
1 курс стомат
.pdfLanguage Development
1. Look through the text about the muscular system and answer the following questions.
1.What does the muscular system consist of?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.What functions do the muscles perform?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.How can the structure of muscle be characterized?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.How many muscles are there in the human body and what are their types?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.Where are muscles located?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.What tasks do the muscles of head and neck perform?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
7.List the major muscles of the head and the neck.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.Choose one muscle of the head or neck and describe its location and functions.
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
21
2. Finish the following sentences using the information from the text:.
1.Muscles are responsible for _____________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.Striated muscles are also known as ______
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.Smooth muscles are controlled __________
______________________________________.
4.Cardiac muscles provide ________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.The muscles of the head and neck perform
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.Skeletal muscles work with bones to give our
body the ability |
|
. |
7.Four muscles of mastication include ____
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.Six extrinsic eye muscles provide _______
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3. Determine the muscles:
1.Elevates and retracts mandible, assists in side to side movement of mandible.
2.Draws back scalp, wrinkles forehead, raises eyebrows.
3.Elevates mandible when chewing and slightly protracts it.
4.Draws angles of the mouth upward and outward; major muscle used in smiling and laughing.
5.Draws back scalp, wrinkles forehead.
a.frontal muscle
b.greater zygomatic muscle
c.temporal muscle
d.occipitofrontal muscle
e.masseter
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Grammar in Use
Present Perfect Active
Утвердительная форма
I / We / You / |
|
have |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
They |
|
|
|
seen |
|
a dentist. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
He / She / It |
|
has |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Отрицательная форма |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I / We / You / |
|
haven’t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
They |
|
|
|
seen |
|
a dentist. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
He / She / It |
|
hasn’t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Вопросы |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
have |
I / we / you |
|
|
|
|
|
||
(Why) |
|
/ they |
|
seen |
|
a dentist? |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
has |
he / she / it |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Сигнальные слова: before (now) (до насто-
ящего момента), ever (когда-либо), never (before) (никогда (ранее), up till now, so far
(до этих пор), since/for (с (какого-то момента)/в течение (какого-то времени); just (только что), yet (еще), recently (в последнее время), lately (недавно), already (уже).
Present Perfect используется для обозначения:
1 Действий в прошлом, которые продолжаются до настоящего момента: e.g. His muscles have been weak since birth.
2 Действия, которые произошли в неопределенном прошлом:
e.g. Have you seen the doctor yet?
1. Fill in the table with the proper forms of the irregular verbs. Memorise them:
began
bite
brought
choose
cut
пить
ate
went
знать
feel
saw
speak
spread
think
2. Complete the sentences with the proper form of the verb in the Present Perfect.
1.How many exams _______ you __________
(to pass) up till now?
2.________ you ever _________ (to eat) beans?
3.My friend __________ never ____________
(to read) about facial muscles before.
4.‘Oh, mummy! What am I to do? I __________
just ______________ (to swallow) a coin!’
5.‘Congratulations! I know your son___________
______________ (to write) the best essay on bioethics.’
6.The patient says that he ________ not
_________ (to chew) gums for more than a year.
7.‘What _____________________ (to happen)?’ ‘Oh, everything’s OK. The kitten _______ just
_____________ (to break) a cup.’
8.‘We _______________________ (to study) all muscles in Anatomy classes already. But I can’t say I know them all. It’s just impossible!’
3. Say whether the sentences are true or false. Correct the false sentences.
e.g. Scientists have used x-rays in medicine for more than 150 years. – No, they haven’t. They have used them since 1895.
1.I have known my best friend since I was 5 years old.
2.My parents have just bought a new RangeRover for me.
3.Up to now I’ve visited ten countries.
4.I have never eaten a pine-apple.
5.Our lecturer has promised to put excellent marks to all of us.
6.I haven’t been home since last Sunday.
7.I have never taken any drugs.
8.I have never treated a patient with caries yet.
9.I’ve been very happy since I entered Medical
Academy.
