
- •Contents
- •Symbols and Abbreviations
- •Symbols
- •Greek Symbols
- •Subscripts
- •Abbreviations
- •Preface
- •Road Map of the Book
- •The Arrangement
- •Suggested Route for the Coursework
- •First Semester
- •Second Semester
- •Suggestions for the Class
- •Use of Semi-empirical Relations
- •1 Introduction
- •1.1 Overview
- •1.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •1.1.2 Coursework Content
- •1.2 Brief Historical Background
- •1.3 Current Aircraft Design Status
- •1.3.1 Forces and Drivers
- •1.3.2 Current Civil Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.3.3 Current Military Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.4 Future Trends
- •1.4.1 Civil Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.4.2 Military Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.5 Learning Process
- •1.6 Units and Dimensions
- •1.7 Cost Implications
- •2 Methodology to Aircraft Design, Market Survey, and Airworthiness
- •2.1 Overview
- •2.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •2.1.2 Coursework Content
- •2.2 Introduction
- •2.3 Typical Design Process
- •2.3.1 Four Phases of Aircraft Design
- •2.3.2 Typical Resources Deployment
- •2.3.3 Typical Cost Frame
- •2.3.4 Typical Time Frame
- •2.4 Typical Task Breakdown in Each Phase
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Study Phase (Feasibility Study)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design Phase (Full-Scale Product Development)
- •2.4.1 Functional Tasks during the Conceptual Study (Phase 1: Civil Aircraft)
- •2.4.2 Project Activities for Small Aircraft Design
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Design (6 Months)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design (Product Development) (12 Months)
- •2.5 Aircraft Familiarization
- •Fuselage Group
- •Wing Group
- •Empennage Group
- •Nacelle Group
- •Undercarriage Group
- •2.6 Market Survey
- •2.7 Civil Aircraft Market
- •2.8 Military Market
- •2.9 Comparison between Civil and Military Aircraft Design Requirements
- •2.10 Airworthiness Requirements
- •2.11 Coursework Procedures
- •3 Aerodynamic Considerations
- •3.1 Overview
- •3.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •3.1.2 Coursework Content
- •3.2 Introduction
- •3.3 Atmosphere
- •3.4 Fundamental Equations
- •3.5.1 Flow Past Aerofoil
- •3.6 Aircraft Motion and Forces
- •3.6.1 Motion
- •3.6.2 Forces
- •3.7 Aerofoil
- •3.7.1 Groupings of Aerofoils and Their Properties
- •NACA Four-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Five-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Six-Digit Aerofoil
- •Other Types of Aerofoils
- •3.9 Generation of Lift
- •3.10 Types of Stall
- •3.10.1 Gradual Stall
- •3.10.2 Abrupt Stall
- •3.11 Comparison of Three NACA Aerofoils
- •3.12 High-Lift Devices
- •3.13 Transonic Effects – Area Rule
- •3.14 Wing Aerodynamics
- •3.14.1 Induced Drag and Total Aircraft Drag
- •3.15 Aspect Ratio Correction of 2D Aerofoil Characteristics for 3D Finite Wing
- •3.16.1 Planform Area, SW
- •3.16.2 Wing Aspect Ratio
- •3.16.4 Wing Root (Croot) and Tip (Ctip) Chord
- •3.16.6 Wing Twist
- •3.17 Mean Aerodynamic Chord
- •3.18 Compressibility Effect: Wing Sweep
- •3.19 Wing Stall Pattern and Wing Twist
- •3.20.1 The Square-Cube Law
- •3.20.2 Aircraft Wetted Area (AW) versus Wing Planform Area (Sw)
- •3.20.3 Additional Vortex Lift
- •3.20.4 Additional Surfaces on Wing
- •3.21 Finalizing Wing Design Parameters
- •3.22 Empennage
- •3.22.1 H-Tail
- •3.22.2 V-Tail
- •3.23 Fuselage
- •3.23.2 Fuselage Length, Lfus
- •3.23.3 Fineness Ratio, FR
- •3.23.4 Fuselage Upsweep Angle
- •3.23.5 Fuselage Closure Angle
- •3.23.6 Front Fuselage Closure Length, Lf
- •3.23.7 Aft Fuselage Closure Length, La
- •3.23.8 Midfuselage Constant Cross-Section Length, Lm
- •3.23.9 Fuselage Height, H
- •3.23.10 Fuselage Width, W
- •3.23.11 Average Diameter, Dave
- •3.23.12 Cabin Height, Hcab
- •3.23.13 Cabin Width, Wcab
- •3.24 Undercarriage
- •3.25 Nacelle and Intake
- •3.26 Speed Brakes and Dive Brakes
- •4.1 Overview
- •4.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •4.1.2 Coursework Content
- •4.2 Introduction
- •4.3 Aircraft Evolution
- •4.4 Civil Aircraft Mission (Payload-Range)
- •4.5 Civil Subsonic Jet Aircraft Statistics (Sizing Parameters and Regression Analysis)
- •4.5.1 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Number of Passengers
- •4.5.2 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Operational Empty Mass
- •4.5.3 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Fuel Load
- •4.5.4 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Wing Area
- •4.5.5 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Engine Power
- •4.5.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area
- •4.5.7 Wing Loading versus Aircraft Span
- •4.6 Civil Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.7 Fuselage Group
- •4.7.1 Fuselage Width
- •4.7.2 Fuselage Length
- •4.7.3 Front (Nose Cone) and Aft-End Closure
- •4.7.4 Flight Crew (Flight Deck) Compartment Layout
