
- •Оглавление
- •Метод Main
- •Ввод и вывод
- •Компиляция и выполнение
- •Общая структура программы на c#
- •Main() и аргументы командной строки
- •Общие сведения
- •Аргументы командной строки
- •Отображение аргументов командной строки
- •Доступ к аргументам командной строки с помощью оператора "foreach"
- •Значения, возвращаемые методом Main()
- •Пример результатов выполнения
- •Общие сведения о типах данных
- •Приведение
- •Результат
- •Упаковка-преобразование и распаковка-преобразование3
- •Производительность
- •Упаковка-преобразование4
- •Описание5
- •Результат
- •Распаковка-преобразование6
- •Описание7
- •Результат
- •Преобразование массива байтов в значение типа "int"8
- •Пример9
- •Преобразование строки в значение типа "int"
- •Преобразование шестнадцатеричных строк10
- •Массивы
- •Общие сведения о массивах
- •Массивы как объекты
- •Результат
- •Одномерные массив
- •Массивы типов значений и ссылочных типов.
- •Многомерные массивы
- •Инициализация массива
- •Массивы массивов
- •Результат
- •Использование оператора foreach с массивами
- •Передача массивов в качестве параметров
- •Передача одномерных массивов в качестве параметров
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Результат 1
- •Передача многомерных массивов в качестве параметров
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Передача массивов при помощи параметров ref и out
- •Пример 1
- •Пример 2
- •Неявно типизированные массивы11
- •Неявно типизированные массивы в инициализаторах объектов12
- •Использование строк
- •Работа со строками Escape-знаки
- •Точные строки: символ @
- •Доступ к отдельным знакам
- •Смена регистра
- •Сравнения
- •Разделение строки на подстроки
- •Строки с нулевыми значениями и пустые строки
- •Использование класса StringBuilder13
- •Анализ строк с помощью метода разделения
- •Навигация по содержимому строки с помощью строковых методов
- •Анализ строк с помощью регулярных выражений14
- •Объединение нескольких строк
- •Изменение содержимого строки
- •Определение наличия числового значения в строке
- •Надежное программирование
- •Безопасность
- •Базовые типы кодировки
- •Типы форматирования
- •Общие сведения о форматировании
- •Описатели формата
- •Анализ и описатели формата
- •Метод ToString и описатели формата
- •Поставщики формата15
- •Составное форматирование
- •Форматирование базовых типов
- •Форматирование для различных языков и региональных параметров16
- •Составное форматирование
- •Строка составного формата
- •Синтаксис элементов форматирования
- •Выравнивание
- •Компонент строки формата
- •Оформление фигурных скобок17
- •Порядок обработки18
- •Примеры кода
- •Строки числовых форматов
- •Строки стандартных числовых форматов
- •Примечания Настройки панели управления
- •Свойства NumberFormatInfo
- •Целочисленные типы и типы с плавающей запятой
- •Бесконечности действительных чисел с плавающей запятой и NaN
- •Строки настраиваемых числовых форматов19
- •Примечания Бесконечности действительных чисел с плавающей запятой и NaN
- •Настройки панели управления
- •Строки формата с фиксированной запятой и округлением
- •Разделители секций и условное форматирование20
- •Два примера настраиваемых форматов
- •Регулярные выражения в .Net Framework
- •Регулярные выражения как язык
- •Escape-знаки
- •Выполнение действия со строками с помощью основных строковых операций
- •Разбор строк
- •Разбор числовых строк
- •Операторы и выражения
- •Операторы
- •Выражения
- •Литералы и простые имена
- •Выражения вызова
- •Операторы
- •Анонимные функции
- •Эволюция делегатов в c#
- •Лямбда-выражения22
- •Выражения-лямбды
- •Лямбды операторов
- •Лямбды со стандартными операторами запросов
- •Вывод типа в лямбда-выражениях
- •Область действия переменной в лямбда-выражениях
- •Использование лямбда-выражений вне linq
- •Анонимные методы
- •Заметки
- •Перегружаемые операторы
- •Операторы преобразования23
- •Общие сведения об операторах преобразования
- •Использование операторов преобразования
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Результат 1
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Результат 2
- •Реализация определенных пользователем преобразований между структурами
- •Надежное программирование
- •Перегрузка операторов для реализации класса комплексных чисел
- •Переопределение Equals
- •Объекты, классы и структуры
- •Интерфейсы
- •Универсальные типы
- •Статические типы
- •Объекты
- •Экземпляры структуры и экземпляры класса
- •Идентификация объекта и идентификация значения26
- •Объявление классов
- •Создание объектов
- •Наследование классов
- •Описание
- •Результат
- •Общие сведения о классах
- •Структуры
- •Общие сведения о структурах
- •Использование структур
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Результат
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Результат
- •Наследование
- •Абстрактные и запечатанные классы и члены классов
- •Абстрактные классы и члены классов
- •Запечатанные классы и члены классов
- •Определение абстрактных свойств
- •Полиморфизм
- •Общие сведения о полиморфизме
- •Управление версиями с помощью ключевых слов "Override" и "New"
- •Переопределение и выбор метода29
- •Использование ключевых слов "Override" и "New"
- •Переопределение метода ToString
- •Порядок переопределения метода OnString в классе или структуре
- •Интерфейсы
- •Общие сведения об интерфейсах
- •Явная реализация интерфейса33
- •Явная реализация членов интерфейса
- •Надежное программирование
- •Явная реализация членов интерфейса с наследованием
- •Надежное программирование
- •Параметры методов
- •Возвращаемые значения
- •Передача параметров
- •Передача параметров типа значения
- •Пример. Передача типов значений с помощью значения.