22

4. Fill in the table with the signal words. The first line is made for you:
before, the day before yesterday, recently, ever, never, last weekend, up till now, last year, yet, so far, since 1998, in 1998, just, lately, yesterday, for 5 years, 5 years ago
Present Perfect |
Past Simple |
|
|
before |
the day before yesterday |
_____________ |
____________________ |
_____________ |
____________________ |
_____________ |
____________________ |
_____________ |
____________________ |
_____________ |
____________________ |
_____________ |
|
_____________ |
|
_____________ |
|
_____________ |
|
_____________ |
|
Now put the verbs in the following sentences into Present Perfect using the necessary signal words. e.g. Why didn’t you attend the lectures
yesterday? – Why haven’t you attended the lectures since Monday?
1.Ms Forsyte became a professor last week.
_______________________________________
2.The boy cut his finger 5 minutes ago.
_______________________________________
3.Last time my mother grew vegetables in 2005.
_______________________________________
4.Did you visit your parents last month?
_______________________________________
5.Complete the sentences with the proper forms of the verbs in Present Perfect or Past Simple.
1.This patient ____________ (to have) severe toothache the day before yesterday.
2.___________ you ever___________ (to have) any allergic reactions?
3.The students ______________________ (to finish) five experiments so far.
4.Why ___________ not you _____________ (to answer) the phone yesterday evening?
5.Why ___________ not you _____________ (to answer) your mother’s e-mail yet?
6.I _____________ (to live) with my parents when I was 16.
7.I _______________ (not to live) with my parents since I was 16.
8.‘When _______ you last __________ (to see) your dentist?’ ‘I ____________________ (to visit) him since last September.’
9.Can you imagine this? My friend ___________
__________ (to take) part in five (!) conferences recently!
10.On oral examination, the patient __________
(to feel) pain when the dentist ______________
(to start) probing her periodontal tissues.
11.The patient ______________ (to have) muscle spasms several times lately.
6. Project.
Surf the Internet. Find out what the ideal percentage of muscle mass is for men and women. What happens if a person has not enough muscle mass? excessive muscle mass?
Prepare the presentation.
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Tick () the statements that are true.
