
1 курс стомат
.pdf2.How many anatomical terms should first-year students learn every day? (expect)
They ___________________________________
______________________________________.
3.What is the most complicated organ in the human body? (suppose)
One ___________________________________
______________________________________.
4.Why do students of dentistry learn Latin?
(assume) It ____________________________
_________________________________.
5.What is the most difficult subject in the first year? (consider) They ____________________
__________________________________.
6.What should a student do if (s)he has a lot of absences in English? (believe) It _____________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
2. Put the following active sentences into the passive voice. Use by only when necessary:
1.Doctor Brown will give you some advice.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
2.A famous professor will deliver a lecture on splanchnology next Monday
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
3.Fleming discovered penicillin.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
4.They told me that we should attend all the lectures.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
5.Someone founded Harvard University in 1636.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
6.People speak English in many countries around the world.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
7.The lecturer will give an English book to the ten best students.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
8.John wrote an essay yesterday.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
3. Fill in the gaps with the proper forms of the verbs in Simple (Active or Passive) or Continuous Active.
The oral cavity ____________1 (to begin) at the border between the skin and the lips. The roof of the mouth _____________2 (to form) by the hard palate. The oral cavity _____________3 (to lead) into the oropharynx, which ______________4 (to include) the soft palate, the back of the tongue and the tonsils. The inner surface of the cheeks
_____________5 (to form) the sides of the oral cavity. The lowest part of the oral cavity _______6 (to be) the floor of the mouth, which __________7 (to cover) by the tongue.
The function of the oral cavity and its structures
_________8 (to be) to begin the process of digestion. The oral cavity ______________9 (to receive) food, ___________10 (to chew) and
____________11 (to mix) it with saliva and then
__________12 (to start) the swallowing process. The taste buds on the tongue ____________13 (to provide) the different sensations of taste. The oral cavity ____________14 (to play) an important role in speech. The mouth _____ also _______15 (to use) for breathing, drinking, facial expressions and social interactions (such as kissing).
4. Project.
Surf the Internet. Find out information about human body parts that have survived their owners
(like Einstein’s brain). Do you think it ethical to preserve body parts of the dead people? Why? Why not?
Choose a story that has impressed you most and prepare the presentation.
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Tick () the statements that are true.
I can describe the major parts of the human body
I can name the main parts of the trunk, head and limbs
I can talk about internal organs and organ systems
I can use impersonal sentences
11

UNIT XI. THE SKELETON AND BONES____________
In this unit
talking about the major parts of the skeleton
describing different functions of bones
Infinitive and its functions
Warm-Up Activities
1. Study the major bones of the skeleton. Mind the pronunciation of the words of Latin origin. Provide their Latin equivalents (if you can!).
auditory / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
cartilage / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
cervical / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
clavicle / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
condyle / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
cranium / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
hyoid / |
/ |
|
|
|
|
ligament / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
lumbar / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
mandible / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
maxilla / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
occipital / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
periosteum / |
/ |
|
|
|
|
scapula / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
spinal cord / |
/ |
|
|
|
|
sternum / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
temporomandibular |
|
|
|
||
/ |
|
/ |
|
|
|
thoracic / |
|
/ |
|
|
|
vertebra (pl. vertebrae) / |
|
|
|
||
)/ |
|
|
|
|
|
vertebral column / |
|
|
|
||
/ |
|
|
|
|
|
zygomatic / |
/ |
|
|
|
|
2. Memorize the following words you will need in this unit. |
|
|
|||
articulate / |
|
/ v соединять |
joint / |
/ n сустав |
|
bone marrow / |
/ костный мозг |
movable / |
/ adj подвижный |
||
cancellous (spongy) bone / |
protect / |
|
/ v защищать |
||
|
/ губчатое вещество кости |
protuberance / |
/ n выпуклость, |
||
eye socket / |
/ n глазная впадина |
бугорок |
|
|
|
facilitate / |
|
/ v облегчать |
shoulder / |
/ n плечо |
|
girdle / |
/ n пояс |
skull / |
/ n череп |
||
immobile / |
|
/ adj неподвижный |
support / |
|
/ v поддерживать |
joint / |
/ n сустав |
taste / |
/ n вкус |
||
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
Reading
The Skeleton and the Bones
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the body.
