
- •Contents
- •Symbols and Abbreviations
- •Symbols
- •Greek Symbols
- •Subscripts
- •Abbreviations
- •Preface
- •Road Map of the Book
- •The Arrangement
- •Suggested Route for the Coursework
- •First Semester
- •Second Semester
- •Suggestions for the Class
- •Use of Semi-empirical Relations
- •1 Introduction
- •1.1 Overview
- •1.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •1.1.2 Coursework Content
- •1.2 Brief Historical Background
- •1.3 Current Aircraft Design Status
- •1.3.1 Forces and Drivers
- •1.3.2 Current Civil Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.3.3 Current Military Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.4 Future Trends
- •1.4.1 Civil Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.4.2 Military Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.5 Learning Process
- •1.6 Units and Dimensions
- •1.7 Cost Implications
- •2 Methodology to Aircraft Design, Market Survey, and Airworthiness
- •2.1 Overview
- •2.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •2.1.2 Coursework Content
- •2.2 Introduction
- •2.3 Typical Design Process
- •2.3.1 Four Phases of Aircraft Design
- •2.3.2 Typical Resources Deployment
- •2.3.3 Typical Cost Frame
- •2.3.4 Typical Time Frame
- •2.4 Typical Task Breakdown in Each Phase
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Study Phase (Feasibility Study)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design Phase (Full-Scale Product Development)
- •2.4.1 Functional Tasks during the Conceptual Study (Phase 1: Civil Aircraft)
- •2.4.2 Project Activities for Small Aircraft Design
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Design (6 Months)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design (Product Development) (12 Months)
- •2.5 Aircraft Familiarization
- •Fuselage Group
- •Wing Group
- •Empennage Group
- •Nacelle Group
- •Undercarriage Group
- •2.6 Market Survey
- •2.7 Civil Aircraft Market
- •2.8 Military Market
- •2.9 Comparison between Civil and Military Aircraft Design Requirements
- •2.10 Airworthiness Requirements
- •2.11 Coursework Procedures
- •3 Aerodynamic Considerations
- •3.1 Overview
- •3.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •3.1.2 Coursework Content
- •3.2 Introduction
- •3.3 Atmosphere
- •3.4 Fundamental Equations
- •3.5.1 Flow Past Aerofoil
- •3.6 Aircraft Motion and Forces
- •3.6.1 Motion
- •3.6.2 Forces
- •3.7 Aerofoil
- •3.7.1 Groupings of Aerofoils and Their Properties
- •NACA Four-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Five-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Six-Digit Aerofoil
- •Other Types of Aerofoils
- •3.9 Generation of Lift
- •3.10 Types of Stall
- •3.10.1 Gradual Stall
- •3.10.2 Abrupt Stall
- •3.11 Comparison of Three NACA Aerofoils
- •3.12 High-Lift Devices
- •3.13 Transonic Effects – Area Rule
- •3.14 Wing Aerodynamics
- •3.14.1 Induced Drag and Total Aircraft Drag
- •3.15 Aspect Ratio Correction of 2D Aerofoil Characteristics for 3D Finite Wing
- •3.16.1 Planform Area, SW
- •3.16.2 Wing Aspect Ratio
- •3.16.4 Wing Root (Croot) and Tip (Ctip) Chord
- •3.16.6 Wing Twist
- •3.17 Mean Aerodynamic Chord
- •3.18 Compressibility Effect: Wing Sweep
- •3.19 Wing Stall Pattern and Wing Twist
- •3.20.1 The Square-Cube Law
- •3.20.2 Aircraft Wetted Area (AW) versus Wing Planform Area (Sw)
- •3.20.3 Additional Vortex Lift
- •3.20.4 Additional Surfaces on Wing
- •3.21 Finalizing Wing Design Parameters
- •3.22 Empennage
- •3.22.1 H-Tail
- •3.22.2 V-Tail
- •3.23 Fuselage
- •3.23.2 Fuselage Length, Lfus
- •3.23.3 Fineness Ratio, FR
- •3.23.4 Fuselage Upsweep Angle
- •3.23.5 Fuselage Closure Angle
- •3.23.6 Front Fuselage Closure Length, Lf
- •3.23.7 Aft Fuselage Closure Length, La
- •3.23.8 Midfuselage Constant Cross-Section Length, Lm
- •3.23.9 Fuselage Height, H
- •3.23.10 Fuselage Width, W
- •3.23.11 Average Diameter, Dave
- •3.23.12 Cabin Height, Hcab
- •3.23.13 Cabin Width, Wcab
- •3.24 Undercarriage
- •3.25 Nacelle and Intake
- •3.26 Speed Brakes and Dive Brakes
- •4.1 Overview
- •4.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •4.1.2 Coursework Content
- •4.2 Introduction
- •4.3 Aircraft Evolution
- •4.4 Civil Aircraft Mission (Payload-Range)
- •4.5 Civil Subsonic Jet Aircraft Statistics (Sizing Parameters and Regression Analysis)
- •4.5.1 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Number of Passengers
- •4.5.2 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Operational Empty Mass
- •4.5.3 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Fuel Load
- •4.5.4 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Wing Area
- •4.5.5 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Engine Power
- •4.5.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area
- •4.5.7 Wing Loading versus Aircraft Span
