
- •The ok accountant успешный бухгалтер
- •Contents
- •От авторов
- •Unit 1 What Is Accounting
- •Accounting
- •Exhibit 1. Users and Uses of Accounting Information
- •Information
- •|Unit 2. Evolution of accounting
- •Venture Trading
- •Early History
- •Unit 3 accounting profession
- •The Profession of Accounting in the usa
- •Nature of Accounting Work
- •The Changing Genderization of the Work Force
- •Unit 4 Bookkeeping getting started
- •Bookkeeping
- •2. Complete the following sentences by using Gerunds of the verbs in brackets; translate the sentences into Russian.
- •1. Referring to round figures
- •2. Percentages
- •5. Ratio
- •Drawings 3672.00
- •Unit 5 financial reporting
- •Financial Statements
- •The Balance Sheet
- •Text 3 The Income Statement
- •Intangible asset accounts receivable short-term liabilities bank debts
- •Snark International Balance Sheet
- •31 December ___
- •Supplementary reading Unit I What Is Accounting Accountancy
- •Early History of Accounting
- •The Forms that Companies Take
- •Changing Skills, Changing Job Titles
- •Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu
- •Real People Profiles
- •Interviewing Tips
- •Bookkeeping
- •Tapescripts
- •Dialogue 1
- •Dialogue 2
- •Answer Key
- •Appendix Guidelines to Summarizing and Abstracting Summaries
- •Steps in Summarizing
- •Abstracts
- •Introducing the subject / theme of the text:
- •Introducing the key ideas, facts and arguments:
- •● The author makes/gives a comparison of … with… / between … and…
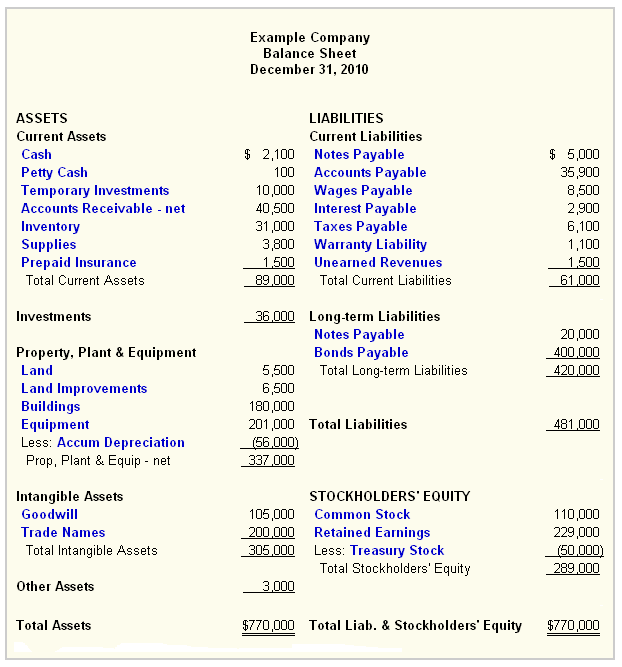
The Balance Sheet
The Balance sheet is a listing of the organization’s resources (assets), obligations (liabilities), and owner’s claims (equity) at a point in time. In this sense, the balance sheet is like a snapshot of the organization’s financial position, frozen at a specific point in time.
Assets are resources that a company owns that have value. This typically means they can either be sold or used by the company to make products or provide services that can be sold. Assets are generally listed based on how quickly they will be converted into cash. Current assets are things a company expects to convert to cash within one year. Typical current assets include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, inventory and the portion of prepaid liabilities which will be paid within a year. Noncurrent assets include fixed assets that are used to operate the business but not available for sale, such as plants, trucks, equipment, and office furniture.
Assets are frequently tangible – they can be seen or handled (e.g., cash, merchandise inventory, or equipment), or evidence of their existence can be observed (e.g. accounts receivable). Intangible assets include goodwill, patents, copyrights, trademarks, franchises, and similar valuable but nonphysical things controlled by the business.
Liabilities are amounts of money that a company owes to others. This can include all kinds of obligations, like money borrowed from a bank to launch a new product, rent for use of a building, money owed to suppliers for materials, payroll a company owes to its employees, environmental cleanup costs, or taxes owed to the government. Liabilities also include obligations to provide goods or services to customers in the future.
Liabilities are generally listed based on their due dates. Liabilities are said to be either current or long-term. Current liabilities are obligations a company expects to pay off within the year. Long-term liabilities are obligations due more than one year away.
Owners’ equity is sometimes referred to as net assets, or net worth. It’s the money that would be left if a company sold all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities. This leftover money belongs to the shareholders, or the owners, of the company. The owners’ equity section of a corporation is called stockholders’ equity and has two parts: contributed and earned capital, or retained earnings.
The following equation summarizes what a balance sheet shows:
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNERS' EQUITY
A company's assets have to equal, or "balance," the sum of its liabilities and shareholders' equity.
A company’s balance sheet is set up like the basic accounting equation shown above. On the left side of the balance sheet, companies list their assets. On the right side, they list their liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Sometimes balance sheets show assets at the top, followed by liabilities, with shareholders’ equity at the bottom.
2. Say if the following statements are true or false.
1) The balance sheet is often compared with a moving picture of the organization’s financial performance.
2) Noncurrent assets are fixed assets available for sale.
3) Tangible assets include goodwill, patents, copyrights, trademarks, etc.
4) Money owed to suppliers is listed under liabilities.
5) Obligations that a company expects to pay off within a year are long-term liabilities.
6) On the balance sheet company’s assets have to equal liabilities plus owner’s equity.
7) Net worth is the money left if the company sells all its assets and paid all its liabilities.
3. Answer the following questions.
1) What comparison is commonly used to describe the meaning of the balance sheet?
2) How are assets classified?
3) What is the difference between current and noncurrent assets?
4) What current assets are shown on the sample balance sheet given?
5) What does the word intangible mean and why is it used as a term to denote such assets as goodwill and copyrights?
6) In what order are liabilities listed?
7) What long-term liabilities are represented on the example balance sheet?
8) What is owner’s equity?
9) What has to be “balanced” on a company’s balance sheet?
10) What are the possible varieties of arranging data on the balance sheet?
