
Бауманн У., Перре М. - Клиническая психология
.pdf(Heckhausen & Kuhl, 1985).
» ,
»: ,
; ,
.
.
,
.
. , ,
, , ,
.
.
,
. ).
, ,
. , ,
( , ).
.
;
. , ,
,
(Pekrun, 1988). ,
( ,
) ( ; . ).
, .
2.1.3. :
, « » (Gollwitzer, 1996): , .
,
( ). « » ,
,
. , ( .
Heckhausen & Kuhl, 1985). ,
« »; Gollwitzer & Malzacher, 1996).
.
. , ,
.
,
(« »). ,
( ).
.
. ,
.
( ).
(Lewin, 1938; Miller, 1959).
, , , ,
( :
).
( , ),
, . .
.
( , ,
)
.
, ,
, . . , (
, ,
). ,
.
,
).
.
,
). ,
, , ,
,
( . . ,
, ). ,
,
.
2.1.4. :
. : )
,
; ) ( ) ,
. , ,
,
(Gollwitzer, 1996).
, ,
.
,
.
».
( , , ).
. ,
, , .
;
.
, .
( , ).
,
. ,
( , )
, ).
, (
).
, .
, , , . . , ,
,
.
,
.
, ,
, , ,
, .
, , ,
, . , , ,
, ,
.
, , , ,
, .
,
,
.
---
, : )
, )
, ( . ., ,
), ) (
/ , ; )
.
.
, ,
, , ( , ).
,
, ( :
).
, ,
.
,
.
, ,
, , ,
. .
,
. , ,
.
, , ,
,
. .
,
( . Abramson, Seligman & Teasdale, 1978; Robins & Block, 1989; Metalsky, Joiner, Hardin & Abramson, 1993) .
2.3. :
(Abramson, Seligman & Teasdale, 1978; . Buchanan & Seligman, 1995)
(Seligman, 1975). ,
(
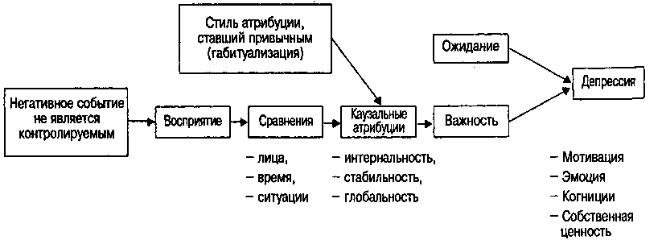
» ).
( ), ,
, ,
( . . 31.2.1).
. 31.2.1.
,
, ,
, , («
») . ,
,
. , ,
, .
, ,
. ,
, , .
, , . .
, .
( . Buchanan & Seligman, 1995; Peterson & Seligman, 1984; Metalsky, Joiner, Hardin & Abramson, 1993; Sweeney, Anderson & Bailey, 1986; Robins, 1988; Robins & Block, 1989). ,
. ,
, .
( , Mikulincer, 1988; Sacks & Bugental, 1987; . . 31.2.2). ,
.
31.2.2. (Sacks & Bugental, 1987)
. ,
— . .
—
.
-. 80 , 40
.
-. 40
( )
. (n = 20) ,
( n = 20) — .
,
, .
- . (Attributional Style Questionnaire, ASQ; Seligman ., 1979),
(Multiple Affect Adjective Check List, MAACL; Zuckerman & Lubin, 1965).
.
, ,
( . .
, ) 20 ,
.
. , .
,
, ,
,
.
, ,
. (
),
( ,
).
.
---
, ,
« »
(Pekrun, 1988; . Buchanan & Seligman, 1995; Metalsky, Joiner, Hardin & Abramson, 1993; Smith, Haynes, Lazarus & Pope, 1993). ,
. ,
(
), ,
( ,
; . Kuhl, 1981; 1983). ,
, : ,
, ,
(Pekrun, 1988; . . 31.2.2).
3.
,
.
. ,
.
,
.
3.1.
, ,
( . 37):
) (
). .
.
) ( , ,
. .), ( ) ,
,
. ,
, , , .
( : )
. ,
( , ;
).
( . Asendorpf, 1989; Mosher & White, 1981).
) . ,
,
, .
, .
.
3.2.
,
( ) ( . 37).
,
. , ,
( , ). ,
, .
, , , ,
. ,
, , -
.
, . .
, ,
.
( , ),
.
. ,
,
, , . ,
( . 31.3).
3.3.
( . 36).
.
) , ,
,
.
(Beck, 1967), ,
(Kuhl, 1981; 1983).
.
) ,
, . .
.
)
, . , ,
,
.
, ,
.
) ,
.
, .
( , .),
« », , ,
( ,
). , ,
( , , . Mintz, 1968).
3.4.
,
( . 35).
( DSM-IV)
. , ,
. , ,
, ( ,
).
, , , . .
.
, ,
. .
.
.
, , ,
, ,
.
3.5. ,
,
,
( . Cox & Klinger, 1988; . 34).
,
. .
) , ,
).
) , .
) ( , ,
, ).
) , )
(
,
).
) ,
,
( . Silbereisen & Reitzle, 1987).
) ).
,
, ,
.
. , , ,
, ). , , ,
,
,
. ,
.
4.
Abramson, L. Y., Seligman, M. E. P. & Teasdale, J. D. (1978). Learned helplessness in humans: Critique and reformulation. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 87, 49-74.
Asendorpf, J. (1989). Soziale Gehemmtheit und ihre Entwicklung. Berlin: Springer. Beck, A. T. (1967). Depression. New York: Harper & Row.