- •4.7.5 Cabin Crew and Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.6 Seat Arrangement, Pitch, and Posture (95th Percentile) Facilities
- •4.7.7 Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.8 Cargo Container Sizes
- •4.7.9 Doors – Emergency Exits
- •4.8 Wing Group
- •4.9 Empennage Group (Civil Aircraft)
- •4.10 Nacelle Group
- •4.11 Summary of Civil Aircraft Design Choices
- •4.13 Military Aircraft Mission
- •4.14.1 Military Aircraft Maximum Take-off Mass (MTOM) versus Payload
- •4.14.2 Military MTOM versus OEM
- •4.14.3 Military MTOM versus Fuel Load Mf
- •4.14.4 MTOM versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.5 MTOM versus Engine Thrust (Military)
- •4.14.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.7 Aircraft Wetted Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.15 Military Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.16 Fuselage Group (Military)
- •4.17 Wing Group (Military)
- •4.17.1 Generic Wing Planform Shapes
- •4.18 Empennage Group (Military)
- •4.19 Intake/Nacelle Group (Military)
- •4.20 Undercarriage Group
- •4.21 Miscellaneous Comments
- •4.22 Summary of Military Aircraft Design Choices
- •5 Aircraft Load
- •5.1 Overview
- •5.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •5.1.2 Coursework Content
- •5.2 Introduction
- •5.2.1 Buffet
- •5.2.2 Flutter
- •5.3 Flight Maneuvers
- •5.3.1 Pitch Plane (X-Z) Maneuver (Elevator/Canard-Induced)
- •5.3.2 Roll Plane (Y-Z) Maneuver (Aileron-Induced)
- •5.3.3 Yaw Plane (Z-X) Maneuver (Rudder-Induced)
- •5.4 Aircraft Loads
- •5.4.1 On the Ground
- •5.4.2 In Flight
- •5.5.1 Load Factor, n
- •5.6 Limits – Load and Speeds
- •5.6.1 Maximum Limit of Load Factor
- •5.6.2 Speed Limits
- •5.7 V-n Diagram
- •5.7.1 Low-Speed Limit
- •5.7.2 High-Speed Limit
- •5.7.3 Extreme Points of a V-n Diagram
- •Positive Loads
- •Negative Loads
- •5.8 Gust Envelope
- •6.1 Overview
- •6.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •6.1.2 Coursework Content
- •6.2 Introduction
- •Closure of the Fuselage
- •6.4 Civil Aircraft Fuselage: Typical Shaping and Layout
- •6.4.1 Narrow-Body, Single-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.2 Wide-Body, Double-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.3 Worked-Out Example: Civil Aircraft Fuselage Layout
- •6.5.1 Aerofoil Selection
- •6.5.2 Wing Design
- •Planform Shape
- •Wing Reference Area
- •Wing Sweep
- •Wing Twist
- •Wing Dihedral/Anhedral
- •6.5.3 Wing-Mounted Control-Surface Layout
- •6.5.4 Positioning of the Wing Relative to the Fuselage
- •6.6.1 Horizontal Tail
- •6.6.2 Vertical Tail
- •6.8 Undercarriage Positioning
- •6.10 Miscellaneous Considerations in Civil Aircraft
- •6.12.1 Use of Statistics in the Class of Military Trainer Aircraft
- •6.12.3 Miscellaneous Considerations – Military Design
- •6.13 Variant CAS Design
- •6.13.1 Summary of the Worked-Out Military Aircraft Preliminary Details
- •7 Undercarriage
- •7.1 Overview
- •7.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •7.1.2 Coursework Content
- •7.2 Introduction
- •7.3 Types of Undercarriage
- •7.5 Undercarriage Retraction and Stowage
- •7.5.1 Stowage Space Clearances
- •7.6 Undercarriage Design Drivers and Considerations
- •7.7 Turning of an Aircraft
- •7.8 Wheels
- •7.9 Loads on Wheels and Shock Absorbers
- •7.9.1 Load on Wheels
- •7.9.2 Energy Absorbed
- •7.11 Tires
- •7.13 Undercarriage Layout Methodology
- •7.14 Worked-Out Examples
- •7.14.1 Civil Aircraft: Bizjet
- •Baseline Aircraft with 10 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •Shrunk Aircraft (Smallest in the Family Variant) with 6 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •7.14.2 Military Aircraft: AJT
- •7.15 Miscellaneous Considerations
- •7.16 Undercarriage and Tire Data
- •8 Aircraft Weight and Center of Gravity Estimation
- •8.1 Overview
- •8.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •8.1.2 Coursework Content
- •8.2 Introduction
- •8.3 The Weight Drivers
- •8.4 Aircraft Mass (Weight) Breakdown
- •8.5 Desirable CG Position
- •8.6 Aircraft Component Groups
- •8.6.1 Civil Aircraft
- •8.6.2 Military Aircraft (Combat Category)
- •8.7 Aircraft Component Mass Estimation
- •8.8 Rapid Mass Estimation Method: Civil Aircraft
- •8.9 Graphical Method for Predicting Aircraft Component Weight: Civil Aircraft
- •8.10 Semi-empirical Equation Method (Statistical)
- •8.10.1 Fuselage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.2 Wing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.3 Empennage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.4 Nacelle Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Jet Type (Includes Pylon Mass)
- •Turboprop Type
- •Piston-Engine Nacelle
- •8.10.5 Undercarriage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Tricycle Type (Retractable) – Fuselage-Mounted (Nose and Main Gear Estimated Together)
- •8.10.6 Miscellaneous Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.7 Power Plant Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans
- •Turboprops
- •Piston Engines
