
- •Contents
- •Symbols and Abbreviations
- •Symbols
- •Greek Symbols
- •Subscripts
- •Abbreviations
- •Preface
- •Road Map of the Book
- •The Arrangement
- •Suggested Route for the Coursework
- •First Semester
- •Second Semester
- •Suggestions for the Class
- •Use of Semi-empirical Relations
- •1 Introduction
- •1.1 Overview
- •1.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •1.1.2 Coursework Content
- •1.2 Brief Historical Background
- •1.3 Current Aircraft Design Status
- •1.3.1 Forces and Drivers
- •1.3.2 Current Civil Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.3.3 Current Military Aircraft Design Trends
- •1.4 Future Trends
- •1.4.1 Civil Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.4.2 Military Aircraft Design: Future Trends
- •1.5 Learning Process
- •1.6 Units and Dimensions
- •1.7 Cost Implications
- •2 Methodology to Aircraft Design, Market Survey, and Airworthiness
- •2.1 Overview
- •2.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •2.1.2 Coursework Content
- •2.2 Introduction
- •2.3 Typical Design Process
- •2.3.1 Four Phases of Aircraft Design
- •2.3.2 Typical Resources Deployment
- •2.3.3 Typical Cost Frame
- •2.3.4 Typical Time Frame
- •2.4 Typical Task Breakdown in Each Phase
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Study Phase (Feasibility Study)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design Phase (Full-Scale Product Development)
- •2.4.1 Functional Tasks during the Conceptual Study (Phase 1: Civil Aircraft)
- •2.4.2 Project Activities for Small Aircraft Design
- •Phase 1: Conceptual Design (6 Months)
- •Phase 3: Detailed Design (Product Development) (12 Months)
- •2.5 Aircraft Familiarization
- •Fuselage Group
- •Wing Group
- •Empennage Group
- •Nacelle Group
- •Undercarriage Group
- •2.6 Market Survey
- •2.7 Civil Aircraft Market
- •2.8 Military Market
- •2.9 Comparison between Civil and Military Aircraft Design Requirements
- •2.10 Airworthiness Requirements
- •2.11 Coursework Procedures
- •3 Aerodynamic Considerations
- •3.1 Overview
- •3.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •3.1.2 Coursework Content
- •3.2 Introduction
- •3.3 Atmosphere
- •3.4 Fundamental Equations
- •3.5.1 Flow Past Aerofoil
- •3.6 Aircraft Motion and Forces
- •3.6.1 Motion
- •3.6.2 Forces
- •3.7 Aerofoil
- •3.7.1 Groupings of Aerofoils and Their Properties
- •NACA Four-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Five-Digit Aerofoil
- •NACA Six-Digit Aerofoil
- •Other Types of Aerofoils
- •3.9 Generation of Lift
- •3.10 Types of Stall
- •3.10.1 Gradual Stall
- •3.10.2 Abrupt Stall
- •3.11 Comparison of Three NACA Aerofoils
- •3.12 High-Lift Devices
- •3.13 Transonic Effects – Area Rule
- •3.14 Wing Aerodynamics
- •3.14.1 Induced Drag and Total Aircraft Drag
- •3.15 Aspect Ratio Correction of 2D Aerofoil Characteristics for 3D Finite Wing
- •3.16.1 Planform Area, SW
- •3.16.2 Wing Aspect Ratio
- •3.16.4 Wing Root (Croot) and Tip (Ctip) Chord
- •3.16.6 Wing Twist
- •3.17 Mean Aerodynamic Chord
- •3.18 Compressibility Effect: Wing Sweep
- •3.19 Wing Stall Pattern and Wing Twist
- •3.20.1 The Square-Cube Law
- •3.20.2 Aircraft Wetted Area (AW) versus Wing Planform Area (Sw)
- •3.20.3 Additional Vortex Lift
- •3.20.4 Additional Surfaces on Wing
- •3.21 Finalizing Wing Design Parameters
- •3.22 Empennage
- •3.22.1 H-Tail
- •3.22.2 V-Tail
- •3.23 Fuselage
- •3.23.2 Fuselage Length, Lfus
- •3.23.3 Fineness Ratio, FR
- •3.23.4 Fuselage Upsweep Angle
- •3.23.5 Fuselage Closure Angle
- •3.23.6 Front Fuselage Closure Length, Lf
- •3.23.7 Aft Fuselage Closure Length, La
- •3.23.8 Midfuselage Constant Cross-Section Length, Lm
- •3.23.9 Fuselage Height, H
- •3.23.10 Fuselage Width, W
- •3.23.11 Average Diameter, Dave
- •3.23.12 Cabin Height, Hcab
- •3.23.13 Cabin Width, Wcab
- •3.24 Undercarriage
- •3.25 Nacelle and Intake
- •3.26 Speed Brakes and Dive Brakes
- •4.1 Overview
- •4.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •4.1.2 Coursework Content
- •4.2 Introduction
- •4.3 Aircraft Evolution
- •4.4 Civil Aircraft Mission (Payload-Range)
- •4.5 Civil Subsonic Jet Aircraft Statistics (Sizing Parameters and Regression Analysis)
- •4.5.1 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Number of Passengers
- •4.5.2 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Operational Empty Mass
- •4.5.3 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Fuel Load
- •4.5.4 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Wing Area
- •4.5.5 Maximum Takeoff Mass versus Engine Power
- •4.5.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area
- •4.5.7 Wing Loading versus Aircraft Span
- •4.6 Civil Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.7 Fuselage Group
- •4.7.1 Fuselage Width
- •4.7.2 Fuselage Length
