
1 курс стомат
.pdf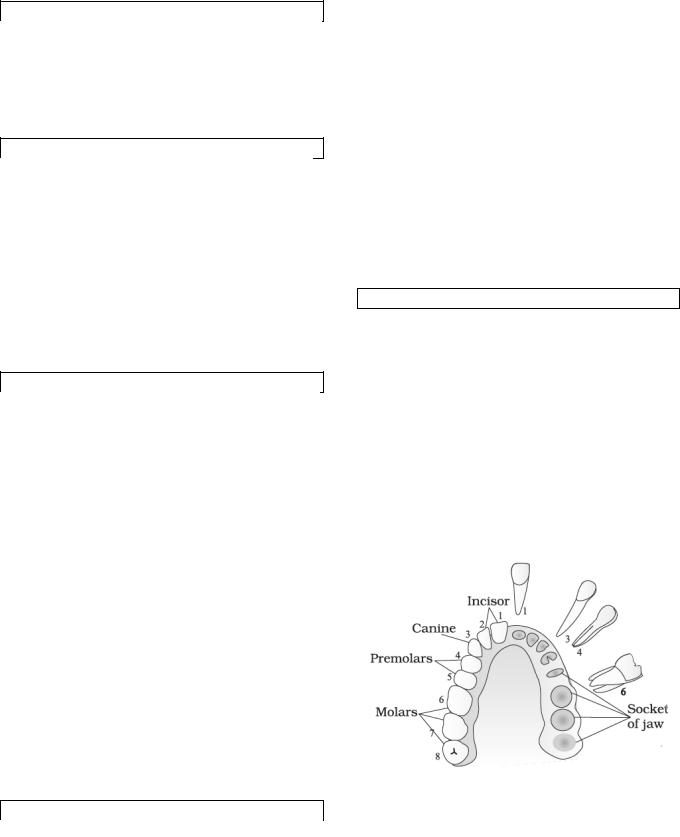
Reading
The Teeth
1.
The teeth are a group of hard organs found in the oral cavity. We use teeth to masticate food into tiny pieces. They also provide shape to the mouth and face and are important components in producing speech.
2.
A tooth can be divided into three main parts: the crown, the neck and the root. Found above the gum line, the crown is the enlarged region of the tooth involved in chewing. Like an actual crown, the crown of a tooth has many ridges on its top surface to help in the chewing of food.
The tooth narrows into a neck at the gum line. Below the gum line is the part of the tooth called the root, which anchors the tooth into a bony socket known as an alveolus.
3.
Each tooth consists of four layers. An outer layer of enamel, white, nonporous, wholly inorganic and extremely hard, covers the crown of the tooth. The middle layer of the tooth is composed of dentine, which is less hard than enamel and similar in composition to bone. The dentine forms the main bulk of each tooth and is covered by enamel on the crown portion and by cementum on the roots. Dentine is nourished by the pulp, which is the innermost portion of the tooth. The pulp consists of cells, tiny blood vessels, and a nerve and occupies a cavity located in the center of the tooth. The pulp canal is long and narrow with an enlargement, called the pulp chamber, in the coronal end. It communicates with the body’s general nutritional and nervous systems through the apical foramina at the end of the roots. The exterior surface of the root is covered in a bonelike mixture of calcium and collagen fibers known as cementum.
4.
Humans have two successive sets of teeth during their life: primary or deciduous teeth and permanent ones.
The primary dentition consists of 20 teeth - four incisors, two canines, and four molars in each jaw. Primary teeth are smaller than the permanent ones, whiter and more prone to wear. The primary teeth begin to appear about six months after birth, and the primary dentition is completed by age 2 and a half. Shedding begins about age 5 or 6 and is finished by age 13. The primary teeth fall out when their roots are resorbed as the permanent teeth push toward the mouth cavity in the course of their growth. The permanent dentition consists of 32 teeth, including four incisors, two canines, four premolars, and six molars in each jaw.
5.
The four front teeth in each arch are called incisors, and their function is to cut food with their sharp thin edges. On each side of the incisors, at the corners of the mouth, are the canines. These teeth have one cusp and are used for holding or grasping food, and are very strong, stable teeth. Behind the canines are the premolars, which are designed for holding food like the canines because they have cusps, but they also function to crush food. The teeth farthest back in the mouth are the molars. These teeth have broad chewing surfaces with four or five cusps, and are designed for grinding food.