Boller, F. & Grafman, J. (Eds.). (1993). Handbook of neuropsychology. Amsterdam: Elsevier. Brunstein, J. C. & Maier, G. W. (1996). Persönliche Ziele: Ein Überblick zum Stand der Forschung.
Psychologische Rundschau, 47, 146-160.
Buchanan, G. B. & Seligman, M. E. P. (Eds.). (1995). Explanatory style. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Cox, W. M. & Klinger, E. (1988). A motivational model of alcohol use. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 97, 168-180.
Gollwitzer, P. (1996). Das Rubikonmodell der Handlungsphasen. In J. Kuhl & H. Heckhausen (Hrsg.), Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4, S. 531-582). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Gollwitzer, P. M. & Malzacher, J. T. (1996). Absichten und Vorsätze. In J. Kuhl & H. Heckhausen (Hrsg.), Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4, S. 427-468). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Goschke, T. (1996). Wille und Kognition: Zur funktionalen Architektur der intentionalen Handlungssteuerung. In J. Kuhl & H. Heckhausen (Hrsg.), Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4, S. 583-663). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Heckhausen, H. (1989). Motivation und Handeln (2. Aufl.). Berlin: Springer.
Heckhausen, H. & Kuhl, J. (1985). From wishes to actions: The dead ends and short cuts on the long way to action. In M. Frese & J. Sabini (Eds.), Goal-directed behavior: The concept of action in psychology (pp. 134-159). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kuhl, J. (1981). Motivational and functional helplessness. The moderating effect of state versus action orientation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 40, 155-170.
Kuhl, J. (1983). Motivation, Konflikt und Handlungskontrolle. Berlin: Springer.
Kuhl, J. (1996). Wille und Freiheitserleben: Formen der Selbststeuerung. In J. Kuhl & H. Heckhausen (Hrsg.), Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4, S. 665-765). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Kuhl, J. & Beckmann, J. (Eds.). (1994). Volition and personality. Action versus state orientation.
Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Kuhl, J. & Heckhausen, H. (Hrsg.). (1996). Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Lewin, K. (1938). The conceptual representation and the measurement of psychological forces.
Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Libet, B. (1985). Unconscious cerebral initiative and the role of conscious will in voluntary action. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 8, 529-566.
Metalsky, G. I., Joiner, T. E., Hardin, T. S. & Abramson, L. Y. (1993). Depressive reactions to failure in a naturalistic setting: A test of the hopelessness and self-esteem theories of depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 102, 101-109.
Mikulincer, M. (1988). A case study of three theories of learned helplessness: The role of test importance. Motivation and Emotion, 12, 371-383.
Miller, N. E. (1959). Liberalization of basic S-R-concepts: Extensions to conflict behavior, motivation, and social learning. In S. Koch (Ed.), Psychology: A study of a science (Vol. 2). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mintz, R. S. (1968). Psychotherapy of the suicidal patient. In H. L. P. Resnick (Ed.), Suicidal behaviors
(pp. 271-296). Boston: Little & Brown.
Mosher, D. L. & White, B. B. (1981). On differentiating shame and shyness. Motivation and Emotion, 5, 61-74.
Norman, D. A. & Shallice, T. (1986). Attention to action. Willed and automatic control of behavior. In R. J. Davidson, G. E. Schwarz & D. Shapiro (Eds.), Consciousness and self-regulation. Advances in research and theory (Vol. 4, pp. 1-18). New York: Plenum Press.
Pekrun, R. (1988). Emotion, Motivation und Persönlichkeit. München: Psychologie Verlags Union. Peterson, C. & Seligman, M. E. P. (1984). Causal explanations as a risk factor for depression: Theory
and evidence. Psychological Review, 91, 347-374.
Robins, C. J. (1988). Attributions and depression: Why is the literature so inconsistent? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 880-889.
Robins, C. J. & Block, P. (1989). Cognitive theories of depression viewed from a diathesis-stress perspective: Evaluations of the modeis of Beck and of Abramson, Seligman and Teasdale. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 13, 297-313.
Sacks, C. H. & Bugental, D. B. (1987). Attributions as moderators of affective and behavioral response to failure. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 53, 939-947.
Seligman, M. E. P. (1975). On depression, development and death. San Francisco: Freeman.
Seligman, M. E. P., Abramson, L Y., Semmel, A. & von Baeyer, C. (1979). Depressive attributional style Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 88, 242-247.
Silbereisen, R. K. & Reitzle, M. (1978). Selbstwertgefühl, Freizeitpräferenzen und Drogenmißbrauch im Jugendalter. In H. P. Frey & K. Hauer (Hrsg.), Identität (S. 125-138). Stuttgart: Enke.
Smith, C. A., Haynes, K. N., Lazarus, R. S. & Pope, L. K. (1993). In search of «hot» cognitions: Attributions, appraisals, and their relation to emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65, 916929.
Sokolowski, K. (1996). Wille und Bewußtheit. In J. Kuhl & H. Heckhausen (Hrsg.), Motivation, Volition und Handlung (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Motivation und Emotion, Bd. 4, S. 485-530). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Sweeny, P. D., Anderson, K. & Bailey, S. (1986). Attributional style in depression: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50, 947-991.
Tucker, D. M. & Williamson, P. A. (1984). Asymmetric neural control Systems in human selfregulation. Psychological Review, 91, 185-215.
Zuckerman, M. & Lubin, B. (1965). Manual for the Multiple Affect Adjective Check List. San Diego, CA: Educational Testing Service.
31.3. :
1.
« » ( . 31.2)
:
;
2);
;
4)(
) .
,
.
( , )
. , , , , —
. , :
, , ,