In a newborn baby it is made up of more than 300 parts, most of which are made of cartilage. Over time, most of this cartilage turns into bone. As the baby grows, some of its bones fuse together to form bigger bones. By adulthood, the skeleton contains 206 bones and associated cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
Wherever two bones meet there is a joint.
In some places, such as the bones in the skull, the joints are locked together and do not move. Most joints are movable, though, and are coated with a fluid that acts as a lubricant. Ligaments are a tough connective tissue that links bones together at the joints. Cartilage is another connective tissue found at the end of the bones and in the joints.
The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton is formed by the skull, the vertebral column, the rib cage and the sternum or breastbone and contains 80 bones. The appendicular skeleton has 126 bones, including the pectoral (shoulder) girdles, the pelvic girdle and the bones of the lower and upper limbs.
The human skeleton serves six major functions.
These are:
1.Protection: skeleton provides mechanical protection for many of the body’s internal organs, reducing the risk of injury to them.
2.Shape: because of their rigid nature, bones provide a framework around which the body is built.
3.Support: the skeleton supports the softer tissues and provides points of attachments for most skeletal muscles.
4.Assisting in movements: muscles are attached to bones. Therefore, when the associated muscles contract, they cause bones to move.
5.Blood production: erythrocytes and leucocytes are produced in bone marrow of some bones.
6.Storage of minerals: bone tissues store several minerals, including calcium and phosphorus.
13
Skull is the skeleton of the head consisting of the cranium and mandible.
Total number of bones in the skull is 29 (8 cranial and 14 facial bones) and then also 7 associated bones (6 auditory ossicles and the hyoid bone). Cranial part of the skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures, which are held by sutural ligaments. It envelops and protects the brain. Contrary to this, the mandible is united to the cranium by a mobile synovial joint called the temporomandibular joint.
The cranium consists of the following bones:
Frontal bone (1)
Parietal bones (2)
Occipital bone (1)
Temporal bones (2)
Sphenoid bone (1)
Ethmoid bone (1)
The frontal bone forms the forehead and portions of the eye sockets (or orbits). The occipital bone, at the base of the skull contains a large opening, called the foramen magnum, through which the spinal cord passes.
On each side of the opening is the occipital condyle, - two round protuberances, - by means of which the skull articulates with the first cervical vertebra. The organs of hearing are situated in the temporal bone, one on each side. The openings leading into these organs can also be seen on each side.
Facial bones include the following ones:
Zygomatic bones (2)
Maxillae (2)
Nasal bones (2)
Lacrimal bones (2)
Vomer (1)
Palatine bones (2)
Inferior conchae (2)
Mandible (1)
The facial skeleton serves to protect the brain; house and protect the sense organs of smell, sight, and taste; and provide a frame on which the soft tissues of the face can act to facilitate eating, facial expression, breathing, and speech.

Vocabulary Practice
1.Look at the words in bold type in the above text and explain them.
