
Теория управления / Л4-Миль-Мур-СА / pics / 6-sequential logic-31
.pdf
example
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
old |
|
new |
|
|
|
|
state |
|
state |
|
output |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
8 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
4 |
5 |
7 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
5 |
6 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
6 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
7 |
4 |
7 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
8 |
2 |
6 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A.J. Han Vinck |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 1:
Group together states with same outputs
(1,3,6,8) (2,5) (4,7)
Step 2: further subdivide groups into subgroups with same transition
(1,3,6,8) (2,5) (4) (7)
STOP:
4 Representants: 1, 2, 4, 7
41

Example: reduced table
|
|
|
input |
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
old |
|
|
new |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
state |
|
|
state |
|
|
|
output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
|
4 |
|
2 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
7 |
|
4 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
A.J. Han Vinck |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Another example
Old state |
new state |
output |
|||
|
|
input = 0 |
|
input = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
A |
|
B |
|
C |
0 |
B |
|
A |
|
C |
0 |
C |
|
D |
|
C |
0 |
D |
|
D |
|
E |
1 |
E |
|
A |
|
F |
0 |
F |
|
B |
|
G |
0 |
G |
|
A |
|
E |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 1: Group together: same output
[ A B C E F G] [D]
Step 2: group according to transition
[A,B,E,F,G] [C] [D]
Step 2: group according to transition
[A,B] [E,F,G] [C] [D]
Step 2: group according to transition [A,B] [E,F,G] [C] [D]
no change: END
DEF: two states are equivalent if and only if, for any input of length k, k > 0, they give rise to the same output.
A.J. Han Vinck |
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
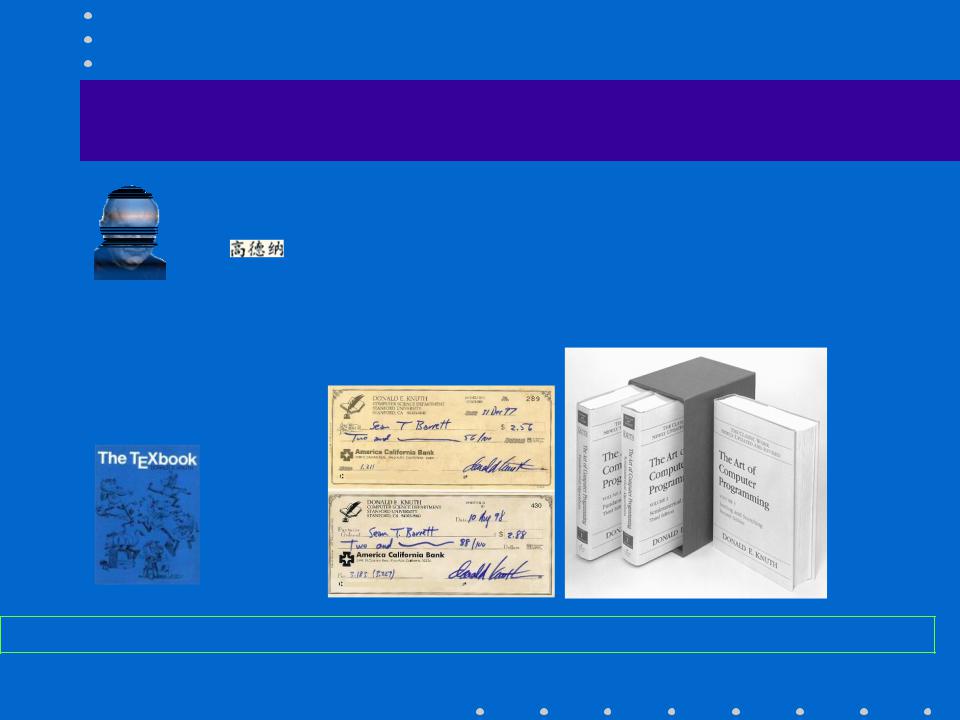
A famous computer scientist
http://www-cs-faculty.stanford.edu/~knuth/
Donald E. Knuth
Professor Emeritus of The Art of Computer Programming at Stanford University
The Art of Computer Programming (TAOCP)
Famous quote: Beware of bugs in the above code; I have only proved it correct, not tried it.
A.J. Han Vinck |
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

example
•Check for sub-string 100 in a binary sequence
Example: input |
00101000100000 |
|
output |
00001000100000 |
time: |
Binary input sequence |
|
–Output = 1 if 100 detected |
|
|
–Output = 0 otherwise |
clock
•Every time unit, the system
–Output = 1 if true
–Output = 0 otherwise
A.J. Han Vinck |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

