The Clipboard Ring tab of the Toolbox

890 |
Part X |
APPENDIXES |
|
|
|
The Toolbox can also be customized by adding tabs and tools. You can use the Customize Toolbox command from the Tools menu to open the Customize Toolbar dialog box.
The Task List Window
Visual Studio .NET allows you to mark the code present in your application with comments. The Task List window helps track errors and warnings. These comments are displayed in the table format. To view these errors, you need to doubleclick the message and determine the exact location of the error.
You can open the Task List window by selecting the Other Windows command from the View menu and then selecting the Task List command from the submenu. The Task List window is shown in Figure C-12.
FIGURE C-12 The Task List window
You can also add comments for the errors in the code, which may be useful for later references. Figure C-13 shows a comment for an error in the code.
FIGURE C-13 A comment for an e rror in the code

VISUAL STUDIO .NET IDE Appendix C 891
Managing Windows
The windows that are displayed in Visual Studio .NET IDE can be managed according to your requirements. The following options are available to perform this function. The next sections will discuss them in detail.
Hiding Windows
To hide a window, you use the Auto Hide feature of the Visual Studio .NET IDE. The window is then displayed as a tab, which can be clicked to maximize the hidden window. You can apply the Auto Hide feature to various tools of IDE, such as Solution Explorer, Task List, and Toolbox.The Auto Hide feature may be enabled or disabled by toggling the pushpin icon in the upper-right corner of the window. Figure C-14 shows the Auto Hide feature of the Visual Studio .NET IDE.
FIGURE C-14 The Auto Hide feature of Visual Studio .NET IDE
Docking Windows
You can drag the windows present in IDE as per your requirements by using the docking windows feature provided by Visual Studio .NET. The windows can be attached or left free-standing as per your requirements.
