
- •Definition of economics
- •Modern definition of the subject
- •1.3 Scarcity
- •1.4.Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- •2.1.Types of industry
- •2.2. Sectors of business
- •2.3. Classification of business
- •2.4. Forms of business
- •Forms of business
- •6.1. Field Research
- •6.2.Desk Research
- •Price of market balance: p – price, q - quantity of good, s – supply,
- •5 P rule
- •The purpose of tight fiscal policy is:
- •Side Effects of Tight Fiscal Policy
- •21.1. Law of comparative advantage
- •21.2. Absolute Advantage
- •Origin of the theory
- •Example
- •Unit 20 Balance of payments
- •Bookkeeping system
- •Foreign Exchange
- •Unit 24 Underground Economy
- •Unit 25 Preferred and Common Stocks
- •Unit 26 Economic Functions of Government
- •Unit 39 Factors of Production
- •Intrinsic
- •Need of venture capital
- •Main alternatives to venture capital
- •Basic roles
- •[Edit]Management skills
- •[Edit]Formation of the business policy
- •Levels of management
- •[Edit]Top-level managers
- •[Edit]Middle-level managers
- •[Edit]low-level managers
- •International trade
- •U nited States
[Edit]low-level managers
Consist of supervisors, section leads, foremen, etc. They focus on controlling and directing. They usually have the responsibility of assigning employees tasks, guiding and supervising employees on day-to-day activities, ensuring quality and quantity production, making recommendations, suggestions, and upchanneling employee problems, etc. First-level managers are role models for employees that provide:
Basic supervision.
Motivation.
Career planning.
Performance feedback.
supervising the staffs.
Strategic management is a field that deals with the major intended and emergent initiatives taken by general managers on behalf of owners, involving utilization of resources, to enhance the performance of firms in their external environments.[1] It entails specifying the organization's mission, vision and objectives, developing policies and plans, often in terms of projects and programs, which are designed to achieve these objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the policies and plans, projects and programs. A balanced scorecard is often used to evaluate the overall performance of the business and its progress towards objectives. Recent studies and leading management theorists have advocated that strategy needs to start with stakeholders expectations and use a modified balanced scorecard which includes all stakeholders.
Strategic management is a level of managerial activity under setting goals and over Tactics. Strategic management provides overall direction to the enterprise and is closely related to the field of Organization Studies. In the field of business administration it is useful to talk about "strategic alignment" between the organization and its environment or "strategic consistency." According to Arieu (2007), "there is strategic consistency when the actions of an organization are consistent with the expectations of management, and these in turn are with the market and the context." Strategic management includes not only the management team but can also include the Board of Directors and other stakeholders of the organization. It depends on the organizational structure.
“Strategic management is an ongoing process that evaluates and controls the business and the industries in which the company is involved; assesses its competitors and sets goals and strategies to meet all existing and potential competitors; and then reassesses each strategy annually or quarterly [i.e. regularly] to determine how it has been implemented and whether it has succeeded or needs replacement by a new strategy to meet changed circumstances, new technology, new competitors, a new economic environment., or a new social, financial, or political environment.”
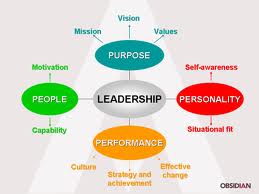
UNIT 57 LEADERSHIP
T
 he
question of leadership has been investigated since ancient times by
many scientists. Since Platen and Aristotle times people were
interested in a variety of skills that make a person a leader.
Nowadays leadership is a social process of cooperation of a head and
the members of a team which is oriented to the reaching a purpose.