2.Match the words with their definitions:
1. framework |
a. prevents the bones at the |
|
|
joints from becoming |
|
|
dislocated. |
|
|
|
|
2. cartilage |
b. transmits the weight from |
|
|
the head, the trunk and the |
|
|
upper extremities down to |
|
|
the lower extremities at the |
|
|
hip joints, which help |
|
|
humans maintain their |
|
|
upright posture |
|
|
|
|
3. ligament |
c. hard structure consisting |
|
|
of inorganic material that |
|
|
supports and protects the |
|
|
soft parts of the body and |
|
|
provides attachment for |
|
|
muscles |
|
|
|
|
4. axial skeleton |
d. cranial bones protect the |
|
|
brain, vertebrae protect the |
|
|
spinal cord, and rib cage |
|
|
protects vital organs such as |
|
|
heart and lungs. |
|
|
|
|
5. protection |
e. provides the movement of |
|
|
the body and protection of |
|
|
some organs |
|
|
|
|
6. appendicular |
f. smooth and flexible tissue |
|
skeleton |
that lets one bone slide |
|
|
smoothly over another |
|
|
|
|
3. Match synonyms to the following words: |
||
|
|
|
1. maxilla |
|
a. immovable |
|
|
|
2. skull |
|
b. glide |
|
|
|
3. jaw bone |
|
c. maintain |
|
|
|
4. spine |
|
d. united |
|
|
|
5. breastbone |
|
e. help |
|
|
|
6. orbit |
|
f. vertebral column |
|
|
|
7 facilitate |
|
g. limb |
|
|
|
8. extremity |
|
h. eye socket |
|
|
|
9. support |
|
i. sternum |
|
|
|
10. linked |
|
g. torso |
|
|
|
11. slide |
|
k. cranium |
|
|
|
12. immobile |
|
l. upper jaw |
|
|
|
13. rib cage |
|
m. mandible |
|
|
|
14. trunk |
|
n. thoracic cage |
14
4. Translate the names of the bones into English and Latin (if you can!). Describe the structure of the cranium and the facial part of the skull.
Russian |
English |
Latin |
|
|
|
Лобная |
Frontal bone |
Os frontale |
кость |
|
|
Клиновидная |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Решётчатая |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Носовая |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Слёзная |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Верхняя |
|
|
челюсть |
|
|
Нижняя |
|
|
челюсть |
|
|
Теменная |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Затылочная |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Височная |
|
|
кость |
|
|
Скуловая |
|
|
кость |
|
|
5. Fill in the gaps with the past participles. Translate the sentences.
defined, repaired, provided, covered, enclosed, found, divided, produced
1. Short bones are as being
approximately as wide as they are long.
2. Yellow bone marrow is mainly a fatty tissue, while the red bone marrow is where the majority
of blood cells are |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
3. The periosteum is richly |
|
with nerve |
|
fibers, lymphatic vessels and blood vessels.
4. |
Cartilage is |
|
in the joints, the rib cage, |
||||
the ear, the nose, in the throat and between |
|||||||
intervertebral disks. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
5. |
Bone is a living material |
by itself |
|||||
when it is fractures. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
6. |
Both ends of long bone are |
|
|
with |
|||
hyaline cartilage to help protect the bone and aid shock absorption.
7. The brain is almost entirely by
the cerebral cranium with the exception of the foramen magnum and other foramina at the skull base.
8. The skull is into the braincase (cerebral
cranium) and the face (visceral cranium).
6. Сomplete the following statements with the given words:
periosteum, cartilage, appendicular skeleton, bone marrow, cancellous bone, joint, compact bone, axial skeleton
1. |
|
|
is a tough, connective, |
|
|
|
||||||
nonvascular, elastic tissue. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
2. |
Structural areas where two or more bones |
|||||||||||
come together are |
|
|
. |
|
|
|
||||||
3. |
The portion of the skeleton that consists of the |
|||||||||||
upper extremities and shoulder girdle plus the |
||||||||||||
lower extremities and pelvic girdle is |
|
|
. |
|||||||||
4. |
The lighter bone that is found in the interior of |
|||||||||||
bones is |
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
5. |
|
|
|
|
forms the outer layer of |
|||||||
bones where it is needed for strength. |
|
|
|
|||||||||
6. |
The portion of the skeleton that consists of the |
|||||||||||
skull, spinal column, ribs, and sternum is the |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
7. |
A specialized connective tissue that covers all |
|||||||||||
bones of the body is the |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
||||||
8. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
is found |
mainly in |
||||
the flat bones such as hip bone, breast bone, skull, ribs, vertebrae and shoulder blades, and in the cancellous ("spongy") material at the proximal ends of the long bones femur and humerus.