- •4.7.3 Front (Nose Cone) and Aft-End Closure
- •4.7.4 Flight Crew (Flight Deck) Compartment Layout
- •4.7.5 Cabin Crew and Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.6 Seat Arrangement, Pitch, and Posture (95th Percentile) Facilities
- •4.7.7 Passenger Facilities
- •4.7.8 Cargo Container Sizes
- •4.7.9 Doors – Emergency Exits
- •4.8 Wing Group
- •4.9 Empennage Group (Civil Aircraft)
- •4.10 Nacelle Group
- •4.11 Summary of Civil Aircraft Design Choices
- •4.13 Military Aircraft Mission
- •4.14.1 Military Aircraft Maximum Take-off Mass (MTOM) versus Payload
- •4.14.2 Military MTOM versus OEM
- •4.14.3 Military MTOM versus Fuel Load Mf
- •4.14.4 MTOM versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.5 MTOM versus Engine Thrust (Military)
- •4.14.6 Empennage Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.14.7 Aircraft Wetted Area versus Wing Area (Military)
- •4.15 Military Aircraft Component Geometries
- •4.16 Fuselage Group (Military)
- •4.17 Wing Group (Military)
- •4.17.1 Generic Wing Planform Shapes
- •4.18 Empennage Group (Military)
- •4.19 Intake/Nacelle Group (Military)
- •4.20 Undercarriage Group
- •4.21 Miscellaneous Comments
- •4.22 Summary of Military Aircraft Design Choices
- •5 Aircraft Load
- •5.1 Overview
- •5.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •5.1.2 Coursework Content
- •5.2 Introduction
- •5.2.1 Buffet
- •5.2.2 Flutter
- •5.3 Flight Maneuvers
- •5.3.1 Pitch Plane (X-Z) Maneuver (Elevator/Canard-Induced)
- •5.3.2 Roll Plane (Y-Z) Maneuver (Aileron-Induced)
- •5.3.3 Yaw Plane (Z-X) Maneuver (Rudder-Induced)
- •5.4 Aircraft Loads
- •5.4.1 On the Ground
- •5.4.2 In Flight
- •5.5.1 Load Factor, n
- •5.6 Limits – Load and Speeds
- •5.6.1 Maximum Limit of Load Factor
- •5.6.2 Speed Limits
- •5.7 V-n Diagram
- •5.7.1 Low-Speed Limit
- •5.7.2 High-Speed Limit
- •5.7.3 Extreme Points of a V-n Diagram
- •Positive Loads
- •Negative Loads
- •5.8 Gust Envelope
- •6.1 Overview
- •6.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •6.1.2 Coursework Content
- •6.2 Introduction
- •Closure of the Fuselage
- •6.4 Civil Aircraft Fuselage: Typical Shaping and Layout
- •6.4.1 Narrow-Body, Single-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.2 Wide-Body, Double-Aisle Aircraft
- •6.4.3 Worked-Out Example: Civil Aircraft Fuselage Layout
- •6.5.1 Aerofoil Selection
- •6.5.2 Wing Design
- •Planform Shape
- •Wing Reference Area
- •Wing Sweep
- •Wing Twist
- •Wing Dihedral/Anhedral
- •6.5.3 Wing-Mounted Control-Surface Layout
- •6.5.4 Positioning of the Wing Relative to the Fuselage
- •6.6.1 Horizontal Tail
- •6.6.2 Vertical Tail
- •6.8 Undercarriage Positioning
- •6.10 Miscellaneous Considerations in Civil Aircraft
- •6.12.1 Use of Statistics in the Class of Military Trainer Aircraft
- •6.12.3 Miscellaneous Considerations – Military Design
- •6.13 Variant CAS Design
- •6.13.1 Summary of the Worked-Out Military Aircraft Preliminary Details
- •7 Undercarriage
- •7.1 Overview
- •7.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •7.1.2 Coursework Content
- •7.2 Introduction
- •7.3 Types of Undercarriage
- •7.5 Undercarriage Retraction and Stowage
- •7.5.1 Stowage Space Clearances
- •7.6 Undercarriage Design Drivers and Considerations
- •7.7 Turning of an Aircraft
- •7.8 Wheels
- •7.9 Loads on Wheels and Shock Absorbers
- •7.9.1 Load on Wheels
- •7.9.2 Energy Absorbed
- •7.11 Tires
- •7.13 Undercarriage Layout Methodology
- •7.14 Worked-Out Examples
- •7.14.1 Civil Aircraft: Bizjet
- •Baseline Aircraft with 10 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •Shrunk Aircraft (Smallest in the Family Variant) with 6 Passengers at a 33-Inch Pitch
- •7.14.2 Military Aircraft: AJT
- •7.15 Miscellaneous Considerations
- •7.16 Undercarriage and Tire Data
- •8 Aircraft Weight and Center of Gravity Estimation
- •8.1 Overview
- •8.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •8.1.2 Coursework Content
- •8.2 Introduction
- •8.3 The Weight Drivers
- •8.4 Aircraft Mass (Weight) Breakdown
- •8.5 Desirable CG Position
- •8.6 Aircraft Component Groups
- •8.6.1 Civil Aircraft
- •8.6.2 Military Aircraft (Combat Category)
- •8.7 Aircraft Component Mass Estimation
- •8.8 Rapid Mass Estimation Method: Civil Aircraft
- •8.9 Graphical Method for Predicting Aircraft Component Weight: Civil Aircraft
- •8.10 Semi-empirical Equation Method (Statistical)
- •8.10.1 Fuselage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.2 Wing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.3 Empennage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.4 Nacelle Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Jet Type (Includes Pylon Mass)
- •Turboprop Type
- •Piston-Engine Nacelle
- •8.10.5 Undercarriage Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Tricycle Type (Retractable) – Fuselage-Mounted (Nose and Main Gear Estimated Together)
