
11 ALGEBRA
.pdf
TEST 1A |
|
|
|
TEST 1B |
|
|
|
TEST 1C |
|
|
|
TEST 1D |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
E |
9. |
B |
1. |
D |
9. |
D |
1. |
D |
9. |
B |
1. |
E |
9. |
C |
|||||||
2. |
B |
10. |
C |
2. |
B |
10. |
A |
2. |
A |
10. |
A |
2. |
A |
10. |
D |
|||||||
3. |
E |
11. |
D |
3. |
D |
11. |
A |
3. |
B |
|
|
|
3. |
D |
|
|
|
|||||
4. |
C |
12. |
B |
4. |
B |
12. |
C |
4. |
E |
|
|
|
4. |
B |
|
|
|
|||||
5. |
E |
13. |
C |
5. |
B |
13. |
B |
5. |
C |
|
|
|
5. |
C |
|
|
|
|||||
6. |
A |
14. |
A |
6. |
C |
14. |
E |
6. |
E |
|
|
|
6. |
A |
|
|
|
|||||
7. |
A |
|
|
|
7. |
D |
|
|
|
7. |
E |
|
|
|
7. |
B |
|
|
|
|||
8. |
D |
|
|
|
8. |
A |
|
|
|
8. |
A |
|
|
|
8. |
C |
|
|
|
|||
TEST 1E |
|
|
|
TEST 1F |
|
|
|
TEST 2A |
|
|
|
TEST 2B |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
D |
9. |
A |
1. |
B |
9. |
A |
1. |
B |
9. |
B |
1. |
B |
9. |
E |
|||||||
2. |
A |
10. |
B |
2. |
A |
10. |
A |
2. |
B |
10. |
A |
2. |
D |
10. |
B |
|||||||
3. |
E |
11. |
E |
3. |
C |
11. |
B |
3. |
E |
11. |
C |
3. |
B |
11. |
B |
|||||||
4. |
B |
12. |
D |
4. |
E |
12. |
E |
4. |
D |
12. |
B |
4. |
E |
12. |
C |
|||||||
5. |
C |
13. |
B |
5. |
C |
13. |
E |
5. |
B |
13. |
E |
5. |
A |
13. |
A |
|||||||
6. |
A |
14. |
C |
6. |
D |
14. |
C |
6. |
C |
14. |
E |
6. |
D |
14. |
C |
|||||||
7. |
D |
15. |
A |
7. |
D |
15. |
C |
7. |
A |
15. |
D |
7. |
D |
15. |
D |
|||||||
8. |
C |
16. |
D |
8. |
B |
16. |
B |
8. |
B |
16. |
D |
8. |
D |
16. |
D |
|||||||
TEST 2C |
|
|
|
TEST 3A |
|
|
|
TEST 3B |
|
|
|
TEST 3C |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
A |
9. |
C |
1. |
D |
11. |
B |
1. |
A |
11. |
B |
1. |
A |
11. |
B |
||||||||
2. |
D |
10. |
E |
2. |
A |
12. |
A |
2. |
D |
12. |
C |
2. |
D |
12. |
C |
||||||||
3. |
D |
11. |
C |
3. |
E |
13. |
D |
3. |
D |
13. |
E |
3. |
C |
13. |
E |
||||||||
4. |
E |
14. |
D |
4. |
D |
14. |
C |
4. |
B |
14. |
D |
||||||||||||
4. |
D |
12. |
B |
||||||||||||||||||||
5. |
E |
15. |
D |
5. |
D |
15. |
D |
5. |
D |
15. |
B |
||||||||||||
5. |
C |
13. |
B |
||||||||||||||||||||
6. |
C |
16. |
E |
6. |
C |
16. |
D |
6. |
A |
16. |
C |
||||||||||||
6. |
B |
14. |
B |
7. |
B |
17. |
C |
7. |
C |
17. |
C |
7. |
B |
17. |
B |
||||||||
7. |
C |
15. |
A |
8. |
D |
18. |
D |
8. |
D |
18. |
A |
8. |
B |
18. |
B |
||||||||
9. |
B |
19. |
E |
9. |
D |
19. |
B |
9. |
D |
19. |
B |
||||||||||||
8. |
E |
16. |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||
10. |
B |
20. |
D |
10. |
E |
20. |
C |
10. |
D |
20. |
D |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Answers to Exercises |
359 |

TEST 3D |
|
|
|
TEST 3E |
|
|
|
TEST 3F |
|
|
|
TEST 3G |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
C |
11. |
B |
1. |
C |
11. |
B |
1. |
E |
11. |
B |
1. |
D |
11. |
D |
||||||||
2. |
A |
12. |
C |
2. |
C |
12. |
C |
2. |
C |
12. |
A |
2. |
E |
12. |
B |
||||||||
3. |
A |
13. |
D |
3. |
B |
13. |
B |
3. |
E |
13. |
E |
3. |
B |
13. |
E |
||||||||
4. |
E |
14. |
C |
4. |
A |
14. |
A |
4. |
B |
14. |
C |
4. |
E |
14. |
B |
||||||||