The incisors and canines are called anterior teeth, because they are located in the front of the mouth, while the premolars and molars are called posterior teeth because they are located in the back of the mouth.
31

Vocabulary Practice
1.Look at the words in bold type in the above text and explain them.
2.Match the words and word combinations with their definitions and translate them:
1. apical foramen |
a) not as hard as enamel, |
|
|
forms the bulk of the |
|
|
tooth and can be |
|
|
sensitive if the protection |
|
|
of the enamel is lost |
|
|
|
|
2. neck |
b) these fibers anchor the |
|
|
tooth to the jaw bone and |
|
|
act as shock absorbers |
|
|
for the tooth which is |
|
|
subjected to heavy forces |
|
|
during chewing |
|
|
|
|
3. cementum |
c) it consists mainly of |
|
|
calcium phosphate and |
|
|
calcium carbonate and |
|
|
protects the rest of the |
|
|
tooth from chemical |
|
|
attack by acids |
|
|
|
|
4. pulp |
d) the tissue is called the |
|
|
nerve |
|
|
|
|
5. periodontal |
e) narrowing part of a |
|
ligament |
tooth between the tooth |
|
|
crown and the tooth root |
|
|
|
|
6. dentine |
f) the opening at the root |
|
|
of a tooth, through which |
|
|
nerves, lymphatic and |
|
|
blood vessels enter the |
|
|
pulp cavity of the tooth |
|
|
|
|
7. enamel |
g) calcium-rich layer that |
|
|
covers the root of a tooth |
|
|
|
|
3. Match the synonyms and translate them: |
||
|
|
|
1. alveolus |
|
a) deciduous |
|
|
|
2. gum |
|
b) cervix |
|
|
|
3. premolar |
|
c) opening |
|
|
|
4. foramen |
|
d) chew |
|
|
|
5. front |
|
e) tony socket |
|
|
|
6. neck |
|
f) pointed |
|
|
|
7. appear |
|
g) finished |
|
|
|
8. completed |
|
h) anterior |
|
|
|
9. tapered |
|
i) bicuspid |
|
|
|
10. masticate |
|
j) gingiva |
|
|
|
11. primary |
|
k) erupt |
32
4. Fill in the table with the missing words and translate them:
Verb |
Noun |
Adjective |
|
|
|
|
|
found |
|
|
|
|
growth |
|
|
|
|
|
|
different |
|
|
|
|
|
successive |
|
|
|
erupt |
|
|
|
|
|
communicate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
covering |
|
|
|
|
|
enlargement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
nourished |
|
|
|
|
|
preferred |
|
|
|
|
composition |
|
|
|
|
occupy |
|
|
|
|
|
extend |
|
|
|
|
|
5. Complete the sentences with the missing words:
following, surrounding, erupting, covering, resembling
1. Roots are tapered structures
the roots of plants, and each tooth may have between one to three roots.
2. Cementum provides grip for the periodontal ligaments that anchor the root to the
alveolus.
3. The first permanent teeth
are the permanent first molars, right behind the last 'milk' molars of the primary dentition.
4. The primary teeth typically erupt in the
order: central incisors, lateral incisors,
first molars, canines, and second molars. |
|
|
5. Gum is the soft tissue |
|
the |
necks of the teeth. |
|
|
5. Form present and past participles of the following verbs and translate them:
to provide
to mix
to compose
to occupy
to erupt
to design
to narrow
to hold
to grind
to complete

Language Development
1. Look through the text about the muscular system and answer the following questions.
1.What are teeth?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.What functions do the teeth perform?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.List the main parts of the tooth. Describe each of these.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.What are the main layers of a tooth?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.What are the major functions of the enamel? the pulp?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.How many dentitions do humans normally have? What teeth does each dentition consist of?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
7.What are the anterior teeth? What are they used for?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.Name the posterior teeth. What is their function?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2. Read the text. Check the meaning of the words in bold with a dictionary:
Wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth are the third and final set of molars that most people get in their late teens or early twenties. Sometimes these teeth can be a valuable asset to the mouth when healthy and properly aligned, but more often, they are misaligned and require removal.
