
- •1.1. Foreign language communicative competence
- •1.2. Foreign language communicative competence and plurilingual and intercultural education
- •1.3. Framework for foreign language communicative competence
- •1.4. Definition of methodology
- •1. The majority of people study English so that they were able:
- •2. The statement that people's speech both in the native and foreign languages is influenced by a social context means:
- •4. By Foreign Language Communicative Competence I mean:
- •5. Choose two correct items.
- •2.1. Fundamental categories and notions of methodology
- •Example 1
- •2.2. History of methodology
- •2.2.1. The Classical Greek Method
- •2.2.3. The Direct Method
- •6. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers. The Direct Method:
- •7. From the multiple choice below choose three correct answers. The principles of the Direct Method:
- •3.1. New methods created between the 1930s and 1970s
- •3.1.1. Influence of Philology on Creating New Methods of Teaching Foreign Languages. Structural Approaches
- •3.1.2. Palmer's Method
- •3.1.3. Audio-Lingual Methods
- •3.1.4. Tasks and Drills Topical of the 1930s and 1970s
- •3.2. Communicative methods
- •3.2.1. Community Language Learning as Method of Humanistic Approach
- •3.2.2 Some organizational peculiarities of the cll
- •3.2.3. Method of Total Physical Response as Comprehension-Based Method
- •3.2.4. Kitajgorodskaya's Method of Activation of Individual and Group Potential
- •The principle of concentration and distribution of teaching material.
- •1. The methods created between the 1930 and 1970
- •2. From the multiple choice below choose four correct answers. Community Language Learning
- •3. The Method of Transformations and the Modelling Method
- •4. The main idea of all Communicative Methods is
- •4.1. Postulates of methodology
- •4.2. General considerations of integrated, or interactive, teaching
- •4.3. Methodological techniques of integrated, or interactive, teaching
- •Conditions of its Implementation
- •Teacher's Behaviour
- •Grammatical item
- •1. The goal of the first stage is to create conditions for learners' comprehending the suggested language items intuitively and spontaneously, e.G.:
- •4.3.2. Oral speech — visual-and-graphic situation with things and objects of everyday practice to present grammatical point
- •A phonetic item
- •2. The goal of the second stage is to form in learners initial imitative reading of the text.
- •4.4. Polyfunctional sequences of learners' activities as technique of interactive, or integrated, teaching
- •4.4.1. Teaching Reading through Polyfunctional Sequences of Learners' Activities
- •10. Read the text trying to notice in what it differs from your the version you have written.
- •Reading Tasks
- •1. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers
- •2. A teacher is dependent in his choice of the text-book on
- •4. A language form is trapped by sense when
- •2. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers.
- •5.1. Lesson as basic link of language instruction
- •5.2. Psychological peculiarities of lesson
- •5.3. Standard lessons
- •5.4. Planning standard lessons
- •Beginning Stage of Lesson Plan
- •Greeting and warming- up 2 m
- •5.5. Lesson procedure
- •1. Write down the number of the item in which the general goal of the lesson is formulated most correctly.
- •2. Choose the correct:
- •4. The lesson plan of a novice teacher should consist of:
- •5. When processual motivation is applied students
- •6. Practical and Educational Tasks of the lesson are to be included into:
- •6. Formation of foreign language speech
- •6.1. Distinguishing characteristics of plot lessons
- •6.2. Quizzing-game lesson
- •6.4. Auction lesson
- •6.5. Press-conference lesson
- •6.6. Round-table lesson
- •6.7. Brain-storming lesson
- •6.8. Discussion lesson
- •6.9. Debate lesson
- •6.12. Project lesson
- •7. Some psycholiguistic peculiarities
- •7.1. Psycholinguistic peculiarities of speech. Subject of psycholinguistics
- •7.2. Universal object code
- •7. 3. Significative structure of word
- •7.4. Importance of mental operations of translating one component of word into its other component
- •1. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers. Generating meaning in speech is controlled by:
- •2. From the multiple choice below choose three correct answers. In the Universal Object Code:
- •4. In language instruction:
- •8.1. Developing sound-motor-spelling and image relationships
- •Mastering speaking
- •Mastering reading
- •Mastering writing
- •8.2. Contents of learners' theoretical and practical knowledge in phonetics
- •8.3. Requirements for secondary school learners' skills in pronunciation
- •8.4. List of phonetic items of the english language to be studied in secondary school
- •Vowels in open, closed and conventionally open syllables.