- •8.10.8 Systems Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.9 Furnishing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.10 Contingency and Miscellaneous – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.11 Crew – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.12 Payload – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.13 Fuel – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11 Worked-Out Example – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11.1 Fuselage Group Mass
- •8.11.2 Wing Group Mass
- •8.11.3 Empennage Group Mass
- •8.11.4 Nacelle Group Mass
- •8.11.5 Undercarriage Group Mass
- •8.11.6 Miscellaneous Group Mass
- •8.11.7 Power Plant Group Mass
- •8.11.8 Systems Group Mass
- •8.11.9 Furnishing Group Mass
- •8.11.10 Contingency Group Mass
- •8.11.11 Crew Mass
- •8.11.12 Payload Mass
- •8.11.13 Fuel Mass
- •8.11.14 Weight Summary
- •Variant Aircraft in the Family
- •8.12 Center of Gravity Determination
- •8.12.1 Bizjet Aircraft CG Location Example
- •8.12.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position Relative to Aircraft and Components
- •8.13 Rapid Mass Estimation Method – Military Aircraft
- •8.14 Graphical Method to Predict Aircraft Component Weight – Military Aircraft
- •8.15 Semi-empirical Equation Methods (Statistical) – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.1 Military Aircraft Fuselage Group (SI System)
- •8.15.2 Military Aircraft Wing Mass (SI System)
- •8.15.3 Military Aircraft Empennage
- •8.15.4 Nacelle Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.5 Power Plant Group Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.6 Undercarriage Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.7 System Mass – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.8 Aircraft Furnishing – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.11 Crew Mass
- •8.16.1 AJT Fuselage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.2 AJT Wing Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.3 AJT Empennage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.4 AJT Nacelle Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.5 AJT Power Plant Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.6 AJT Undercarriage Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.7 AJT Systems Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.8 AJT Furnishing Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.9 AJT Contingency Group Mass Example
- •8.16.10 AJT Crew Mass Example
- •8.16.13 Weights Summary – Military Aircraft
- •8.17 CG Position Determination – Military Aircraft
- •8.17.1 Classroom Worked-Out Military AJT CG Location Example
- •8.17.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position and Components Masses
- •9 Aircraft Drag
- •9.1 Overview
- •9.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •9.1.2 Coursework Content
- •9.2 Introduction
- •9.4 Aircraft Drag Breakdown (Subsonic)
- •9.5 Aircraft Drag Formulation
- •9.6 Aircraft Drag Estimation Methodology (Subsonic)
- •9.7 Minimum Parasite Drag Estimation Methodology
- •9.7.2 Computation of Wetted Areas
- •Lifting Surfaces
- •Fuselage
- •Nacelle
- •9.7.3 Stepwise Approach to Compute Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.8 Semi-empirical Relations to Estimate Aircraft Component Parasite Drag
- •9.8.1 Fuselage
- •9.8.2 Wing, Empennage, Pylons, and Winglets
- •9.8.3 Nacelle Drag
- •Intake Drag
- •Base Drag
- •Boat-Tail Drag
- •9.8.4 Excrescence Drag
- •9.8.5 Miscellaneous Parasite Drags
- •Air-Conditioning Drag
- •Trim Drag
- •Aerials
- •9.9 Notes on Excrescence Drag Resulting from Surface Imperfections
- •9.10 Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.12 Subsonic Wave Drag
- •9.13 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.14 Low-Speed Aircraft Drag at Takeoff and Landing
- •9.14.1 High-Lift Device Drag
- •9.14.2 Dive Brakes and Spoilers Drag
- •9.14.3 Undercarriage Drag
- •9.14.4 One-Engine Inoperative Drag
- •9.15 Propeller-Driven Aircraft Drag
- •9.16 Military Aircraft Drag
- •9.17 Supersonic Drag
- •9.18 Coursework Example: Civil Bizjet Aircraft
- •9.18.1 Geometric and Performance Data
- •Fuselage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Wing (see Figure 9.13)
- •Empennage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Nacelle (see Figure 9.13)
- •9.18.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.18.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.18.6 Induced Drag
- •9.18.7 Total Aircraft Drag at LRC
- •9.19 Coursework Example: Subsonic Military Aircraft
- •9.19.1 Geometric and Performance Data of a Vigilante RA-C5 Aircraft
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •9.19.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component CDpmin
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.19.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.19.6 Induced Drag
- •9.19.7 Supersonic Drag Estimation
- •9.19.8 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.20 Concluding Remarks
- •10 Aircraft Power Plant and Integration