When wisdom teeth are misaligned, they may position themselves horizontally, be angled toward or away from the second molars, or be angled inward or outward. Poor alignment of wisdom teeth can crowd or damage adjacent teeth, the jawbone, or nerves.
Wisdom teeth also can be impacted -- they are enclosed within the soft tissue and/or the jawbone or only partially break through or erupt through the gum.
Partial eruption of the wisdom teeth allows an opening for bacteria to enter around the tooth and cause an infection, which results in pain, swelling, jaw stiffness, and general illness. Partially erupted teeth are also more prone to tooth decay and gum disease because their hard-to- reach location and awkward positioning makes brushing and flossing difficult.
3. Study the diagram of impacted wisdom teeth. Guess which pathology is shown in each picture and which problems it may cause.
33
4.Say whether the following sentences are true (T) or false (F). Correct the false ones:
1.Everyone develops four wisdom teeth, typically in their early 20s. ______
2.Third molars received their name, “wisdom teeth,” because a moderate amount of wisdom is supposedly achieved in life about the time they appear. _______
3.If wisdom teeth are not removed, they will become impacted or cause crowding. This is why so many people require orthodontic treatment (braces). _____
4.The primary symptom for indicating you have an impacted wisdom tooth is pain. ______
5.It is difficult to brush and floss wisdom teeth because they are much bigger than other teeth of the dentition. ______
5. Label each tooth. Match the teeth with their shape and functions:
|
1. Shape – single rooted, |
|
crowns are arched and |
|
angled toward one sharp |
|
incisal edge. |
|
Function – to cut or incise |
|
food with their thin edges. |
A. ________ |
|
|
|
|
2. Shape – anchored with the |
|
longest root, one pointed |
|
cusp. |
|
Function – used for holding, |
|
grasping, and tearing food. |
|
Referred to as the |
B. ________ |
cornerstone of the mouth. |
|
|
|
|
|
3. Shape – maxillary first |
|
premolars have a bifurcated |
|
root, all others have one root, |
|
one prominent cusp with one |
|
or two lesser lingual cusps. |
|
Function – holding food, like |
C. ________ |
canines because they have |
|
cusps; also to crush food. |
|
|
|
4. Shape – bifurcated or |
|
trifurcated roots, broad |
|
chewing surfaces with four to |
|
five cusps. |
|
Function – grinding food. |
D. ________ |
|
|
|
34
Grammar in Use
Относительные придаточные предложения
Относительные придаточные предложения
вводятся такими относительными местоимениями: who, whom, which, that и whose и могут:
1.Относиться к подлежащему, когда относительное придаточное предложение является подлежащим в предложении (то есть за словами who, that, etc. сразу следует сказуемое).
a) Мы используем who или that, когда говорим о людях.
e.g. Robert Hook was the scientist who/that introduced the term “cell”.
b) Мы используем which или that, когда говорим о неодушевленных предметах.
e.g. Dentine is nourished by the pulp, which/that is the innermost portion of the tooth. c) мы используем whose, когда говорим о предметах, принадлежащих людям.
e.g. Dr Gary J. Nabel was the physician whose new methods were used to treat cancer.
2.Относиться к дополнению, когда относительное придаточное предложение является дополнением в предложении (то есть за словами who, that, etc. следует сначала подлежащее, а затем сказуемое). a) Мы используем who, whom, that или
вообще не используем союз, когда говорим о людях.
e.g. He is the professor who/whom/that we respect most. = He is the professor we respect most.
b) Мы используем which, that или вообще не используем союз, когда говорим о предметах.
e.g. Wisdom teeth are the third and final set of molars that/which most people get in their late teens or early twenties. = Wisdom teeth are the third and final set of molars most people get in their late teens or early twenties.
c) Мы используем of which, когда говорим об одном предмете, соотносящемся с другим.
e.g. This is his new book the publication of which made him famous.
1. Join these sentences using who or which. (That can be used in all of them, too).
1.These are incisors. They cut food with their sharp edges.
_____________________________________
_____________________________________.
2.This is our best student. She can speak five languages.
_____________________________________
____________________________________.
3.This is the article. It should be read by all dental students.