7. Guess which anatomical terms are made of these letters:
1.ville cac _________________;
2.bilde man _________________;
3.girled _________________;
4.cage tirla _________________;
5.curi man _________________;
6.lmniaget _________________.
15
Language Development
1. Look through the text about the skeleton and answer the following questions.
1.How would you define a skeleton?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.What is the structure of the skeleton? What two parts Is it divided into?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.What are the functions of the skeleton?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.Give the definition of the skull.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.How are the bones of the skull held together?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.Which bones constitute the cranium? What structures do they form?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
7.List the facial bones. Which of these are paired? single?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.What layers are there in the bone? What substances do the bones contain?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.

2. Say whether the following sentences are true (T) or false (F). Correct the false ones.
1. There are about 300 bones in the human body. 2. Cartilage consists of collagen. ____
3.There are 60 bones in the human skull. ____
4.Our teeth form part of the skeletal system, but
are not counted as bones. |
____ |
|
5. |
The joints in our cranium are movable while |
|
our hip joints are immobile. |
____ |
|
6. |
The bones in babies' skulls are not yet fused |
|
together, which allows the skull to change shape
slightly during birth. |
____ |
7. The only movable bone in the human face is |
|
the maxilla. |
____ |
3. Read the text and insert the missing words:
Structure of Bones
Almost every bone in the body consists of these layers: periosteum, compact bone, cancellous bone and bone marrow. Periosteum is a whitish
_ containing nerves and blood
vessels. It supplies the cells from which the hard bone below the periosteum is built up. It is the periosteum that is responsible for the life of the bone and it is capable of repair. Its ____ _
contains osteoblasts (cells associated with the bone formation). Beneath the periosteum there is a dense, rigid . It forms the outer
layer of bone. It is so dense that surgeons must use a saw or a bone bur to cut through it. Holes and channels run through the compact bone, carrying blood, ____ and nerves to its inner
parts. Inside this layer is cancellous or spongy bone. Cancellous bone has cells with large spaces in between them like a honeycomb. The spaces in this network are filled with a gelatinous red and yellow bone marrow. Red bone marrow
red and white blood cells and platelets.
Yellow bone marrow stores fat and releases it when it is needed somewhere in the body.
Bones contain large amounts of a protein called collagen as well as minerals, including calcium and phosphorous. Collagen gives bones their elasticity. Calcium is what gives bones their strength. minerals are stored in the
bone, and the bones release them when they are needed by other parts of the body.
1. lymphatic vessels |
4. inner layer |
2. produces |
5. extra |
3. connective tissue |
6. compact bone |
16
Grammar in Use
Инфинитив и его функции
Simple Active |
Simple Passive |
|
|
Словарная форма |
to be + Past Participle |
глагола |
|
|
|
to check |
to be checked |
to consult |
to be consulted |
to give |
to be given |
to take |
to be taken |
to destroy |
to be destroyed |
|
|
Внимание:
1. В некоторых предложениях to опускают, например, после модальных глаголов:
e.g. You should learn the names of all bones by heart.
2. Чтобы образовать отрицательную форму инфинитива, мы ставим not перед ним:
e.g. I came here not to watch, but to help.
Инфинитив с частицей to используется:
1.Чтобы обозначить цель действия (тогда 'to' имеет то же значение, как 'in order to' или 'so as to' (чтобы)):
e.g. The facial skeleton serves to protect the brain.
2.В качестве подлежащего:
e.g. To choose your future profession is really very difficult.
3. В качестве дополнения:
e.g. They expected to be given more books on this topic.
4.С существительными или местоимениями, чтобы указать, как они могут быть использованы:
e.g. Do you have any nice book to read?
5.После прилагательных в таких конструкциях:
It is + прилагательное + to-инфинитив e.g. It is challenging to work as a surgeon.
It is + прилагательное + for кого-либо + to-инфинитив.
e.g. It is hard for students to do everything they should.
