
- •Calcium-binding by proteins
- •Calmodulin and troponin C
- •Kinases regulated by calmodulin
- •Calcium-dependent enzymes that are not regulated by calmodulin
- •Paradigms of calcium signalling
- •Triggering neurotransmitter secretion
- •Initiation of contraction in skeletal muscle
- •Smooth muscle contraction
- •References

Calcium effectors
An important downstream consequence of NOS activation is the effect of NO on cellular Ca2 homeostasis.29 Many of the effects of NO are mediated by cGMP and the consequent activation of G kinase. This can phosphorylate and inactivate PLC and IP3 receptors,30 and modulate SOCe.31 It also inhibits Ca2 release from intracellular stores in a variety of cells,32 (but not endothelial cells or liver). Finally, in sea urchin eggs, the generation of cyclic ADP-ribose (see page 204), an activator of ryanodine receptors in these cells, is cGMP-dependent.33 How these actions are coordinated in the control of Ca2 concentration is not yet clear.
Calcium-dependent enzymes that are not regulated by calmodulin
While calmodulin is a widely distributed mediator of enzymes that are not in themselves Ca2 -binding proteins, it is not the only Ca2 -sensing intermediate. Furthermore, there are many enzymes that respond to Ca2
changes directly. Such Ca2 -sensitive proteins usually have one or more high affinity binding sites and these may be in the form of EF-hand motifs, C2 domains, or other structures. We now consider some specific examples.
Neuronal calcium sensors
The complex morphology of nerve cells and the confinement to microdomains of preand postsynaptic Ca2 signals requires localized Ca2 sensors and effectors. While calmodulin is a multipurpose sensor, a set of more specific Ca2 sensor proteins exists. These are the neuronal Ca2 sensors or NCS proteins, and although not restricted to neurons, they are most diverse in mammalian neuronal tissue (14 genes). They fulfil a wide range of functions, some of which are quite specific. They all possess four EF-hand motifs, but their sequence similarity with calmodulin is very limited ( 20% identity) and unlike calmodulin, they remain compact structures when they have bound Ca2 .34
The majority of mammalian NCS proteins bear an N-terminal myristoyl group (others are palmitoylated) and some of them, most notably the retinal protein recoverin, conceal this group when Ca2 is not bound. Such proteins are cytosolic at resting Ca2 levels, but adhere to membranes when Ca2 is elevated. This effect is reversible and the conformational change is termed a Ca2 /myristoyl switch. Those that do not conceal the acyl group are
permanently associated with the membrane. When the Ca2 /myristoyl switch is operated by Ca2 in retinal rod cells, recoverin is recruited to the plasma membrane exposing a binding site for rhodopsin kinase on its surface. This prevents the kinase from phosphorylating rhodopsin and so extends the lifetime the photoexcited state. Under bright illumination, at low Ca2 levels, the excited rhodopsin is rapidly deactivated, allowing adaptation (see Figure 6.11, page 173). Also among the human NCS proteins are three guanylyl
233

Signal Transduction
Exocytosis is the fusion of the membrane of a secretory vesicle with the plasma membrane, allowing the vesicle contents to be released to the exterior without affecting the integrity of the cell.
cyclase-activating proteins (GCAP1–3) that are also expressed only in retina. These are permanently associated with their guanylyl cyclase effectors and in the light at low Ca2 levels, they stimulate cGMP formation. In the dark, at high Ca2 levels, they have the opposite effect and inhibit cGMP formation (Figure 6.7, page 169).
Calpain
Calpain is a member of a widely distributed family of cytosolic, Ca2 -activated cysteine proteases, possessing EF-hand sites.35 It cleaves a wide range
of intracellular proteins, modifying their functions, often destructively. It operates in cell death pathways and is involved in neurodegeneration and apoptosis. It also degrades cytoskeletal and other proteins in the vicinity of the plasma membrane and is thought to be involved in processes where remodelling of the cytoskeleton takes place.
Although selective, the effects of this neutral protease are mostly irreversible, which is perhaps one reason why cells do not permit Ca2 levels to remain high for a prolonged period. To make additionally sure, calpain is also held in check by calpastatin.35 This not only inhibits its activity, but also prevents it from binding to membranes.
Synaptotagmin
In neurons and in many types of endocrine cell, the release of a neurotransmitter or hormone by exocytosis is activated by an increase in intracellular Ca2 . This event is mediated by a Ca2 -sensitive protein (or proteins). Among the numerous proteins that are present on the surface of secretory vesicles or secretory granules is synaptotagmin.36,37 This is a highly conserved transmembrane protein having two C2 domains in its cytosolic chain, and it is thought to be the Ca2 sensor for exocytosis. Indeed, it
has been shown to bind Ca2 ions at physiological concentrations. This is discussed below (page 236).