5. |
C |
15. |
E |
5. |
E |
15. |
C |
5. |
D |
15. |
B |
5. |
D |
15. |
A |
||||||||
6. |
A |
16. |
C |
6. |
B |
16. |
A |
6. |
A |
16. |
A |
6. |
B |
16. |
A |
||||||||
7. |
B |
17. |
A |
7. |
D |
17. |
D |
7. |
E |
17. |
D |
7. |
A |
17. |
B |
||||||||
8. |
D |
18. |
D |
8. |
D |
18. |
D |
8. |
C |
18. |
C |
8. |
A |
18. |
E |
||||||||
9. |
E |
19. |
D |
9. |
B |
19. |
D |
9. |
D |
19. |
C |
9. |
E |
19. |
E |
||||||||
10. |
C |
20. |
C |
10. |
B |
20. |
A |
10. |
D |
20. |
C |
10. |
C |
20. |
A |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
TEST 3H |
|
|
|
TEST 3K |
|
|
|
TEST 3L |
|
|
|
|
TEST 4A |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
C |
11. |
A |
1. |
C |
11. |
B |
1. |
C |
11. |
D |
1. |
C |
9. |
B |
||||||||
2. |
E |
12. |
B |
2. |
A |
12. |
A |
2. |
B |
12. |
E |
2. |
E |
10. |
B |
||||||||
3. |
C |
13. |
C |
3. |
B |
13. |
D |
3. |
B |
13. |
A |
3. |
C |
11. |
D |
||||||||
4. |
D |
14. |
C |
4. |
B |
14. |
C |
4. |
D |
14. |
B |
||||||||||||
4. |
B |
12. |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||
5. |
E |
15. |
A |
5. |
E |
15. |
B |
5. |
D |
15. |
B |
||||||||||||
5. |
E |
13. |
E |
||||||||||||||||||||
6. |
A |
16. |
B |
6. |
B |
16. |
D |
6. |
C |
16. |
B |
||||||||||||
7. |
C |
17. |
C |
7. |
D |
17. |
D |
7. |
B |
17. |
D |
6. |
D |
14. |
C |
||||||||
8. |
B |
18. |
E |
8. |
E |
18. |
D |
8. |
D |
18. |
D |
7. |
C |
15. |
B |
||||||||
9. |
C |
19. |
E |
9. |
D |
19. |
C |
9. |
A |
19. |
A |
||||||||||||
8. |
C |
16. |
D |
||||||||||||||||||||
10. |
C |
20. |
E |
10. |
A |
20. |
E |
10. |
A |
20. |
E |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
TEST 4B |
|
|
|
TEST 4C |
|
|
|
TEST 4D |
|
|
|
TEST 5A |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
B |
9. |
A |
1. |
E |
9. |
E |
1. |
D |
9. |
C |
1. |
E |
9. |
B |
||||||||
2. |
D |
10. |
E |
2. |
B |
10. |
B |
2. |
B |
10. |
D |
2. |
E |
10. |
B |
||||||||
3. |
E |
11. |
B |
3. |
E |
11. |
D |
3. |
A |
11. |
A |
3. |
B |
11. |
A |
||||||||
4. |
A |
12. |
D |
4. |
A |
12. |
D |
4. |
C |
12. |
B |
4. |
E |
12. |
D |
||||||||
5. |
D |
13. |
B |
5. |
C |
13. |
C |
5. |
E |
13. |
E |
5. |
C |
13. |
E |
||||||||
6. |
B |
14. |
A |
6. |
D |
14. |
B |
6. |
B |
14. |
C |
6. |
A |
14. |
C |
||||||||
7. |
A |
15. |
B |
7. |
A |
15. |
A |
7. |
E |
15. |
D |
7. |
E |
15. |
B |
||||||||
8. |
C |
16. |
B |
8. |
D |
16. |
B |
8. |
C |
16. |
D |
8. |
C |
16. |
A |
||||||||
TEST 5B
1. |
D |
5. |
D |
9. |
B |
13. |
C |
2. |
E |
6. |
C |
10. |
D |
14. |
A |
3. |
E |
7. |
E |
11. |
D |
15. |
C |
4. |
A |
8. |
A |
12. |
C |
16. |
B |
360 |
Answers to Exercises |

A
absolute value function: a function which is always defined positively: if f(x) 0 then |f(x)| = f(x), and if f(x) < 0 then |f(x)|= –f(x).
antiderivative: a function F(x) + c for which F (x) = f(x).
antilogarithm: The antilogarithm of a number a is the number whose logarithm is equal to a. x is the antilogarithm of log x: x = antilog (log x) or x = log–1(log x).