- •Пример. Передача типов значений с помощью ссылки.
- •Пример. Замена типов значений.
- •Передача параметров ссылочного типа
- •Пример. Передача ссылочных типов по значению
- •Результат
- •Рассмотрение кода
- •Пример. Передача ссылочных типов по ссылке
- •Результат
- •Рассмотрение кода
- •Пример. Перестановка двух строк
- •Результат
- •Рассмотрение кода
- •Конструкторы
- •Использование конструкторов
- •Конструкторы экземпляров
- •Пример 1
- •Результат
- •Пример 2
- •Результат
- •Пример 3
- •Результат
- •Закрытые конструкторы35
- •Результат
- •Статические конструкторы36
- •Результат
- •Создание конструктора копии
- •Деструкторы
- •Заметки
- •Использование деструкторов для освобождения ресурсов.
- •Высвобождение ресурсов явным образом
- •Результат
- •Инициализаторы объектов и коллекций
- •Инициализаторы объектов и анонимные типы37
- •Инициализаторы объектов и типы, допускающие значение null
- •Инициализаторы коллекций
- •Инициализация объектов без вызова конструктора
- •Компиляция кода38
- •Инициализация словаря с помощью инициализатора коллекции39
- •Компиляция кода
- •Константы
- •Вложенные типы
- •Модификаторы доступа
- •Доступность класса и структуры
- •Доступность члена класса и структуры
- •Другие типы
- •Разделяемые классы и методы40
- •Разделяемый класс
- •Ограничения
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Результат
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Разделяемые методы
- •Статические классы и члены статических классов
- •Статические классы
- •Когда следует использовать статические классы
- •Статические члены
- •Входные данные
- •Пример результатов выполнения.
- •Определение различия между передачей структуры и ссылки класса в метод
- •Анонимные типы41
- •Заметки
- •Возвращение поднаборов свойств элементов в запросе
- •Компиляция кода
- •Методы расширения
- •Неявно типизированные локальные переменные
- •Var и анонимные типы
- •Заметки
- •Свойства
- •Результат
- •Общие сведения о свойствах
- •Использование свойств
- •Метод доступа get
- •Метод доступа set
- •Заметки
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Результат 1 Employee number: 101 Employee name: Claude Vige
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Результат 2
- •Рассмотрение кода
- •Пример 3 Описание
- •Введенные данные
- •Результат 3
- •Свойства интерфейса
- •Пример результатов выполнения
- •Асимметричные методы доступа
- •Ограничения модификаторов доступа в методах доступа
- •Модификаторы доступа в переопределяющих методах доступа
- •Реализация интерфейсов
- •Домен доступности к методу доступа
- •Результат
- •Примечания
- •Объявление и использование свойств чтения и записи
- •Надежное программирование
- •Автоматически реализуемые свойства
- •Реализация облегченного класса с автоматически реализуемыми свойствами
- •Индексаторы
- •Общие сведения об индексаторах
- •Использование индексаторов
- •Заметки
- •Пример 1 Описание
- •Индексирование с использованием других значений
- •Пример 2 Описание
- •Результат
- •Надежное программирование
- •Индексаторы в интерфейсах
- •Результат
- •Сравнение свойств и индексаторов
- •Делегаты
- •Общие сведения о делегатах
- •Использование делегатов
- •Делегаты с именованными методами и делегаты с анонимными методами
- •Заметки
- •Пример 1
- •Результат
- •Пример 2
- •Результат
- •Использование делегатов вместо интерфейсов
- •Ковариация и контрвариация в делегатах
- •Пример 1 (ковариация) Описание
- •Пример 2 (контрвариация) Описание
- •Объединение делегатов (многоадресные делегаты)
- •Объявление, создание экземпляра и использование делегата
- •Надежное программирование
- •События
- •Общие сведения о событиях
- •Подписка и отмена подписки на события
- •Подписка на события в среде ide Visual Studio
- •Подписка на события программными средствами
- •Подписка на события при помощи анонимного метода
- •Отмена подписки
- •Отмена подписки на событие
- •Публикация событий, соответствующих рекомендациям .Net Framework
- •Порядок публикации событий, основанных на шаблоне EventHandler
