
Higher_Mathematics_Part_2
.pdfThe general solution of the initial equation is:
y= (C1 cos x + C2 sin x)e2x + e2x .
11.Find the general solution if the right hand member not zero equation y′′ − 7 y′ + 6 y = (x − 2)e x .
Solution . Evaluate the homogeneous equation at first y′′ − 7 y′ + 6y = 0 .
We would obtain:
k2 −7k +6 = 0; k1 =1; k2 = 6; y = C1ex +C2 e6x .
Control number of the right side of right hand member not zero equation z = 1 is simple root of the characteristic equation (divisible by r = 1).
Partial solution of right side member not zero equation according to the 3.2 table 3.4 could by found in a form
|
|
|
y* = x(B |
0 |
+ B x)e x = (B |
0 |
x + B x2 )e x . |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|||
Find derivatives y′* |
and |
|
|
y′′* : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
y′* = (B |
0 |
+ 2B x)e x + (B |
0 |
x + B x2 )e x , |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
y′′* = 2B e x |
+ 2(B |
0 |
+ 2B x)e x + (B |
0 |
x + B x2 )e x , |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
||||
after substituting |
y* , y′* |
and |
|
y′′* in the initial equation |
|||||||||||||
|
|
e x (2B + 2(B |
0 |
+ 2B x) + (B |
0 |
x + B x2 )) − |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|||
− 7e x (B |
0 |
+ 2B x + (B |
0 |
x + B x2 )) + 6(B |
0 |
x + B x2 )e x = (x − 2)e x . |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||||
After simplifying we would obtain the equation: −10B1x + 2B1 − 5B0 = x − 2.
Comparing the coefficients of the same order x :
x1 : |
− 10B1 = 1, |
|
from this |
|
|
|
− 5B0 |
|
|
x0 : 2B1 |
= −2, |
|
||
The general solution of initial equation is:
|
|
|
9 |
|
x |
2 |
|
y = C e x + C |
2 |
e6x + |
x − |
|
e x . |
||
|
|
|
|||||
1 |
|
25 |
10 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
12. Solve the Cauchy’s test
y′′ − 5y′ + 6y = 13sin 3x, |
y(0) = 1, |
y′(0) = 0 . |
|
Solution. Characteristics equation k 2 − 5k + 6 = 0 |
has roots e2x , e3x – |
||
fundamental system |
|
|
|
The general solution of homogeneous equation y′′ − 5y′ + 6y = 0 . Then |
|||
y = C e2x + C |
2 |
e3x . |
|
1 |
|
|
|
221 |
|
|
|

Right side of these equation can be written in such a form : 13sin 3x = e0 x (0 cos 3x + 13sin 3x),
then control value of right |
side z = 0 +3i =3i, . So for |
this case in formula |
||||||||||||||
(3.29) Pn (x) = 0, Qm (x) =13. |
Because z = 3i |
|
is not a root of characteristics |
|||||||||||||
equation then we would obtain partial solution in such a form |
|
|
||||||||||||||
y* = A cos 3x + B |
0 |
sin 3x . |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Find derivatives : |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y′* = −3A sin 3x + 3B |
0 |
cos 3x, |
y′′* = −9A cos 3x − 9B |
0 |
sin 3x. |
|||||||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
||
After putting the values |
y* , y′* and y′′* and simplifying in initial equation |
|||||||||||||||
we would obtain. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−3(A0 + 5B0 ) cos 3x + 3(5A0 − B0 ) sin 3x = 13sin 3x. |
||||||||||||||||
Compare the coefficients |
|
when sin 3x and cos 3x : |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
− 3(A0 + 5B0 ) = 0 |
A0 = |
5 |
, B0 = − |
1 |
. |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
6 |
|
|
||||||||
3(5A0 − B0 ) = 13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Therefore, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y* = |
5 |
cos 3x − |
1 |
sin 3x |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
6 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
is a partial solution of right hand member not zero equation, and general solution of those equation can be written as follows:
y = y + y* = C1e2x + C2e3x + 16 (5cos 3x − sin 3x).