I can talk about the muscles and their types
I can define different functions of the muscles
I can describe location and role of muscles of the head and neck
I can use Present Perfect Active
23
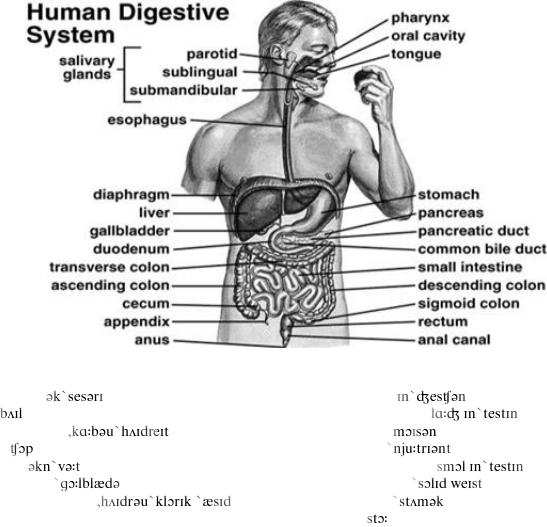
UNIT XIII. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM______________
In this unit
talking about the digestive system
describing organs of the GI system and their functions
speaking on the process of digestion
Past and Future Perfect Active
|
the average adult. |
species of bacteria. |
Warm-Up Activities |
The adult stomach has a very small |
|
1. Read the following interesting facts about the |
volume when empty but can expand to |
|
digestive system. |
hold up to 1.5 liters of food when full. |
|
|
Our salivary glands produce around 1.5 |
On average, the human adult male's small |
|
liters of saliva each day. |
intestine is 6.9 m long, and the female's |
|
Once swallowed, bolus (food) travels |
7.1 m. |
|
down through the esophagus to the |
The small intestine is responsible for over |
|
stomach, taking about 7 seconds to get |
90 percent of digestion and absorption of |
|
there. |
most nutrients. |
|
The liver is the second largest (after skin) |
GI system plays host to more than 500 |
|
single organ in the body, weighing 2 kg in |
|
2. Study the structure of the digestive system. Be sure you can translate all the terms into Russian.
3. Memorize the following words you will need in this unit.
accessory / |
|
/ adj вспомогательный |
bile / /n желчь |
|
|
carbohydrate / |
|
/ n углеводы |
chop / / v крошить |
||
convert / |
/ v превращать |
|
gallbladder / |
|
/ n желчный пузырь |
hydrochloric acid / |
/ |
|
соляная кислота |
|
|
ingestion / |
/ v глотание |
large intestine / |
/ кишечник |
moisten /` |
/ v увлажнять, смачивать |
nutrient / |
/ n питательное вещество |
small intestine / |
/тонкая кишечник |
solid waste / |
/ твердые отходы; кал |
stomach / |
/ n желудок |
store / /v хранить
24
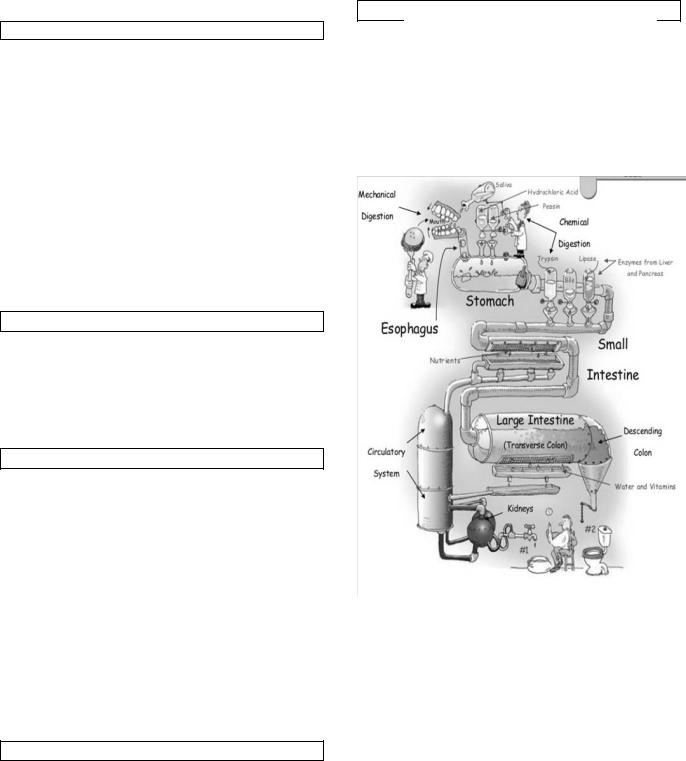
Reading
The Digestive System
Organs of the Digestive System
The digestive system is a group of organs working together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body. Food passes through a long tube inside the body known as the alimentary canal or the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). The alimentary canal is made up of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
In addition to the alimentary canal, there are several important accessory organs that help your body to digest food - teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Functions of the Digestive System
To achieve the goal of providing energy and nutrients to the body, four major functions take place in the digestive system: ingestion of food, its digestion, absorption of nutrients, and excretion of indigestible remains.
The Mouth
Food begins its journey through the digestive system in the mouth. Teeth chop food into small pieces, which are moistened by saliva before the tongue and other muscles push the food into the pharynx.
Surrounding the mouth are three sets of salivary glands. The salivary glands are accessory organs that produce a watery secretion known as saliva. Saliva helps to moisten food and begins the digestion of carbohydrates. The body also uses saliva to lubricate food as it passes through the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus to the stomach.
The Stomach
The stomach is a muscular sac that is located on the left side of the abdominal cavity, just inferior to the diaphragm. It contains hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes that continue the digestion of food that began in the mouth.
The Intestines
After being in the stomach, food enters the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. It then enters the jejunum and then the ileum (the final part of the small intestine). In the small intestine, bile, produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder, pancreatic enzymes, and other digestive enzymes produced by the inner wall of the small intestine help in the digestion of food.