- •Создание событий базового класса в производных классах
- •Вызов и прием событий
- •Реализация событий интерфейса
- •Реализация событий интерфейса в классе
- •Пример44
- •Использование словаря для хранения экземпляров событий
- •Универсальные шаблоны
- •Общие сведения об универсальных шаблонах
- •Введение в универсальные шаблоны
- •Преимущества универсальных шаблонов
- •Параметры универсального типа
- •Рекомендации по именованию параметра типа
- •Пространства имен
- •Общие сведения о пространствах имен
- •Использование пространств имен
- •Доступ к пространствам имен
- •Псевдонимы пространств имен
- •Использование пространств имен для управления областью действия
- •Полные имена
- •Использование квалификатора псевдонима пространства имен
- •Типы, допускающие значения null
- •Общие сведения о типах, допускающих значения null
- •Использование типов, допускающих значение null
- •Примеры допускающих значение null типов
- •Члены допускающих значение null типов
- •Явные преобразования
- •Неявные преобразования
- •Операторы
- •Оператор ??
- •Идентификация типа, допускающего значение null
- •Небезопасный код и указатели
- •Общие сведения о небезопасном коде
- •Буферы фиксированного размера
- •Заметки
- •Типы указателей45
- •Преобразования указателей
- •Неявные преобразования указателей
- •Явные преобразования указателей
- •Результат
- •Выражения указателей Получение значения переменной указателя
- •Получение адреса переменной
- •Доступ к члену с использованием указателя
- •Доступ к элементу массива с использованием указателя
- •Управление указателями Увеличение и уменьшение указателей
- •Арифметические операции над указателями
- •Сравнение указателей
- •Использование указателей для копирования массива байтов
- •Комментарии xml-документации
- •Рекомендуемые теги для комментариев документации
- •Использование xml-документации
- •Компиляция кода
- •Надежное программирование
- •Домены приложений
- •Общие сведения о доменах приложений
- •Выполнение кода в другом домене приложения
- •Сборки и глобальный кэш сборок
- •Общие сведения о сборках
- •Атрибуты
- •Общие сведения об атрибутах
- •Использование атрибутов
- •Общие атрибуты
- •Заметки
- •Использование нескольких идентификаторов
- •Атрибут Obsolete
- •Глобальные атрибуты
- •Исключения и обработка исключений
- •Общие сведения об исключениях
- •Использование исключений
- •Обработка исключений
- •Блоки catch
- •Блоки finally
- •Создание и генерация исключений
- •Чего следует избегать при генерации исключений
- •Определение классов исключений
- •Исключения, создаваемые компилятором
- •Обработка исключений с помощью блока try-catch
- •Примечания
- •Выполнение кода очистки с использованием блока finally
- •Взаимодействие
- •Использование вызова неуправляемого кода для воспроизведения звукового файла
- •Компиляция кода Чтобы скомпилировать этот код, выполните следующие действия47
- •Создание потоков
- •Общие сведения
- •Использование потоков
- •Синхронизация потоков
- •Ключевое слово lock
- •Мониторы
- •События синхронизации и дескрипторы ожидания
- •Мьютексные объекты
- •Создание и завершение потоков
- •Синхронизация потока-производителя и потока-потребителя
- •Использование пула потоков
- •Отражение
- •Общие сведения об отражении
- •Библиотеки c#
- •Создание и использование библиотек dll на языке c#
- •Выполнение
- •Результат
- •Компиляция кода
- •Безопасность
- •Рекомендации по безопасности, касающиеся языка c# в отдельности
- •Использование неуправляемых функций dll
- •Применение экспортированных функций dll
- •Подробный обзор вызова неуправляемого кода
- •Идентификация функций в библиотеках dll
- •Создание класса, содержащего функции dll
- •Создание прототипов в управляемом коде
- •Основы описания
- •Настройка описания
- •Задание точки входа
- •Вызов функции dll
- •Передача структур
- •Объявление и передача структур
- •Объявление и передача классов
- •Файловый и потоковый ввод-вывод
- •Основы файлового ввода-вывода
- •Классы, используемые в файловом вводе и выводе
- •Классы, используемые для чтения и записи в поток