And now we would consider such constants C1 and C2 . Condition y(0) =1 can be written as follows:
|
1=C +C + |
5 |
. |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
||
Thus, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y′ = 2C e2x + |
3C |
e3x |
− |
1 |
(5sin 3x +cos 3x) , |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
and condition y′(0) = 0 is equivalent to the equation 0 = 2C +3C |
2 |
−0, 5 . |
||||||||||||
After solution of this linear system |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
+C2 + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
C1 |
6 |
=1, |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
−0.5 = 0, |
|
|
||||||
|
2C +3C |
2 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
we would obtain C = 0, |
C = |
1 |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6
In this case the solution of Cauchy’s test will be obtained: 222

|
|
|
|
|
|
−2x |
|
|
|
−3x |
= 0, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
C ′e |
+C ′e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
C ′(−2e−2x ) +C |
′(−3e−3x ) = |
|
; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
= |
|
e−2x |
|
e−3x |
|
= −e−5x , |
|
|
|
1 = |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
e−3x |
|
|
= − |
|
|
e−3x |
, |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
−3e−3x |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
−2e−2x −3e−3x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+e2x |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+e2x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
e−2x |
0 |
|
|
|
|
−2x |
|
|
|
|
2x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3x |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
= |
|
− 2e |
− |
2x |
1 |
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
; |
C′ |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
C |
′ |
= − |
|
|
|
|
; |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+ e |
2x |
|
|
1 |
1 |
+ e |
2x |
|
|
2 |
|
1+ e |
2x |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1+ e2x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
C = |
|
|
e2x |
dx = |
1 |
|
d(e2x |
+ 1) |
= |
1 |
ln(1+ e2x ) + C |
|
; |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
∫ 1+ e2x |
2 ∫ e2x |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
+ 1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
C =− |
|
e3x dx |
= |
ex = t |
=− |
|
t2 dt |
|
|
=−(t −arctg t) |
+C |
4 |
= |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
2 |
|
∫ 1 |
+e2x |
|
ex dx = dt |
|
∫ 1+t2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
So, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
=−(ex −arctg ex ) +C4 . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
−2x |
1 |
|
|
|
2x |
|
|
|
|
|
−3x |
|
x |
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
y = e |
|
|
|
|
ln(1+e |
|
|
) +C3 |
−e |
e |
|
|
−arctg e |
|
+C4 |
|
– |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is the general solution of the given equation where, |
C3 ,C4 |
|
are |
arbitrary |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
constants. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Т.3 |
|
|
|
Class and self assignments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Find the general solutions of the given homogeneous equations.
1. |
y′′ − 3y′ + 2y = 0 . |
2. |
y′′ − 6y′ + 8y = 0 . |
||
3. |
y′′ − 2y′ + y = 0 . |
4. |
y′′ + 4y′ + 4y = 0 . |
||
5. |
y′′ − 2y′ + 2y = 0 . |
6. |
y′′′ − y′′ − y′ + y = 0 . |
||
7. |
y′′ + y′ + y = 0 . |
8. |
y′′′ − 3y′′ + 3y′ − y = 0 . |
||
9. |
y′′′ + y = 0 . |
10. |
y (4) |
+ y = 0 . |
|
11. |
y (4) |
+ 5y′′ + 4y = 0 . |
12. |
y (5) |
+ 8y′′′ + 16y′ = 0 . |
13. |
y (5) |
− 5y (4) + 12 y′′′ − 16y′′ + 12 y′ − 4y = 0 . |
|
||
Find the general solutions of the right hand member not zero equations.
14. y′′ − 7 y′ + 12y = 5 . |
15. y′′ − 7 y′ + 6y = sin x . |
16. y′′ + y′ + y = 3e2x . |
17. y′′ + 2y′ − 3y = 4e− x . |
|
224 |

18.y′′ − 8y′ + 7 y = 3x2 + 7x + 8 .
19.y′′ − 2y′ + 4y = (x + 2) e3x .
20.y′′ − 2y′ = x3 + 2x − 1 .
21.y′′ − 6y′ + 25y = 2 sin x + 3 cos x .
22.y′′ + y = (3x + 2) sin 2x + (x 2 + x + 2) cos 2x .
23.y′′ + 4y = sin 2x .
24.y′′′ − y′′ = −3x + 1 .
25.y′′ − 2y′ + y = 4e x .
26.y′′ + y = xe x + 2e− x .