It is + прилагательное + of кого-либо + to- инфинитив.
e.g. It is unkind of the professor to put me a bad mark.
1. Choose the correct form (the infinitive with or without to).
1.May I _____________ (to take) this pen?
2.They’ll ________ (to go) to Moscow ________
(to take) part in the International Congress.
3._________ (to be) or _______ (not to be), that is the question.
4.Where is Bob? – He’s gone to the library ____
(to get) prepared for the report in Chemistry.
5.It is such a pity that Jane caught a cold and had ___________ (to leave) earlier.
6.Surgeons must __________ (to use) a saw or a bone bur __________ (to cut) through bones.
7.These are stupid words ___________ (to say).
8.Is it difficult for you _____ (to study) dentistry?
2. Fill in the gaps with Active or Passive Simple Infinitives.
1.The NHS provides treatment for all, regardless of the ability _________ (to pay).
2.The organs of hearing can ___________ (to see) on each side of the head.
3.Muscled attached to the bones cause them
___________ (to move).
4.The patient agreed __________________ (to operate) on in two months.
5.My friend needs a laptop __________ (to make) a presentation.
6.It is not very pleasant ___________ (to treat) by a dentist whom you don’t know well.
7.My little brother was eager ____________ (to give) a very big car for his birthday.
8.What do you like more, ___________ (to give) presents or ______________ (to give) presents?
3. Answer the following questions using the proper forms of the infinitive.
e.g. What is the most difficult thing for you in Anatomy? – The most difficult thing is to memorise words in Latin.
1.What is the easiest thing about being a student?
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.Why have you entered the medical university?
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.What do you think is the most difficult job for your friend? for your parents? for yourself?
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.What are you going to do after classes today?
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.What do you think is an absolutely impossible thing for you?
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.Project.
Medical students should learn lots of information by heart. Surf the Internet and find out some tips how to memorise words or figures effectively.
Share the information with your group mates. Prepare the presentation.
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Tick () the statements that are true.
I can talk about the major parts of the skeleton
I can describe different functions of the bones
I can list all the bones of the skull in English
I can use the infinitive in different functions
17

UNIT XII. MUSCLES______________________________
In this unit
talking about the muscles and their types
defining different functions of muscles
describing location and role of muscles of head and neck
Present Perfect Active
Warm-Up Activities
1.Read the following interesting facts about the muscles.
The word muscle is derived from the Latin term musculus, meaning "little mouse".
To take one step, you use 200 muscles
There are more than 40 muscles in the face, without them we could not eat, speak, communicate, express feelings or kiss.
Scientists estimate that your eye muscles move over 100,000 times a day.
The masseter (used for chewing) is one of the strongest muscles in the human body, it is capable of pulling up to 80 times its own weight.
The human tongue consists of 16 separate muscles, not one as many people think.
It takes 17 muscles to smile and 43 to frown.
2.The information below describes different records of muscles. Fill in the gaps with the names of the muscles from the box:
the heart, the eye muscles, the sartorius, the soleus, the tongue, the masseter, the gluteus maximus
The longest muscle in the human body is
____________1. This narrow muscle of the thigh passes obliquely across the front of the thigh and helps rotate the leg to the position assumed in sitting cross-legged.
In terms of absolute force, the strongest muscle in the body is _____________2, the prime mover of the jaw for chewing. It can create force of 55 lbs. on the incisors or 200 lbs. on the molars. The hardest-working muscle in the body is
_____________3. It pumps 2 oz. blood at every heartbeat, at least 2,500 gallons daily.
The muscle that can pull with the greatest force is ______________4, underneath the calf muscle. It is this muscle that keeps us from falling backward while standing up, and it is essential to running, walking and dancing.