- •Общие классы потокового ввода и вывода
- •Ввод-вывод и безопасность
- •Создание списка каталогов
- •Надежное программирование
- •Считывание из нового файла данных и запись в этот файл
- •Надежное программирование
- •Копирование каталогов
- •Открытие файла журнала и добавление в него данных
- •Запись текста в файл
- •Считывание текста из файла
- •Надежное программирование
- •Считывание символов из строки
- •Результат
- •Запись символов в строку
- •Надежное программирование
- •Добавление или удаление записей списка управления доступом
- •Чтобы добавить или удалить элемент списка управления доступом из файла
- •Чтобы добавить или удалить элемент acl из каталога
- •Компиляция кода
- •Сжатие файлов
- •Создание потоков
- •Создание класса Writer
- •Коллекции и структуры данных
- •Определение коллекций
- •Выбор класса коллекции
- •Знакомство с решениями, проектами и элементами
- •Контейнеры: проекты и решения
- •Элементы: файлы, ссылки, подключения к данным
- •Решения как контейнеры
- •Решения
- •Преимущества
- •Файлы определения
- •Проекты как контейнеры
- •Шаблоны проектов
- •Файлы проекта
- •Элементы проектов
- •Использование интегрированной среды разработки Visual c#
- •Введение в интегрированную среду разработки
- •Средства Visual c#
- •Доступ к средствам в интегрированной среде разработки
- •Окна редактора и конструктора форм Windows
- •Обозреватель решений и конструктор проектов
- •Окна компилятора, отладчика и списка ошибок
- •Настройка интегрированной среды разработки
- •Создание проекта
- •Создание нового проекта
- •Состав проекта Свойства
- •Ресурсы
- •Другие файлы исходного кода
- •Изменение свойств проекта
- •Создание пользовательского интерфейса
- •Добавление элементов управления
- •Задание свойств
- •Обработка событий
- •Редактирование кода
- •Списки завершения
- •Краткие сведения
- •Список членов
- •Сведения о параметрах
- •Добавление директив using
- •Оптимизация кода
- •Фрагменты кода
- •Подчеркивание волнистой линией
- •Средства обеспечения удобочитаемости кода Форматирование кода
- •Структура
- •Выделение цветом
- •Навигация и поиск
- •Представление классов
- •Навигация ctrl-tab
- •Панели переходов
- •Поиск в файлах
- •Обозреватель объектов
- •Стеки навигации
- •Построение и отладка
- •Параметры построения
- •Ошибки построения
- •Сравнение отладочной и выпускной конфигураций
- •Отладка
- •Моделирование и анализ кода
- •Конструктор классов
- •Обозреватель объектов
- •Метаданные как источник
- •Анализ управляемого кода
- •Добавление и редактирование ресурсов
- •Добавление ресурсов в проекты
- •Редактирование ресурсов
- •Компиляция ресурсов в сборки
- •Доступ к ресурсам во время выполнения
- •Получение справки
- •Локальная справка и справка в Интернете
- •Поиск по f1
- •Указатель
- •Содержание
- •Инструкции
- •Динамическая справка
- •Примеры
- •Оптимизация
- •Многопроектная оптимизация
- •Диалоговое окно "Предварительный просмотр изменений"
- •Допускающая наличие ошибок оптимизация
- •Извлечение метода
- •Оптимизация кода с помощью операции "извлечение метода"
- •Чтобы воспользоваться операцией "извлечение метода"
- •Переименовать
- •Операции переименования
- •Переименование идентификаторов
- •Чтобы переименовать идентификатор
- •Превращение локальной переменной в параметр
- •Заметки
- •Превращение локальной переменной в параметр
- •Чтобы выполнить превращение локальной переменной в параметр
- •Разметка кода цветом
- •Лексемы
- •Контекстные ключевые слова
- •Разметка цветом для обозначения парности фигурных скобок
- •Разметка цветом и жирным шрифтом
- •Разметка цветом и выделение цветным фоном
Использование неуправляемых функций dll
Вызов неуправляемого кода — это служба, которая позволяет управляемому программному коду вызывать неуправляемые функции, реализованные в библиотеках динамической компоновки (DLL), например, функции библиотек Win32 API. Вызов неуправляемого кода обнаруживает и вызывает экспортируемую функцию и при необходимости выполняет маршалинг ее аргументов (целых чисел, строк, массивов, структур и так далее) через границы взаимодействия.