- •Vowels before -le.
- •1. If sound-motor-spelling and image relationships are well developed in learners:
- •2. The most important skill to be developed in learners while teaching read ing is skill in:
- •4. The practical goal of studying pronunciation in a secondary school is:
- •9. Theoretical fundamentals
- •In dialogical speech
- •9.1. Spontaneity of speech
- •9.3. Interlocutors' personal interest to solve non-linguistic tasks in oral speech interaction
- •9.4. Level of formation of habits and skills in pronunciation, grammar and lexis
- •Vm sorry to hear that.
- •9.5. Level of formation of sociocultural activity
- •9.6. Skill of applying speech stimulating phrases
- •9.7. Speaking and understanding strategies in dialogical speech
- •1. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers. Speech can be considered spontaneous and unprepared if
- •2. From the multiple choice below choose two correct answers. Situational character of speech helps learners to develop
- •4. Choose the correct:
- •In reading
- •10.1. Significance of reading
- •It is through reading that people get most of the information available in the world.
- •10.2. Definition of reading
- •10.3. Comparison of reading skills of fluent readers and beginning readers. Tasks in teaching reading
- •Skill of using various reading strategies
- •For you to Choose
- •For you to Choose
- •10.4. Bilateral nature of reading in teaching
- •In English.
- •10.5.2. Imitative Reading as Means of Developing Technique of Reading at Starting and Beginning Stages of Teaching
- •Sequence I
- •Chart 2
- •10.6.2. Preventive Work Preceding Teaching Reading for Meaning
- •10.6.3. Teaching Skimming Reading
- •10.6.4. Teaching General Reading
- •10.6.5. Teaching Close Reading
- •10.6.6. Teaching Searching Reading
- •1. It is important to teach reading foreign languages in Ukraine because
- •11.1. Active, or productive, command of language. Passive, or receptive, command of language
- •Grammar
- •In order to show the animation Pete switched on the dvd.
- •1 To inform clients about the terms of delivering the goods, the firm
- •3 3 Them by telephone.
- •11.3. From first-time presentation of grammatical structure to forming grammatical speech competence
- •12. Theoretical fundamentals of formation
- •In secondary school
- •12.1. Vocabulary learning as central to language acquisition
- •12.2. Goals of teaching vocabulary
- •12.3. Main factors favouring acquisition of foreign language vocabulary
- •12.4. Functional groups of vocabulary. Ways of increasing them
- •2. From the multiple choice below choose two factors which do not favour bet- r understanding and memorizing meanings of unknown words.
- •3. A group of words or combinations of words which people are able to com- rehend though they have never seen them before are called
- •4. From the multiple choice below choose as many correct answers as you can. The clues to understand new words are based on
- •Bibliography
A phonetic item
The goal of the first stage is to create conditions for learners' assimilating the suggested phonemical item intuitively and spontaneously.
It is achieved by means of the first-time presentation of a phonemic item in microtexts (in which it is given in bold type) supplied with illustrative pictures. The task to the learners is as follows: "Listen and try to understand what these texts are about." This is a task in listening comprehension.
The teacher works with two pointing rods. With one he points at the combination of letters sh and with the other at the visual images of words containing it. The teacher reads the texts twice or thrice expressing some affective exaggeration, using various gestures, movements and mine.
F ig.
9.
ig.
