
- •Central Nervous System
- •Introduction
- •The Brain
- •The Brain
- •Embryonic Development
- •Embryonic Development
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Primary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Adult Neural Canal Regions
- •Development of Flexures
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Regions of the Brain
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Fissures of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Medial Surface of Right Hemisphere
- •Position of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Motor Areas
- •Primary Motor Cortex
- •Pyramidal cells
- •Pyramidal Tracts
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Broca’s area
- •Broca’s area
- •Frontal Eye Field
- •Sensory Areas
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Synaptic Chain
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Motor and Sensory Somatotopy
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Areas
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Gustatory (taste) Cortex
- •Vestibular (equilibrium) Cortex
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Association Areas
- •Association Areas
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •General Interpretation Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Insula
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •The Diencephanlon
- •The Diencephalon
- •The Diencephalon
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Mammillary Bodies
- •Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Autonomic Control Center
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Regulation of Hunger & Thirst
- •Regulation of Water Balance
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Control of Endocrine Functioning
- •Formation of Memory
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •Medulla
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Cerebellar Processing 1
- •Cerebellar Processing 2
- •Cerebellar Processing 3
- •Cerebellar Processing 4
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Functional Brain Systems
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic system
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •Protection of the Brain
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Pia Mater
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •The Choroid Plexus
- •CSF Circulation
- •CSF Circulation
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •Homeostatic Imbalances
- •The Brain

Motor Areas
Cortical areas controlling motor functions lie in the posterior part of the frontal lobes
Motor areas include the primary motor cortex, the premotor cortex, Broca’s area, and the front eye field

Primary Motor Cortex
The primary motor cortex is located in the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe of each hemisphere
Large neurons (pyramidal cells) in these gyri allow us to consciously control the precise or skill voluntary movements of our skeletal muscles

Pyramidal cells
These long axons, which
project to the spinal cord, |
|
Dendrites |
|
form the massive |
|
|
|
voluntary motor tracts |
|
called the pyramidal, or |
|
corticospinal tracts |
|
All other descending |
|
motor tracts issue from |
|
brain stem nuclei and |
|
consists of chains of two, |
|
three, or more neurons |
|
Table 11.1

Pyramidal Tracts
The lateral corticospinal tract consists of the long axons of the pyramidal cells located within the primary motor cortex

Motor
Somatotopy
Body is represented spatially in the primary motor cortex of each hemisphere
Most of the neurons in these gyri control muscles in body areas having the most precise motor control
The areas with the most control (face, tongue, and hands)

Motor
Somatotopy
Motor innervation is contralateral; left primary motor controls right side of body
The image is useful to conceptualize areas of synergistic function
However, a given muscle may be controlled by several cortical neurons recruited for several specific actions
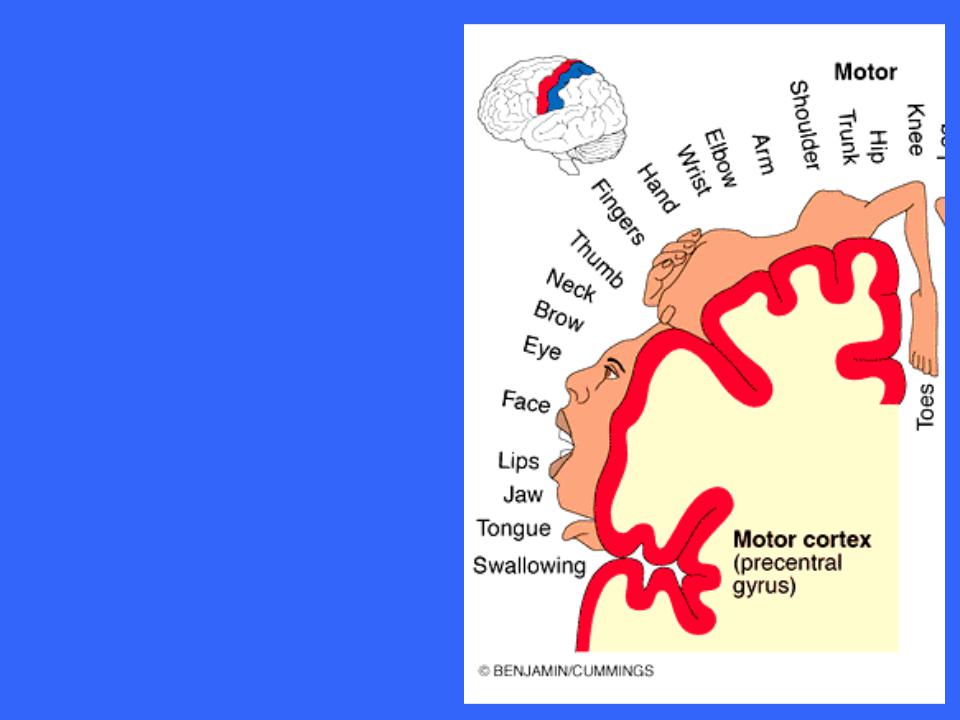
Motor
Somatotopy
Damage to the localized areas of the primary motor cortex paralyzes the muscles controlled by this area
If the lesion is in the right hemisphere, the left side will be paralyzed
Only voluntary control is lost as the muscles can still contract reflexively

Premotor Cortex
The premotor cortex controls motor skills of repetitive or patterned nature (typing or piano)
The premotor cortex coordinates the movement of several muscle groups to act simultaneously or sequentially

Premotor Cortex
The premotor cortex sends activating impulses to the primary motor cortex
Also influences motor actively more directly by supplying about 15% of pyramidal tract fibers
A memory bank of skilled motor activities

Premotor Cortex
This area appears to involved with motor planning
It controls voluntary actions that depend on sensory feedback