DAG kinase
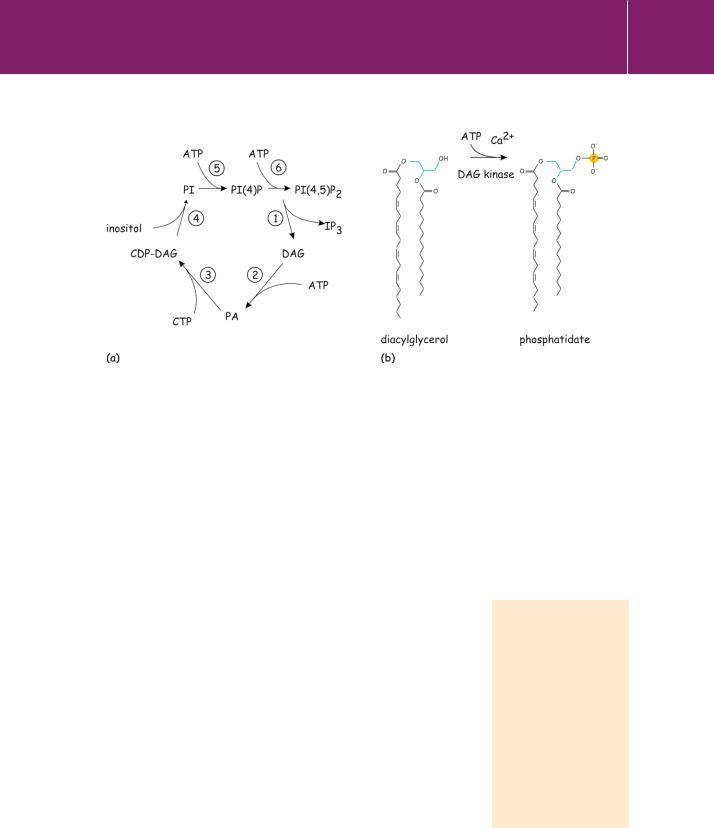
The hydrophobic second messenger diacylglycerol (DAG) formed by the phospholipases PLC and (indirectly) by PLD (see Chapter 5) is the activator of protein kinase C (PKC, see Chapter 9). It is short-lived because it is rapidly phosphorylated to form phosphatidate by diacylglycerol kinase. This reaction is part of the cycle that regenerates phosphatidylinositol (Figure 8.5) and since it removes DAG, it acts to terminate the activation of PKC. Of the eight known isoforms of DAG kinase, , , and possess EF-hand motifs and are Ca2 -dependent.38
Ras GEFs and GAPs
Regulation of the GTPase Ras involves effectors that sense Ca2 directly and those that are activated by Ca2 -calmodulin. The calmodulin-dependent
234
Calcium effectors
Fig 8.5 Phosphoinositide formation and metabolism.
(a) The inositol lipid cycle. Numbers indicate enzymes as follows: (1) phospholipase C, (2) diacylglycerol kinase, (3) CDP-diacylglycerol synthase,
(4) phosphatidylinositol synthase, (5) phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase, (6) phosphatidylinositol-4 phosphate 5-kinase. (b) The formation of phosphatidate from DAG.
RasGRF proteins that are guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are mentioned above. In addition to these, there is a family of five calmodulinindependent GEFs that act on both the Ras and Rap GTPases. These possess EF-hands, but although they show Ca2 sensitivity their main stimulus appears to be diacylglycerol. For this reason they are called calcium and DAG-regulated GEFs or CalDAG-GEFs.13 In order for an exchange factor
to engage Ras, it must locate to the plasma membrane and the cytosolic CalDAG-GEFs have DAG-binding C1 domains that enable them to do this. (RasGRP2, a member of this family, is an exception, and uses myristoylation and palmitoylation to locate at the membrane surface).
While GTPase signalling is initiated by GEFs, it is turned off by the GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) that activate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. The most prominent Ca2 -sensitive GAP for Ras is p120RasGAP (see page 108). This has a C2 domain which could enable the protein to bind to the plasma membrane in a Ca2 -dependent way. However, it has recently been shown that the enzyme attaches to the membrane by associating with the Ca2 -sensing protein annexin VI.39
Two members of the GAP1 family are Ca2 -dependent. These are CAPRI (Ca2 -promoted Ras inactivator) and RASAL (Ras GTPase-activating-like), both of which have tandem C2 domains at the N-terminus, followed by a RasGAP domain, a PH domain, and a Btk domain. The C2 domains enable the GAPs to translocate from the cytosol to the membrane when Ca2 is elevated. Binding at the membrane switches on the GAP activity, so terminating Ras activation
The annexins are a family of soluble intracellular proteins that bind to phospholipids in a Ca2 -dependent fashion. They interact with intracellular membranes and some associate with the cytoskeleton.40 They have mostly -helical structures and bind Ca2 at loops on one surface. This enables them to bind to negatively charged membrane surfaces.
235
