
- •А.Р. Еферова о.В. Кердяшева Английский язык
- •Предисловие автора
- •Unit 1. Modern shipbuilding
- •I. Master the Active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the text “Marine engineers.”
- •V. Translate the following sentences from English into Russian:
- •VI. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VII. Use the words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VIII. Retell the text “Modern shipbuilding.” unit 2. Ship model basin
- •I. The words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Insert the missing word using the text:
- •V. Ask as many questions as possible to the following questions:
- •VI. Translate the text: “Ship grounding”
- •VII. Retell the text “Ship model basin.” unit 3. Shipyards in russia.
- •I. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Complete the following sentences using the text:
- •VI. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VII. Translate the text: “Pyotr Velikiy”
- •VIII. Retell the text “Admiralty Shipyards.” unit 4. Naval architecture
- •I. The words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Make sentences of your own, using the following words and word combinations:
- •V. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •VI. Complete the following sentences using the text:
- •VII. Translate the text “The Naval Architect.”
- •VIII. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •IX. Retell the text “Naval Architecture.” unit 5. Classification society
- •I. Master the Active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •V. Translate the text “International Maritime Organization.”
- •VI. Make up sentences using following words and word combinations:
- •VII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •Unit 6. Response amplitude operator
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Insert the missing words, using the text:
- •V. Comment on the use of infinitive in the text.
- •VI. Translate the text “Methods for calculating.”
- •VII. Use the following words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VIII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following questions:
- •IX. Retell the text “Response amplitude operator.” unit 7. Ship stability
- •I. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the text: “Stabilizer Fins.”
- •V. Comment on the use of Participle II.
- •VI. These are answers. Ask questions to these sentences.
- •VII. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VIII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following questions:
- •IX. Retell the text: “Ship stability.” unit 8. Shipyard
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Translate the text: “Ship’s cradle.”
- •VI. Insert the missing word using the text:
- •VII. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VIII. Retell the text: “Shipyard” unit 9. Anchor windlass
- •I. Master the active vocabulary
- •II. Read and translate the following text.
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Translate the text “Devil’s claw.”
- •VI. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •Unit 10. Capstan
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the text “Gypsies and Wildcats.”
- •V. Insert the missing words in following sentences:
- •VI. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •VII. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •VIII. Translate the text “a jackline”
- •IX. Retell the text “Capstan” unit 11. Winch
- •I. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the text “a tiller.”
- •V. Complete the following sentences:
- •VI. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •VII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •VIII. Comment on the use of Passive Voice.
- •IX. Retell the text “Winch.” unit 12. A ship
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •V. Translate the text “a ship through Renaissance.”
- •VI. Complete the following sentences:
- •VII. Sailing ships are ships which are propelled solely by means of sails.
- •VIII. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •IX. Retell the text “a ship.” unit 13. Reciprocating diesel engine
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Complete the following sentences, using the text:
- •VI. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •VII. Translate the text “Propulsion systems.”
- •VIII. Retell the text “Reciprocating diesel engines.” unit 14. The keel
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •VII. Speak on types of a keel. Unit 15. Ballast tank
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Read and translate the text “Aka”
- •Unit 16. Captain’s bridge
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the following text: “Balanced rudder.”
- •V. Insert the missing word
- •VI. Ask as many questions as possible
- •Unit 17. Engine room
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask the questions to the following sentences:
- •V. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •VI. Translate the text: “a bilge keel”
- •VII. Translate the following sentences form Russian into English:
- •VIII. Retell the text “Engine room.” unit 18. Cathedrall hull
- •I. Master the active vocabulary:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Read and translate the text: “abs Steels”
- •Unit 19. Bulbous bow
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the following text: “Coaming”
- •V. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VI. Use the following words and word combinations in sentences of your own:
- •VII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •VIII. Insert the missing word, using the text:
- •IX. Retell the text: “Bulbous bow.” unit 20. Deck
- •I. Try to remember the following words and word combinations:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the following text: “Common names for decks.”
- •V. Retell the text “Deck.” unit 21. Construction of decks
- •I. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •Methods in wood
- •Methods in metal
- •Methods in fiberglass
- •VI. Use the following words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VII. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VIII. Ask as many questions as possible to the following questions:
- •IX. Retell the text “Construction of decks.” unit 22. Bow
- •I. Words to be remembered:
- •II. Read and translate the following text:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Translate the text: “Figurehead”
- •V. Use the following words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VI. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •VII. Insert the missing word using the text:
- •VIII. Retell the text “Bow.” unit 23. Anchor
- •I. Read and translate the following text:
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Ask as many questions as possible:
- •IV. Translate the text “Anchoring gear”
- •V. Use the following words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VI. Complete the following sentences using the text:
- •VII. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VIII. Retell the text “Anchor.” unit 24. Chine
- •I. Read and translate the following text:
- •II. Master the Active Vocabulary:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Read and translate the text: “Plank hulls”
- •V. Ask as many questions as possible:
- •VI. Comment on the use of Participle I, II.
- •VII. Read and think about the types of chine hulls. Constructing a chined hull
- •Unit 25. Rudder
- •II. Master the Active Vocabulary:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following questions:
- •V. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VI. Use the following words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VII. Read and translate the text “Chinese rudders.”
- •VII. Retell the text: “Rudder.” unit 26. Stern
- •I. Read and translate the following text:
- •II. Master the Active Vocabulary:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Make up sentences using the following words and word combinations:
- •VI. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VII. Translate the text: “Steering engine.”