_____________________________________
____________________________________.
4.This is Professor Pikalyuk. He is my uncle’s friend.
_____________________________________
_____________________________________.
5.The word canine comes from the Latin caninus. It means relating to dogs.
_____________________________________
_____________________________________.
2. Tick the sentence if the underlined relative pronouns can be left out, or write ‘No’ if it cannot.
1.It is considered that primary teeth are essential in the development of the oral cavity. _____
2.The permanent teeth replacements develop from the same tooth germs as the primary teeth, which provide guides for permanent teeth eruptions. _____
3.Also the muscles of the jaw and the formation of the jaw bones depend on the primary teeth that maintain proper spacing for permanent teeth.
_____
4.The roots of primary teeth provide an opening that the permanent teeth erupt through. _____
5.Children whose teeth do not develop properly may have problems with speaking and chewing of food. _____
6.One knows that in almost all European languages the primary teeth are called "milk teeth". _____
35
3. Rewrite each pair of sentences as one sentence containing the relative pronoun, or no relative pronoun (zero).
1.All teeth have a pulp. It communicates with the nervous system of the body. (which)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.Dmitri Menedeleyev is a scientist. We are studying his works. (whose)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.This is a very useful book. I bought it in the book market. (that)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.This is the picture of the permanent dentition. Katya drew it as a part of her project. (zero)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.Today there will be a lectire for the students. They will take part in the conference. (who)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.It was a very famous monument. Its destruction impressed everyone. (of which)
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.Project.
Surf the Internet. Find out what happens when the primary teeth are being replaced by the permanent ones.
Are there other mammals which have several dentitions during their lifetime? What species are champions in the number of teeth in nature? Prepare the presentation.
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Tick () the statements that are true.
I can talk about the teeth and their structure
I can define different layers of a tooth
I can describe location, shape and function of different types of teeth
I can use relative sentences
UNIT XV. THE ORAL CAVITY______________________
In this unit
talking about the structure of the oral cavity
describing functions of the organs of the mouth
speaking on location and functions of salivary glands
One Word Substitutes
Warm-Up Activities
1. Read the following interesting facts about the muscles.
Our mouth is inhabited by 500 to 1000 different types of bacteria, 70 to 80 different types of fungi and a few viruses and parasites.
People, whose mouth has a narrow roof, are more likely to snore. This is because they have less oxygen going through their nose.
If your mouth were completely dry, you would not be able to distinguish the taste of anything.
Humans have unique tongue prints, just like fingerprints.
Sir William Osler was the first to refer to the mouth as the "mirror" of the body. Early signs of many of the common degenerative diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and disease of metabolism are seen intraorally before they are physically apparent elsewhere.
Chewing depends on hands! If you are right handed, you will be likely to chew your food on your right side. If you are left hander, you will be inclined to chew your food on your left side.
The strongest muscle in proportion to its size in the human body is the tongue.
2. Study the structure of the oral cavity. Be sure you can translate all the terms into Russian. What dentition is in the diagram? Why? Name all the teeth in both upper and lower jaws.
3. Read the text. Put questions to each part of the text to cover its contents.
4. Memorize the following words you will need in this unit. |
|
|||
debris / |
/ n pl. остатки, инородные |
increase / |
/ v увеличивать, повышать |
|
вещества |
|
line / / v выстилать |
||
environment / |
/ n (окружающая) |
rough / / adj шершавый, грубый |
||
среда |
|
|
separate / |
/ v отделять |
fat / / n жир |
|
smell / |
/ n запах; обоняние |
|
fill / / v заполнять |
|
soft / / adj мягкий |
||
fluid / |
/ n жидкость |
|
surround / |
/ v окружать |
hard / |
/ adj твердый |
|
taste bud / |
/ вкусовой сосочек |
hollow / |
/ adj полый |
|
(рецептор) |
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
Reading
The Structure of the Oral Cavity
1.