- •4.6 Civil Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.7 Fuselage Group
- •4.7.1 Fuselage Width
- •4.7.2 Fuselage Length
- •4.7.3 Front (Nose Cone) and Aft-End Closure
- •4.7.4 Flight Crew (Flight Deck) Compartment Layout
- •4.7.5 Cabin Crew and Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.6 Seat Arrangement, Pitch, and Posture (95th Percentile) Facilities
- •4.7.7 Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.8 Cargo Container Sizes
- •4.7.9 Doors – Emergency Exits
- •4.8 Wing Group
- •4.9 Empennage Group (Civil Aircraft)
- •4.10 Nacelle Group
- •4.11 Summary of Civil Aircraft Design Choices
- •4.13 Military Aircraft Mission
- •4.14.1 Military Aircraft Maximum Take-off Mass (MTOM) versus Payload
- •4.14.2 Military MTOM versus OEM
- •4.14.3 Military MTOM versus Fuel Load Mf
- •4.14.4 MTOM versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.5 MTOM versus Engine Thrust (Military)
- •4.14.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.7 Aircraft Wetted Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.15 Military Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.16 Fuselage Group (Military)
- •4.17 Wing Group (Military)
- •4.17.1 Generic Wing Planform Shapes
- •4.18 Empennage Group (Military)
- •4.19 Intake/Nacelle Group (Military)
- •4.20 Undercarriage Group
- •4.21 Miscellaneous Comments
- •4.22 Summary of Military Aircraft Design Choices
- •5 Aircraft Load
- •5.1 Overview
- •5.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •5.1.2 Coursework Content
- •5.2 Introduction
- •5.2.1 Buffet
- •5.2.2 Flutter
- •5.3 Flight Maneuvers
- •5.3.1 Pitch Plane (X-Z) Maneuver (Elevator/Canard-Induced)
- •5.3.2 Roll Plane (Y-Z) Maneuver (Aileron-Induced)
- •5.3.3 Yaw Plane (Z-X) Maneuver (Rudder-Induced)
- •5.4 Aircraft Loads
- •5.4.1 On the Ground
- •5.4.2 In Flight
- •5.5.1 Load Factor, n
- •5.6 Limits – Load and Speeds
- •5.6.1 Maximum Limit of Load Factor
- •5.6.2 Speed Limits
- •5.7 V-n Diagram
- •5.7.1 Low-Speed Limit
- •5.7.2 High-Speed Limit
- •5.7.3 Extreme Points of a V-n Diagram
- •Positive Loads
- •Negative Loads
- •5.8 Gust Envelope
- •6.1 Overview
- •6.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •6.1.2 Coursework Content
- •6.2 Introduction
- •Closure of the Fuselage
- •6.4 Civil Aircraft Fuselage: Typical Shaping and Layout
- •6.4.1 Narrow-Body, Single-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.2 Wide-Body, Double-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.3 Worked-Out Example: Civil Aircraft Fuselage Layout
- •6.5.1 Aerofoil Selection
- •6.5.2 Wing Design
- •Planform Shape
- •Wing Reference Area
- •Wing Sweep
- •Wing Twist
- •Wing Dihedral/Anhedral
- •6.5.3 Wing-Mounted Control-Surface Layout
- •6.5.4 Positioning of the Wing Relative to the Fuselage
- •6.6.1 Horizontal Tail
- •6.6.2 Vertical Tail
- •6.8 Undercarriage Positioning
- •6.10 Miscellaneous Considerations in Civil Aircraft
- •6.12.1 Use of Statistics in the Class of Military Trainer Aircraft
- •6.12.3 Miscellaneous Considerations – Military Design
- •6.13 Variant CAS Design
- •6.13.1 Summary of the Worked-Out Military Aircraft Preliminary Details
- •7 Undercarriage
- •7.1 Overview
- •7.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •7.1.2 Coursework Content
- •7.2 Introduction
- •7.3 Types of Undercarriage
- •7.5 Undercarriage Retraction and Stowage
- •7.5.1 Stowage Space Clearances
- •7.6 Undercarriage Design Drivers and Considerations
- •7.7 Turning of an Aircraft
- •7.8 Wheels
- •7.9 Loads on Wheels and Shock Absorbers
- •7.9.1 Load on Wheels
- •7.9.2 Energy Absorbed
- •7.11 Tires
- •7.13 Undercarriage Layout Methodology
- •7.14 Worked-Out Examples
- •7.14.1 Civil Aircraft: Bizjet
- •Baseline Aircraft with 10 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •Shrunk Aircraft (Smallest in the Family Variant) with 6 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •7.14.2 Military Aircraft: AJT
- •7.15 Miscellaneous Considerations
- •7.16 Undercarriage and Tire Data
- •8 Aircraft Weight and Center of Gravity Estimation
- •8.1 Overview
- •8.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •8.1.2 Coursework Content
- •8.2 Introduction
- •8.3 The Weight Drivers
- •8.4 Aircraft Mass (Weight) Breakdown
- •8.5 Desirable CG Position
- •8.6 Aircraft Component Groups
- •8.6.1 Civil Aircraft
- •8.6.2 Military Aircraft (Combat Category)
- •8.7 Aircraft Component Mass Estimation
- •8.8 Rapid Mass Estimation Method: Civil Aircraft
- •8.9 Graphical Method for Predicting Aircraft Component Weight: Civil Aircraft
- •8.10 Semi-empirical Equation Method (Statistical)
- •8.10.1 Fuselage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.2 Wing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.3 Empennage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.4 Nacelle Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Jet Type (Includes Pylon Mass)