argument: 1. a variable in a mathematical expression whose value determines the dependent variable (such as x in f(x) = y). 2. the number or expression denoted by x in the logarithmic expression logax.
asymptote: a line which the graph of a function approaches but never touches.
addend: a number that is added to another number.
associative property: An operation is associative if you can group the numbers in the operation in any way without changing the answer. Addition and multiplication are both associative, since
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and a(bc) = (ab)c.
B
boundary: a curve or a point which limits a region or a line.
base: 1. a number (such as 5 in 57) that is raised to a power. 2. the number or expression denoted by a in the logarithmic expression logax.
basic exponential function: a function of the form f(x) = ax for a > 0, a 1.
basic logarithmic function: a function of the form f:(0, ) , f(x) = logax for a > 0, a 1.
bijection (bijective function): a mathematical function that is both one-to-one and onto.
binomial expansion: the set of terms in the expansion of a binomial expression which is raised to a particular power.
binomial expression: a mathematical expression which is the sum or difference of two terms.
bit: a basic unit of computer data that can take one of two values, such as 0 for false and 1 for true.
byte: a sequence of 8 bits which is processed as a single unit of information.
C
constant of integration: the constant term c which must be added when calculating an indefinite integral.
continuous function: a function whose graph is a continuous line, with no breaks.
characteristic: the integer part of a common logarithm. 2 is the characteristic of log 500 = 2.699.
cologarithm: the logarithm of the reciprocal of a positive number x, written colog x.
common logarithm: a logarithm to the base 10. The common logarithm of a number x is written as log x.
compound interest: interest which is calculated based on the sum of an original principal and any previous interest.
critical value: a value of a variable which makes all or part of an expression zero.
cube root: The cube root of a number x is the number whose cube is x. 2 is the cube root of 8 since 23 = 8.
coefficient: a number which is multiplied by a variable in an algebraic expression.
collinear: If two or more points are collinear, they are on the same straight line.
combination: a selection of objects chosen from a group without considering the order.
Answers to Exercises |
361 |

combination lock: a lock which can be opened only by turning a set of dials in a special sequence.
commutative property: An operation is commutative if you can change the order of the numbers in the operation without changing the result. Subtraction is not commutative, since 3 – 5 5 – 3.
complement of an event: the set of all outcomes in a sample space that are not in the event.
conditional probability: the probability of an event occurring if another related event has already occurred.
constant term: a term in an expression that does not change with the variable.