- •10.1 Overview
- •10.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •10.1.2 Coursework Content
- •10.2 Background
- •10.4 Introduction: Air-Breathing Aircraft Engine Types
- •10.4.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet
- •10.4.2 Turbofan: Bypass Engine
- •10.4.3 Afterburner Engine
- •10.4.4 Turboprop Engine
- •10.4.5 Piston Engine
- •10.6 Formulation and Theory: Isentropic Case
- •10.6.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.2 Bypass Turbofan Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.3 Afterburner Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.4 Turboprop Engine: Formulation
- •Summary
- •10.7 Engine Integration with an Aircraft: Installation Effects
- •10.7.1 Subsonic Civil Aircraft Nacelle and Engine Installation
- •10.7.2 Turboprop Integration to Aircraft
- •10.7.3 Combat Aircraft Engine Installation
- •10.8 Intake and Nozzle Design
- •10.8.1 Civil Aircraft Intake Design: Inlet Sizing
- •10.8.2 Military Aircraft Intake Design
- •10.9 Exhaust Nozzle and Thrust Reverser
- •10.9.1 Civil Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application
- •10.9.2 Civil Aircraft Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.9.3 Coursework Example of Civil Aircraft Nacelle Design
- •Intake Geometry (see Section 10.8.1)
- •Lip Section (Crown Cut)
- •Lip Section (Keel Cut)
- •Nozzle Geometry
- •10.9.4 Military Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application and Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.10 Propeller
- •10.10.2 Propeller Theory
- •Momentum Theory: Actuator Disc
- •Blade-Element Theory
- •10.10.3 Propeller Performance: Practical Engineering Applications
- •Static Performance (see Figures 10.34 and 10.36)
- •In-Flight Performance (see Figures 10.35 and 10.37)
- •10.10.5 Propeller Performance at STD Day: Worked-Out Example
- •10.11 Engine-Performance Data
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Continuous Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •Idle Rating
- •10.11.1 Piston Engine
- •10.11.2 Turboprop Engine (Up to 100 Passengers Class)
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •10.11.3 Turbofan Engine: Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans with a BPR Around 4 (Smaller Engines; e.g., Bizjets)
- •Turbofans with a BPR around 5 or 7 (Larger Engines; e.g., RJs and Larger)
- •10.11.4 Turbofan Engine – Military Aircraft
- •11 Aircraft Sizing, Engine Matching, and Variant Derivative
- •11.1 Overview
- •11.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •11.1.2 Coursework Content
- •11.2 Introduction
- •11.3 Theory
- •11.3.1 Sizing for Takeoff Field Length
- •Civil Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •Military Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •11.3.2 Sizing for the Initial Rate of Climb
- •11.3.3 Sizing to Meet Initial Cruise
- •11.3.4 Sizing for Landing Distance
- •11.4 Coursework Exercises: Civil Aircraft Design (Bizjet)
- •11.4.1 Takeoff
- •11.4.2 Initial Climb
- •11.4.3 Cruise
- •11.4.4 Landing
- •11.5 Coursework Exercises: Military Aircraft Design (AJT)
- •11.5.1 Takeoff – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.2 Initial Climb – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.3 Cruise – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.4 Landing – Military Aircraft
- •11.6 Sizing Analysis: Civil Aircraft (Bizjet)
- •11.6.1 Variants in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.6.2 Example: Civil Aircraft
- •11.7 Sizing Analysis: Military Aircraft
- •11.7.1 Single-Seat Variant in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.8 Sensitivity Study
- •11.9 Future Growth Potential
- •12.1 Overview
- •12.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •12.1.2 Coursework Content
- •12.2 Introduction
- •12.3 Static and Dynamic Stability
- •12.3.1 Longitudinal Stability: Pitch Plane (Pitch Moment, M)
- •12.3.2 Directional Stability: Yaw Plane (Yaw Moment, N)
- •12.3.3 Lateral Stability: Roll Plane (Roll Moment, L)
- •12.3.4 Summary of Forces, Moments, and Their Sign Conventions
- •12.4 Theory
- •12.4.1 Pitch Plane
- •12.4.2 Yaw Plane
- •12.4.3 Roll Plane
- •12.6 Inherent Aircraft Motions as Characteristics of Design
- •12.6.1 Short-Period Oscillation and Phugoid Motion
- •12.6.2 Directional and Lateral Modes of Motion
- •12.7 Spinning
- •12.8 Design Considerations for Stability: Civil Aircraft
- •12.9 Military Aircraft: Nonlinear Effects
- •12.10 Active Control Technology: Fly-by-Wire
- •13 Aircraft Performance
- •13.1 Overview
- •13.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •13.1.2 Coursework Content
- •13.2 Introduction
- •13.2.1 Aircraft Speed
- •13.3 Establish Engine Performance Data
- •13.3.1 Turbofan Engine (BPR < 4)
- •Takeoff Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •13.3.2 Turbofan Engine (BPR > 4)
- •13.3.3 Military Turbofan (Advanced Jet Trainer/CAS Role – Very Low BPR) – STD Day
- •13.3.4 Turboprop Engine Performance
- •Takeoff Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •13.4 Derivation of Pertinent Aircraft Performance Equations