- •Turboprop Type
- •Piston-Engine Nacelle
- •8.10.5 Undercarriage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Tricycle Type (Retractable) – Fuselage-Mounted (Nose and Main Gear Estimated Together)
- •8.10.6 Miscellaneous Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.7 Power Plant Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans
- •Turboprops
- •Piston Engines
- •8.10.8 Systems Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.9 Furnishing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.10 Contingency and Miscellaneous – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.11 Crew – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.12 Payload – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.13 Fuel – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11 Worked-Out Example – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11.1 Fuselage Group Mass
- •8.11.2 Wing Group Mass
- •8.11.3 Empennage Group Mass
- •8.11.4 Nacelle Group Mass
- •8.11.5 Undercarriage Group Mass
- •8.11.6 Miscellaneous Group Mass
- •8.11.7 Power Plant Group Mass
- •8.11.8 Systems Group Mass
- •8.11.9 Furnishing Group Mass
- •8.11.10 Contingency Group Mass
- •8.11.11 Crew Mass
- •8.11.12 Payload Mass
- •8.11.13 Fuel Mass
- •8.11.14 Weight Summary
- •Variant Aircraft in the Family
- •8.12 Center of Gravity Determination
- •8.12.1 Bizjet Aircraft CG Location Example
- •8.12.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position Relative to Aircraft and Components
- •8.13 Rapid Mass Estimation Method – Military Aircraft
- •8.14 Graphical Method to Predict Aircraft Component Weight – Military Aircraft
- •8.15 Semi-empirical Equation Methods (Statistical) – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.1 Military Aircraft Fuselage Group (SI System)
- •8.15.2 Military Aircraft Wing Mass (SI System)
- •8.15.3 Military Aircraft Empennage
- •8.15.4 Nacelle Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.5 Power Plant Group Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.6 Undercarriage Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.7 System Mass – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.8 Aircraft Furnishing – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.11 Crew Mass
- •8.16.1 AJT Fuselage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.2 AJT Wing Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.3 AJT Empennage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.4 AJT Nacelle Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.5 AJT Power Plant Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.6 AJT Undercarriage Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.7 AJT Systems Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.8 AJT Furnishing Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.9 AJT Contingency Group Mass Example
- •8.16.10 AJT Crew Mass Example
- •8.16.13 Weights Summary – Military Aircraft
- •8.17 CG Position Determination – Military Aircraft
- •8.17.1 Classroom Worked-Out Military AJT CG Location Example
- •8.17.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position and Components Masses
- •9 Aircraft Drag
- •9.1 Overview
- •9.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •9.1.2 Coursework Content
- •9.2 Introduction
- •9.4 Aircraft Drag Breakdown (Subsonic)
- •9.5 Aircraft Drag Formulation
- •9.6 Aircraft Drag Estimation Methodology (Subsonic)
- •9.7 Minimum Parasite Drag Estimation Methodology
- •9.7.2 Computation of Wetted Areas
- •Lifting Surfaces
- •Fuselage
- •Nacelle
- •9.7.3 Stepwise Approach to Compute Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.8 Semi-empirical Relations to Estimate Aircraft Component Parasite Drag
- •9.8.1 Fuselage
- •9.8.2 Wing, Empennage, Pylons, and Winglets
- •9.8.3 Nacelle Drag
- •Intake Drag
- •Base Drag
- •Boat-Tail Drag
- •9.8.4 Excrescence Drag
- •9.8.5 Miscellaneous Parasite Drags
- •Air-Conditioning Drag
- •Trim Drag
- •Aerials
- •9.9 Notes on Excrescence Drag Resulting from Surface Imperfections
- •9.10 Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.12 Subsonic Wave Drag
- •9.13 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.14 Low-Speed Aircraft Drag at Takeoff and Landing
- •9.14.1 High-Lift Device Drag
- •9.14.2 Dive Brakes and Spoilers Drag
- •9.14.3 Undercarriage Drag
- •9.14.4 One-Engine Inoperative Drag
- •9.15 Propeller-Driven Aircraft Drag
- •9.16 Military Aircraft Drag
- •9.17 Supersonic Drag
- •9.18 Coursework Example: Civil Bizjet Aircraft
- •9.18.1 Geometric and Performance Data
- •Fuselage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Wing (see Figure 9.13)
- •Empennage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Nacelle (see Figure 9.13)
- •9.18.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.18.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.18.6 Induced Drag