D
definite integral: the area between the graph of a continuous function f(x) on an interval [a, b] and the x-axis.
derivative: the rate of change of a function at a given point.
differentiable function: a function which has a derivative at a given point.
differential: the expression dx which shows the variable in an integral.
differentiation: the process of finding the derivative of a function.
discontinuity: a point at which a mathematical function is not continuous.
decibel scale: a scale based on common logarithms, which is used to measure the relative intensity of sounds.
decreasing function: a function whose value never increases as the value of the variable increases.
defective: if something is defective, it does not work properly.
dependent events: If the occurrence of an event A affects the probability of another event B then A and B are dependent events.
die (plural: dice): a small cube with spots on each face that show the numbers from 1 to 6.
dominant: In genetics, a dominant gene has priority over other genes.
E
e (Euler number): the irrational number 2.71828183..., which forms the base of natural logarithms.
equivalent: If two equations have the same solution set then they are called equivalent equations.
Euler logarithm: another name for a natural logarithm.
exponent: a number written above and to the right of an expression, which shows the power to which the expression should be raised. 2 is the exponent in both 32 and (x – 5)2.
exponential decay: a change in the amount of a quantity over time, which can be modeled by a decreasing exponential function.
exponential equation: an equation in which the variable appears in an exponent.
exponential function: a function whose independent variable is in the exponent, such as f(x) = ax for a > 0, a 1 or f(x) = c ad(x + p) + k for a, c, d, p, k and a > 0, a 1.
exponential growth: a change in the amount of a quantity over time, which can be modeled by an increasing exponential function.
equally likely: If the probabilities of two simple events are the same, then the events are said to be equally likely.
event: a set of possible outcomes resulting from a particular experiment.
experiment: an activity or process which has observable results. Rolling a die is an experiment.
F
floor function: a function which gives the greatest integer number which is smaller than the value of a given function.
362 |
Answers to Exercises |

fundamental theorem of calculus: the theorem that we use to find the definite integral of a function.
factorial: the product of a given integer and all smaller positive integers, shown with an exclamation mark (!). For example, 3! = 3 2 1 = 6.
H
half-life: the time required for half of the atoms in a radioactive substance to decay.
horizontal shift: moving a graph to the left or right without changing its shape.
horizontal shrink: changing the shape of a graph to fit a smaller horizontal scale.
horizontal stretch: changing the shape of a graph to a fit a bigger horizontal scale.
head (heads): the side of a coin which often has a picture of a person’s head on it. The opposite side is called tails.
I
indefinite integral: the set of all the antiderivatives of a function.
integrable function: a function which has an integral on a given interval.
integral: a mathematical term that can be interpreted as the area under a graph or as a generalization of this area.
integral sign: the sign that we use to show the integral of a function.
integrand: the algebraic expression under the integral sign.
integration: the process of finding the integral of a function.
integration by parts: a technique for finding an integral of the form u v dx by expanding the differential of a product of functions d(uv) and expressing the original integral in terms of a known integral.
interval: the set of all real numbers between two known numbers a and b, written [a, b].
inverse conversion formulas: the formulas for writing the product of two trigonometric functions as the sum or difference of two other trigonometric functions.
identity function: the function defined by f(x) = x.
increasing function: a function whose value never decreases as the value of the variable increases.
index (plural indices): 1. another word for exponent. 2. the number in a radical expression which shows the root to be extracted. 3 is the index in 3 64 .
injection (injective function): a mathematical function that is a one-to-one mapping.
integer: any number which is a member of the set {... –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}.
interest: a charge for borrowed money, or the profit in goods or money that is made on invested capital, calculated as a percentage of the borrowed money or capital.
interpolation: a way of estimating the value of a function between two points by assuming that the graph of the function is a straight line.
irrational number: any real number which cannot be expressed as a fraction.
identity function: a function whose output is identical to its input.
independent event: Two events are independent if the outcome of one event does not affect the outcome of the other.
intersection: the set of elements which are common to two or more sets.
L
Leibniz’s rule: a rule which gives a formula for the differentiation of a definite integral whose limits are functions of the differentiable variables.
lower limit: in a definite integral, the lower limit is the first number in the interval.
