
Construction Economics and Management
.pdfПЕТЕРБУРГСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ ПУТЕЙ СООБЩЕНИЯ
Кафедра «Иностранные языки»
Р. И. ВОРОНЦОВ
CONSTRUCTION ECONOMICS
AND MANAGEMENT
Учебное пособие по английскому языку для студентов 4 курса
Санкт-Петербург
2014
|
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
Unit 1. General Provisions ........................................................................................ |
3 |
|
1.1 |
What is Construction Economics? .............................................................. |
3 |
1.2 |
A Construction Company............................................................................ |
6 |
1.3 |
The Project Life Cycle ................................................................................ |
9 |
Unit 2. Estimations and Design............................................................................... |
13 |
|
2.1 |
Cost Estimates ........................................................................................... |
13 |
2.2 |
Stages of Design........................................................................................ |
16 |
2.3 |
Feasibility Study........................................................................................ |
19 |
Unit 3. On a Construction Site ................................................................................ |
22 |
|
3.1 |
Construction Resources............................................................................. |
22 |
3.2 |
Materials Management.............................................................................. |
25 |
3.3 |
Construction Planning............................................................................... |
28 |
Unit 4. Contracting .................................................................................................. |
31 |
|
4.1 |
Awarding Contracts .................................................................................. |
31 |
4.2 |
Types of Contracts in Construction .......................................................... |
34 |
Unit 5. Presentations ............................................................................................... |
37 |
|
5.1 |
Presenting a Company .............................................................................. |
37 |
5.2 |
Presenting a Project................................................................................... |
41 |
Glossary................................................................................................................... |
44 |
|
References ............................................................................................................... |
48 |
|
2
UNIT 1
GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1What is Construction Economics?
1.What is economics? What do economists study? Make sure you know some of the basic terms:
goods and services |
market |
demand and supply |
cost |
production |
competition |
price |
scarcity |
2. Use suffixes –(t)ion and –ment to form nouns.
|
VERB |
|
|
NOUN |
|
|
VERB |
|
|
NOUN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
apply |
____________ |
develop |
____________ |
|||||||
construct |
____________ |
|
justify |
____________ |
|||||||
|
agree |
____________ |
|
solve |
____________ |
||||||
|
invest |
____________ |
identify |
____________ |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Match the words on the left with their Russian equivalents on the right.
1) inception |
a) управление |
2) allocation |
b) проектирование |
3) budgeting |
c) завершение |
4) procurement |
d) распределение |
5) managing |
e) осуществимость |
6) feasibility |
f) закупки, снабжение |
7) completion |
g) начало |
8) design |
h) составление сметы |
4. Read and translate these word collocations.
Construction economics; construction industry; construction project; construction budget; resource allocation; cost planning; investment justification; cost control; project development; value for money.
3
5. Study the definitions of Construction Economics and answer the questions.
There is lack of agreement on a definition for Construction Economics (CE). Broadly, there are three views of CE. The first follows P. Hillebrandt and her definition of CE as the application of ‘economics to the study of the construction firm, the construction process and the construction industry’. A second view is based on the classic definition of economics as ‘the study of the allocation of scarce resources’ by L. Robbins. The third approach is somewhat more eclectic, but could be described as economics with a focus on construction.
(G. de Valence. Theory and Construction Economics. Modern Construction Economics. London; N.Y.: Spon Press, 2011)
Construction Economics is all about managing the finances, budgeting and other processes for construction projects.
(http://www.mmp.ie/what-is-construction-economics-and-why-is-it-needed-in-ireland/)
Construction Economics is the total process of economizing construction project from inception to completion. It refers to practicing economical solutions while not sacrificing the benefits or comfort one can obtain from that particular project. In other words it is the process of achieving best of quality in least possible time with best possible lowest cost.
(http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_construction_economics?)
1)What are the three general views of CE?
2)In what way is CE related to general economics?
3)What does CE manage in construction projects?
4)What does CE help to achieve?