- •9.18.7 Total Aircraft Drag at LRC
- •9.19 Coursework Example: Subsonic Military Aircraft
- •9.19.1 Geometric and Performance Data of a Vigilante RA-C5 Aircraft
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •9.19.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component CDpmin
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.19.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.19.6 Induced Drag
- •9.19.7 Supersonic Drag Estimation
- •9.19.8 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.20 Concluding Remarks
- •10 Aircraft Power Plant and Integration
- •10.1 Overview
- •10.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •10.1.2 Coursework Content
- •10.2 Background
- •10.4 Introduction: Air-Breathing Aircraft Engine Types
- •10.4.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet
- •10.4.2 Turbofan: Bypass Engine
- •10.4.3 Afterburner Engine
- •10.4.4 Turboprop Engine
- •10.4.5 Piston Engine
- •10.6 Formulation and Theory: Isentropic Case
- •10.6.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.2 Bypass Turbofan Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.3 Afterburner Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.4 Turboprop Engine: Formulation
- •Summary
- •10.7 Engine Integration with an Aircraft: Installation Effects
- •10.7.1 Subsonic Civil Aircraft Nacelle and Engine Installation
- •10.7.2 Turboprop Integration to Aircraft
- •10.7.3 Combat Aircraft Engine Installation
- •10.8 Intake and Nozzle Design
- •10.8.1 Civil Aircraft Intake Design: Inlet Sizing
- •10.8.2 Military Aircraft Intake Design
- •10.9 Exhaust Nozzle and Thrust Reverser
- •10.9.1 Civil Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application
- •10.9.2 Civil Aircraft Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.9.3 Coursework Example of Civil Aircraft Nacelle Design
- •Intake Geometry (see Section 10.8.1)
- •Lip Section (Crown Cut)
- •Lip Section (Keel Cut)
- •Nozzle Geometry
- •10.9.4 Military Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application and Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.10 Propeller
- •10.10.2 Propeller Theory
- •Momentum Theory: Actuator Disc
- •Blade-Element Theory
- •10.10.3 Propeller Performance: Practical Engineering Applications
- •Static Performance (see Figures 10.34 and 10.36)
- •In-Flight Performance (see Figures 10.35 and 10.37)
- •10.10.5 Propeller Performance at STD Day: Worked-Out Example
- •10.11 Engine-Performance Data
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Continuous Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •Idle Rating
- •10.11.1 Piston Engine
- •10.11.2 Turboprop Engine (Up to 100 Passengers Class)
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •10.11.3 Turbofan Engine: Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans with a BPR Around 4 (Smaller Engines; e.g., Bizjets)
- •Turbofans with a BPR around 5 or 7 (Larger Engines; e.g., RJs and Larger)
- •10.11.4 Turbofan Engine – Military Aircraft
- •11 Aircraft Sizing, Engine Matching, and Variant Derivative
- •11.1 Overview
- •11.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •11.1.2 Coursework Content
- •11.2 Introduction
- •11.3 Theory
- •11.3.1 Sizing for Takeoff Field Length
- •Civil Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •Military Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •11.3.2 Sizing for the Initial Rate of Climb
- •11.3.3 Sizing to Meet Initial Cruise
- •11.3.4 Sizing for Landing Distance
- •11.4 Coursework Exercises: Civil Aircraft Design (Bizjet)
- •11.4.1 Takeoff
- •11.4.2 Initial Climb
- •11.4.3 Cruise
- •11.4.4 Landing
- •11.5 Coursework Exercises: Military Aircraft Design (AJT)
- •11.5.1 Takeoff – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.2 Initial Climb – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.3 Cruise – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.4 Landing – Military Aircraft
- •11.6 Sizing Analysis: Civil Aircraft (Bizjet)
- •11.6.1 Variants in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.6.2 Example: Civil Aircraft
- •11.7 Sizing Analysis: Military Aircraft
- •11.7.1 Single-Seat Variant in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.8 Sensitivity Study
- •11.9 Future Growth Potential
- •12.1 Overview
- •12.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •12.1.2 Coursework Content
- •12.2 Introduction
- •12.3 Static and Dynamic Stability
- •12.3.1 Longitudinal Stability: Pitch Plane (Pitch Moment, M)
- •12.3.2 Directional Stability: Yaw Plane (Yaw Moment, N)
- •12.3.3 Lateral Stability: Roll Plane (Roll Moment, L)
- •12.3.4 Summary of Forces, Moments, and Their Sign Conventions
- •12.4 Theory
- •12.4.1 Pitch Plane
- •12.4.2 Yaw Plane
- •12.4.3 Roll Plane
- •12.6 Inherent Aircraft Motions as Characteristics of Design