- •13.4.1 Takeoff
- •Balanced Field Length: Civil Aircraft
- •Takeoff Equations
- •13.4.2 Landing Performance
- •13.4.3 Climb and Descent Performance
- •Summary
- •Descent
- •13.4.4 Initial Maximum Cruise Speed
- •13.4.5 Payload Range Capability
- •13.5 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Worked-Out Examples (Bizjet)
- •13.5.1 Takeoff Field Length (Bizjet)
- •Segment A: All Engines Operating up to the Decision Speed V1
- •Segment B: One-Engine Inoperative Acceleration from V1 to Liftoff Speed, VLO
- •Segment C: Flaring Distance with One Engine Inoperative from VLO to V2
- •Segment E: Braking Distance from VB to Zero Velocity (Flap Settings Are of Minor Consequence)
- •Discussion of the Takeoff Analysis
- •13.5.2 Landing Field Length (Bizjet)
- •13.5.3 Climb Performance Requirements (Bizjet)
- •13.5.4 Integrated Climb Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.5 Initial High-Speed Cruise (Bizjet)
- •13.5.7 Descent Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.8 Payload Range Capability
- •13.6 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Military Aircraft (AJT)
- •13.6.2 Takeoff Field Length (AJT)
- •Distance Covered from Zero to the Decision Speed V1
- •Distance Covered from Zero to Liftoff Speed VLO
- •Distance Covered from VLO to V2
- •Total Takeoff Distance
- •Stopping Distance and the CFL
- •Distance Covered from V1 to Braking Speed VB
- •Verifying the Climb Gradient at an 8-Deg Flap
- •13.6.3 Landing Field Length (AJT)
- •13.6.4 Climb Performance Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.5 Maximum Speed Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.6 Fuel Requirements (AJT)
- •13.7 Summary
- •13.7.1 The Bizjet
- •14 Computational Fluid Dynamics
- •14.1 Overview
- •14.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •14.1.2 Coursework Content
- •14.2 Introduction
- •14.3 Current Status
- •14.4 Approach to CFD Analyses
- •14.4.1 In the Preprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.2 In the Flow Solver (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.3 In the Postprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.5 Case Studies
- •14.6 Hierarchy of CFD Simulation Methods
- •14.6.1 DNS Simulation Technique
- •14.6.2 Large Eddy Simulation (LES) Technique
- •14.6.3 Detached Eddy Simulation (DES) Technique
- •14.6.4 RANS Equation Technique
- •14.6.5 Euler Method Technique
- •14.6.6 Full-Potential Flow Equations
- •14.6.7 Panel Method
- •14.7 Summary
- •15 Miscellaneous Design Considerations
- •15.1 Overview
- •15.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •15.1.2 Coursework Content
- •15.2 Introduction
- •15.2.1 Environmental Issues
- •15.2.2 Materials and Structures
- •15.2.3 Safety Issues
- •15.2.4 Human Interface
- •15.2.5 Systems Architecture
- •15.2.6 Military Aircraft Survivability Issues
- •15.2.7 Emerging Scenarios
- •15.3 Noise Emissions
- •Approach
- •Sideline
- •15.3.1 Summary
- •15.4 Engine Exhaust Emissions
- •15.5 Aircraft Materials
- •15.5.1 Material Properties
- •15.5.2 Material Selection
- •15.5.3 Coursework Overview
- •Civil Aircraft Design
- •Military Aircraft Design
- •15.6 Aircraft Structural Considerations
- •15.7 Doors: Emergency Egress
- •Coursework Exercise
- •15.8 Aircraft Flight Deck (Cockpit) Layout
- •15.8.1 Multifunctional Display and Electronic Flight Information System
- •15.8.2 Combat Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.3 Civil Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.4 Head-Up Display
- •15.8.5 Helmet-Mounted Display
- •15.8.6 Hands-On Throttle and Stick
- •15.8.7 Voice-Operated Control
- •15.9 Aircraft Systems
- •15.9.1 Aircraft Control Subsystem
- •15.9.2 Engine and Fuel Control Subsystems
- •Piston Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1 to 1.5% of the MTOW)
- •Turbofan Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1.5 to 2% of the MTOW)
- •Fuel Storage and Flow Management
- •15.9.3 Emergency Power Supply
- •15.9.4 Avionics Subsystems
- •Military Aircraft Application
- •Civil Aircraft Application
- •15.9.5 Electrical Subsystem
- •15.9.6 Hydraulic Subsystem
- •15.9.7 Pneumatic System
- •ECS: Cabin Pressurization and Air-Conditioning
- •Oxygen Supply
- •Anti-icing, De-icing, Defogging, and Rain-Removal Systems
- •Defogging and Rain-Removal Systems
- •15.9.8 Utility Subsystem
- •15.9.9 End-of-Life Disposal
- •15.10 Military Aircraft Survivability
- •15.10.1 Military Emergency Escape
- •15.10.2 Military Aircraft Stealth Consideration
- •15.11 Emerging Scenarios
- •Counterterrorism Design Implementation
- •Health Issues
- •Damage from Runway Debris
- •16 Aircraft Cost Considerations
- •16.1 Overview
- •16.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •16.1.2 Coursework Content
- •16.2 Introduction
- •16.3 Aircraft Cost and Operational Cost
- •Operating Cost
- •16.4 Aircraft Costing Methodology: Rapid-Cost Model
- •16.4.1 Nacelle Cost Drivers
- •Group 1
- •Group 2
- •16.4.2 Nose Cowl Parts and Subassemblies