- •8.10.6 Miscellaneous Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.7 Power Plant Group – Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans
- •Turboprops
- •Piston Engines
- •8.10.8 Systems Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.9 Furnishing Group – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.10 Contingency and Miscellaneous – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.11 Crew – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.12 Payload – Civil Aircraft
- •8.10.13 Fuel – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11 Worked-Out Example – Civil Aircraft
- •8.11.1 Fuselage Group Mass
- •8.11.2 Wing Group Mass
- •8.11.3 Empennage Group Mass
- •8.11.4 Nacelle Group Mass
- •8.11.5 Undercarriage Group Mass
- •8.11.6 Miscellaneous Group Mass
- •8.11.7 Power Plant Group Mass
- •8.11.8 Systems Group Mass
- •8.11.9 Furnishing Group Mass
- •8.11.10 Contingency Group Mass
- •8.11.11 Crew Mass
- •8.11.12 Payload Mass
- •8.11.13 Fuel Mass
- •8.11.14 Weight Summary
- •Variant Aircraft in the Family
- •8.12 Center of Gravity Determination
- •8.12.1 Bizjet Aircraft CG Location Example
- •8.12.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position Relative to Aircraft and Components
- •8.13 Rapid Mass Estimation Method – Military Aircraft
- •8.14 Graphical Method to Predict Aircraft Component Weight – Military Aircraft
- •8.15 Semi-empirical Equation Methods (Statistical) – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.1 Military Aircraft Fuselage Group (SI System)
- •8.15.2 Military Aircraft Wing Mass (SI System)
- •8.15.3 Military Aircraft Empennage
- •8.15.4 Nacelle Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.5 Power Plant Group Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.6 Undercarriage Mass Example – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.7 System Mass – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.8 Aircraft Furnishing – Military Aircraft
- •8.15.11 Crew Mass
- •8.16.1 AJT Fuselage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.2 AJT Wing Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.3 AJT Empennage Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.4 AJT Nacelle Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.5 AJT Power Plant Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.6 AJT Undercarriage Mass Example (Based on CAS Variant)
- •8.16.7 AJT Systems Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.8 AJT Furnishing Group Mass Example (Based on AJT Variant)
- •8.16.9 AJT Contingency Group Mass Example
- •8.16.10 AJT Crew Mass Example
- •8.16.13 Weights Summary – Military Aircraft
- •8.17 CG Position Determination – Military Aircraft
- •8.17.1 Classroom Worked-Out Military AJT CG Location Example
- •8.17.2 First Iteration to Fine Tune CG Position and Components Masses
- •9 Aircraft Drag
- •9.1 Overview
- •9.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •9.1.2 Coursework Content
- •9.2 Introduction
- •9.4 Aircraft Drag Breakdown (Subsonic)
- •9.5 Aircraft Drag Formulation
- •9.6 Aircraft Drag Estimation Methodology (Subsonic)
- •9.7 Minimum Parasite Drag Estimation Methodology
- •9.7.2 Computation of Wetted Areas
- •Lifting Surfaces
- •Fuselage
- •Nacelle
- •9.7.3 Stepwise Approach to Compute Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.8 Semi-empirical Relations to Estimate Aircraft Component Parasite Drag
- •9.8.1 Fuselage
- •9.8.2 Wing, Empennage, Pylons, and Winglets
- •9.8.3 Nacelle Drag
- •Intake Drag
- •Base Drag
- •Boat-Tail Drag
- •9.8.4 Excrescence Drag
- •9.8.5 Miscellaneous Parasite Drags
- •Air-Conditioning Drag
- •Trim Drag
- •Aerials
- •9.9 Notes on Excrescence Drag Resulting from Surface Imperfections
- •9.10 Minimum Parasite Drag
- •9.12 Subsonic Wave Drag
- •9.13 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.14 Low-Speed Aircraft Drag at Takeoff and Landing
- •9.14.1 High-Lift Device Drag
- •9.14.2 Dive Brakes and Spoilers Drag
- •9.14.3 Undercarriage Drag
- •9.14.4 One-Engine Inoperative Drag
- •9.15 Propeller-Driven Aircraft Drag
- •9.16 Military Aircraft Drag
- •9.17 Supersonic Drag
- •9.18 Coursework Example: Civil Bizjet Aircraft
- •9.18.1 Geometric and Performance Data
- •Fuselage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Wing (see Figure 9.13)
- •Empennage (see Figure 9.13)
- •Nacelle (see Figure 9.13)
- •9.18.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •Nacelle
- •Pylon
- •9.18.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.18.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.18.6 Induced Drag
- •9.18.7 Total Aircraft Drag at LRC
- •9.19 Coursework Example: Subsonic Military Aircraft