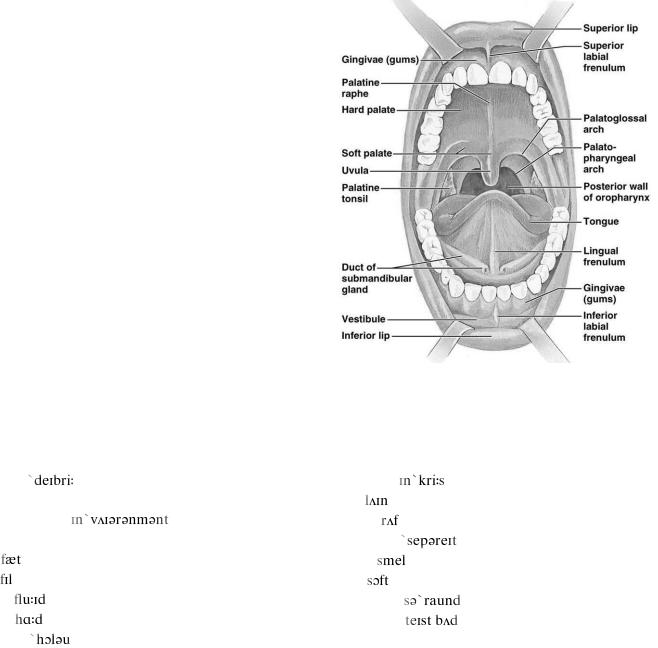
Mouth, also called the oral cavity, is a hollow oval-shaped cavity that allows food and air to enter the body. The mouth also plays a major role in the production of speech through the movements of the tongue, lips and cheeks. The outer surfaces of the mouth – cheeks, upper and lower lips - are facial structures containing mimic muscles. Inside the mouth there are the teeth, tongue, tonsils, salivary glands, hard and soft palates, and the epiglottis. The mouth is divided into two sections: the vestibule, the area between the cheeks and the teeth, and the oral cavity proper. The latter section is mostly filled by the tongue, a large muscle firmly anchored to the floor of the mouth by the frenulum linguae.
2.
The chief structures of the mouth are the teeth, which tear and grind ingested food into small pieces that are suitable for digestion; the tongue, which positions and mixes food and also carries sensory receptors for taste; and the palate, which separates the mouth from the nasal cavity, allowing separate passages for air and for food. All these structures, along with the lips, are involved in the formation of speech sounds by modifying the passage of air through the mouth.
3.
The oral cavity and vestibule are entirely lined by mucous membranes containing numerous small glands that, along with the three pairs of salivary glands, bathe the mouth in fluid, keeping it moist and clear of food and other debris. Specialized membranes form both the gums (gingivae), which surround and support the teeth, and the surface of the tongue, on which the membrane is rougher in texture, containing many small papillae that hold the taste buds.
The mouth’s moist environment and the enzymes within its secretions help to soften food, facilitating swallowing and beginning the process of digestion.
4.
Depending on the types of cells present, salivary glands may be predominantly serous, mucous, or mixed in secretion. Mucus is a thick, clear, and somewhat slimy substance. Serous secretion is a more liquid opalescent fluid composed of water and proteins, such as the digestive enzyme amylase. Secretions can be increased by the presence, thought, or smell of food and also by thermal stimulation.
5.
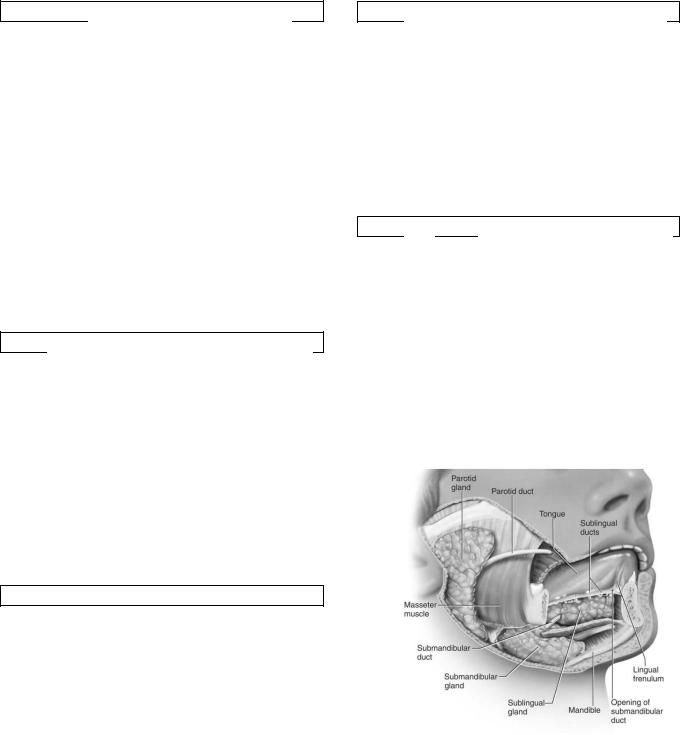
The parotid salivary glands, the largest of the three, are located between the ear and ascending branch of the lower jaw. Each gland is enclosed in a tissue capsule and is composed of fat tissue and cells that secrete mainly serous fluids.