- •16.4.3 Methodology (Nose Cowl Only)
- •Cost of Parts Fabrication
- •Subassemblies
- •Cost of Amortization of the NRCs
- •16.4.4 Cost Formulas and Results
- •16.5 Aircraft Direct Operating Cost
- •16.5.1 Formulation to Estimate DOC
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •16.5.2 Worked-Out Example of DOC: Bizjet
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •OC of the Variants in the Family
- •17 Aircraft Manufacturing Considerations
- •17.1 Overview
- •17.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •17.1.2 Coursework Content
- •17.2 Introduction
- •17.3 Design for Manufacture and Assembly
- •17.4 Manufacturing Practices
- •17.5 Six Sigma Concept
- •17.6 Tolerance Relaxation at the Wetted Surface
- •17.6.1 Sources of Aircraft Surface Degeneration
- •17.6.2 Cost-versus-Tolerance Relationship
- •17.7 Reliability and Maintainability
- •17.8 Design Considerations
- •17.8.1 Category I: Technology-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.2 Category II: Manufacture-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.3 Category III: Management-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.4 Category IV: Operator-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.9 “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.1 Index for “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.2 Worked-Out Example
- •Standard Parameters of the Baseline Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Extended Variant Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Shortened Variant Aircraft
- •17.10 Digital Manufacturing Process Management
- •Process Detailing and Validation
- •Resource Modeling and Simulation
- •Process Planning and Simulation
- •17.10.1 Product, Process, and Resource Hub
- •17.10.3 Shop-Floor Interface
- •17.10.4 Design for Maintainability and 3D-Based Technical Publication Generation
- •Midrange Aircraft (Airbus 320 class)
- •References
- •ROAD MAP OF THE BOOK
- •CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION
- •CHAPTER 3. AERODYNAMIC CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 5. AIRCRAFT LOAD
- •CHAPTER 6. CONFIGURING AIRCRAFT
- •CHAPTER 7. UNDERCARRIAGE
- •CHAPTER 8. AIRCRAFT WEIGHT AND CENTER OF GRAVITY ESTIMATION
- •CHAPTER 9. AIRCRAFT DRAG
- •CHAPTER 10. AIRCRAFT POWER PLANT AND INTEGRATION
- •CHAPTER 11. AIRCRAFT SIZING, ENGINE MATCHING, AND VARIANT DERIVATIVE
- •CHAPTER 12. STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS AFFECTING AIRCRAFT CONFIGURATION
- •CHAPTER 13. AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE
- •CHAPTER 14. COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
- •CHAPTER 15. MISCELLANEOUS DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 16. AIRCRAFT COST CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 17. AIRCRAFT MANUFACTURING CONSIDERATIONS
- •Index
6.3 Shaping and Layout of a Civil Aircraft Configuration |
155 |
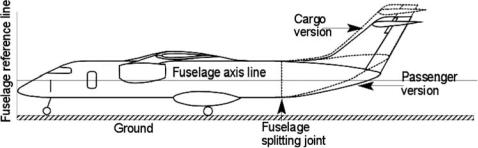
Figure 6.4. Fuselage upsweep angle
6.The minimum number of cabin crew depends on the maximum passenger capacity that the airframe can accommodate. Although not required for up to 19 passengers, a cabin crew is provided by some operators.
7.A pressurized fuselage is invariably circular or near circular to minimize weight. Unpressurized cabins for aircraft operating below 4,300 m (14,000 ft) need not be circular in the cross-section. Smaller utility aircraft demonstrate the benefits of a rectangular cross-section. A box-like rectangular cross-section (see Figure 4.14) would not only offer more leg space but also is considerably less costly to manufacture (e.g., the Short SD360).
8.The FAA and CAA have mandatory requirements on the minimum number of passenger doors, their types, and corresponding sizes dependent on the maximum passenger capacity for which the fuselage is intended to accommodate. This requirement ensures passenger safety: certification authorities stipulate a time limit (e.g., 90 s for big jets) within which all passengers must egress if an unlikely event occurs (e.g., fire). The larger the passenger capacity, the more doors are to be installed. Not all doors are the same size – emergency doors are smaller. Passenger doors have several categories and are described in Section 15.7. All doors are kept locked while airborne.
9.The fuselage provision typically includes a toilet, a galley, and cabin crew seating – the extent depends on the number of passengers and the duration of flight. Chapter 4 describes toilet and galley details. For smaller aircraft with a shorter duration of flight, it is desirable that at least a toilet be provided. To reduce cost, smaller aircraft with a low mission range do not have a toilet, but these aircraft can therefore be uncomfortable.
Closure of the Fuselage
When the seating arrangement is determined in the midfuselage section, it must be closed at the front and aft ends for a streamlined shape, maintaining a fineness ratio from 7 to 14 (see Table 4.3). Typical frontand aft-fuselage closure ratios are in Table 4.4.