Answers to Exercises |
363 |

logarithm: The logarithm x of a number N to a base a is the power to which a must be raised in order to obtain N: x = logaN means ax = N.
logarithmic function: a function whose independent variable is in a logarithm, such as f(x) = logax. The inverse of a logarithmic function is an exponential function.
logarithmic spiral (equiangular spiral): a spiral whose radius grows exponentially with its angle to the x-axis. It is defined by the polar equation r = a eb where r is the distance from the origin, is the angle with the x-axis, and a and b are arbitrary constants.
lottery: a drawing of tickets or numbers at random in which prizes are given to the winning tickets or numbers.
M
Mean Value Theorem: a theorem that is used to find a number c in an interval [a, b] such that f(c) is the ratio of the definite integral on the given interval to the difference of a and b.
mantissa: the part of a logarithm which lies to the right of the decimal point. 0.699 is the mantissa of log 500 = 2.699.
monotone (monotonic) function: a function which is either increasing or decreasing.
mutually exclusive events: events that cannot happen together at the same time.
N
natural logarithm: a logarithm to the base e. The natural logarithm of a number x is written ln x.
natural number: any number which is a member of the set {1, 2, 3, ...}.
nth root: b is an nth root of a if and only if bn = a.
O
one-to-one function: a function for which f(x1) f(x2) for any x1 x2.
onto function: a function for which, for any y in the range, there is at least one x in the domain such that f(x) = y.
outcome: an observable result of an experiment.
P
partial fraction: when a complicated fraction is given we can write it as the sum of simpler fractions. These fractions are called partial fractions.
primitive of a function: the antiderivative of a function.
parameter: a variable that can be varied or changed in an expression.
pH scale: a scale which is used to measure the amount of acid in a solution. A low pH number represent a high acidity, and a high pH number represents a high basicity.
power: a number or expression which is the result of a number multiplying a number by itself, as indicated by an exponent. 8 is the third power of 2: 23 = 8.
principal: a sum of money which is borrowed or invested.
principal nth root: the positive nth root of a number. 2 and –2 are square roots of 4, but only 2 is the principal square root of 4.
palindrome: a word or phrase that reads the same backward as forward. 12421 is a palindromic number.
permutation: an ordered arrangement of some or all of the elements in a given set.
prime number: a number that can only be divided by itself and 1.
probability: a measure of how likely it is that an event will occur.
364 |
Answers to Exercises |
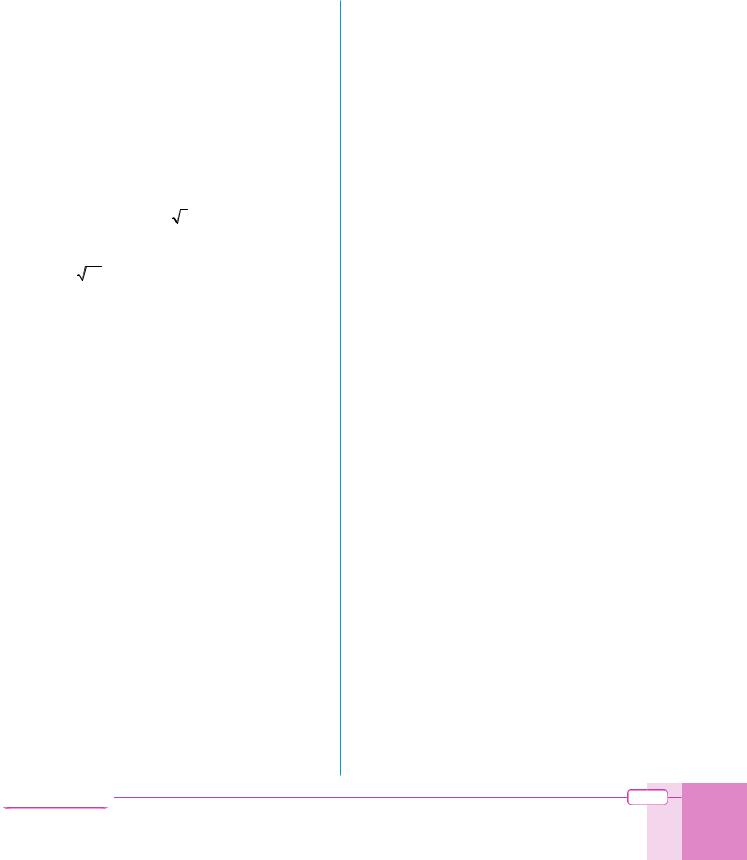
R
radical function: a function which contains one or more radical expressions such square roots, cube roots, etc.