The second pair, the submaxillary glands, also called submandibular glands, is located along the side of the lower jawbone. A capsule of tissue also surrounds each of these glands, which give off mixed secretions mostly serous in nature.
The third pair, the sublingual glands, is situated beneath the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth, near the chin region. They are not covered by a capsule and are therefore more dispersed throughout the surrounding tissue. These glands secrete a mixed fluid that is mainly mucus.
37
Vocabulary Practice
1.Look at the words in bold type in the above text and explain them.
2.Match the words with their definitions:
1. palate |
a) prevents pathogens and |
|
dirt from entering the body |
|
and prevents bodily tissue |
|
from losing moisture |
|
|
2. papillae |
b) vocalized form of human |
|
communication |
|
|
3. mucus |
c) the roof of the mouth |
|
|
4. speech |
d) the little bumps on the top |
|
of the tongue that help grip |
|
food while the teeth are |
|
chewing; they contain the |
|
taste buds |
|
|
5. chin |
e) parotid, sublingual and |
|
submandibular ones |
|
|
6. soft palate |
f) the sensory impression of |
|
food or other substances on |
|
the tongue and is one of the |
|
five traditional senses |
|
|
7. salivary |
g) works with the tongue to |
glands |
produce movements that help |
|
you swallow and force food |
|
into the esophagus |
|
|
8. taste |
h) the area of the face below |
|
the lower lip including the |
|
mandibular prominence. |
|
|
3. Complete the sentences with the words from the box:
taste buds, frenulum of tongue, amylase, facial muscles, sense organ, epiglottis
5) are used to move
our eyelids, our lips, and make any kind of mimicry.
6) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of starch into simpler compounds is known as ___ .
4. Insert the correct preposition or conjunction (here are the odd ones, too):
through, by, or, for, along with, both… and, of, between, and, into, along, beneath, but, in, to, throughout
1)The tongue helps to produce speech ______
altering _____ stopping the flow _____ air _____
the mouth to produce the sounds _____ many consonants.
2)The hard _____ soft palates work together to separate the mouth _____ the nasal cavity.
3)The tongue forms the inferior portion _____
the mouth _____ often moves _____ the mouth to occupy almost any region _____ the hollow cavity.
4)Many salivary glands release their secretion
______ the mouth _______ many tiny ducts.
5)The strongest muscle ______ proportion
_____ its size _____ the human body is the tongue.
6)The mouth is divided _____ two sections: the vestibule, the area ______ the cheeks and the teeth, and the oral cavity proper.
1)______________ prevents food and drink from entering the larynx and trachea, directing it instead into the esophagus.
2)The vertical fold of mucous membrane under the tongue, attaching it to the floor of the mouth is called _______________.
3)_______________ is an organ having nerve endings (in the skin, viscera, eye, ear, nose or mouth) that respond to stimulation.
4)_______________ are located on the tongue and back of the throat and are responsible for our sensation of taste.