- •9.19.1 Geometric and Performance Data of a Vigilante RA-C5 Aircraft
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.2 Computation of Wetted Areas, Re, and Basic CF
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage (same procedure as for the wing)
- •9.19.3 Computation of 3D and Other Effects to Estimate Component CDpmin
- •Fuselage
- •Wing
- •Empennage
- •9.19.4 Summary of Parasite Drag
- •9.19.5 CDp Estimation
- •9.19.6 Induced Drag
- •9.19.7 Supersonic Drag Estimation
- •9.19.8 Total Aircraft Drag
- •9.20 Concluding Remarks
- •10 Aircraft Power Plant and Integration
- •10.1 Overview
- •10.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •10.1.2 Coursework Content
- •10.2 Background
- •10.4 Introduction: Air-Breathing Aircraft Engine Types
- •10.4.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet
- •10.4.2 Turbofan: Bypass Engine
- •10.4.3 Afterburner Engine
- •10.4.4 Turboprop Engine
- •10.4.5 Piston Engine
- •10.6 Formulation and Theory: Isentropic Case
- •10.6.1 Simple Straight-Through Turbojet Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.2 Bypass Turbofan Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.3 Afterburner Engine: Formulation
- •10.6.4 Turboprop Engine: Formulation
- •Summary
- •10.7 Engine Integration with an Aircraft: Installation Effects
- •10.7.1 Subsonic Civil Aircraft Nacelle and Engine Installation
- •10.7.2 Turboprop Integration to Aircraft
- •10.7.3 Combat Aircraft Engine Installation
- •10.8 Intake and Nozzle Design
- •10.8.1 Civil Aircraft Intake Design: Inlet Sizing
- •10.8.2 Military Aircraft Intake Design
- •10.9 Exhaust Nozzle and Thrust Reverser
- •10.9.1 Civil Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application
- •10.9.2 Civil Aircraft Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.9.3 Coursework Example of Civil Aircraft Nacelle Design
- •Intake Geometry (see Section 10.8.1)
- •Lip Section (Crown Cut)
- •Lip Section (Keel Cut)
- •Nozzle Geometry
- •10.9.4 Military Aircraft Thrust Reverser Application and Exhaust Nozzles
- •10.10 Propeller
- •10.10.2 Propeller Theory
- •Momentum Theory: Actuator Disc
- •Blade-Element Theory
- •10.10.3 Propeller Performance: Practical Engineering Applications
- •Static Performance (see Figures 10.34 and 10.36)
- •In-Flight Performance (see Figures 10.35 and 10.37)
- •10.10.5 Propeller Performance at STD Day: Worked-Out Example
- •10.11 Engine-Performance Data
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Continuous Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •Idle Rating
- •10.11.1 Piston Engine
- •10.11.2 Turboprop Engine (Up to 100 Passengers Class)
- •Takeoff Rating
- •Maximum Climb Rating
- •Maximum Cruise Rating
- •10.11.3 Turbofan Engine: Civil Aircraft
- •Turbofans with a BPR Around 4 (Smaller Engines; e.g., Bizjets)
- •Turbofans with a BPR around 5 or 7 (Larger Engines; e.g., RJs and Larger)
- •10.11.4 Turbofan Engine – Military Aircraft
- •11 Aircraft Sizing, Engine Matching, and Variant Derivative
- •11.1 Overview
- •11.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •11.1.2 Coursework Content
- •11.2 Introduction
- •11.3 Theory
- •11.3.1 Sizing for Takeoff Field Length
- •Civil Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •Military Aircraft Design: Takeoff
- •11.3.2 Sizing for the Initial Rate of Climb
- •11.3.3 Sizing to Meet Initial Cruise
- •11.3.4 Sizing for Landing Distance
- •11.4 Coursework Exercises: Civil Aircraft Design (Bizjet)
- •11.4.1 Takeoff
- •11.4.2 Initial Climb
- •11.4.3 Cruise
- •11.4.4 Landing
- •11.5 Coursework Exercises: Military Aircraft Design (AJT)
- •11.5.1 Takeoff – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.2 Initial Climb – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.3 Cruise – Military Aircraft
- •11.5.4 Landing – Military Aircraft
- •11.6 Sizing Analysis: Civil Aircraft (Bizjet)
- •11.6.1 Variants in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.6.2 Example: Civil Aircraft
- •11.7 Sizing Analysis: Military Aircraft
- •11.7.1 Single-Seat Variant in the Family of Aircraft Design
- •11.8 Sensitivity Study
- •11.9 Future Growth Potential
- •12.1 Overview
- •12.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •12.1.2 Coursework Content
- •12.2 Introduction
- •12.3 Static and Dynamic Stability
- •12.3.1 Longitudinal Stability: Pitch Plane (Pitch Moment, M)
- •12.3.2 Directional Stability: Yaw Plane (Yaw Moment, N)
- •12.3.3 Lateral Stability: Roll Plane (Roll Moment, L)
- •12.3.4 Summary of Forces, Moments, and Their Sign Conventions
- •12.4 Theory
- •12.4.1 Pitch Plane
- •12.4.2 Yaw Plane
- •12.4.3 Roll Plane
- •12.6 Inherent Aircraft Motions as Characteristics of Design
- •12.6.1 Short-Period Oscillation and Phugoid Motion
- •12.6.2 Directional and Lateral Modes of Motion
- •12.7 Spinning