After passing through the small intestine, food passes into the large intestine. In the large intestine, some of the water and electrolytes (chemicals like sodium) are removed from the food. Many microbes (bacteria like Bacteroides,
Lactobacillus acidophilus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella) in the large intestine help in the digestion process. The first part of the large intestine is called the cecum, to which the
appendix is attached. Food then travels upward in the ascending colon. The food travels across the abdomen in the transverse colon, goes back down the other side of the body in the descending colon, and then through the sigmoid colon. Solid waste is then stored in the rectum until it is excreted via the anus.
25
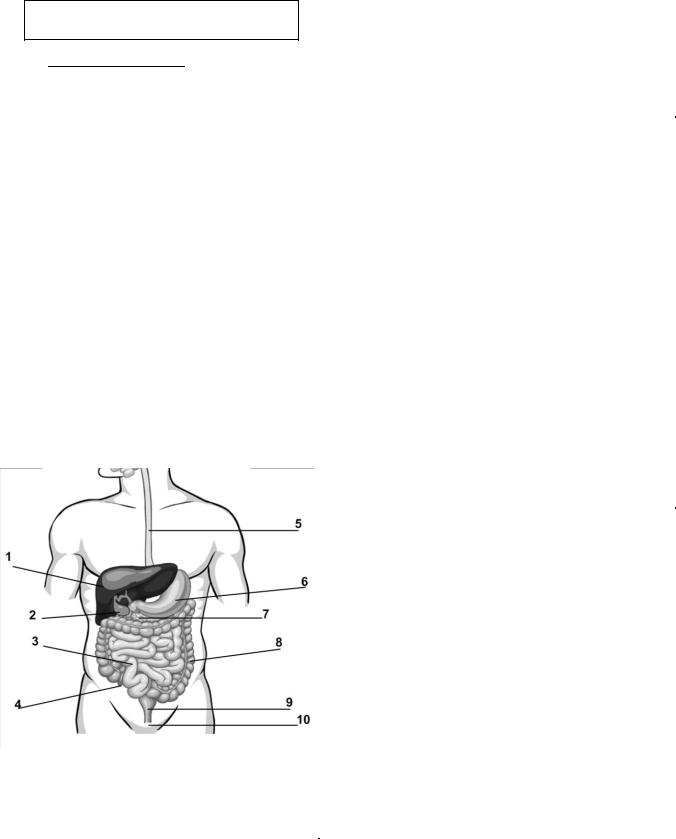
Vocabulary Practice
1.Look at the words in bold type in the above text and explain them.
2.Complete the sentences with the words from the box:
esophagus, excretion, chyme, saliva, absorption, ingestion, digestion
1. Most takes place in the
walls of the small intestine.
2. The final function of the digestive system is the
|
of waste in a process known as |
|
defecation. |
|
|
3. Mechanical |
|
begins with |
the chewing of food by the teeth and is continued through the muscular mixing of food by the
stomach and intestines. |
|
|
4. The mouth is responsible for |
|
, |
as it is the orifice through which all food enters |
|
|
the body. |
|
|
5. Food in the stomach that is partly digested and
mixed with stomach acids is called |
|
. |
|
|||
6. |
|
uses rhythmic muscle movements |
||||
(called peristalsis) to force food from the throat |
|
|
||||
into the stomach. |
|
|
||||
7. |
|
|
contains enzymes that break |
|
|
|
down carbohydrates (starch) into smaller molecules.