Find the general solutions of the right hand member not zero equations by the method of arbitrary constants variation.
27.y′′ + y = sin1 x .
28.y′′ − y′ = 2 − x e x .
x3
Solve using Cauchy’s method.
29. |
y ′′+4y ′+4 y = 3e−x , y(0) = y′(0) = 0 . |
30. |
y′′+4y =sin 2x , y(0) = y′(0) = 0 . |
 Answers
Answers
1. |
y = C1e x + C2e2x . |
|
|
|
|
2. y = C1e2x + C2e4x . |
|
3. y = C1e x + C2 xe x . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
4. |
y = (C1 + C2 x)e−2x . |
|
5. y = (C1 cos x + C2 sin x) e x . 6. |
y = C1e x + C2 xe x + C3e− x . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
x . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
y = (C1 cos |
3 |
x + C |
|
|
|
3 x) e− |
|
|
|
|
y = C1e x + C2 xe x + C3 x 2e x . |
|||||||||||||||||||
7. |
2 sin |
|
2 |
|
8. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
y = C1e− x + (C2 cos |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
2 |
x (C1 cos |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
||||||
9. |
|
|
x + C3 sin |
|
x)e 2 . |
10. |
y = e |
|
2 |
x + C2 sin |
x) + |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
− |
2 |
x |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y = C1 sin x + C2 cos x + C3 sin 2x + |
||||||||||
+e |
2 |
(C3 cos |
|
x |
+C4 sin |
x) . |
11. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
2 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. y = C1ex + |
||||||
+C4 cos 2x . |
|
|
12. |
y = C1 + (C2 + C3 x) cos 2x + (C4 + C5 x) sin 2x . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
+C2ex cos x + C3ex sin x + C4xex cos x + C5xex sin x . |
|
|
|
14. y = C1e3x + C2e4x + |
5 |
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|||
225

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
x (C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
15. |
y = C ex + C |
e6x + |
7 |
|
|
|
5 |
sin x . |
|
|
|
16. |
y = e− |
|
cos 3 x + C |
|
|
|
|
3 x) + 3 e2x . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
cos x + |
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
sin |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
74 |
|
|
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
17. |
y = C e x |
+ C |
2 |
e−3x |
− e− x . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. |
y = C ex + C |
e7x + |
3 |
x2 |
+ |
97 |
x + |
1126 |
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
343 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
19. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
3x 1 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
20. y |
= C1 + C2e |
2x |
− |
1 |
x |
4 |
− |
1 |
|
x |
3 |
− |
||||||||||||||||||
y = (C1 cos |
|
|
3x + C2 sin |
|
3x)e |
|
+ e |
|
|
|
x + |
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7 |
|
49 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
− |
7 |
x2− |
3 |
x .21. y = e3x (C |
cos 4x + C |
2 |
sin 4x) + |
14cos x + 5sin x |
. |
|
|
22. y = C cos x + C |
sin x − |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
102 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
− |
9x2 + 9x + 28 |
cos 2x − |
x + 2 |
sin 2x . |
|
23. |
y = C cos 2x + C sin 2x − |
1 |
x cos 2x . |
|
24. y = C ex |
+ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
+C |
2 |
+ C x + |
x3 + x2 . |
|
|
25. y = (C |