- •12.8 Design Considerations for Stability: Civil Aircraft
- •12.9 Military Aircraft: Nonlinear Effects
- •12.10 Active Control Technology: Fly-by-Wire
- •13 Aircraft Performance
- •13.1 Overview
- •13.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •13.1.2 Coursework Content
- •13.2 Introduction
- •13.2.1 Aircraft Speed
- •13.3 Establish Engine Performance Data
- •13.3.1 Turbofan Engine (BPR < 4)
- •Takeoff Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Bizjet): Standard Day
- •13.3.2 Turbofan Engine (BPR > 4)
- •13.3.3 Military Turbofan (Advanced Jet Trainer/CAS Role – Very Low BPR) – STD Day
- •13.3.4 Turboprop Engine Performance
- •Takeoff Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Climb Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •Maximum Cruise Rating (Turboprop): Standard Day
- •13.4 Derivation of Pertinent Aircraft Performance Equations
- •13.4.1 Takeoff
- •Balanced Field Length: Civil Aircraft
- •Takeoff Equations
- •13.4.2 Landing Performance
- •13.4.3 Climb and Descent Performance
- •Summary
- •Descent
- •13.4.4 Initial Maximum Cruise Speed
- •13.4.5 Payload Range Capability
- •13.5 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Worked-Out Examples (Bizjet)
- •13.5.1 Takeoff Field Length (Bizjet)
- •Segment A: All Engines Operating up to the Decision Speed V1
- •Segment B: One-Engine Inoperative Acceleration from V1 to Liftoff Speed, VLO
- •Segment C: Flaring Distance with One Engine Inoperative from VLO to V2
- •Segment E: Braking Distance from VB to Zero Velocity (Flap Settings Are of Minor Consequence)
- •Discussion of the Takeoff Analysis
- •13.5.2 Landing Field Length (Bizjet)
- •13.5.3 Climb Performance Requirements (Bizjet)
- •13.5.4 Integrated Climb Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.5 Initial High-Speed Cruise (Bizjet)
- •13.5.7 Descent Performance (Bizjet)
- •13.5.8 Payload Range Capability
- •13.6 Aircraft Performance Substantiation: Military Aircraft (AJT)
- •13.6.2 Takeoff Field Length (AJT)
- •Distance Covered from Zero to the Decision Speed V1
- •Distance Covered from Zero to Liftoff Speed VLO
- •Distance Covered from VLO to V2
- •Total Takeoff Distance
- •Stopping Distance and the CFL
- •Distance Covered from V1 to Braking Speed VB
- •Verifying the Climb Gradient at an 8-Deg Flap
- •13.6.3 Landing Field Length (AJT)
- •13.6.4 Climb Performance Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.5 Maximum Speed Requirements (AJT)
- •13.6.6 Fuel Requirements (AJT)
- •13.7 Summary
- •13.7.1 The Bizjet
- •14 Computational Fluid Dynamics
- •14.1 Overview
- •14.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •14.1.2 Coursework Content
- •14.2 Introduction
- •14.3 Current Status
- •14.4 Approach to CFD Analyses
- •14.4.1 In the Preprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.2 In the Flow Solver (Menu-Driven)
- •14.4.3 In the Postprocessor (Menu-Driven)
- •14.5 Case Studies
- •14.6 Hierarchy of CFD Simulation Methods
- •14.6.1 DNS Simulation Technique
- •14.6.2 Large Eddy Simulation (LES) Technique
- •14.6.3 Detached Eddy Simulation (DES) Technique
- •14.6.4 RANS Equation Technique
- •14.6.5 Euler Method Technique
- •14.6.6 Full-Potential Flow Equations
- •14.6.7 Panel Method
- •14.7 Summary
- •15 Miscellaneous Design Considerations
- •15.1 Overview
- •15.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •15.1.2 Coursework Content
- •15.2 Introduction
- •15.2.1 Environmental Issues
- •15.2.2 Materials and Structures
- •15.2.3 Safety Issues
- •15.2.4 Human Interface
- •15.2.5 Systems Architecture
- •15.2.6 Military Aircraft Survivability Issues
- •15.2.7 Emerging Scenarios
- •15.3 Noise Emissions
- •Approach
- •Sideline
- •15.3.1 Summary
- •15.4 Engine Exhaust Emissions
- •15.5 Aircraft Materials
- •15.5.1 Material Properties
- •15.5.2 Material Selection
- •15.5.3 Coursework Overview
- •Civil Aircraft Design
- •Military Aircraft Design
- •15.6 Aircraft Structural Considerations
- •15.7 Doors: Emergency Egress
- •Coursework Exercise
- •15.8 Aircraft Flight Deck (Cockpit) Layout
- •15.8.1 Multifunctional Display and Electronic Flight Information System
- •15.8.2 Combat Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.3 Civil Aircraft Flight Deck
- •15.8.4 Head-Up Display
- •15.8.5 Helmet-Mounted Display
- •15.8.6 Hands-On Throttle and Stick
- •15.8.7 Voice-Operated Control
- •15.9 Aircraft Systems
- •15.9.1 Aircraft Control Subsystem
- •15.9.2 Engine and Fuel Control Subsystems
- •Piston Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1 to 1.5% of the MTOW)
- •Turbofan Engine Fuel Control System (The total system weight is approximately 1.5 to 2% of the MTOW)
- •Fuel Storage and Flow Management
- •15.9.3 Emergency Power Supply
- •15.9.4 Avionics Subsystems
- •Military Aircraft Application