- •12.6.1 Short-Period Oscillation and Phugoid Motion
- •12.6.2 Directional and Lateral Modes of Motion
- •12.7 Spinning
- •12.8 Design Considerations for Stability: Civil Aircraft
- •12.9 Military Aircraft: Nonlinear Effects
- •12.10 Active Control Technology: Fly-by-Wire
- •13 Aircraft Performance
- •13.1 Overview
- •13.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •13.1.2 Coursework Content
- •13.2 Introduction
- •13.2.1 Aircraft Speed
- •13.3 Establish Engine Performance Data
- •13.3.1 Turbofan Engine (BPR < 4)
- •Takeoff Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •13.3.2 Turbofan Engine (BPR > 4)
- •13.3.3 Military Turbofan (Advanced Jet Trainer/CAS Role – Very Low BPR) – STD Day
- •13.3.4 Turboprop Engine Performance
- •Takeoff Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •13.4 Derivation of Pertinent Aircraft Performance Equations
- •13.4.1 Takeoff
- •Balanced Field Length: Civil Aircraft
- •Takeoff Equations
- •13.4.2 Landing Performance
- •13.4.3 Climb and Descent Performance
- •Summary
- •Descent
- •13.4.4 Initial Maximum Cruise Speed
- •13.4.5 Payload Range Capability
- •13.5 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Worked-Out Examples (Bizjet)
- •13.5.1 Takeoff Field Length (Bizjet)
- •Segment A: All Engines Operating up to the Decision Speed V1
- •Segment B: One-Engine Inoperative Acceleration from V1 to Liftoff Speed, VLO
- •Segment C: Flaring Distance with One Engine Inoperative from VLO to V2
- •Segment E: Braking Distance from VB to Zero Velocity (Flap Settings Are of Minor Consequence)
- •Discussion of the Takeoff Analysis
- •13.5.2 Landing Field Length (Bizjet)
- •13.5.3 Climb Performance Requirements (Bizjet)
- •13.5.4 Integrated Climb Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.5 Initial High-Speed Cruise (Bizjet)
- •13.5.7 Descent Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.8 Payload Range Capability
- •13.6 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Military Aircraft (AJT)
- •13.6.2 Takeoff Field Length (AJT)
- •Distance Covered from Zero to the Decision Speed V1
- •Distance Covered from Zero to Liftoff Speed VLO
- •Distance Covered from VLO to V2
- •Total Takeoff Distance
- •Stopping Distance and the CFL
- •Distance Covered from V1 to Braking Speed VB
- •Verifying the Climb Gradient at an 8-Deg Flap
- •13.6.3 Landing Field Length (AJT)
- •13.6.4 Climb Performance Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.5 Maximum Speed Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.6 Fuel Requirements (AJT)
- •13.7 Summary
- •13.7.1 The Bizjet
- •14 Computational Fluid Dynamics
- •14.1 Overview
- •14.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •14.1.2 Coursework Content
- •14.2 Introduction
- •14.3 Current Status
- •14.4 Approach to CFD Analyses
- •14.4.1 In the Preprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.2 In the Flow Solver (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.3 In the Postprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.5 Case Studies
- •14.6 Hierarchy of CFD Simulation Methods
- •14.6.1 DNS Simulation Technique
- •14.6.2 Large Eddy Simulation (LES) Technique
- •14.6.3 Detached Eddy Simulation (DES) Technique
- •14.6.4 RANS Equation Technique
- •14.6.5 Euler Method Technique
- •14.6.6 Full-Potential Flow Equations
- •14.6.7 Panel Method
- •14.7 Summary
- •15 Miscellaneous Design Considerations
- •15.1 Overview
- •15.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •15.1.2 Coursework Content
- •15.2 Introduction
- •15.2.1 Environmental Issues
- •15.2.2 Materials and Structures
- •15.2.3 Safety Issues
- •15.2.4 Human Interface
- •15.2.5 Systems Architecture
- •15.2.6 Military Aircraft Survivability Issues
- •15.2.7 Emerging Scenarios
- •15.3 Noise Emissions
- •Approach
- •Sideline
- •15.3.1 Summary
- •15.4 Engine Exhaust Emissions
- •15.5 Aircraft Materials
- •15.5.1 Material Properties
- •15.5.2 Material Selection
- •15.5.3 Coursework Overview
- •Civil Aircraft Design
- •Military Aircraft Design
- •15.6 Aircraft Structural Considerations
- •15.7 Doors: Emergency Egress
- •Coursework Exercise
- •15.8 Aircraft Flight Deck (Cockpit) Layout
- •15.8.1 Multifunctional Display and Electronic Flight Information System
- •15.8.2 Combat Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.3 Civil Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.4 Head-Up Display
- •15.8.5 Helmet-Mounted Display
- •15.8.6 Hands-On Throttle and Stick
- •15.8.7 Voice-Operated Control
- •15.9 Aircraft Systems
- •15.9.1 Aircraft Control Subsystem
- •15.9.2 Engine and Fuel Control Subsystems
- •Piston Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1 to 1.5% of the MTOW)
- •Turbofan Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1.5 to 2% of the MTOW)
- •Fuel Storage and Flow Management