+ C |
2 |
x)e x |
+ 2x 2e x . |
26. y = C cos x + C |
2 |
sin x + |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
+e− x + |
|
1 |
(x − 1)ex . 27. y = (C |
+ ln |
|
sin x |
|
) sin x + (C |
2 |
− x) cos x . |
28. |
y = |
ex |
+ C + |
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
+C2ex |
. 29. y =1,5x2e−2x . 30. |
|
y = − |
cos 2x + |
sin 2x . |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Т.3 |
|
Individual tasks |
|
|
3.1. Find the general solutions of |
linear homogeneous equations |
|||
3.1.1. а) |
y′′ + y′ − 2y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 2y′ + 5y = 0 . |
|
3.1.2. а) |
y′′ − 4y′ = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ + 4y′ + 4y = 0 . |
|
3.1.3. а) |
2y′′ − y′ − y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 2y′ + 10y = 0 . |
|
3.1.4. а) |
y′′ + 6y′ + 13y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 4y′ + 4y = 0 . |
|
3.1.5. а) |
2y′′ − 3y′ − 5y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ + 2y′ + 10y = 0 . |
|
3.1.6. |
а) |
y′′ − 9y = 0 ; |
б) |
3y′′ + 12y′ + 15y = 0 . |
3.1.7. |
а) |
y′′ − 2y′ − 3y = 0 ; |
б) |
3y′′ − 4y′ + 4y = 0 . |
3.1.8. |
а) |
4y′′ + 4y′ + 5y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ + 8y′ + 16y = 0 . |
3.1.9. |
а) |
4y′′ − 8y′ + 5y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 8y′ + 20y = 0 . |
3.1.10. а) |
y′′ − 4y′ + 5y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 6y′ + 8y = 0 . |
|
3.1.11. а) |
y′′ − 4y′ + 29y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 7 y′ + 10y = 0 . |
|
3.1.12. а) |
4y′′ − 4y′ + y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ + 2y′ + 5y = 0 . |
|
3.1.13. а) |
y′′ + 7 y′ + 12y = 0 ; |
б) |
4y′′ + 4y′ + y = 0 . |
|
3.1.14. а) |
y′′ + 2y′ − 8y = 0 ; |
б) |
9y′′ − 12y′ + 4y = 0 . |
|
3.1.15. а) |
4y′′ − 12y′ + 9y = 0 ; |
б) |
5y′′ − 6y′ + 5y = 0 . |
|
3.1.16. а) |
y′′ + y′ + y = 0 ; |
б) |
y′′ − 4y′ = 0 . |
|
|
|
|
226 |
|
3.3. Find general the solutions of linear homogeneous equations with right part of special form.
3.3.1. |
y′′ − 2 y′ + y = xe x . |
3.3.2. |
y′′ + y = x sin x . |
|
3.3.3. |
y′′ − 6 y′ + 9 y = e x sin x . |
3.3.4. |
y ′′+2 y′+5y = ex sin 2x . |
|
3.3.5. |
y′′ − 6 y′ + 9 y = 2x2 − 2x + 3 . |
3.3.6. |
y′′ − 2y′ + 2 y = e x cos x . |
|
3.3.7. |
y′′ + 4 y′ + 5y = x2 + 3 . |
3.3.8. |
y′′ − 3y′ + 2y = 2xe x . |
|
3.3.9. |
y′′ + 2 y′ = 2 + x − x2 . |
3.3.10. |
4y′′ − 16y′ + 15y = e1,5x . |
|
3.3.11. |
y′′ + 4y′ + 4y = e−2x + e x . |
3.3.12. y′′ − y′ = 2x2 . |
||
3.3.13. |
y′′ + y′ = e− x + x + 1 . |
3.3.14. y′′ + 2y′ + 10y = xe− x . |
||
3.3.15. |
y′′ + y′ − 2y = e x cos x . |
3.3.16. y′′ + 2y′ + y = e− x + sin x . |
||
3.3.17. |
y′′+4y = cos 2x . |
3.3.18. y′′ + 9y = xe3x . |
||
3.3.19. |
y′′ − 2y′ + 2y = e x sin 2x . |
3.3.20. |
y′′ + 9y = e3x . |
|
3.3.21. |
y′′ − 2y′ + y = e x . |
3.3.22. y′′ − 3y′ = 1 − 2x − x2 . |
||
3.3.23. |
y′′ + 4y′ − 5y = xe x . |
3.3.24. y′′ − 4y′ + 4y = e2x . |
||
3.3.25. |
y′′ + 2y′ + 2y = (x + 1)e x . |
3.3.26. y′′ + 2y′ + 5y = cos x . |
||
3.3.27. y′′ + 4y′ + 3y = e− x + x2 . |
3.3.28. y′′ + 4y′ + 8y = cos 2x . |
|||
3.3.29. y′′ − 3y′ + 2y = e2x . |
3.3.30. y′′ − 8y′ = sin 4x + x . |
|||
3.4. Solve Cauchy’s test for equations of the second order. |
||||
3.4.1. y′′ + 4y′ + 8y = sin 4x , |