6.You are a construction economist. What tasks do you have to perform? Read the following text for reference.
The construction economist has a range of roles and responsibilities all of which involve keeping projects running within budget and without too many financial headaches. He has to ensure that construction projects are developed efficiently and economically sensibly.
Typical tasks include:
Preparing a construction budget
Cost planning to ensure good value for money design and engineering
Justifying investments
Identifying feasibility of a project
Advising procurement routes, logistics and choice of contracts
Administering cost control during the course of construction projects
(Adapted from: http://www.mmp.ie/what-is-construction-economics-and-why-is-it-needed-in-ireland/)
4
7. Match the words on the left with the words on the right to make collocations from the texts in exercises 5&6.
1) scarce |
a) control |
2) cost |
b) a project |
3) project |
c) investments |
4) plan |
d) resources |
5) develop |
e) feasibility |
6) justify |
f) routes |
7) procurement |
g) costs |
8.Use the word collocations from exercise 7 to complete the sentences. Put the verbs in the correct form if necessary.
1)To ensure value for money design and engineering we need to ___________
very carefully.
2)A construction economist has to identify ____________ and ____________.
3)L. Robbins considers that the main task of an economist is to allocate
________________.
4)Our construction firm _____________ of a railway bridge last year.
5)My job is to prepare construction budgets and to administer ____________.
9.Match the adjectives and their definitions. Which of them are close synonyms?
1)Efficient
2)Sensible
3)Feasible
4)Economical
5)Cost-effective
a)providing good service in relation to the amount of time or money spent
b)doing something well with no waste of time and money
c)that is possible and likely to be achieved
d)giving the best possible benefits in comparison with the money that is spent
e)reasonable; practical
10. Translate into English. |
|
разработка проекта строительства |
строительная смета |
планирование затрат |
распределение ресурсов |
обоснование инвестиций |
контроль затрат |
11.Use the word collocations from exercise 10 to translate the sentences.
1)Задачами экономиста в области строительства является обоснование инвестиций и планирование затрат.
2)Необходимо осуществлять эффективный контроль затрат в течение всего проекта.
3)Распределение ресурсов – важный элемент разработки проекта.
5
4)Строительные сметы составляются, чтобы обеспечить хорошее соотношение цены и качества при проектировании и строительстве.
12.Describe the job of a construction economist.
1.2A Construction Company
1.Do you know any successful construction companies? What kind of work do they do? In what way are they organized? Would you like to be part of some construction company in future?
2.Match the verbs and their definitions.
1) to report |
a) |
to find new people to join a company |
2) to recruit |
b) |
to deal with an area of work |
3) to handle |
c) |
to organize something in a particular order |
4) to supply |
d) |
to be under one’s supervision |
5) to purchase |
e) |
to provide something necessary |
6) to estimate |
f) |
to calculate the cost approximately |
7) to arrange |
g) |
to buy something |
3. Match the synonyms. |
|
|
1) organizational |
|
a) staff |
2) costs |
|
b) role |
3) function |
|
c) expenses |
4) wages |
|
d) profit |
5) human resources |
|
e) corporate |
6) income |
|
f) salary |
4. Read the abstract and answer the questions.
A construction company’s organizational structure refers to both the arrangement of job roles and the reporting and operational relationships between and within these roles. A variety of roles and responsibilities – including marketing, purchasing, human resources, finance, pre-construction tasks and construction operations – most often make such a corporate structure organized according to departments, functions or areas of responsibilities most appropriate to organizational design.
(http://smallbusiness.chron.com/organizational-structure-construction-company-77196.html)
1)What is the principle the company’s organizational structure is based on?
2)What are the units of a corporate structure?
3)What are the roles and responsibilities involved into construction business?
