
- •Definition of economics
- •Modern definition of the subject
- •1.3 Scarcity
- •1.4.Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- •2.1.Types of industry
- •2.2. Sectors of business
- •2.3. Classification of business
- •2.4. Forms of business
- •Forms of business
- •6.1. Field Research
- •6.2.Desk Research
- •Price of market balance: p – price, q - quantity of good, s – supply,
- •5 P rule
- •The purpose of tight fiscal policy is:
- •Side Effects of Tight Fiscal Policy
- •21.1. Law of comparative advantage
- •21.2. Absolute Advantage
- •Origin of the theory
- •Example
- •Unit 20 Balance of payments
- •Bookkeeping system
- •Foreign Exchange
- •Unit 24 Underground Economy
- •Unit 25 Preferred and Common Stocks
- •Unit 26 Economic Functions of Government
- •Unit 39 Factors of Production
- •Intrinsic
- •Need of venture capital
- •Main alternatives to venture capital
- •Basic roles
- •[Edit]Management skills
- •[Edit]Formation of the business policy
- •Levels of management
- •[Edit]Top-level managers
- •[Edit]Middle-level managers
- •[Edit]low-level managers
- •International trade
- •U nited States
Example
C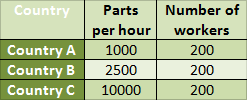 ountry
C has the absolute advantage.
ountry
C has the absolute advantage.
Country A can produce 1000 parts per hour with 200 workers.
Country B can produce 2500 parts per hour with 200 workers.
Country C can produce 10000 parts per hour with 200 workers.
Considering that labor and material costs are all equivalent, Country C has the absolute advantage over both Country B and Country A because it can produce the most parts per hour at the same cost as other nations. Country B has an absolute advantage over Country A because it can produce more parts per hour with the same number of employees. Country A has no absolute advantage because it can't produce more goods than either Country B or Country C given the same input.
Unit 20 Balance of payments
Balance of payments (BOP) accounts are an accounting record (расчетная запись) of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world. These transactions include payments for the country's exports and imports of goods, services, financial capital, and financial transfers. The BOP accounts summarize international transactions for a specific period, usually a year, and are prepared in a single currency, typically the domestic currency for the country concerned. Sources of funds for a nation, such as exports or the receipts of loans (поступление займов) and investments, are recorded as positive or surplus items. Uses of funds, such as for imports or to invest in foreign countries, are recorded as negative or deficit items.
When all components of the BOP accounts are included they must sum to zero with no overall surplus or deficit. For example, if a country is importing more than it exports, its trade balance will be in deficit, but the shortfall (дефицит) will have to be counter-balanced (уравновешенный) in other ways – such as by funds earned from its foreign investments, by running down (использование, истощение) central bank reserves or by receiving loans from other countries.
While the overall BOP accounts will always balance when all types of payments are included, imbalances (дисбаланс) are possible on individual elements of the BOP, such as the current account, the capital account excluding the central bank's reserve account, or the sum of the two. Imbalances in the latter sum can result in surplus countries accumulating wealth, while deficit nations become increasingly indebted (находящиеся в долгу). The term "balance of payments" often refers to this sum: a country's balance of payments is said to be in surplus (equivalently, the balance of payments is positive) by a certain amount if sources of funds (such as export goods sold and bonds sold) exceed uses of funds (such as paying for imported goods and paying for foreign bonds purchased) by that amount. There is said to be a balance of payments deficit (the balance of payments is said to be negative) if the former are less than the latter.
UNIT 21 Types of Banks
There are several types of banks in the world, and each has a specific role and function - as well as a domain (область) - in which they operate. In broad strokes (в общих чертах), banks may be divided into several groups on the basis of their activities and these include investment banks, retail, private, business, online bank and also corporate banks. Many of the larger banks have multiple divisions covering some or all of these categories.
