
- •The ok accountant успешный бухгалтер
- •Contents
- •От авторов
- •Unit 1 What Is Accounting
- •Accounting
- •Exhibit 1. Users and Uses of Accounting Information
- •Information
- •|Unit 2. Evolution of accounting
- •Venture Trading
- •Early History
- •Unit 3 accounting profession
- •The Profession of Accounting in the usa
- •Nature of Accounting Work
- •The Changing Genderization of the Work Force
- •Unit 4 Bookkeeping getting started
- •Bookkeeping
- •2. Complete the following sentences by using Gerunds of the verbs in brackets; translate the sentences into Russian.
- •1. Referring to round figures
- •2. Percentages
- •5. Ratio
- •Drawings 3672.00
- •Unit 5 financial reporting
- •Financial Statements
- •The Balance Sheet
- •Text 3 The Income Statement
- •Intangible asset accounts receivable short-term liabilities bank debts
- •Snark International Balance Sheet
- •31 December ___
- •Supplementary reading Unit I What Is Accounting Accountancy
- •Early History of Accounting
- •The Forms that Companies Take
- •Changing Skills, Changing Job Titles
- •Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu
- •Real People Profiles
- •Interviewing Tips
- •Bookkeeping
- •Tapescripts
- •Dialogue 1
- •Dialogue 2
- •Answer Key
- •Appendix Guidelines to Summarizing and Abstracting Summaries
- •Steps in Summarizing
- •Abstracts
- •Introducing the subject / theme of the text:
- •Introducing the key ideas, facts and arguments:
- •● The author makes/gives a comparison of … with… / between … and…
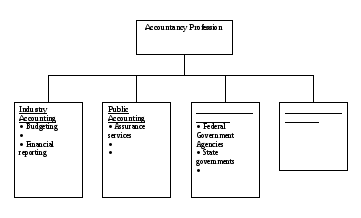
The Profession of Accounting in the usa
The four general fields of accountancy include (1) industry accounting, (2) public accounting, (3) governmental accounting and (4) education, each of which has several accounting specialty areas. In the USA close to 45 percent of accountants work in public accounting and 47 percent work in industry accounting. Of the remaining 8 percent, 6 percent work in governmental accounting and 3 percent in education.
Industry Accounting. A company employs an industry (or management) accountant to perform its internal (management) accounting activities and to prepare its financial reports. A high-level manager, such as the company’s controller, usually coordinates these activities. This manager frequently reports directly to the organization’s top management, such as the chief financial officer. The Certificate of Management Accounting (the CMA) is granted to those who meet specific educational and professional standards and who pass a CMA examination administered by the Institute of Management Accountants.
Management accounting activities encompass several areas: budgeting, cost accounting, and financial reporting, as well as designing and operating accounting systems, internal auditing, and tax accounting.
Public Accounting. A public accountant is an independent professional who provides accounting services to clients for a fee. Many accountants practice public accounting as individual practitioners; others work in public accounting firms, which include local and regional companies. In addition, to provide accounting to large corporations, some of which span the world in their activities, many large public accounting firms have offices in most international cities.
Most public accountants are certified public accountants (CPAs). A CPA has met certain state requirements and holds a license issued by the state in which he or she works. All CPAs must pass the Uniform CPA Examination given by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).
Decision-makers need assurance that the information they use is valid. Auditing evolved from a need for assurance services. Auditing involves the examination, by an independent CPA, of a company’s accounting records and financial statements. The CPA expresses a professional, unbiased opinion about the fairness of the accounting information in the financial statements.
Governmental Accounting. Certain governmental agencies also employ accountants. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS), for example, is responsible for the collection of the federal income taxes. State revenue agencies also perform similar functions. These agencies hire accountants to provide accounting information for use in administration of these activities.
Administrators of federal, state, municipal, and other not-for-profit organizations such as colleges and universities, hospitals, are responsible for the organizations’ efficient and effective operations. Being not-for-profit organizations financed in part by public funds, they are required to use somewhat different accounting procedures. These organizations hire accountants to design and operate their accounting systems.
How does a student prepare for the accounting profession? Persons considering entering the accounting profession should begin by doing some self-analysis to determine whether they enjoy mathematical, problem- or puzzle-solving, or other analytical activities; by taking some aptitude tests; or by talking with accounting teachers or practitioners about their work. Anyone interested in becoming an accounting professional should expect to enter a rigorous five-year education program and to earn a master’s degree in order to qualify to enter the profession and to sit for the CPA examination. To build a base for rising to the top of the profession, students should select courses that help them learn how to think and to define and solve problems. The courses should help them develop analytical (logical, mathematical, statistical), communication (oral, reading, writing), computer, and interpersonal skills. These skills greatly enhance and facilitate all aspects of what accountants attempt to do.
Chart 1. Accountancy Profession in the USA
 2.
Complete the sentences by matching the beginnings with appropriate
endings.
2.
Complete the sentences by matching the beginnings with appropriate
endings.
|
1) A person considering entering the accounting profession should 2) Anyone wishing to become an accounting professional in the USA expects to 3) Industry accountants 4) Public accountants 5) Government accountants 6) Not-for-profit organizations |
a. perform management accounting activities and prepare a company’s financial reports. b. enter a 5-year education program and sit for the CPA examination. c. use different accounting procedures. d. provide accounting services to clients for a fee. e. analyze his/her capabilities and take aptitude tests. f. work for government agencies and not-for-profit organizations. |
3. Answer the following questions.
1) What areas of accountancy are distinguished in the USA?
2) What is the percentage of accountants working in each area?
3) What professional qualification is granted to those who meet specific professional standards in industry accounting?
4) What activities does industry accounting involve?
5) What is the difference between industry accountants and public accountants?
6) How does one become a CPA in the USA?
7) Why did auditing evolve?
8) Who performs auditing functions in the USA?
9) What governmental agencies employ accountants?
10) What functions do government accountants perform?
11) Why are accounting procedures in not-for-profit organizations different from those in profit-seeking organizations?
12) What skills are deemed necessary for a modern accountant?
Describe the accountancy profession in the USA, using Chart 1.
Text 2
1. Read the text and pick out the accounting careers mentioned; arrange them in the hierarchy.