The fuselage upsweep angle of the aft-end closure depends on the type of aircraft. If it has a rear-loading ramp as in a cargo version, then the upsweep angle is higher, as shown in Figure 6.4. The fuselage clearance angle, θ , depends on the main-wheel position of the undercarriage relative to the aircraft CG position (see
156 |
Configuring Aircraft |
Chapter 7). The typical angle for θ is between 12 and 16 deg to approach CLmax at aircraft rotation.
The next step is to construct a fuselage axis and set the zero reference plane normal to the fuselage axis, as explained in Section 3.23. In Figure 6.4, the fuselage axis is shown passing through the tip of the nose cone, where the zero reference plane starts. In this book, the zero reference plane is at the nose of the aircraft (it could be ahead of the nose cone tip). The zero reference plane and the fuselage axis are data for measuring relative distances of various aircraft components and for aerodynamic geometries for use in calculations.
The fuselage axis is an arbitrary line but it must be in the plane of aircraft symmetry. In general, for aircraft with a constant fuselage section, the fuselage axis is placed conveniently in the middle of the aircraft. The fuselage axis line could be the fuselage centerline. It is easier to assess if the reference lines are vertical and horizontal. If the aircraft’s normal position on the ground does not render the aircraft centerline horizontal, then the ground is tilted to show it with the associated angle. For simplification, this book keeps the centerline and ground horizontal, as shown in Figure 6.4. For military and smaller civil aircraft, there is no constant fuselage section, and the aircraft centerline must be conveniently chosen; it is the designer’s choice as long as the reference lines are clearly defined and adhered to for the entire life cycle of an aircraft that could encounter design modifications in its service life. The other possible choice is the fuselage axis as the principal inertia axis.
An interesting concept is to make variants of a modular fuselage – that is, with two types of aft ends easily interchangeable (see Figure 6.4). One type is for the conventional passenger version with a pointed aft-end closure, the other is for the cargo version with an increased upsweep to accommodate a rear-loading ramp. It can even be a “quick-change” version, swapping the type of fuselage needed for the mission; the changeover joint is located behind the main undercarriage.
Attaching the wing to the fuselage could have a local effect on the fuselage external shape. Following are the basic types of attachments:
1.Carry-through wing box. For larger aircraft, this is separately constructed and attached to the fuselage recess. Subsequently, wings are mated at each side in accurate assembly jigs. For smaller aircraft, it could be integral to the wing and then attached to the fuselage recess. In that case, the wing box is built into the wing, either in two halves or as a tip-to-tip assembly. A fairing at the junction reduces the interference drag. These wing boxes are primarily suited to civil aircraft designs. A central wing box is a part of the wing structure that integrates with the fuselage and is positioned high, low, or at a convenient mid-location (see Section 3.16).
2.Central beam and root attachments. These have a simpler construction and therefore are less costly, suited to smaller aircraft.
3.Wing roots (with multispar) joined to a series of fuselage frames. These are mostly suited to military aircraft designs. They are heavier and can be tailored to varying fuselage contours. The wing root is then secured to the fuselage structure, sometimes outside the shell, with attachments.
4.Strut/braced wing support. This is suited to smaller, low-speed, high-wing aircraft. Some low-wing agricultural aircraft have braced wings. Struts add to drag
6.3 Shaping and Layout of a Civil Aircraft Configuration |
157 |
but for a low-speed operation, the increment can be tolerated when it is less costly to build and lighter in construction.
5.Swing wing. Attachment of a swing wing is conveniently outside the fuselage such that the pivots have space around them to allow wing rotation.
For smaller aircraft, the wing must not pass through the fuselage interior, which would obstruct passenger movement. If the wing is placed outside the fuselage (i.e., top or bottom), then a large streamlined fairing on the fuselage would accommodate the wing box. The example of the Cessna Excel shows a low-wing design; the DO328 includes a fairing for the high-wing design. The Dornier 328 (see Figure 3.33) conceals the fairing that merges with the fuselage mould lines. The extra volume could be beneficial; however, to arrive at such a configuration, a proper DOC analysis must demonstrate its merits. High-wing aircraft must house the undercarriage in a fuselage fairing, although some turboprop aircraft have the undercarriage tucked inside the engine nacelles positioned below the wing (see Figure 10.19).
6.3.2 Considerations in Configuring the Wing
Following are general considerations important for designing the wing:
Geometry |
Aerodynamics |
||
(1) |
wing reference area, SW |
(1) |
drag |
(2) |
span and aspect ratio |
(2) |
lift and moment |
(3) |
aerofoil section, t/c ratio |
(3) |
stall, critical Mach |
(4) |
sweep, twist, dihedral, taper |
(4) |
high-lift devices |
(5) |
position (for the CG) |
(5) |
control surfaces |
(6) |
glove/yehudi, if any |
(6) |
wing/tail position |
Structure (affecting weight |
|
|
|
and external geometry) |
Systems |
||
(1) |
spar and rib positions |
(1) |
control linkage |
(2) |
stiffness, aeroelasticity, and |
(2) |
fuel system |
|
torsion stability |
(3) |
electrical |
(3) |
fuel volume |
(4) |
anti-icing |
(4)undercarriage and nacelle, if any
(5)weight
The first task for wing design is to select a suitable aerofoil. This book does not undertake aerofoil design; rather, it uses established 2D aerofoil data from the public domain (the aerofoil data in Appendix C are sufficient for this book). Industry takes an arduous route to extract as much benefit from its in-house research that is kept commercial in confidence. It is an established technology in which there is a diminishing return on investment. However, the differences between the best designs and those in the public domain are enough to encourage industrial competition. The next task is to configure a wing planform with a reference area typically for the class of aircraft. It is not determined by the passenger number as in the fuselage; the initial wing size is determined from statistics. Subsequently, the prelimi- nary wing reference area must be sized using the methodology described in Chapter 11.
