
- •Практическая грамматика английского языка
- •Часть 1
- •I семестр
- •In this unit you are to revise the main grammar phenomena Form a
- •In this unit you are:
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part c. Mini-test
- •I. Guess
- •In this unit you are:
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part c. Translation and editing section
- •Part d. Revision exercises
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part c. Translation and editing section
- •Part d. Revision exercises
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •But: How long is it since you last saw her?–It is ages since I last saw her.
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part d. Revision exercises
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •I / he / she / it we / you / they had been working
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part c. Translation section and editing section
- •Part d. Revision exercises
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •Other Ways of Referring to the Future
- •Part b. Practical Exercises
- •Part c. Translation section and editing section
- •Part d. Revision exercises
- •Part a. Theoretical Material
- •Part b. Practical exercises
- •Part a. Tenses
- •Part b. General Practice
- •Part c. Translation
Part a. Theoretical Material
Past Simple
Formation. The past simple is formed by adding –ed to the stem from regular verbs or by changing the root in some other ways for irregular verbs.
The paradigm of the verb in the past indefinite
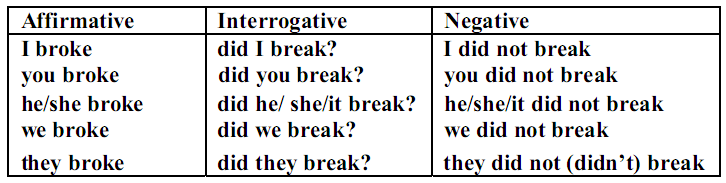
The auxiliary did also occurs in affirmative forms in cases when the speaker wishes to emphasize his statement, as in: But I assure you, he did tell me of it himself. Actually, I did see him once last week.
Spelling Rules:
• when the verb ends in -e only -d is added: change – changed;
• when the verb ends in -y preceded by a consonant, -y is changed into -i and -ed is added: study – studied;
• when a one-syllable verb ends in a single consonant (except c, w, z, y) preceded by a short stressed vowel or if a verb ends in a stressed syllable -er, -ur, the final consonant is doubled and -ed is added: stop – stopped, plan – planned, occur – occurred;
BUT if the preceding vowel is long or unstressed (except -er, -ur), the final consonant remains single: perform – performed;
• a final -l is always doubled in British English: travel – travelled;
• irregular past tense forms must be memorized because they are not related to simple forms in any predictable way. There are approximately 150 of them in all.
Main uses
The past simple is used to denote:
1) single completed actions in the past: Sony and Philips invented the CD in early 1980s.
2) repeated or habitual actions in the past: We moved house a lot when I was a kid.
3) general truths about the past: Early clocks were usually very unreliable.
4) permanent situations and states in the past: Did the ancient Egyptians have more advanced technology than other civilizations?
5) a succession of single past events, facts or states: Frank turned on the TV and sat on the sofa.
Time expressions used with the Past Simple include yesterday, last night / week / month / year / Monday, two days / weeks / months / years ago / how long ago / then / when / in 1992 and etc.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is formed analytically by the auxiliary verb to be in the past indefinite and participle I of the notional verb.
The paradigm of the verb in the past continuous

Main uses
The past continuous is used to denote:
1) actions in progress at a particular moment in the past: Were you chatting online at midnight last night?
2) actions in progress around a particular moment in the past: At the turn of the twenties centuries many scientists were making discoveries in physics and other sciences.
3) temporary situations and serious of actions in the past: At that time, I was working for a large software company.
4) changing and developing situations in the past: I was getting frustrated with my internet provider.
5) annoying or amusing past habits (usually with always): When she was young, Tina was always taking things apart to see how they worked.
6) background information in a story: It was raining outside and people were making their way home.
7) two actions in progress at the same time (simultaneous actions): While I was playing a computer game, my brother was doing his homework.
8) a polite request or suggestion (referring to the present): I was wondering if you’d like to help me.
Ways of talking about the past habits
We use used to + infinitive to refer to past habits and states. In such cases, used to can be replaced by the Past Simple with no difference in meaning: He used to go out when he was younger. = He went out when he was younger.
We use the Past Simple not used to, for actions which happened at a definite time in the past: He visited Paris last month.
Forms: He used to live in Paris. He didn’t use to live in Paris. Did he use to live in Paris?
Be used to / get used to:
Be used to + noun / pronoun / -ing form: to be accustomed to, to be in habit of
Get used to + noun / pronoun / -ing form: become accustomed to
Look at the following examples of how we use be/get used to: She wasn’t used to working at night (She wasn’t accustomed to working at night). Simon had never lived in a tropical country before, but he quickly got used to it (He became accustomed to it).
Used to and Would: Contrast
Would is also used to talk about past habits.
When we use would to talk about a past habit, it is necessary to use a past time reference. Used to can be used with or without a past time reference: I used to go out late. Before I got this job, I used to / would go out a lot.
When we talk about past situations (not actions), we can use used to but we can’t use would: We used to live in a flat in the town centre.