y(0) = 0 , |
y′(0) = 1. |
||
3.4.2. y′′ − 3y′ + 2y = e x , |
y(0) = 2 , |
y′(0) = 1. |
||
3.4.3. y′′ + y′ + y = cos 2x , |
y(0) = −1, |
y′(0) = 3 . |
||
3.4.4. y′′ − 4y′ + 3y = x2 − 3x , |
y(0) = 2 , |
y′(0) = 4 . |
||
3.4.5. y′′ + 2y′ + 5y = e2x , |
y(0) = 0 , |
y′(0) = 0 . |
||
3.4.6. y′′ − 10 y′ + 9 y = xe x , |
y(0) = 1 , |
y′(0) = 0 . |
||
3.4.7. |
y′′ − 4y′ + 4y = e2x , |
y(0) = 1 , |
y′(0) = 1. |
|
3.4.8. |
y′′ − 2y′ + 2y = 3x − 2 , |
y(0) = −2 , |
y′(0) = 2 . |
|
3.4.9. |
y′′ + 5y′ − 6y = e4x , |
y(0) = 3 , |
y′(0) = 2 . |
|
3.4.10. y′′ + 2y′ + 10y = x2 − 4 , |
y(0) = 0 , |
y′(0) = 4 . |
||
3.4.11. y′′ − 4y′ = x2 − 5x + 2 , |
y(0) = 0 , |
y′(0) = −1 . |
||
3.4.12. y′′ − 2y′ + y = e x , |
y(0) = 3 , |
y′(0) = 5 . |
||
3.4.13. y′′ + 9y = sin 3x , |
y(0) = 2 , |
y′(0) = −1 . |
||
3.4.14. y′′ + 2 y′ + 2 y = e x sin 3x , |
y(0) = 1 , |
y′(0) = 3 . |
||
|
228 |
|
|
|
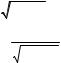

3.5.17. y′′ − 4y′ + 5y = |
e2x sin x |
. |
|
3.5.18. |
y′′ − 4y′ + 4y = |
|
x |
e2x . |
|||||||
|
|
|
sin2 x + 1 |
|
|
|
|
x |
+ 1 |
|
|
||||
3.5.19. y′′ − 4y′ + 5y = |
|
|
e2x |
. |
3.5.20. y′′ + 2y′ + y = e− x arctg x . |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 + sin 2 x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3.5.21. y′′ + 2y′ + y = |
|
e |
− x |
|
3.5.22. |
y′′ − 3y′ + 2y = |
|
e x |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|||||
x2 |
|
|
|
|
e x + |
|
|||||||||
|
|
− 1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
||||||||
3.5.23. y′′ + 3y′ + 2y = cos(e x ) . |
|
3.5. 24. |
y′′ + 4 y′ + 3y = arctg(ex ) . |
||||||||||||
3.5.25. y′′ + y = |
sin x |
. |
|
3.5.26. y′′ + 2y′ + y = e− x ln x . |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
cos2 x − |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
cos 3x |
|
|
||||
3.5.27. y′′ + 2y′ + y = 3 |
xe− x . |
|
3.5.28. |
y′′ + 9y = |
. |
|
|||||||||
|
sin2 3x + 1 |
|
|||||||||||||
3.5.29. y′′ − 2y′ + y = ex |
1− x . |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
3.5.30. y′′ + 5y′ + 6 y = e− x ln(1 + e x ) .
Topic 4. Simultaneous differential equations
Normal simultaneous differential equations. Methods of eliminating and integrated combinations of solving simultaneous differential equations in normal form. Simultaneous differential equations with constant coefficients. Generalized Euler’s method.
Literature: [2, 3, chapter 3.3], [3, chapter 8, §6], [4, chapter 8, § 26], [6, chapter 11, item 11.5], [7, chapter 13, §§29—30], [8, 2 chapter, §§6].
Т.4 |
General theoretical information |
|
|
4.1. Normal simultaneous differential equations
Simultaneous differential equations of 1st kind (or first order):
|
dy1 |
= |
f |
|
(t, y |
, |
y |
|
|
, .., y |
|
|
), |
|
|||||
|
|
2 |
n |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
dt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dy2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= f2 (t, y1 |
, y2 |
, .., yn ), |
(3.33) |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
dt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dyn |
|
= |
f |
n |
(t, y |
, y |
2 |
, .., y |
n |
), |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
dt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
230 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