5. Match the synonyms:
1. separate |
a) change |
|
|
2. hollow |
b) mainly |
|
|
3. modify |
c) under |
|
|
4. swallow |
d) lower |
|
|
5. mostly |
e) divide |
|
|
6. beneath |
f) roof of the mouth |
|
|
7. submaxillary glands |
g) empty |
|
|
8. slimy |
h) ingest |
|
|
9. inferior |
i) gingivae |
10. palate |
j) mucous |
11. gums |
k) submandibular |
|
glands |
38
Language Development
1. Look through the text about the oral cavity and answer the following questions.
1.How would you define the oral cavity and its functions?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.What is the structure of the mouth?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.What structures does the mouth contain?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.What tissue lines the oral cavity?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.Where are the taste buds located?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.What role do saliva and enzymes play?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
7.What are the functions of salivary secretions?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.What are three major salivary glands and what kind of secretion do they produce?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2. Complete the sentences:
1)Secretions can be increased by __________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
2)Specialized membranes form both the gums (gingivae) and ___________________________
_______________________________________
3)The sublingual glands are situated beneath
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
4)The parotid salivary glands are composed of
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
5)The mouth is divided into ________________
_______________________________________
6)The structures involved in the formation of speech sounds by modifying the passage of air through the mouth are _____________________
_______________________________________
3. Read the case studies, use your knowledge of anatomy and physiology and choose the correct answer:
3a A 19-year-old female came into the clinic after a tongue piercing resulted in an infection. Her piercing was in the middle part of her tongue. Where are most likely to see swollen lymph nodes?
a)submandibular lymph nodes;
b)submental lymph nodes;
c)inferior deep cervical lymph nodes;
d)superior deep cervical lymph nodes
3b A coffee-lover purchases a venti mocha from Starbucks and tells the barista to make it
‘extra hot’. During the first sip, he burns the very tip of his tongue. Which nerve carries the sensation?
a)trigeminal nerve;
b)facial nerve;
c)glossopharyngeal nerve;
d)vagus nerve;
e)hypoglossal nerve
39

3c A patient presents to your office complaining of her tongue feeling funny. On further examination you determine the patient has lost general sensation and taste to the posterior 1/3 of her tongue. Knowing the anatomy of the tongue, which nerve is mostly likely damaged?
a)hypoglossal nerve;
b)chorda tympany nerve;
c)lingual nerve;
d)buccal nerve;
e)glossopharyngeal nerve
3d A 32-year-old patient presents to the emergency room after a car accident. He undergoes a full Cranial Nerve exam and is asked to stick his tongue out. The tongue deviates to the left. Which nerve is likely to be damaged?
a)right vagus
b)left hypoglossal
c)left glossopharengeal
d)right facial
4. Read the text “Structure of the Oral Cavity” again and find:
1.the external surfaces of the oral cavity:
_______________________________________.
2.the sections which the mouth is divided into:
_______________________________________.
3.a structure which anchors the tongue to the floor of the mouth:
_______________________________________.
4.an explanation of the word mucus:
_______________________________________.
5.a structure which divides the oral cavity and the nose:
_______________________________________.
6.a synonym to the submaxillary glands:
_______________________________________.
7.an example of digestive enzymes contained in the saliva:
_______________________________________.
8.four things which can increase production of saliva:
_______________________________________.
9.the name of the largest salivary glands:
_______________________________________.
Grammar in Use
Слова-заместители
one, ones, that, those, there, do
Если возможно, мы избегаем повторения слова или фразы, которые были использованы ранее. Одним из способов избежать такого повторения являются слова-
заместители that, one, do, и there.
Слово- |
Замеща- |
Пример |
замес- |
емое |
|
титель |
слово |
|
|
|
|
one/ones |
человек / |
See those two girls? |
|
предмет |
Helen is the one on |
|
|
the left / the tall one. |
|
|
Let’s do some |
|
|
exercises. The ones |
|
|
the lecturer has told |
|
|
you to do. |
|
|
|
that/those |
человек / |
The curriculum here |
|
предмет |
is like that in |
|
|
Cambridge. |
|
|
Skeletal muscles are |
|
|
those attached to |
|
|
the skeleton. |
|
|
|
do (do it, |
действие |
Can you help me |
do so) |
|
with this report? – I’ll |
|
|
do it (= help you with |
|
|
this report) at once. |
|
|
|
there |
место |
Are you going to the |
|
|
clinic today? – Yes. |
|
|
– Then I’ll see you |
|
|
there. |
|
|
|
При выборе слов-заместителей предметов мы используем one/ones с прилагательными или самостоятельно, а that/those – с предложными сочетаниями. (См. примеры.)
Мы часто употребляем one и ones после Which ... в вопросах:
e.g. There are lots of books here. Which ones are yours?
Мы используем do so и do it / that в качестве заместителей глагольных сочетаний.
e.g. I asked her to prepare the presentation herself but she didn’t want to do so.
40