Based on the great number of scientific works the leader is
considered as a person who combines the skills and personal
characteristics with the help of which the impact to the group is
made by the means of force or motivation. The structure of leadership
skills is made according to the peculiarities of the professional
work of future specialists. The specific of work of economists is
considered as a mixture of economic oriented activities which are
connected with planning, management, valuation of work results, as
well as cooperation and motivation. The professional work of
economists’ demands performing tasks connected with gathering and
the analyses the information, decision – making, self-motivation
and stimulating the team members. Also it demands the skills
concerning negotiation and cooperation between staff. The economists
should know how to find resources, to arrange the process of
production, to analyze and to find the result. Managers activity is
occurred in groups so it demands cooperation and collaboration
skills. Based on the mentioned kinds of activity the leadership
skills of economists consists of personal and psychological
component, communication and creative one, business component and
socio-group component. Having leadership skills as a part of
professional characteristics, the specialist is able to achieve much
more in his career. Even if he doesn’t become a leader, he will
increase his professional level which will make his work more
effective and profitable.
he
question of leadership has been investigated since ancient times by
many scientists. Since Platen and Aristotle times people were
interested in a variety of skills that make a person a leader.
Nowadays leadership is a social process of cooperation of a head and
the members of a team which is oriented to the reaching a purpose.
Based on the great number of scientific works the leader is
considered as a person who combines the skills and personal
characteristics with the help of which the impact to the group is
made by the means of force or motivation. The structure of leadership
skills is made according to the peculiarities of the professional
work of future specialists. The specific of work of economists is
considered as a mixture of economic oriented activities which are
connected with planning, management, valuation of work results, as
well as cooperation and motivation. The professional work of
economists’ demands performing tasks connected with gathering and
the analyses the information, decision – making, self-motivation
and stimulating the team members. Also it demands the skills
concerning negotiation and cooperation between staff. The economists
should know how to find resources, to arrange the process of
production, to analyze and to find the result. Managers activity is
occurred in groups so it demands cooperation and collaboration
skills. Based on the mentioned kinds of activity the leadership
skills of economists consists of personal and psychological
component, communication and creative one, business component and
socio-group component. Having leadership skills as a part of
professional characteristics, the specialist is able to achieve much
more in his career. Even if he doesn’t become a leader, he will
increase his professional level which will make his work more
effective and profitable.
UNIT 58 TAXES
T axes
are fixed legislature
required
payments
that
are paid by
individuals
and legal entities
in
the
state budget.
Through
taxes generated
financial
resources of the state,
which
accumulate
in
the budget system
of
the country.
axes
are fixed legislature
required
payments
that
are paid by
individuals
and legal entities
in
the
state budget.
Through
taxes generated
financial
resources of the state,
which
accumulate
in
the budget system
of
the country.
Tax payers are:
Residents receiving either income originating from the territory of Ukraine or foreign income.
Non-residents receiving income originating from the territory of Ukraine.
T axes
can be direct (added to the cost on the stage of production) and
indirect (added to the cost on the stage of selling). Direct taxes
are divided into personal (income tax) and real (tax on land,
property, rent tax)
axes
can be direct (added to the cost on the stage of production) and
indirect (added to the cost on the stage of selling). Direct taxes
are divided into personal (income tax) and real (tax on land,
property, rent tax)
Income tax – a tax, levied on the sum of the gross income of citizens in terms of money over the past year. Part of the income tax is levied on current income and monthly in the form of lump-sum payments.
A person is a tax resident in Ukraine if he has a place of residence in Ukraine. If the person has a permanent place of residence in Ukraine and another country, the person is deemed to be resident of Ukraine if his centre of vital interests is in Ukraine, or if he stays in Ukraine at least 183 days during the tax year(calendar year). This is the general rule which is subject to any features provided by the Agreement of avoidance of double taxation.
Ukraine Personal income tax rates for 2011 are 0%, 1%, 5%, 15%,17% ,30%.