rational function: a function which is written as the quotient of polynomials.
reducible function: a function that can be written in a simpler form, or as the multiplication of simpler functions.
radical sign: the sign ñ or n (where n is an integer greater than or equal to 2) in a radical expression.
radicand: the quantity under a radical sign. 27 is the radicand in 3 27 .
rational number: any real number which can be expressed as a fraction.
real number: any rational or irrational number.
reflection: changing the shape of a graph by reflecting it along a line.
Richter scale: a scale based on common logarithms which is used to describe the strength of an earthquake.
root of an equation (solution): a value of a variable in an equation which makes the equation true.
root of a number: a number which equals a given number when raised to an integer power. 3 and –3 are roots of 9.
random: If something is done or chosen at random it is done or chosen without any plan.
recessive: A recessive gene is a gene which is present in an organism but not dominant
S
sign function: a function that gives the sign of a function f(x). If f(x) is positive then the sign function has value +1, if f(x) is 0 then the sign is 0 and when f(x) is negative its signum is –1.
solid of revolution: a solid figure that is generated by rotating any curve or the graph of a function around the x or y axis.
substitution method: the method for finding the integral of a function by using different and suitable variables instead of x.
surface of revolution: the surface area of a solid of revolution.
scientific notation: a number in scientific notation is expressed as the product of a number between 1 and 10 and an appropriate power of 10. 1.591 × 103 is a number in scientific notation. 1591 is the same number in normal notation.
slide rule: a device used for multiplying and dividing numbers which makes use of the property log(ab) = log a + log b. A slide rule has a body and a slide marked with logarithmic scales, and a movable cursor.
square root: A square root of a number x is a number whose square is x, denoted by ñx. The square root of 9 is 3: ñ9 = 3.
surjection (surjective function): a mathematical function that is an onto function.
sample space: a list of all the possible outcomes of an experiment.
shuffle: if you shuffle a pack of cards, you mix it to make a random order or arrangement.
spinner: a small object in the shape of a polygon with a pin or stick through its center, which is used to make a random choice.
subset: a set which is contained in another set
successive: successive objects or actions follow in order one after another.
systematic: if an activity is systematic, it is done according to a careful plan in a methodical way.
T
tan x/2 substitution: a method for integrating a function which includes linear expressions of sin x and cos x by using the substitution t = tan (x/2).
Answers to Exercises |
365 |

trigonometric substitution: a method for finding the integral of a radical expression which includes expressions such as x2 ± a2 or a2± x2.
transcendental number: a number that is real but not algebraic, i.e. it is not a root of any polynomial equation with rational coefficients. e and are examples of transcendental numbers.
tail (tails): the reverse side of a coin that usually shows how much the coin is worth and which does not show the head of a person.
tree diagram: a schematic diagram that starts from a set of roots and shows all the possible outcomes of an event.
trial: a systematic opportunity for an event to occur.
U
upper limit: in a definite integral, the upper limit is the last number in the interval.
uniformity criterion: The uniformity criterion states that any part of a task can be done in the same number of ways.
union: the set of elements which are in any of a group of sets.
urn: a large, decorative container which is sometimes used to hold lottery tickets or other items which are chosen at random.
V
volume of revolution: the volume of a solid of revolution.
vertical shift: moving a graph upwards or downwards without changing its shape.
vertical shrink: changing the shape of a graph to fit a smaller vertical scale.
vertical stretch: changing the shape of a graph to a bigger vertical scale.
366 |
Answers to Exercises |