- •15.9.3 Emergency Power Supply
- •15.9.4 Avionics Subsystems
- •Military Aircraft Application
- •Civil Aircraft Application
- •15.9.5 Electrical Subsystem
- •15.9.6 Hydraulic Subsystem
- •15.9.7 Pneumatic System
- •ECS: Cabin Pressurization and Air-Conditioning
- •Oxygen Supply
- •Anti-icing, De-icing, Defogging, and Rain-Removal Systems
- •Defogging and Rain-Removal Systems
- •15.9.8 Utility Subsystem
- •15.9.9 End-of-Life Disposal
- •15.10 Military Aircraft Survivability
- •15.10.1 Military Emergency Escape
- •15.10.2 Military Aircraft Stealth Consideration
- •15.11 Emerging Scenarios
- •Counterterrorism Design Implementation
- •Health Issues
- •Damage from Runway Debris
- •16 Aircraft Cost Considerations
- •16.1 Overview
- •16.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •16.1.2 Coursework Content
- •16.2 Introduction
- •16.3 Aircraft Cost and Operational Cost
- •Operating Cost
- •16.4 Aircraft Costing Methodology: Rapid-Cost Model
- •16.4.1 Nacelle Cost Drivers
- •Group 1
- •Group 2
- •16.4.2 Nose Cowl Parts and Subassemblies
- •16.4.3 Methodology (Nose Cowl Only)
- •Cost of Parts Fabrication
- •Subassemblies
- •Cost of Amortization of the NRCs
- •16.4.4 Cost Formulas and Results
- •16.5 Aircraft Direct Operating Cost
- •16.5.1 Formulation to Estimate DOC
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •16.5.2 Worked-Out Example of DOC: Bizjet
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •OC of the Variants in the Family
- •17 Aircraft Manufacturing Considerations
- •17.1 Overview
- •17.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •17.1.2 Coursework Content
- •17.2 Introduction
- •17.3 Design for Manufacture and Assembly
- •17.4 Manufacturing Practices
- •17.5 Six Sigma Concept
- •17.6 Tolerance Relaxation at the Wetted Surface
- •17.6.1 Sources of Aircraft Surface Degeneration
- •17.6.2 Cost-versus-Tolerance Relationship
- •17.7 Reliability and Maintainability
- •17.8 Design Considerations
- •17.8.1 Category I: Technology-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.2 Category II: Manufacture-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.3 Category III: Management-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.4 Category IV: Operator-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.9 “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.1 Index for “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.2 Worked-Out Example
- •Standard Parameters of the Baseline Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Extended Variant Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Shortened Variant Aircraft
- •17.10 Digital Manufacturing Process Management
- •Process Detailing and Validation
- •Resource Modeling and Simulation
- •Process Planning and Simulation
- •17.10.1 Product, Process, and Resource Hub
- •17.10.3 Shop-Floor Interface
- •17.10.4 Design for Maintainability and 3D-Based Technical Publication Generation
- •Midrange Aircraft (Airbus 320 class)
- •References
- •ROAD MAP OF THE BOOK
- •CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION
- •CHAPTER 3. AERODYNAMIC CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 5. AIRCRAFT LOAD
- •CHAPTER 6. CONFIGURING AIRCRAFT
- •CHAPTER 7. UNDERCARRIAGE
- •CHAPTER 8. AIRCRAFT WEIGHT AND CENTER OF GRAVITY ESTIMATION
- •CHAPTER 9. AIRCRAFT DRAG
- •CHAPTER 10. AIRCRAFT POWER PLANT AND INTEGRATION
- •CHAPTER 11. AIRCRAFT SIZING, ENGINE MATCHING, AND VARIANT DERIVATIVE
- •CHAPTER 12. STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS AFFECTING AIRCRAFT CONFIGURATION
- •CHAPTER 13. AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE
- •CHAPTER 14. COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
- •CHAPTER 15. MISCELLANEOUS DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 16. AIRCRAFT COST CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 17. AIRCRAFT MANUFACTURING CONSIDERATIONS
- •Index
4.5 Civil Subsonic Jet Aircraft Statistics |
109 |
examined in conjunction with Figures 4.4, 4.5, and 4.6, which show the range increase with the MTOM increase.
Fuel mass increases with aircraft size, reflecting today’s market demand for longer ranges. The long-range aircraft fuel load, including reserves, is less than half the MTOM. For the same passenger capacity, there is statistical dispersion at the low end. This indicates that for aircraft with a wider selection of comfort levels and choice of aerodynamic devices, the fuel content is determined by the varied market demand: from short ranges of around 1,400 nm to cross-country ranges of around 2,500 nm. At the higher end, the selection narrows, showing a linear trend. Figure 4.6 indicates that larger aircraft have better structural efficiency, offering a better OEMF; Figure 4.7 indicates that they also have a higher fuel fraction for longer ranges.