6
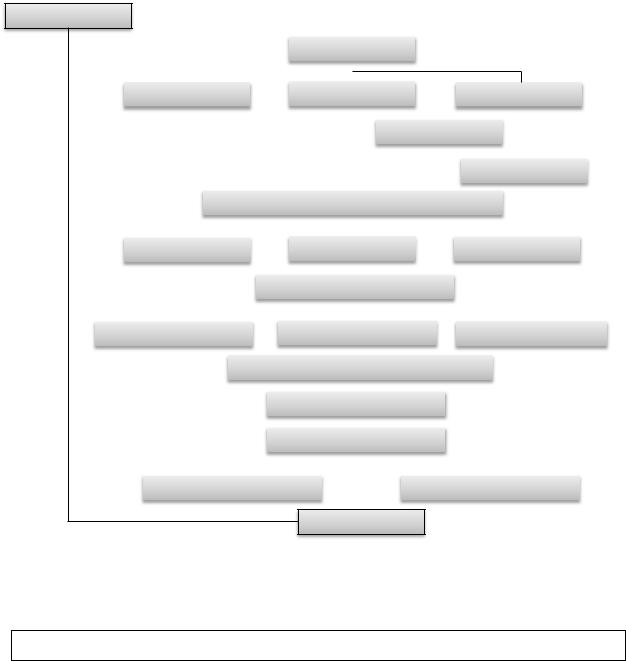
5. Study the organization chart of a construction company (Figure 1).
OWNER
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Health and Safety |
|
|
|
|
Project Managers |
|
|
|
|
Consultants |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Site Managers |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Labourers |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Design |
|
|
|
|
|
Estimating |
|
|
|
|
Marketing |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENGINEERING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Structural Engineering |
|
|
|
|
Mechanical Engineering |
|
|
|
Electrical Engineering |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACCOUNTING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADMINISTRATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Human Resources (HR) |
|
|
|
|
|
Wages and salaries |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEGAL
Fig. 1 The Construction Company Organization Chart
(E. Frendo. English for Construction. Course Book 2. Pearson Education Limited, 2012)
6. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
departments divided external has look part report section top
1)Our company has a simple structure. At the __________ is the owner.
2)There are seven __________. The department heads report to the owner.
3)Operations department consists of a Health and Safety _________ and all the project managers.
4)The site managers and supervisors __________ directly to a project manager.
5)Business Development department is __________ into three sections: Design, Estimating and Marketing.
6)Engineering department also __________ three sections: Structural, Mechanical and Electrical.
7)There are different departments which __________ after materials and equipment, accounting, administration and legal issues.
7
8)Sometimes we have ___________ consultants to help with special jobs. They are not ___________ of the company.
7.Match the descriptions with the departments of a construction company.
1)Our role is to make sure that all the project managers _________________
have the support they need for materials and equipment.
2)There are only five people in our department, two _________________
lawyers and three assistants. We handle all the contracts and claims.
3)The project managers work in our department, but the _________________
people in the project teams come from the other ones. These teams change as the project goes through different phases.
4)Our main role is to work with the clients and the _________________
management to plan the projects and estimate costs. We also help to look for new clients.
5)Our main task is to look after all the income and _________________
outgoings in the company. So we send out the bills to
our clients and pay the suppliers.
6) We are the technical department. We do the calculations _________________
and make sure that things work the way they should. We work a lot with Operations and also Business Development departments.
7)We help to recruit new staff and deal with training and _________________
development. We are also responsible for paying expenses and paying wages and salaries.
8. Match the following collocations. |
|
1) make |
a) of |
2) look |
b) sure |
3) consist |
c) to |
4) report |
d) after |
5) deal |
e) into |
6) be responsible |
f) with |
7) divide |
g) for |
9. Complete the sentences using the word collocations from exercise 9. Consult the organization chart on page 7.
1)The Administration department consists ____________________.
2)The head of the Accounting department reports ____________________.
3)The Engineering department is divided ____________________.
4)The project managers deal ______________________.
5)The Business Development department is responsible _________________.
8
6)The site managers make _____________________.
7)There are three sections in ______________ and ______________.
10.Imagine you are the owner of a construction company. Draw its organization chart. Speak on the company’s departments and their functions.