Retail banks deal directly with consumers and small business owners. They focus on mass market products such as current and savings accounts, mortgages and other loans, and credit cards. By contrast, private banks normally provide wealth management services to high net worth families and individuals.
Business banks provide services to businesses and other organizations that are medium sized, whereas the clients of corporate banks are usually major business entities.
Lastly, investment banks provide services related to financial markets, such as mergers and acquisitions.
Another way in which banks may be categorized is on the basis of their ownership. They might either be privately held or publicly owned banks.
Privately owned banks are motivated by profit in their business operations. Publicly owned banks are held by the state governments of the individual countries and they serve as a nation’s centralized bank, as well as an economic backbone (экономическая основа) for that particular country. They are also known as central banks.
Publicly owned banks (в государственной собственности), which are controlled by the government, have numerous responsibilities pertaining (относящиеся) to the banking sector of the country, such as administering various activities for the commercial banks of that country. They also determine the rates of interest offered by banks doing business in that country, as well as playing a major role in maintaining liquidity in the banking sector.
There are several types of retail banks. These include the offshore, community and savings banks, as well as the community development banks, building societies, postal savings banks (почтово - сберегательный банк - вид сберегательных учреждений в развитых и развивающихся странах, в организационном отношении объединенных с почтовой системой.), ethical banks and Islamic banks.
Offshore banks operate in areas of reduced taxes, as compared to the country in which the investor lives in. This is why most offshore banks are private banks.
Community banks (банковские сообщества) are monetary organizations operated on a local basis, while community development banks cater (обслуживают) to the populations, or markets, that have typically not been served properly.
Postal savings banks are basically savings banks that operate in conjunction with the national postal systems of that country.
Building societies where traditionally mutually owned by their customers. They provide a full range of retail banking services, but with a particular focus on mortgages.
Ethical banks do their business based on their own code of conduct. They only accept investments that they perceive to be useful from a social and environmental point of view. The Islamic Banks perform their business operations as per the Sharia law, the Islamic code of law. In particular, this means that they operate sans interest (без процента).
UNIT 24 STOCK EXCHAGE
A stock exchange is an entity that provides services for stock brokers and traders to trade stocks, bonds, and other securities. Stock exchanges also provide facilities (средства) for issue and redemption (погашения) of securities and other financial instruments including the payment of income and dividends. Securities traded on a stock exchange include shares issued by companies, unit trusts, derivatives (производные ценные бумаги), pooled investment products and bonds.
To be able to trade a security on a certain stock exchange, it must be listed there. Usually, there is a central location at least for record keeping, but trade is increasingly less linked to such a physical place, as modern markets are electronic networks, which gives them advantages of increased speed and reduced cost of transactions. Trade on an exchange is by members only.
The initial offering of stocks and bonds to investors is by definition done in the primary market and subsequent trading is done in the secondary market. A stock exchange is often the most important component of a stock market. Supply and demand in stock markets are driven by various factors that, as in all free markets, affect the price of stocks. On February 8, 1971, NASDAQ, the world's first electronic stock exchange, started its operations.
UNIT 22 PROPERTY RIGHTS
Bundle of rights an entity has in a thing owned. These are among the most basic rights in a free society. No right to property, however, is absolute in any society. Laws created by governments in regards to how individuals can control, benefit from and transfer property. Economic theory contends (доказывает) that government enforcement (правоприменение) of strong property rights is a determinant regarding the level of economic success seen in the area. Individuals will create new forms of property to generate wealth, only when they are assured that their rights to their property will protect them against unjust and/or unlawful actions by other parties. For example, if property rights were not established to prevent a government from freely expropriating foreign created business ventures without proper compensation, then it is unlikely that any foreign company would risk going into that country for risk of losing their entire operation. While property rights regarding physical property has been well established. Many justice systems must now contend with property that solely exists in a digital or virtual setting. For example, who ultimately owns a house built in a game on the Internet, the user that created the house with his character? Or the game development company that created the game who also owns the server in which the house resides in? |
|