9.
A pictorial support to present a phonetic item in an oral speech-visual-and-graphic situation
2. The goal of the second stage is to form in learners initial imitative reading of the text.
The teacher asks for a volunteer to come up to the screen or the poster and read
the text aloud imitating the teacher. Then two more volunteers do the same.
After this the learners use the cards and sitting at their desks read the text
one by one.
3.The goal of the third stage is to introduce elements of oral speech activity with the use of the phonetic item introduced. Tasks in oral speech activity are given.
The teacher works with the pictures and pointing rods in the way it was shown above. However, now she/he puts questions to the picture and answers them in order to show the learners a pattern of their further activity. The questions are intentionally constructed in such a way that it is impossible to answer them avoiding pronouncing words with —sh. To achieve it no general questions are given, because they can be answered with " Yes. " or "No." and do not require answers including words with -sh, e.g.:
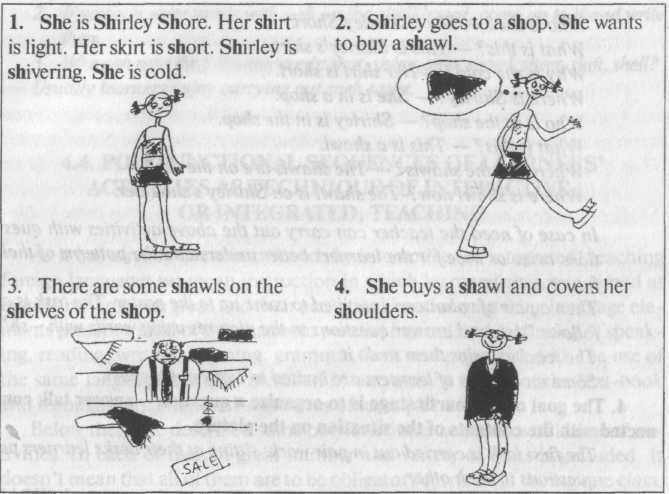
Who is she ? — She is Shirley Shore.
What is this?— This is Shirley's shirt.
Why is she cold? — Her shirt is short.
Where is Shirley ? — She is in a shop.
Who is in the shop ? — Shirley is in the shop.
What is this ? — This is a shawl.
Where are the shawls? — The shawls are on the shelf.
Where is shawl now?- The shawl is on Shirley's shoulder.
In case of need the teacher can carry out the above activities with questions twice or trice for the learners better understand the patterns of their
future activity.
Then a pair of volunteers is invited to come up to the poster. The task is as follows: "Ask and answer questions to the pictures using words with —sh".
The teacher helps them to do it.
Some more pairs of learners are invited to carry out the task. 4. The goal of the fourth stage is to organize a question— answer talk connected with the contents of the situation on the picture.
The first task is carried out in pair work: sitting at their desks learners put
questions to each other.
The second task is carried out individually by each learner: 1." Within
three minutes make up as many questions to the text as you can and write
them down."
The third task is: "Put questions to each other and answer them ". The teacher controls the students, fixes limitations in time and points at those who are to ask and who are to answer questions. 5.The goal of the fifth stage is to organize a free talk with the use of the words containing -sh, however the contents of the talk are not to be connected with those of the picture and the text read. The tasks are as follows:
"Forfive minutes make up and write down as many questions containing the words with —sh which you can find in the text." The teacher is walking from desk to desk helping each learner in making up sentences.
" Talk with each other putting and answering your questions ".
6.The goal of the sixth stage is to check whether the learners have assimilated the introduced phonemic item.
The teacher takes the poster away. The tasks are as follows: 1. Who knows words with —sh ? When the children raise their hands, the
teacher asks them.
2. If you can write words with —sh on the chalkboard, come up to it and write them.
3. Who can read the following words: shut, sheep, ship, shawl, sheet, shift, shell? Usually learners enjoy carrying out such tasks.