1.3The Project Life Cycle
1.What is your idea of the life cycle of a construction project? Put these three stages in the logical order:
construction |
design |
operation |
2. Read and translate these words. What parts of speech do they represent?
Construct – construction; maintain – maintenance; select – selection; deliver – delivery; propose – proposal; implement – implementation; fulfill – fulfillment; dispose – disposal; assess – assessment; erect – erection; accept – acceptance.
3. Build up the word collocations and learn their meanings. a) Match the words to make collocations.
1) life |
a) demands |
2) construction |
b) flow |
3) market |
c) site |
4) cash |
d) cycle |
b)What do you call:
1)an area of land where something is being built?
2)the period of time during which something (for example a project) is developed?
3)the movement of money into and out of business?
4)the desire or need of customers for goods and services?
4.Match the words on the left with their Russian equivalents on the right.
1) construction facility |
a) запуск |
2) feasibility study |
b) разработка проектной документации |
3) preliminary design |
с) технико-экономическое обоснование |
4) detailed design |
d) срок службы (эксплуатации) |
5) start-up |
e) эксплуатация и техобслуживание |
6) operation and maintenance |
f) разработка рабочей документации |
7) useful life |
g) объект строительства |
9
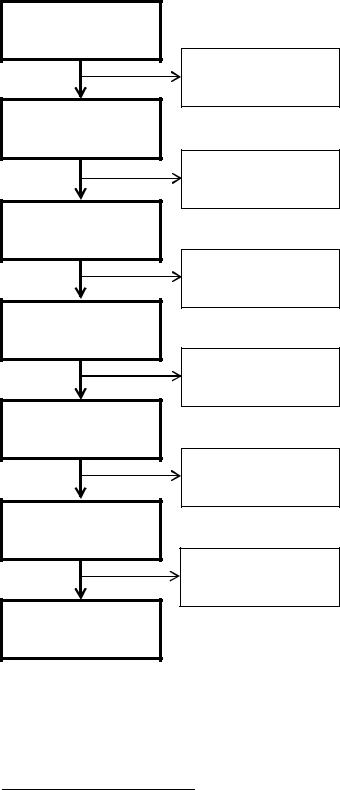
5. Read the text and study the diagram of the project life cycle.
The project life cycle is a process through which a project is implemented from cradle to grave. This process is often very complex; however, it can be decomposed into several stages as indicated in Figure 2. The solutions at various stages are then integrated to obtain the final outcome.
Studying Market Demands or Needs
Conceptual Planning
and Feasibility Study
Design and
Engineering
Procurement and
Construction
Start-up
Operation and
Maintenance
Disposal of Facility
Definition of Project
Objectives and Scope
Conceptual Plan or Preliminary Design
Detailed Construction
Plan (Design)
Completion of
Construction
Acceptance of Facility
Fulfillment of Useful
Life
Fig. 2 The Project Life Cycle
Essentially, a project is conceived to meet market demands or needs in a timely fashion1. Various possibilities may be considered in the conceptual planning stage, and the technological and economic feasibility of each alternative will be assessed and compared in order to select the best possible project. The financing schemes for the proposed alternatives must also be examined, and the project will be programmed with respect to the timing2 for its completion and for available cash flows. After the scope of the project is clearly defined, detailed engineering design will provide the blueprint for construction, and the final budget will serve as the baseline for cost control. In the procurement and construction stage, the delivery of materials and the erection of the facility on site must be carefully planned and controlled. After the construction is completed, there is usually a brief period of start-up of the constructed facility when it is first put into operation. Finally, the management of the facility is turned over to the owner for full operation until the facility lives out its useful life and is designated for demolition or conversion.
(Adapted from: Ch. Hendrickson. Project Management for Construction. 2nd ed. Carnegie Mellon University, 2000. http://pmbook.ce.cmu.edu/)
1in a timely fashion – своевременно; в срок.
2timing – определение срока, временных рамок.
10