3. Label the organs of the GI system:
1. |
6. |
2. |
7. |
3. |
8. |
4. |
9. |
5. |
10. |
4. Match the words with their opposites:
1. inferior |
a. use |
|
|
2. descending |
b. dry |
|
|
3. indigestible |
c. solid |
|
|
4. absorb |
d. many |
|
|
5. store |
e. ascending |
|
|
6. moistened |
f. digestible |
|
|
7. liquid |
g. superior |
|
|
8. several |
h. excrete |
|
|
5. Match the words with their definition:
1. gastric juice |
a. this space is bordered in |
|
the front and to the sides by |
|
the two alveolar arches, |
|
which contain the teeth |
|
|
2. carbohydrates |
b. the part of the body |
|
below the chest that |
|
contains the stomach and |
|
other organs |
|
|
3. nutrients |
c. a pear-shaped, hollow |
|
structure located under the |
|
liver and on the right side of |
|
the abdomen; its primary |
|
function is to store and |
|
concentrate bile |
|
|
4. saliva |
d. the breakdown of large |
|
insoluble food molecules |
|
into small water-soluble |
|
food molecules so that they |
|
can be absorbed into the |
|
watery blood plasma |
5. oral cavity |
e. contains a mixture of |
|
water, inorganic ions, |
|
hydrochloric acid, |
|
pepsinogens, mucus, and |
|
various polypeptides |
|
|
6. gallbladder |
f. contains enzymes playing |
|
a role in breaking down |
|
food particles entrapped |
|
within dental crevices, |
|
protecting teeth from |
|
bacterial decay |
|
|
7. abdomen |
g. our digestive system |
|
changes them into glucose |
|
(blood sugar) |
|
|
8. digestion |
h. components in foods that |
|
an organism uses to survive |
|
and grow |
|
|
26
6. Choose the correct answer:
1.How does food move through your digestive tract?
a)by gravity
b)by wavelike muscle contractions
c)by cilia
d)by chemical absorption
2.The digestive process starts in the:
a)Stomach
b)Esophagus
c)Mouth
d)Bathroom
3.The digestive system consists of:
a)Head, neck and extremities
b)Teeth, tongue and nose
c)Liver, heart and blood vessels
d)Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
4.Which organs help with the absorption of nutrients?
a)Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder and pancreas
b)Liver, heart and spleen
c)Gallbladder, kidneys and appendix
d)Kidneys, liver and bladder
5.The large salivary glands are
a)Parotid glands
b)Submandibular glands
c)Sublingual glands
d)All of the above
6.What tube moves food from the back of your throat to the stomach?
a)Epiglottis
b)Esophagus
c)Feeding tube
d)Pharynx
7.When they reach the stomach, mashed-up food particles mix with:
a)Guava juice
b)Gastric juices
c)Mucus
d)Bile
8.Bile is made up in the:
a)Large intestine
b)Stomach
c)Liver
d)All of the above
Language Development
1. Look through the text about the disgestive system and answer the following questions.
1.What does the digestive system consist of?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
2.What are the accessory organs of the digestive system?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
3.What are the main functions of the digestive system?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
4.Which processes take place in the mouth?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
5.What are the main functions of saliva?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
6.What is a stomach?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
7.Which substances help in the digestion of food in the small intestine?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
8.What are the major divisions of the large intestine?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
______________________________________.
27

2. Read the dialogue about the stomachache, paying attention to the words in bold type, and reproduce it:
P: Good Afternoon, doctor.
D: Good afternoon. What is your problem?
P: I have a strong stomachache and heartburn. D: How long have you had this pain and acidity? P: For 2 months now. It does not go way! I eat and after every meal my stomach hurts. Even at night the pain persists.
D: Tell me, in the last 2 months, have you eaten any kind of heavy food, or something different? P: No.
D: Is the pain continuous or does it come and go? P: It comes and goes.
D: Ok. What we can do first is check your abdomen to see where the pain comes from. (…) D: Ok. As I was telling you before, I am going to examine you. I want to examine your feces to check if you have any kind of parasite. These can affect your stomach.
P: I see.
D: I would also like to examine your upper gastrointestinal system through X-rays and contrast. It is a very simple thing and it does not hurt. You will drink a thick substance. The radiologist will see how you digest the substance and will see the movements of your stomach. We will have this type of examination because your pain could come not from the stomach but from the gallbladder. For now, do not eat greasy food. Do not eat close to your sleep time because it could cause you more acidity. Eat plain food, nothing spicy. As soon as I get the results from the medical test, I will talk to you. Any questions? P: With so many medical tests, I was wondering if I have an ulcer.
D: We need to think of that too. That is why I want that test. I need to explain to you that an X- ray of the upper intestine sometimes cannot detect an ulcer or other irritations. If the pain persists after some antibiotics you will need an endoscopy. An endoscopy is a medical examination in which the doctor inserts a tube through your mouth or nose. Then, the specialist will observe your stomach, from the small intestine to the large one. Any other question? P: No doctor, thank you.