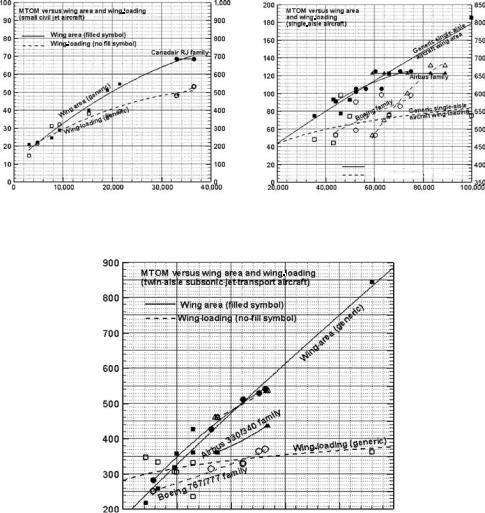
4.5.4 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Wing Area
Whereas the fuselage size is determined from the specified passenger capacity, the wing must be sized to meet performance constraints through a matched engine (see Chapter 11). Figure 4.8 shows the relationships between the wing planform reference area, SW, and the wing-loading versus the MTOM. These graphs are useful for obtaining a starting value (i.e., preliminary sizing) for a new aircraft design that would be refined through the sizing analysis.
Wing-loading, W/Sw, is defined as the ratio of the MTOM to the wing planform reference area. (W/SW = MTOM/wing area, kg/m2, if expressed in terms of weight; then, the unit becomes N/m2 or lb/ft2.) This is a significant sizing parameter and has an important role in aircraft design.
The influence of wing-loading is illustrated in the graphs in Figure 4.8. The tendency is to have lower wing-loading for smaller aircraft and higher wing-loading for larger aircraft operating at high-subsonic speed. High wing-loading requires the assistance of better high-lift devices to operate at low speed; better high-lift devices are heavier and more expensive.
The growth of the wing area with aircraft mass is necessary to sustain flight. A large wing planform area is required for better low-speed field performance, which exceeds the cruise requirement. Therefore, wing-sizing (see Chapter 11) provides the minimum wing planform area to satisfy simultaneously both the takeoff and the cruise requirements. Determination of wing-loading is a result of the wing-sizing exercise.
Smaller aircraft operate in smaller airfields and, to keep the weight and cost down, simpler types of high-lift devices are used. This results in lower wing-loading (i.e., 200 to 500 kg/m2), as shown in Figure 4.8a. Aircraft with a range of more than 3,000 nm need more efficient high-lift devices. It was shown previously that aircraft size increases with increases in range, resulting in wing-loading increases (i.e., from 400 to 700 kg/m2 for midrange aircraft) when better high-lift devices are considered.
Here, the trends for variants in the family of aircraft design can be examined. The Airbus 320 baseline aircraft is in the middle of the family. The A320 family retains the wing to maintain component commonality, which substantially reduces manufacturing cost because not many new modifications are necessary for the variants. This resulted in large changes in wing-loading: The smallest in the family
110 |
Aircraft Classification, Statistics, and Choices for Configuration |
2 Wing area (m )
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
2 |
areaWing(m |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
loading-Wing(kg/m |
|
|
|
loading-Wing(kg/m |
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wing area (fill symbol) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wing-loading (no-fill symbol) |
|
MTOM (kg) |
|
|
|
|
MTOM (kg) |
|
|
(a) Small aircraft |
|
|
|
(b) Midrange single-aisle aircraft |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,050 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wingarea (m |
|
|
|
|
|
700 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
loading-Wing(kg/m |
||
) |
|
|
|
|
|
950 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
900 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
850 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
750 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
650 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
550 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
500 |
|
100,000 |
200,000 |
300,000 |
|
400,000 |
500,000 |
600,000 |
|
MTOM (kg)
(c) Large twin-aisle aircraft
Figure 4.8. Wing area, SW, versus MTOM
(A318) has low wing-loading with excellent field performance, and the largest in the family (A321) has high wing-loading that requires higher thrust-loading to keep field performance from degrading below the requirements. Conversely, the Boeing 737 baseline aircraft started with the smallest in the family and was forced into wing growth with increases in weight and cost; this keeps changes in wing-loading at a moderate level.
Larger aircraft have longer ranges; therefore, wing-loading is higher to keep the wing area low, thereby decreasing drag. For large twin-aisle, subsonic jet aircraft (see Figure 4.8c), the picture is similar to the midrange-sized, single-aisle aircraft but with higher wing-loadings (i.e., 500 to 900 kg/m2) to keep wing size relatively small (which counters the square-cube law discussed in Section 3.20.1). Large aircraft require advanced high-lift devices and longer runways.