The largest muscle in the body is also one of the strongest – ___________________5. This large muscle in the buttocks keeps us standing upright and fights against gravity when we walk up stairs. The most flexible muscles are muscles of
__________6, which can take many shapes and also is always moving, even in sleep.
The most active of muscles are _______
_____________7. Muscles of the eye are constantly moving. In an hour's worth of reading, they can move 10,000 times. Unlike the heart, however, they can get fatigued easily.
3. Memorize the following words you will need in this unit.
adjust / |
|
/ v адаптировать, регулировать |
extension / |
|
/ n вытягивание |
|
band / |
/ n полоска, связка, фасция |
flexion / |
/ n сгибание |
|||
cardiac muscle / |
/ сердечная |
mastication / |
|
/ n жевание |
||
мышца |
|
|
|
rotate / |
/ v вращать(ся) |
|
chew / / v жевать |
smooth muscle / |
/ гладкая мышца |
||||
conscious / |
|
/ adj сознательный |
striated muscle / |
/ поперечно- |
||
contract / |
|
|
/ v сокращаться |
полосатая мышца |
|
|
dilate / |
|
/ v расширять(ся) |
swallow / |
/ v глотать |
||
endurance / |
|
/ n выносливость |
voluntary / |
|
/ adj произвольный |
|
18
Reading
The Muscular System
The muscular system consists of muscles and tendons. It is responsible for the movements of skeleton and various viscera of the body and it is the site of heat production. Each muscle consists of muscle tissue, connective tissues, nerve tissue and vascular (blood) tissue. The muscular system consists of more than 600 individual muscles. However, only three types of muscles have been identified: striated, smooth and cardiac.
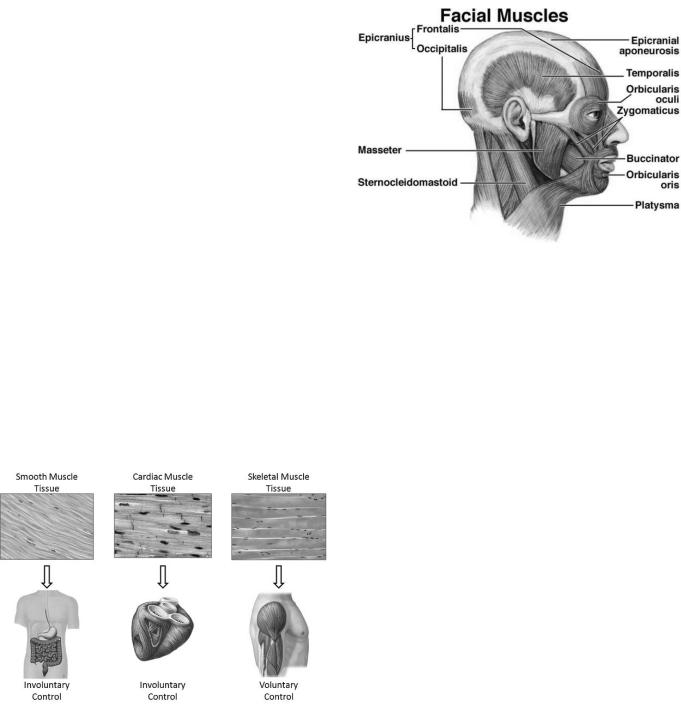
Striated muscles are so named because dark and light bands within the muscle fibers create a striated appearance. Striated muscles are also known as skeletal or voluntary muscles because we have conscious (voluntary) control over these muscles. For example, you decide when you move your arm or leg.
Smooth muscles line all the organs of the digestive tract, blood vessels, ducts of the glands, bladder, and tracheobronchial tree. Smooth muscles are also known as unstriated, involuntary and visceral. Smooth muscles are controlled directly by the autonomic nervous system and are not controlled voluntarily. Cardiac muscles are those muscles that make up the heart. They have the same striated appearance as the skeletal muscles but are involuntary in action. Cardiac muscles provide the main force for circulation of blood throughout human body.
The muscles of the head and neck perform many important tasks, including movement of the head and neck, chewing and swallowing, speech, facial expressions, and movement of the eyes.