- •Civil Aircraft Application
- •15.9.5 Electrical Subsystem
- •15.9.6 Hydraulic Subsystem
- •15.9.7 Pneumatic System
- •ECS: Cabin Pressurization and Air-Conditioning
- •Oxygen Supply
- •Anti-icing, De-icing, Defogging, and Rain-Removal Systems
- •Defogging and Rain-Removal Systems
- •15.9.8 Utility Subsystem
- •15.9.9 End-of-Life Disposal
- •15.10 Military Aircraft Survivability
- •15.10.1 Military Emergency Escape
- •15.10.2 Military Aircraft Stealth Consideration
- •15.11 Emerging Scenarios
- •Counterterrorism Design Implementation
- •Health Issues
- •Damage from Runway Debris
- •16 Aircraft Cost Considerations
- •16.1 Overview
- •16.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •16.1.2 Coursework Content
- •16.2 Introduction
- •16.3 Aircraft Cost and Operational Cost
- •Operating Cost
- •16.4 Aircraft Costing Methodology: Rapid-Cost Model
- •16.4.1 Nacelle Cost Drivers
- •Group 1
- •Group 2
- •16.4.2 Nose Cowl Parts and Subassemblies
- •16.4.3 Methodology (Nose Cowl Only)
- •Cost of Parts Fabrication
- •Subassemblies
- •Cost of Amortization of the NRCs
- •16.4.4 Cost Formulas and Results
- •16.5 Aircraft Direct Operating Cost
- •16.5.1 Formulation to Estimate DOC
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •16.5.2 Worked-Out Example of DOC: Bizjet
- •Aircraft Price
- •Fixed-Cost Elements
- •Trip-Cost Elements
- •OC of the Variants in the Family
- •17 Aircraft Manufacturing Considerations
- •17.1 Overview
- •17.1.1 What Is to Be Learned?
- •17.1.2 Coursework Content
- •17.2 Introduction
- •17.3 Design for Manufacture and Assembly
- •17.4 Manufacturing Practices
- •17.5 Six Sigma Concept
- •17.6 Tolerance Relaxation at the Wetted Surface
- •17.6.1 Sources of Aircraft Surface Degeneration
- •17.6.2 Cost-versus-Tolerance Relationship
- •17.7 Reliability and Maintainability
- •17.8 Design Considerations
- •17.8.1 Category I: Technology-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.2 Category II: Manufacture-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.3 Category III: Management-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.8.4 Category IV: Operator-Driven Design Considerations
- •17.9 “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.1 Index for “Design for Customer”
- •17.9.2 Worked-Out Example
- •Standard Parameters of the Baseline Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Extended Variant Aircraft
- •Parameters of the Shortened Variant Aircraft
- •17.10 Digital Manufacturing Process Management
- •Process Detailing and Validation
- •Resource Modeling and Simulation
- •Process Planning and Simulation
- •17.10.1 Product, Process, and Resource Hub
- •17.10.3 Shop-Floor Interface
- •17.10.4 Design for Maintainability and 3D-Based Technical Publication Generation
- •Midrange Aircraft (Airbus 320 class)
- •References
- •ROAD MAP OF THE BOOK
- •CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION
- •CHAPTER 3. AERODYNAMIC CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 5. AIRCRAFT LOAD
- •CHAPTER 6. CONFIGURING AIRCRAFT
- •CHAPTER 7. UNDERCARRIAGE
- •CHAPTER 8. AIRCRAFT WEIGHT AND CENTER OF GRAVITY ESTIMATION
- •CHAPTER 9. AIRCRAFT DRAG
- •CHAPTER 10. AIRCRAFT POWER PLANT AND INTEGRATION
- •CHAPTER 11. AIRCRAFT SIZING, ENGINE MATCHING, AND VARIANT DERIVATIVE
- •CHAPTER 12. STABILITY CONSIDERATIONS AFFECTING AIRCRAFT CONFIGURATION
- •CHAPTER 13. AIRCRAFT PERFORMANCE
- •CHAPTER 14. COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
- •CHAPTER 15. MISCELLANEOUS DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 16. AIRCRAFT COST CONSIDERATIONS
- •CHAPTER 17. AIRCRAFT MANUFACTURING CONSIDERATIONS
- •Index
10.2 Background |
315 |
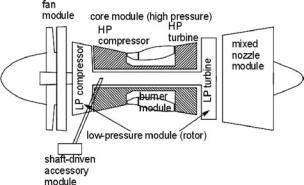
Figure 10.1. Modular concept of gas turbine design
Section 10.7: |
Considerations for engine installation |
Section 10.8: |
Intake and nozzle design |
Section 10.9: |
Nozzle and thrust reversers |
Section 10.10: |
Propeller |
Section 10.11: |
Engine-performance data |
10.1.2 Coursework Content
This chapter creates engine-performance graphs that are used in Chapter 11 for aircraft-performance analysis. In this chapter, readers generate thrust and fuel-flow levels for matched engines at various power settings, speeds, and altitudes, all in a standard atmosphere.
10.2 Background
Gliders were flying long before the Wright brothers first flew, but an engine could not be installed even when automobile piston engines became available – they were too heavy for gliders. The Wright brothers made their own lightweight gasoline engine with the help of Glenn H. Curtiss. Until World War II, aircraft were designed around available engines. Aircraft sizing was a problem – it was not optimized for the mission role but rather based on the number and/or the size of the engine installed.