4.5 Civil Subsonic Jet Aircraft Statistics |
111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
turbofanperThrust(kg) |
|
6,000 |
|
turbofanperThrust(kg) |
|
|
|
turbofanperThrust(kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
loading-Thrust |
14,000 |
|
|
|
|||
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
20,000 |
30,000 |
40,000 |
|
6,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
40,000 |
60,000 |
80,000 |
100,000 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
MTOM (kg) |
|
|
|
|
MTOM (kg) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
(a) Small aircraft |
|
|
|
|
(b) Midsize aircraft |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(kg) |
30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
-Thrustloading |
|
|
|
|
|
turbofanperThrust |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
200,000 |
300,000 |
400,000 |
500,000 |
600,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100,000 |
|
||||||
MTOM (kg)
(c) Large aircraft
Figure 4.9. Total sea-level static thrust versus MTOM
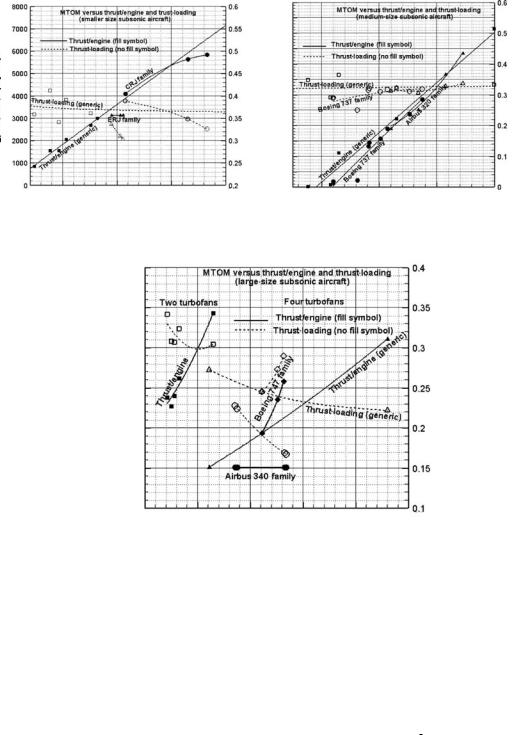
4.5.5 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Engine Power
The relationships between engine sizes and the MTOM are shown in Figure 4.9. Turbofan engine size is expressed as sea-level static thrust (TSLS) in the ISA day at takeoff ratings, when the engine produces maximum thrust (see Chapter 10). These graphs can be used only for preliminary sizing; formal sizing and engine matching are described in Chapter 11.
Thrust-loading (T/W), is defined as the ratio of total thrust (TSLS tot) of all engines to the weight of the aircraft. Again, a clear relationship can be established through regression analysis. Mandatory airworthiness regulations require that multiengine aircraft should be able to climb in a specified gradient (see FAA requirements in Chapter 13) with one engine inoperative. For a twin-engine aircraft,
Thrust-loading
112 |
Aircraft Classification, Statistics, and Choices for Configuration |
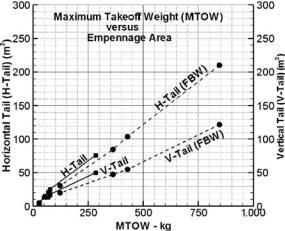
Figure 4.10. Empennage area versus wing area
failure of an engine amounts to a 50% loss of power, whereas for a four-engine aircraft, it amounts to a 25% loss of power. Therefore, the T/W for a two-engine aircraft would be higher than for a four-engine aircraft.
The constraints for engine matching are that it should simultaneously satisfy sufficient takeoff thrust to meet the (1) field length specifications, (2) initial climb requirements, and (3) initial high-speed cruise requirements from market specifications. An increase in engine thrust with aircraft mass is obvious for meeting takeoff performance. Engine matching depends on wing size, number of engines, and type of high-lift device used. Propeller-driven aircraft are rated in power P in kw (hp or shp), which in turn provides the thrust. Turboprops are rated in power loading, P/W, instead of T/W.
Smaller aircraft operate in smaller airfields and are generally configured with two engines and simpler flap types to keep costs down. Figure 4.9a shows thrust growth with size for small aircraft. Here, thrust-loading is from 0.35 to 0.45. Figure 4.9b shows midrange statistics, mostly for two-engine aircraft. Midrange aircraft operate in better and longer airfields than smaller aircraft; hence, the thrust-loading range is at a lower value, between 0.3 and 0.37. Figure 4.9c shows long-range statistics, with some twoand four-engine aircraft – the three-engine configuration is not currently in use. Long-range aircraft with superior high-lift devices and long runways ensure that thrust-loading can be maintained between 0.22 and 0.33; the lower values are for four-engine aircraft. Trends in family variants in each of the three classes are also shown in Figure 4.9.
4.5.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area
Once the wing area is established along with fuselage length and matched engine size, the empennage areas (i.e., H-tail, SH, and V-tail, SV) can be estimated from the static stability requirements. Section 3.22 discusses the empennage tail-volume coefficients to determine empennage areas.
Figure 4.10 shows growth for H-tail and V-tail surface areas with the MTOM. The variants in the families do not show change in empennage areas to maintain component commonality.