Income |
Tax rate |
It is the standard tax rate. This rate usually applies to employment income of up to 10 times the minimum monthly salary, rental income, investment income, in the event of inheritance by any heir from a non-resident testator, income from the sale of an object of movable property. |
15% |
Employment income exceeding 10 times the minimum monthly income. Sale of immovable assets by a non-residence. Inheritance tax when the recipient is non-resident. |
17% |
This rate applies to income from prizes and winnings of residents; to income from prizes and winnings of non-residents originating from Ukraine |
30% |
This rate applies to income from the sale of more than one object of real estate property during a calendar year; In the event of inheritance by the heirs other than the testator's family members of the first degree of kindred. |
5% |
This rate applies to income received by a taxpayer from the first sale of a house, apartment or room not more than once, during a reporting year if the total area of the object exceeds 100 square meters. The subject to taxation is the part of income proportional to the amount of exceeds |
1% |
This rate applies to inheritance from the heirs who are the family members of the first degree of kindred; To income received by a taxpayer from the sale of a house, apartment or room not more than once during a reporting year, if the total surface area of the house, apartment or room does not exceed 100 square meters |
0% |
Personal Tax Deduction in Ukraine
A resident taxpayer may claim a deduction from annual taxable income for a limited amount of documented expenses incurred in the reporting year for:
Secondary professional or higher education of the taxpayer and his family members;
Donations or charitable contributions to non-profit organizations;
Cost of paid services with regard to medical treatment of the taxpayer or a member of his family of the first degree of kindred.
Corporate profit taxation in Ukraine
Ukrainian entities and foreign entities doing business in Ukraine through a permanent establishment are liable for corporate profit tax.
The Corporate Tax Law provides for the taxation of the following persons:
Legal entities organized under the laws of Ukraine and which carry out business in Ukraine;
Foreign entities which get a profit from sources in Ukraine (the profit arises from activities performed or property located in Ukraine, in case of dividends, interest, royalties and other passive income, the income is paid by a resident of Ukraine)
Non-resident legal entities which carry out business activities on the territory of Ukraine through a permanent establishment;
The corporate Tax Law established a basic corporate tax rate of 23%. This is a standard rate from the clean income (i.e. gross income) for the entities and natural persons - private entrepreneurs. However, small legal entities may choose the simplified taxation. Thus VAT - registered entities pay 6% of their sales proceeds under the simplified tax system, while non -VAT - registered entities pay 10%.
Deduction of Tax at Source Payments to non-residents are subject to tax withholding rates as follows:
Dividend - 15%
Interest - 15%
Royalties - 15%
Progressive and Regressive Tax
A progressive tax is a tax by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. "Progressive" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate progresses from low to high, where the average tax rate is less than the marginal tax rate. It can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Progressive taxes attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability-to-pay, as they shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay.
Progressive taxation often must be considered as part of an overall system since tax codes have many interdependent variables. For example, when refundable tax credits and other tax incentives are included across the entire income spectrum, the United States has the most progressive income tax code among its peer nations, although its overall income tax rates are below the (Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development) average.
The term is frequently applied in reference to personal income taxes, where people with more income pay a higher percentage of that income in tax than do those with less income. It can also apply to adjustment of the tax base by using tax exemptions, tax credits, or selective taxation that would create progressive distributional effects. For example, a sales tax on luxury goods or the exemption of basic necessities may be described as having progressive effects as it increases a tax burden on high end consumption or decreases a tax burden on low end consumption respectively.
The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, where the relative tax rate or burden increases as an individual's ability to pay it decreases. Sales taxes are often criticized because low income households must pay a greater share of their disposable income to a sales tax than wealthier households. In between is a proportional tax, where the tax rate is fixed as the amount subject to taxation increases.
A regressive tax is a tax imposed in such a manner that the tax rate decreases as the amount subject to taxation increases. "Regressive" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate progresses from high to low, where the average tax rate exceeds the marginal tax rate. In terms of individual income and wealth, a regressive tax imposes a greater burden (relative to resources) on the poor than on the rich — there is an inverse relationship between the tax rate and the taxpayer's ability to pay as measured by assets, consumption, or income.
It can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Regressive taxes tend to reduce the tax incidence of people with higher ability-to-pay, as they shift the incidence disproportionately to those with lower ability-to-pay. The opposite of a regressive tax is a progressive tax, where the marginal tax rate increases as the amount subject to taxation increases. In between is a flat or proportional tax, where the tax rate is fixed as the amount subject to taxation increases.
The term is frequently applied in reference to fixed taxes, where every person has to pay the same amount of money. The regressivity of a particular tax often depends on the propensity (склонность) of the tax payers to engage in the taxed activity relative to their income. In other words, if the activity being taxed is more likely to be carried out by the poor and less likely to be carried out by the rich, then the tax may be considered regressive. To determine whether a tax is regressive, the income-elasticity of the good being taxed as well as the income-substitution effect must be considered.