D: Good. We’ll see each other soon. Good bye.
28
Grammar in Use
Past Perfect Active
Утвердительная форма
I / We / You / |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
They / He / |
|
had |
done |
the job by 8. |
|||
She / It |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Отрицательная форма |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I / We / You / |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
They / He / |
|
hadn’t |
done |
the job by 8. |
|||
She / It |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Вопросы |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
I / we / |
|
|
|
||
(Why) |
had |
you / they |
done |
the job by 8? |
|||
|
|
/ he / she |
|
|
|
||
|
|
/ it |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Сигнальные слова: наречия: already (уже), before (then) (до того момента), never … before (никогда ранее); союзы: after (после того как), when (когда), as soon as (как только), by the time that (к тому времени когда).
Past Perfect используется:
Чтобы указать на предыдущее действие, то есть на более раннее из двух действий:
e.g. When the doctor arrived the patient had died. = First the patient died. Then the doctor arrived.
When the doctor arrived the patient died. = First the doctor arrived. Then the patient died.
1.Fill in the sentences with Past Perfect or Past Simple of the verbs in brackets.
1.I ___________ (to go) to bed as soon as I ___
____________ (to memorise) all the names of the organs of the GI system.
2.The dentist _____________ (to write) out a prescription after he _______________ (to make) a diagnosis.
3.The child ________ (to have) severe stomachache when he ____________ (to eat) ten pizzas.
4.After Kate _________________ (to complete) her homework, she _____________ (to go) out.
Future Perfect Active
Утвердительная форма
I / We /
You / They will have done the job by 8.
/He / She
/It
Отрицательная форма
I / We /
You / They won’t have done the job by 8.
/He / She
/It
Вопросы
|
|
I / we / |
|
|
(Why) |
will |
you / |
have done |
the job |
|
|
they / he |
|
by 8? |
|
|
/ she / it |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Сигнальные слова: by a certain time in the future (к определенному моменту в будущем), not… till/until something happens in the future (не раньше, чем что-либо произойдет в будущем).
Future Perfect используется:
Чтобы показать, что действие будет уже завершено к определенному моменту в будущем:
e.g. We will have finished this essay by the end of the week.
2. What will you have done/completed by this time in the future? Write the true sentences about yourself using Future Perfect.
1.By the tomorrow morning I ______________
______________________________________.
2.By the end of the week I ________________
______________________________________.
3.By the end of the term I ________________
______________________________________.
4.By the end of the year I ________________
______________________________________.
5.By 2050 I ____________________________
______________________________________.
3. Complete the sentences with the proper forms of the verb in one of the Present, Past or Future tenses.
1.”When ______ you ____________ (to leave) your surgery yesterday?”
“I ____________ (to leave) the surgery after I
______________ (to see) all my patients.”
2.“________ you ever___________ (to be) to Vienna?”
“Yes, I ________. Just last year I ____________
(to go) to The Marriage of Figaro in the famous
Vienna Opera.”
3.Yesterday while I ________________ (to prepare) for the test in chemistry, Jack ________
(to come). He ________________ (to leave) his workbook at university and so he ____________
(to want) to learn with me. We _______________
(to study) the whole evening and _____________
(to finish) by midnight only. I hope we _________
(to get) excellent marks for this test.
4.The orthodontist _____________ (to think) that she ____________ (to put) a denture to Mr Johns next month. By that time he _________________
(to complete) the course of treatment and _____
(to be) ready for installation of his denture.
4.Project.
Surf the Internet. Find out what the words denoting different organs of the digestive system are derived from. Compare their etiology in different languages (for example, English, Latin, Russian, Ukrainian, Crimean Tatar, Chinese, etc.) Prepare the presentation.
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Tick () the statements that are true.