158 |
Configuring Aircraft |
Positioning of the wing relative to the fuselage is an important part of configuring an aircraft. It requires knowledge of the CG position and its range of movement with weight variation (i.e., fuel and payload). Because the aircraft weight distribution is not yet established, it is initially estimated based on experience and past statistics in the aircraft class. If nothing is known, then a designer may position the wing just behind the middle of the fuselage for rear-mounted engines or at the middle of the fuselage for wing-mounted engines. Subsequently, the wing position must be iterated after the aircraft component weights are known and the wing is sized. This may not be easy because moving the wing will alter the CG position – an inexperienced engineer could encounter what is called “wing chasing”; however, this is not a major concern. Here, the “zero reference plane” (typically at the nose of the fuselage) assists in tracking the aircraft-component positions.
A generous wing root fairing is used to reduce interference drag as well as vortex intensity at the aft-fuselage flow. A large aircraft BWB is an extreme example that eliminates wing root fairing problems. There is no analytical expression to specify the fairing curvature – a designer should judge the geometry from past experience and CFD analysis, considering the internal structural layout and the associated weight growth. In principle, a trade-off study between weight growth and drag reduction is needed to establish the fairing curvature. At this stage, visual approximation from past experience is sufficient: Observe the current designs and make decisions.
6.3.3 Considerations in Configuring the Empennage
Following are general considerations important for configuring the empennage (see also Section 6.6):
Geometry |
Aerodynamics |
||
(1) |
H-tail and V-tail reference |
(1) |
drag, lift, moment |
|
area, SH and SV |
(2) |
tail volume coefficient |
(2) |
span and aspect ratio |
(3) |
stall and yaw recovery |
(3) |
aerofoil section, t/c ratio |
(4) |
control and trim surfaces |
(4) |
sweep, twist, or dihedral, |
(5) |
spin recovery |
|
whichever is applicable |
(6) |
balancing |
(5) |
position relative to wing (tail |
(7) |
engine-out cases |
|
arm) |
|
|
(6)position H-tail to
avoid shielding of V-tail
(7)H-tail position (high α clearance, T-tail)
Structure (affecting weight |
|
|
|
and external geometry) |
Systems |
||
(1) |
spar and rib positions |
(1) |
control linkage |
(2) |
stiffness, aeroelasticity, and |
(2) |
control actuation |
|
torsion stability |
(3) |
electrical (if any) |
(3)fuel volume (if any)
(4)weight
6.3 Shaping and Layout of a Civil Aircraft Configuration |
159 |
The descriptions and definitions of the empennage are in Sections 3.22 and 4.9. The dominant civil aircraft empennage consists of the H-tail and V-tail placed symmetrically about the fuselage axis. The H-tail could be positioned anywhere (see Figure 4.24), going through the aft fuselage to the tip of the V-tail forming a T-tail. Some aircraft have twin booms, where the empennage has the same function; the V-tail is split over two booms.
It is important that the V-tail remains effective for the full flight envelope. Shielding of the V-tail, especially the control areas, may prove to be dangerous. A designer must ensure that the V-tail keeps at least 50% of the rudder unshielded (see Figure 4.26) at a high angle of attack. (The canard configuration is not worked out in this book). Also, at a high angle of attack, the H-tail should not remain within the wing wake; otherwise, it must be enlarged to be effective.
If a FBW control system is incorporated, the empennage sizes can be reduced because the aircraft would be able to fly safely under relaxed stabilities. However, this book is not concerned with control laws as design input in an introductory course. The FBW concept is introduced in Chapter 12 but not analyzed. It will not be long until tailless aircraft such as the B2 bomber appear in civil aircraft designs, especially for BWB aircraft.
6.3.4 Considerations in Configuring the Nacelle
Following are general considerations important for configuring the nacelle (see also Section 6.7):
Geometry
(1)diameter (comfort level, appeal)
(2)length, fineness ratio
(3)wing and fuselage position and pylon geometry
(4)ground clearance
(5)cross-section to house accessories
(6)intake geometry and lip section
Structure (affecting weight and external geometry)
(1)engine burst considerations
(2)foreign-object ingestion problems
(3)fuel volume
(4)weight
(5)nose gear collapse
(6)access
Aerodynamics
(1)drag
(2)interference
(3)surface roughness
(4)noise/emission
(5)vibration
(6)thrust and bypass ratio (BPR) level
Systems
(1)control linkage
(2)fuel system
(3)electrical
(4)thrust reverser
(5)fire prevention
(6)anti-icing
Civil aircraft designs are invariably externally pod-mounted on either the wing or the aft fuselage (smaller low-wing turbofan engines). The demonstration of high engine reliability enables an ETOPS clearance by the FAA for a two-engine