Facial muscles, including the greater zygomatic muscle and orbicularis oris, pull on the skin to produce a seemingly infinite number of facial expressions and to move the lips and cheeks during speech and eating.
The muscles of mastication, including the masseter and temporalis, produce the body’s ability to move the mandible, close the mouth, bite, and chew food. Four extrinsic muscle sets connecting the tongue to the surrounding bones move the tongue in virtually any direction, while four intrinsic tongue muscles act to change the shape of the tongue and help facilitate speech. As for the eye, six extrinsic eye muscles provide superior, inferior, lateral, and medial motion, as well as rotation of the eyeball. Located inside the eye, the intrinsic eye muscles work tirelessly to dilate the pupils and focus the lens of the eye to produce clear vision.
Even the middle ear takes part in the muscular system of the head and neck. The muscles of the middle ear contract to dampen the amplitude of vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. Neck muscles contract to adjust the posture of the head throughout the course of a day and have some of the greatest endurance of any muscles in the body.
19

Vocabulary Practice
1.Look at the words in bold type in the above text and explain them.
2.Complete the sentences with the key words:
1) Three major types of muscles in the body are
_____
____________________________________. 2) The muscle that pumps blood throughout your
body is |
|
. |
|
||
3) |
|
|
|
are found in |
|
your digestive system. |
|
|
|||
4) Muscles of |
|
move the |
|||
mandible in several directions to facilitate chewing.
5)She discovered she could not ____________
food or drink, and her husband took her toA&E.
6)The heart _______________ about seventy times a minute.
7)Baby teeth are important because children need healthy teeth to ____________ food and to speak.
8)When she saw the monster, her eyes ____
___________ with horror.
3. Match the words with their opposites:
1. infinite |
a. uncontrolled |
|
|
2. dilate |
b. inferior |
|
|
3. extrinsic |
c. fine |
|
|
4. conscious |
d. force |
|
|
5. frown |
e. limited |
|
|
6. voluntary |
f. extend |
|
|
7. flex |
g. contract |
|
|
8. weakness |
h. unconscious |
|
|
9. superior |
i. smile |
|
|
10. gross |
j. intrinsic |
4. Use the negative prefixes un- / in- /im- /il- /ir- /dis- to form antonyms. Translate them:
controlled
conscious
finite
voluntary
able
possible
striated
direct
tired
responsible
5. Match the words with their definition:
1. smooth |
a. muscle in the jaw responsible |
muscles |
for chewing |
|
|
2. cardiac |
b. working in pairs on the left and |
muscles |
right sides of the body, these |
|
muscles control the flexion and |
|
extension of the head and neck; |
|
working individually, these |
|
muscles rotate the head or flex |
|
the neck laterally to the left or |
|
right |
|
|
3. skeletal |
c. elongated cells, enabling the |
muscles |
muscle to contract and relax |
|
|
4. muscles |
d. cause contractions that move |
of |
food through the intestines, |
mastication |
expand and contract the blood |
|
vessels to regulate blood supply |
|
|
5. masseter |
e. frowning, smiling, etc. |
|
|
6. muscle |
f. they elevate the jaw forcefully |
fibers |
during chewing and gently during |
|
speech. |
|
|
7. facial |
g. these muscles attach to the |
expressions |
bones of skeleton by bundles |
|
of collagen fibers (tendons) and |
|
make voluntary bodily function |
|
possible |
|
|
8. the neck |
h. they have electrical |
muscles |
connections called intercalated |
|
discs, which relay impulses |
|
during the heartbeat |
|
|
6. Find the odd word:
1.endurance, force, strength, weakness, potency;
2.voluntary, conscious, unstriated, controlled, skeletal;
3.visceral, striated, unconscious, involuntary, smooth;
4.rotation, motion, speed, movement, elevation;
5.bladder, lips, cheeks, tongue, eyes.
7. Write out all the names of muscles from the text. Translate them into Russian:
English |
Russian |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20