- •Unit 27. Ship hull structure elements
- •Material Response
- •II. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. These are answers. Ask questions to these sentences:
- •V. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VI. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English:
- •VII. Make up sentences using the following words and word combinations:
- •VIII. Translate the text: “Tumblehome.”
- •IX. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •X. Retell the text: “Ship hull structure elements.” unit 28. Waterline
- •I. Read and translate the following text:
- •II. Words and word combinations to be remembered:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Ask as many questions as possible to the following sentences:
- •V. Use the words and word combinations in the sentences of your own:
- •VI. Translate the text “The summer load line”
- •VII. Insert the missing words using the text:
- •VIII. Retell the text “Waterline.”
- •Vocabulary
VIII. Retell the text “Reciprocating diesel engines.” unit 14. The keel
I. Master the active vocabulary:
a hydrodynamic element – гидродинамический элемент
a beam – балка, брус
a bow – нос (судна)
spine of the structure – основа конструкции
cradle – кильблок
longitudinal strength – продольная прочность
stability – стабильность, устойчивость
foil – фольга, пленка
to stabilize the boat – стабилизировать лодку
winch – лебедка
bilge keel – скуловый киль
II. Read and translate the following text:
The word "keel" comes from Anglo-Saxon cēol = "ship" or "keel".
In boats and ships, keel can refer to either of two parts: a structural element, or a hydrodynamic element. These parts overlap.
A structural keel is a large beam around which the hull of a ship is built. The keel runs in the middle of the ship, from the bow to the stern, and serves as the foundation or spine of the structure, providing the major source of structural strength of the hull. The keel is generally the first part of a ship's hull to be constructed, and laying the keel, or placing the keel in the cradle in which the ship will be built, is often a momentous event in a ship's construction--so much so that the event is often marked with a ceremony, and the term lay the keel has entered the language as a phrase meaning the beginning of any significant undertaking.
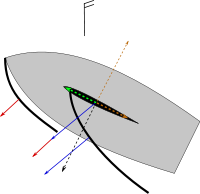
Fig. 14. The keel converts sideways force into a forward force.
The keel contributes substantially to the longitudinal strength and effectively local loading caused when docking the ship. The most common type of keel is the 'flat plate keel', and this is fitted in the majority of ocean-going ship and other vessels. A form of keel found on smaller vessels is the bar keel. The bar keel may be fitted in trawlers, tugs, etc. and this is also found in smaller ferries.
Duct keels are provided in the bottom of some vessels. These run from the forward engine room bulkhead to the collision bulkhead and are utilized to carry the double bottom piping. The piping is then accessible when cargo is loaded.
a) Non-sailing keels
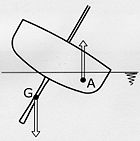
Fig 15. Keels provide extra stability by providing a weight low
enough to significantly lower the centre of gravity.
The keel surface on the bottom of the hull gives the ship greater directional control and stability. In non sailing hulls, the keel helps the hull to move forward, rather than slipping to the side. In traditional boat building, this is provided by the structural keel, which projects from the bottom of the hull along most or all of its length. In modern construction the bar keel or flat-plate keel perform the same function.
b) Sailboat Keels
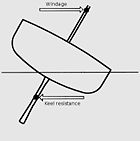
Fig.16 Capsizing effect of a sailing keel
In sailboats, keels use the forward motion of the boat to generate lift to counter the lateral force from the sails. Sailboats have much larger keels than non sailing hulls. Keels are different from centerboards and other types of foils in that keels are made of heavy materials to provide ballast to stabilize the boat. Keels may be fixed, or non-movable or they may retract to allow sailing in shallower waters. Retracting keels may pivot (a swing keel) or slide upwards to retract, and are usually retracted with a winch due to the ballast. Since the keel provides far more stability when lowered than when retracted (due to the greater moment arm involved) the amount of sail carried is generally reduced when sailing with the keel retracted.
There are several types of fixed keels including: full keels, fin keels, winged keels, bulb keels, and twin keels or bilge keels among other designs.
III. Answer the following questions:
What parts does keel consist of?
What is a structural keel?
The keel is generally the first part of a ship’s hull, isn’t it?
What does the term “lay the keel” mean?
Does the keel surface on the bottom of the hull give the ship greater directional control?
What are the keels made of?
What types of fixed keels do you know?
IV. Translate the following sentences from English into Russian:
Canting keels can be found on racing yachts.
Structural keel is suitable with its massive scantling where grounding is possible.
“To lay the keel” means the beginning of any significant undertaking.
Keels may be fixed or non - movable.
Bar keels often being associated with open floors.
V. Comment on the usage of Passive Voice:
The flat plate keel is fitted in the majority of ocean – going ship and other vessels.
Duct keels are provided in the bottom of some vessels.
Keels are made of heavy materials.
The word “keel” is derived from Anglo – Saxon word “cēol.”
VI. Translate the text: “Gunwale”
The gunwale is a nautical term describing the top edge of the side of a boat.
Originally the gunwale was the "Gun ridge" on a sailing warship. This represented the strengthening wale or structural band added to the design of the ship, at and above the level of a gun deck. It was designed to accommodate the stresses imposed by the use of artillery.
In wooden boats, the gunwale remained, mounted inboard of the sheer strake, regardless of the use of gunnery. In modern boats, it is the top edge of the side where there is usually some form of stiffening.
On a canoe, the gunwale is typically the widened edge at the top of the side of the boat, where the edge is reinforced with wood, plastic or aluminum.