TAXES in the USA
T he
United States is a federal republic with autonomous state and local
governments.
Taxes are
imposed in
the United States at
each of these levels. These include taxes on income, property, sales,
imports, payroll, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. Taxes
are imposed on net income of individuals and corporations by the
federal, most state, and some local governments. Residents are taxed
on worldwide income and allowed a credit for foreign taxes. Income
subject to tax is determined under tax rules, not accounting
principles, and includes almost all income from whatever source. Most
business expenses reduce taxable income, though limits apply to a few
expenses. Individuals are permitted to reduce taxable income by
personal allowances and certain nonbusiness expenses, including home
mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions,
and medical and certain other expenses incurred above certain
percentages of income. State rules for determining taxable income
often differ from federal rules. Federal tax rates vary from 15% to
35% of taxable income. State and local tax rates vary by
jurisdiction, and many are graduated. State taxes are generally
treated as a deductible expense for federal tax computation. Certain
alternative taxes may apply.
he
United States is a federal republic with autonomous state and local
governments.
Taxes are
imposed in
the United States at
each of these levels. These include taxes on income, property, sales,
imports, payroll, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. Taxes
are imposed on net income of individuals and corporations by the
federal, most state, and some local governments. Residents are taxed
on worldwide income and allowed a credit for foreign taxes. Income
subject to tax is determined under tax rules, not accounting
principles, and includes almost all income from whatever source. Most
business expenses reduce taxable income, though limits apply to a few
expenses. Individuals are permitted to reduce taxable income by
personal allowances and certain nonbusiness expenses, including home
mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions,
and medical and certain other expenses incurred above certain
percentages of income. State rules for determining taxable income
often differ from federal rules. Federal tax rates vary from 15% to
35% of taxable income. State and local tax rates vary by
jurisdiction, and many are graduated. State taxes are generally
treated as a deductible expense for federal tax computation. Certain
alternative taxes may apply.
P ayroll
taxes are imposed by the federal and all state governments. These
include Social Security and Medicare taxes imposed on both employers
and employees, at a combined rate of 15.3% (13.3% for 2011). Social
Security tax applies only to the first $106,800 of wages in 2009
through 2011. Employers also must withhold income taxes on wages. An
unemployment tax and certain other levies apply.
ayroll
taxes are imposed by the federal and all state governments. These
include Social Security and Medicare taxes imposed on both employers
and employees, at a combined rate of 15.3% (13.3% for 2011). Social
Security tax applies only to the first $106,800 of wages in 2009
through 2011. Employers also must withhold income taxes on wages. An
unemployment tax and certain other levies apply.
Property taxes are imposed by most local governments and many special purpose authorities based on the fair market value of property. School and other authorities are often separately governed, and impose separate taxes. Property tax is generally imposed only on realty, though some jurisdictions tax some forms of business property. Property tax rules and rates vary widely.
Sales taxes are imposed on the price at retail sale of many goods and some services by most states and some localities. Sales tax rates vary widely among jurisdictions, from 0% to 16%, and may vary within a jurisdiction based on the particular goods or services taxed. Sales tax is collected by the seller at the time of sale, or remitted as use tax by buyers of taxable items who did not pay sales tax.
The United States imposes tariffs or customs duties on the import of many types of goods from many jurisdictions. This tax must be paid before the goods can be legally imported. Rates of duty vary from 0% to more than 20%, based on the particular goods and country of origin.
UNIT 59 INTERNATIONAL ECONIMICS
International economics is concerned with the effects upon economic activity of international differences in productive resources and consumer preferences and the institutions that affect them. It seeks to explain the patterns and consequences of transactions and interactions between the inhabitants of different countries, including trade, investment and migration.
International trade studies goods-and-services flows across international boundaries from supply-and-demand factors, economic integration, international factor movements, and policy variables such as tariff rates and trade quotas.[1]
International finance studies the flow of capital across international financial markets, and the effects of these movements on exchange rates.[2]
International monetary economics and macroeconomics studies money and macro flows across countries.[3]