During the late 1930s, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom (who died in England in 1996) and Hans von Ohain in Germany (who died in the United States in 1998) were working independently and simultaneously on reaction-type engines using vane–blade-type precompression before combustion. Their efforts resulted in today’s gas turbine engines; however, at the time, it was difficult for Whittle to convince his peers. By the end of World War II, gas-turbine–powered jet aircraft were in operation.
Post–World War II research led to the rapid advancement of gas turbine development such that from a core gas-generator module, a family of engines can be designed using a modular concept (Figure 10.1); this allowed engine designers to offer engines as specified by aircraft designers. Similar laws in thermodynamicdesign parameters permitted power plants to be scaled (i.e., rubberized) to the requisite size around the core gas-generator module to meet the demands of the
316 |
Aircraft Power Plant and Integration |
mission requirements. The size and characteristics of an engine are determined by matching them with the aircraft mission. It is now possible for both the aircraft and the engine to be sized to the mission role, thereby improving operational economics. Modular engine design also favors low downtime for maintenance.
The potential energy locked in fuel is released through combustion. In gasturbine technology, the high energy of the combustion product can be used in two ways: (1) converted to an increase in the kinetic energy of the exhaust to produce the reactionary thrust (i.e., turbojet and turbofan); or (2) further extracted through an additional turbine to drive a propeller (i.e., turboprop) to generate thrust.
Initially, reactionary-type engines were simple straight-through airflow turbojets (see Figure 10.4). Subsequently, turbojet development improved with the addition of a fan (i.e., long compressor blades that are visible from the outside) in front of the compressor; this is called a turbofan. The intake airmass flow is split into two streams (see Figure 10.5): the core airmass flow passes through the engine as primary flow and is made to burn; the secondary flow through the fan is bypassed (hence, also called the bypass engine) around the engine and remains as cold flow. For this reason, the primary flow is known as hot flow and the secondary bypassed flow is known as cold flow.
Significant general progress has been made in the aircraft power plant design. Engine technology is substantially more complex than aircraft technology. A gasturbine operating environment demands more aerodynamic considerations than an aircraft. Stringent design considerations must accommodate very high stress levels on an engine at elevated temperatures, yet it must be as lightweight as possible. The manufacture of gas turbine parts is also a difficult task – a tough material must be machined in a complex 3D shape to a tight tolerance level. These considerations make gas turbine design a complex technology and requires an involved microprocessor-based management.
Gas turbine engines have a wide range of applications, from land-based, large prime movers for power generation and ships (both civil and military) to weightcritical airborne applications. The theory behind all the types has a common base; however, the hardware design differs, driven by the application requirements and technology level adopted. For example, land-based engines are not weight-critical and do not need to stand alone; therefore, they are less constrained in design. Surface-based gas turbines must run economically for days and/or months, generating significant power compared to standalone, lightweight aircraft engines that run for hours on varying power, altitude, g-load, and airflow demands. Even the largest aircraft gas turbine engines are small compared to land-based engines.
The success of a new gas turbine design is achieved by fully understanding and appreciating previous designs. Progress is made in increments by incorporating proven, newer technologies that emerge in the interim. Gas turbine development has a long gestation period compared to aircraft and it depends on previous designs. Typically, a technology demonstrator leads the way in introducing a new design.
Gas turbine designs have advanced to incorporate sophisticated micro- processor-based control systems with automation, which are called full authority digital electronic control (FADEC) and work in conjunction with the FBW control of aircraft. CAD, CAM, CFD, and FEM are now the standard tools for engine design.
10.2 Background |
317 |
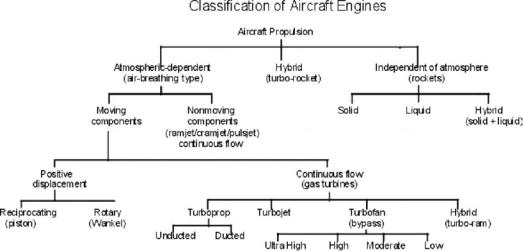
Chart 10.1. Classification of current aircraft engine types
Liquid-cooled aircraft piston engines of more than 3,000 HP have been built. However, except for a few types, they are no longer in production because they are too heavy for the power they generate; in their place, gas turbines predominate. Gas turbine engines have a better thrust-to-weight ratio. Two successful pistons were the World War II types: the Rolls Royce (RR) Merlin and the Griffon, which produced 1,000 to 1,500 HP and weighed approximately 1,500 lb dry. Also, AVGAS is considerably more expensive than aviation turbine fuel (i.e., kerosene) (AVTUR). Today, the biggest piston engine in production is approximately 500 HP. Recently, diesel-fuel piston engines (i.e., less than 250 HP) have entered the general-aviation market. In the homebuilt market, motor gasoline (MOGAS)–powered engines have been used and are approved by the certifying agencies.
Chart 10.1 classifies all types of aircraft engines in current use; this book is concerned only with the air-breathing types.