В этом разделе представлено несколько задач, связанных с использованием неуправляемых функций DLL. Кроме следующих задач, имеются общие аспекты и ссылка, указывающая на дополнительные сведения и примеры.
Применение экспортированных функций dll
Идентифицируйте функции в DLL.
Как минимум, должно быть указано имя функции и имя библиотеки DLL, содержащей функцию.
Создайте класс для хранения функций DLL.
Можно использовать существующий класс, создать отдельный класс для каждой неуправляемой функции либо создать один класс для всего набора связанных неуправляемых функций.
Создайте прототипы в управляемом коде.
[C#] Чтобы идентифицировать DLL и функцию, используйте класс DllImportAttribute. Пометьте метод модификаторами static и extern.
Вызовите функцию DLL.
Вызовите метод созданного управляемого класса так же, как любой другой управляемый метод. Особыми случаями являются передача структур и реализация функций обратного вызова.
A Closer Look at Platform Invoke
Platform invoke relies on metadata to locate exported functions and marshal their arguments at run time. The following illustration shows this process.
A platform invoke call to an unmanaged DLL function
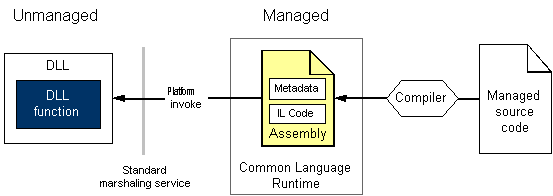
When platform invoke calls an unmanaged function, it performs the following sequence of actions:
Locates the DLL containing the function.
Loads the DLL into memory.
Locates the address of the function in memory and pushes its arguments onto the stack, marshaling data as required.
Note:
Locating and loading the DLL, and locating the address of the function in memory occur only on the first call to the function.
Transfers control to the unmanaged function.
Platform invoke throws exceptions generated by the unmanaged function to the managed caller.
Подробный обзор вызова неуправляемого кода
Для нахождения экспортируемых функций и маршалинга их аргументов во время выполнения вызов неуправляемого кода использует метаданные. Этот процесс показан на следующем рисунке.
Вызов неуправляемой функции DLL из вызова неуправляемого кода
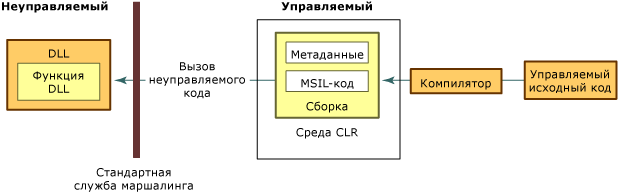
При вызове неуправляемой функции вызов неуправляемого кода выполняет следующую последовательность действий:
Определяет DLL, содержащую функцию.
Загружает DLL в память.
Находит адрес функции в памяти и помещает ее аргументы в стек, осуществив в случае необходимости маршалинг данных.
Примечание.
Обнаружение и загрузка DLL, а также определение адреса функции в памяти выполняется только при первом вызове функции.
Передает управление неуправляемой функции.
Исключения, возникающие при вызове неуправляемой функции, передаются управляемому вызывающему коду.
Identifying Functions in DLLs
The identity of a DLL function consists of the following elements:
Function name or ordinal
Name of the DLL file in which the implementation can be found
For example, specifying the MessageBox function in the User32.dll identifies the function (MessageBox) and its location (User32.dll, User32, or user32). The Microsoft Windows application programming interface (Win32 API) can contain two versions of each function that handles characters and strings: a 1-byte character ANSI version and a 2-byte character Unicode version. When unspecified, the character set, represented by the CharSet field, defaults to ANSI. Some functions can have more than two versions.
MessageBoxA is the ANSI entry point for the MessageBox function; MessageBoxW is the Unicode version. You can list function names for a specific DLL, such as user32.dll, by running a variety of command-line tools. For example, you can use dumpbin /exports user32.dll or link /dump /exports user32.dll to obtain function names.
You can rename an unmanaged function to whatever you like within your code as long as you map the new name to the original entry point in the DLL. For instructions on renaming an unmanaged DLL function in managed source code, see the Specifying an Entry Point.
Platform invoke enables you to control a significant portion of the operating system by calling functions in the Win32 API and other DLLs. In addition to the Win32 API, there are numerous other APIs and DLLs available to you through platform invoke.
The following table describes several commonly used DLLs in the Win32 API.
DLL |
Description of Contents |
GDI32.dll |
Graphics Device Interface (GDI) functions for device output, such as those for drawing and font management. |
Kernel32.dll |
Low-level operating system functions for memory management and resource handling. |
User32.dll |
Windows management functions for message handling, timers, menus, and communications |
