
- •Central Nervous System
- •Introduction
- •The Brain
- •The Brain
- •Embryonic Development
- •Embryonic Development
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Primary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Adult Neural Canal Regions
- •Development of Flexures
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Regions of the Brain
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Fissures of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Medial Surface of Right Hemisphere
- •Position of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Motor Areas
- •Primary Motor Cortex
- •Pyramidal cells
- •Pyramidal Tracts
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Broca’s area
- •Broca’s area
- •Frontal Eye Field
- •Sensory Areas
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Synaptic Chain
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Motor and Sensory Somatotopy
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Areas
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Gustatory (taste) Cortex
- •Vestibular (equilibrium) Cortex
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Association Areas
- •Association Areas
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •General Interpretation Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Insula
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •The Diencephanlon
- •The Diencephalon
- •The Diencephalon
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Mammillary Bodies
- •Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Autonomic Control Center
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Regulation of Hunger & Thirst
- •Regulation of Water Balance
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Control of Endocrine Functioning
- •Formation of Memory
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •Medulla
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Cerebellar Processing 1
- •Cerebellar Processing 2
- •Cerebellar Processing 3
- •Cerebellar Processing 4
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Functional Brain Systems
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic system
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •Protection of the Brain
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Pia Mater
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •The Choroid Plexus
- •CSF Circulation
- •CSF Circulation
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •Homeostatic Imbalances
- •The Brain

Formation of Memory
The nucleus of the mammillary body receives many inputs from the major memoryprocessing structures of the cerebrum, the hippocampal formation and therefore may relate to memory formation

Epithalamus
Epithalamus
The epithalamus is the posterior portion of the diencephalon
It forms the roof of the third ventricle

The Epithalamus
The epithalmus consists of one tiny group of nuclei and a small, unpaired knob called the pineal body
This gland, which derives from ependymal glial cells, is a hormone secreting organ

Epithalamus
The pineal gland extends from the posterior border of the epithalamus
The pineal gland secretes the hormone melatonin which signals the sleep wake cycle
Pinal
Body
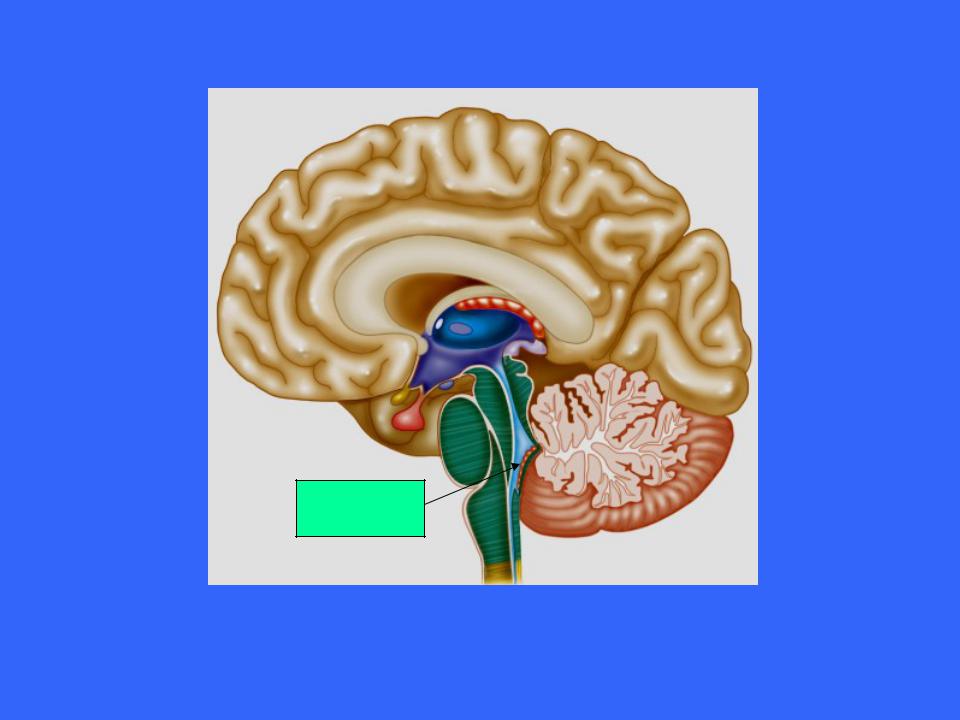
The Epithalamus
Choroid
Plexus
A cerebrospinal fluidforming structure called a choroid plexus is also part of the epithalamus

The Brain Stem
The third of the four major parts of the brain is the brain stem
From superior to inferior, the brain stem is divided into;
–Midbrain
–Pons
–Medulla oblongata
Pons
Medulla
oblongata
Midbrain

The Brain Stem
Each region is roughly an inch long
Together than constitute 2.5% of total brain mass
The brain stem has several functions
–It produce the rigidly programmed, automatic behaviors necessary for our survival
–Acts as a passageway for all the fiber tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord
–It is heavily involved with the innervation of the face and head as 10 of the 12 cranial nerve attach to it

The Brain Stem
The brain stem has the same structural plan as the spinal cord, with outer white matter surrounding an inner region of gray matter
However, there are also nuclei of gray matter located within the white matter

The Midbrain
The midbrain is located between the diencephalon superiorly and the pons inferiorly

The Midbrain
Its central cavity is the cerebral aqueduct, which divides it into a tectum (dorsal surface) and paired cerebral peduncles
From an anterior view the cerebral peduncles appear as columns that hold up the cerebrum