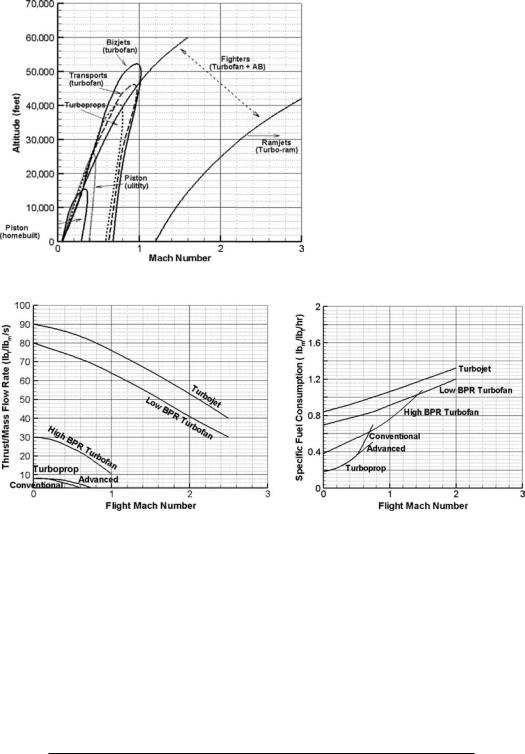
The application domains of the types addressed in this book are shown in Figure 10.2. High BPR turbofans are intended for high-subsonic speeds. At supersonic speeds, the BPR is less than 3. Typically, turboprop-powered aircraft speeds are at and below Mach 0.5. Piston-engine–powered aircraft are at the lowest end of the speed range.
Typical levels of specific thrust (F/m˙ a, lb/lb/s) and specific fuel consumption
(sfc, lb/hr/lb) of various types of gas turbine engines are shown in Figure 10.3. Table 10.1 lists various efficiencies of the different classes of aircraft engines.
Table 10.2 shows the progress made in the last half-century, indicating the advances made in engine-weight savings. Since the 1970s, compliance regarding engine-noise levels has been a requirement of the certifying agencies. Pollution levels due to noise and emissions are steadily decreasing (see Chapter 14).
If required (or preferred), the internal contours of the intake and exhaust of a civil aircraft nacelle pod are designed by engine designers in consultation with airframe designers. Shaping of the nacelle’s external contour is the responsibility of aircraft designers. Military aircraft intakes and exhausts have higher degrees of
318 |
Aircraft Power Plant and Integration |
Figure 10.2. Application domains of various types of air-breathing aircraft engines
(a) Specific Thrust |
(b) Specific Fuel Consumption |
|||
Figure 10.3. Typical performance levels of various gas turbine engines |
||||
Table 10.1. Efficiencies of engine types |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal efficiency |
Propulsive efficiency |
Overall efficiency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current types |
0.60–0.65 |
0.75–0.85 |
0.50–0.55 |
|
Propfan |
0.52–0.55 |
0.80–0.85 |
0.54–0.55 |
|
Propfan (ad) |
0.52–0.55 |
0.70–0.76 |
0.46–0.50 |
|
High BPR |
0.48–0.55 |
0.62–0.68 |
0.40–0.42 |
|
Low BPR |
0.40–0.50 |
0.55–0.60 |
0.35–0.38 |
|
Turbojet |
0.40–0.45 |
0.45–0.52 |
0.28–3.20 |
|
Notes:
Advanced propfan BPR = bypass ratio

10.3 Definitions |
319 |
Table 10.2. Progress in jet engines
|
|
Thrust/weight ratio |
|
|
|
1950s |
(J69 class) |
2.8–3.2 |
1960s |
(JT8D, JT3D class) |
3.2–3.6 |
1970s |
(J79 class) |
4.5–5.0 |
1980s |
(TF34 class) |
6.0–6.5 |
1990s |
(F100, F404 class) |
0.5–8.0 |
Current |
8.0–9.0 |
|
|
|
|
complexity and are design-specific. Military aircraft intake and exhaust ducts are developed by aircraft designers in consultation with engine designers.
10.3 Definitions
This section defines various terms used in jet-engine performance analysis. References [3] through [6] may be consulted for derivations of the expressions.
SFC: The fuel-flow rate required to produce one unit of thrust, or shaft horsepower (SHP):
SFC = (fuel flow rate)/(thrust or power) |
(10.1) |
Units of SFC are in lb/hr per pound of thrust produced (in SI units, gm/s/N) – the lower the better. More precisely, reaction-type engines use TSFC and propellerdriven engines use PSFC, where T and P denote thrust and power, respectively.
For turbofan engines (see Section 10.4.2):
secondary airmass flow over the core engine |
= m˙ s /m˙ p |
|
BPR = primary airmass flow through the core (combustion) |
(10.2) |
Following are the definitions of various types of jet engine efficiencies. The subscripts indicate the gas turbine component station numbers, as shown in Figure 10.4 (in the figure, 5 represents e).
thermal efficiency, ηt = |
mechanical energy produced by the engine |
= |
WE |
heat energy of (air + fuel) |
Q |
= |
Ve2 − V∞2 |
|
1 |
− |
PR |
2Cp(T3 − T2) = |
|
|
1−γ
γ |
(10.3) |
For a particular aircraft speed, V∞, the higher the exhaust velocity Ve, the better is the ηt of the engine. Heat addition at the combustion chamber, q2−3 = Cp(T3 −
T1) ≈ Cp(Tt3 − Tt1).
propulsive efficiency, ηp = |
|
|
useful work done on airplane |
|
||
mechanical energy produced by the engine |
|
|||||
= |
|
WA |
= |
2V∞ |
(10.4) |
|
|
WE |
Ve + V∞ |
|
|||
For subsonic aircraft, Ve V∞. Clearly, for a given engine exhaust velocity, Ve, the higher the aircraft speed, the better is the propulsion efficiency, ηp. A jet aircraft