I can talk about the digestive system
I can describe organs of the GI system and their functions
I can speak on the process of digestion
I can use Past and Future Perfect Active
29
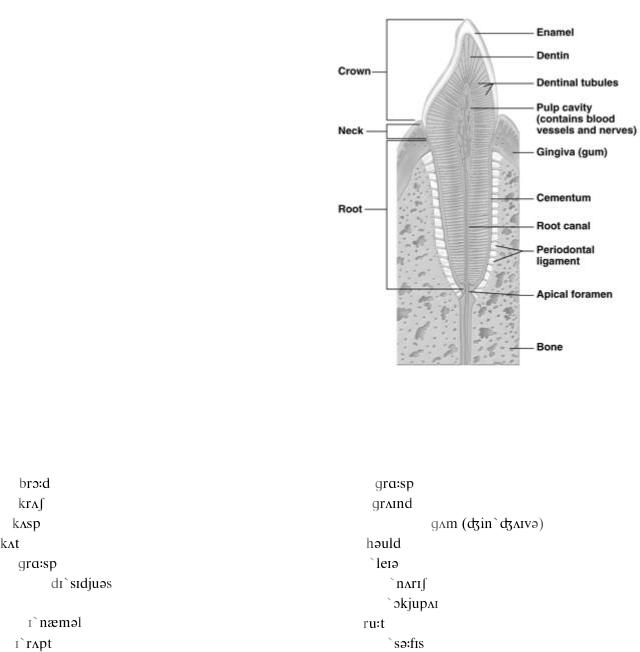
UNIT XIV. TEETH_________________________________
In this unit
talking about the teeth and their structure
defining different layers of a tooth
describing location and function of different types of teeth
Relative Sentences
Warm-Up Activities
1. Read the following interesting facts about the |
2. Study the structure of the tooth. What tooth do |
||||
|
|
|
|||
muscles. |
|
|
you think it is (anterior or posterior, deciduous or |
||
|
|
|
|||
Teeth buds start to grow 9-12 weeks into |
permanent)? |
|
|||
a baby's development when it is still in its |
Read the text on the right and check whether your |
||||
mummy's tummy |
suggestions were correct. |
|
|||
No two people have the same set of |
|
|
|
||
teeth—the teeth are as unique as the |
|
|
|
||
fingerprint. Even identical twins have |
|
|
|
||
different “dental fingerprints”! |
|
|
|
||
The hardest tissue in the body is the |
|
|
|
||
enamel covering our teeth. |
|
|
|
||
Today, around forty percent of people |
|
|
|
||
over 65 years do not have a complete set |
|
|
|
||
of teeth. |
|
|
|
||
Right-handed people tend to chew food |
|
|
|
||
on their right side, while left-handed |
|
|
|
||
people tend to chew on their left side. |
|
|
|
||
Tooth is the only part of the human body |
|
|
|
||
that cannot repair itself |
|
|
|
||
Rabbit’s teeth never stop growing. They |
|
|
|
||
keep them worn down by gnawing on bark |
|
|
|
||
and other hard foods. |
|
|
|
||
Sometimes premolar teeth are referred to |
|
|
|
||
as bicuspids, meaning two cusps, but this |
|
|
|
||
is not always accurate because some |
3. Give the titles to each part of the text, which |
||||
|
|
|
|||
premolars may have three cusps. |
summarize them best. |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
Therefore the term premolar is preferred. |
|
|
|
||
3. Memorize the following words you will need in this unit. |
|
|
|||
broad / |
/ adj широкий |
grasp / |
/ v захватывать, сжимать |
||
crush / |
/ v давить, дробить |
grind / |
/ v irreg. жевать |
|
|
cusp / |
/ n бугорок зуба; острый выступ |
gum (gingiva) / |
/ n десна |
||
cut / / v irreg. резать |
hold / |
/ v irreg. держать |
|
||
grasp / |
|
/ v захватывать, сжимать |
layer / |
/ n слой |
|
deciduous / |
/ adj временный, |
nourish / |
/ v питать |
|
|
молочный (о зубах) |
occupy / |
/ v занимать (место) |
|||
enamel / |
|
/ n эмаль |
root / / n корень |
|
|
erupt / |
|
/ v прорезываться |
surface / |
/ n поверхность |
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