example
Keep 2 bits in memory and look for the next input:
Example: input |
00101000100000 |
|
output |
00001000100000 |
time: |
State table
Old state ( xt-1 xt-2) |
new state(xt xt-1 ) |
output |
= xt xt-1‘ xt-2‘ |
|||
|
|
input xt |
input xt |
|||
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|||
00 |
00 |
|
10 |
0 |
|
1 |
10 |
01 |
|
11 |
0 |
|
0 |
01 |
00 |
|
10 |
0 |
|
0 |
11 |
01 |
|
11 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 equivalent to 11
A.J. Han Vinck |
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
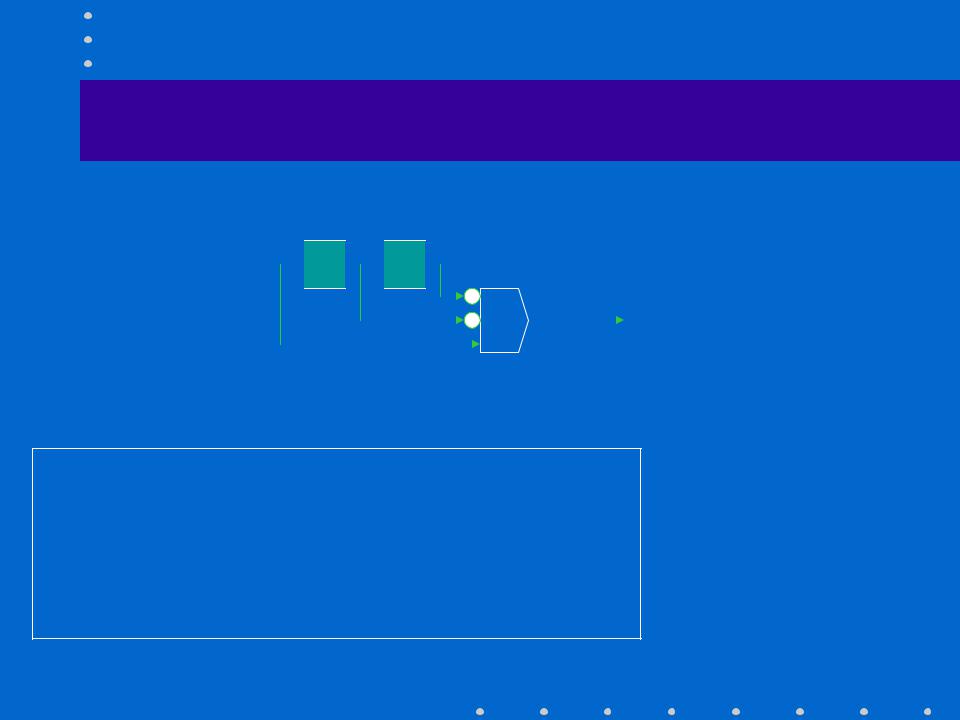
Example implementation
input xt xt-1
xt-1 xt-2
xt-2
Output = xt xt-1‘ xt-2‘
Homework:
Consider the table with reduced number of state
What are the consequences for the implementation?
Draw the Markov state diagram(also in the reduced form)
A.J. Han Vinck |
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
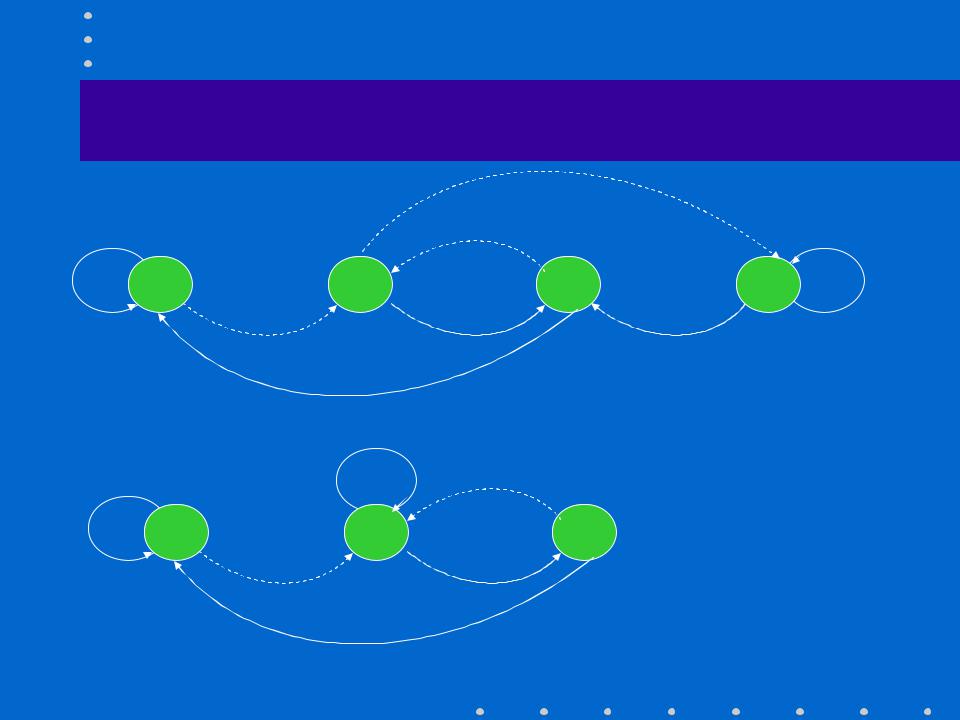
Example, state diagram
State: last 2 incoming bits
Output: 0 or 1
0 |
00 |
10 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Reduced state diagram |
|
|
Output: 0 or 1 |
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
00 |
10/11 |
|
1 |
|
0
0
0
01 |
11 |
0 |
0
0
0 |
|
Q: how many 1‘s do you |
|
|
expect in the output? |
|
01 |
Q: does it depend on the |
0 |
|
|
|
probability of 1 and 0 in |
|
|
|
the input sequence? |
|
|
|
A.J. Han Vinck |
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

We end with shift registers and counters
1.basic registers (serial-parallel)
2.some applications
3.counters
A.J. Han Vinck |
49 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

A basic register
|
|
|
A.J. Han Vinck |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
