
- •I.Overview
- •The Autonomic Nervous System
- •Autonomic versus Somatic NS
- •Autonomic versus Somatic NS
- •Basic Anatomy of ANS
- •Divisions of the ANS
- •I.Overview
- •Sources of Dual Innervation
- •ANS Neurotransmitters
- •Parasympathetic
- •Sympathetic
- •I.Overview
- •Physiological Effects of the ANS
- •Sympathetic Responses
- •Parasympathetic Responses
- •Comparison

I.Overview
II.Anatomy
III. Physiology
Autono
mic
Nervous
System
1

 The Autonomic Nervous System
The Autonomic Nervous System
Regulate activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands
Structures involved
1.general visceral afferent neurons
2.general visceral efferent neurons
3.integration center within the brain
Receives input from limbic system and other regions of the cerebrum
2

 Autonomic versus Somatic NS
Autonomic versus Somatic NS
Somatic nervous system
consciously perceived sensations
excitation of skeletal muscle
one neuron connects CNS to organ
Autonomic nervous system
unconsciously perceived visceral sensations
involuntary inhibition or excitation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glandular secretion
two neurons needed to connect CNS to organ
preganglionic and postganglionic neurons |
3 |
|
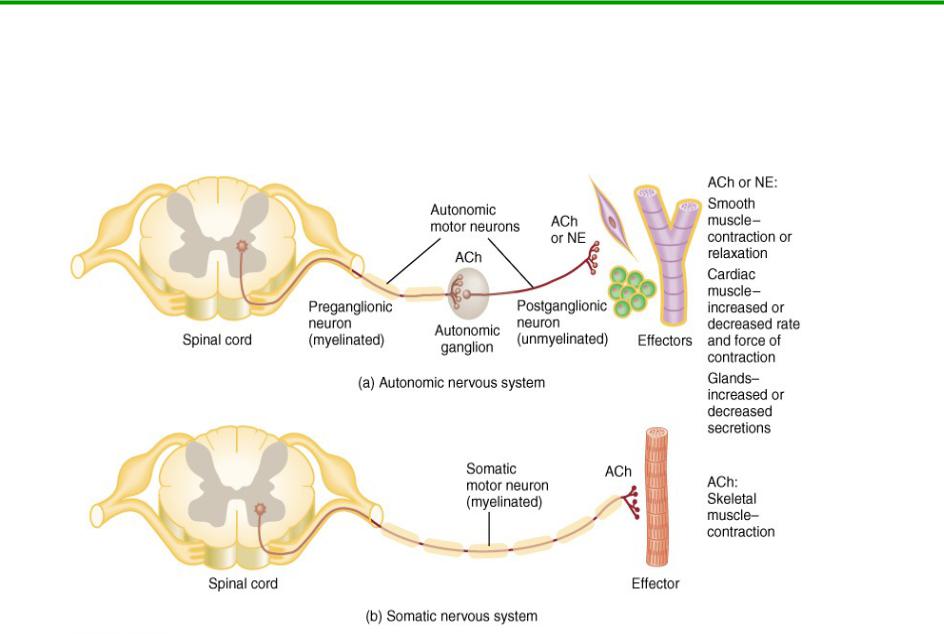
 Autonomic versus Somatic NS
Autonomic versus Somatic NS
Autonomic NS pathway is a 2 neuron pathway
Somatic NS pathway only contains one neuron.
4
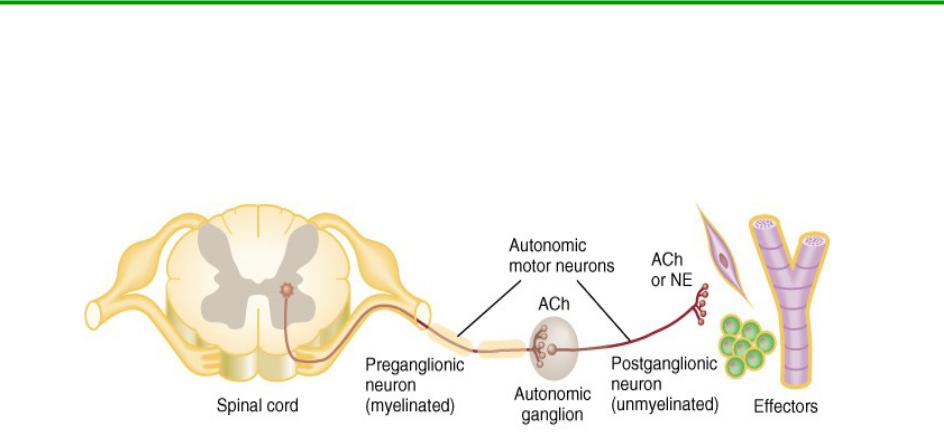
 Basic Anatomy of ANS
Basic Anatomy of ANS
Preganglionic neuron
cell body in brain or spinal cord
axon is myelinated type B fiber that extends to autonomic ganglion
Postganglionic neuron
cell body lies outside the CNS in an autonomic ganglion
axon is unmyelinated type C fiber that terminates in a visceral
effector |
5 |
|
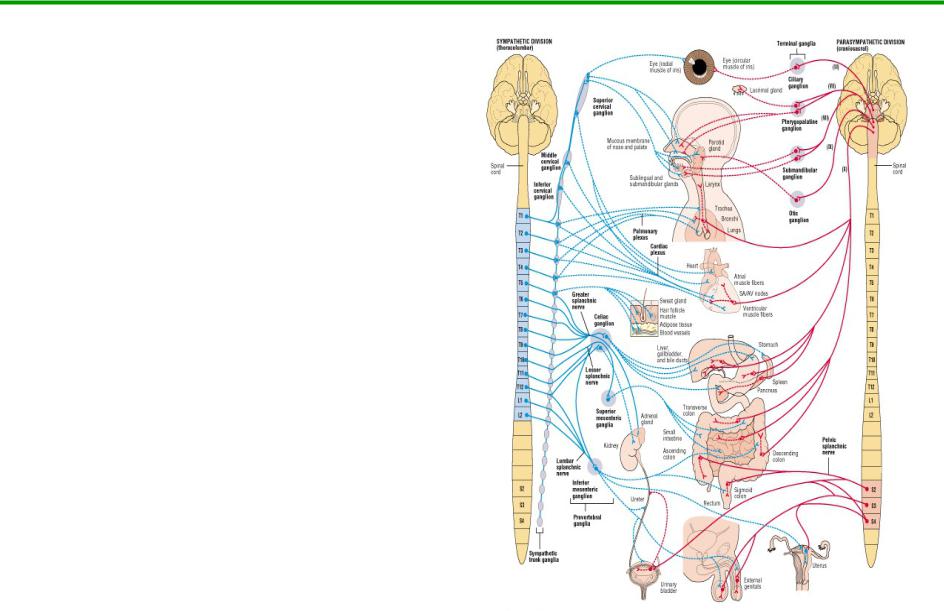
 Divisions of the ANS
Divisions of the ANS
2 major divisions
1.parasympathetic
2.sympathetic
Dual innervation
one speeds up organ
one slows down organ
Sympathetic NS increases heart rate
Parasympathetic NS decreases heart rate
6

I.Overview
II.Anatomy
A.Neurotransmitter
III. Physiology
Autono
mic
Nervous
System
7
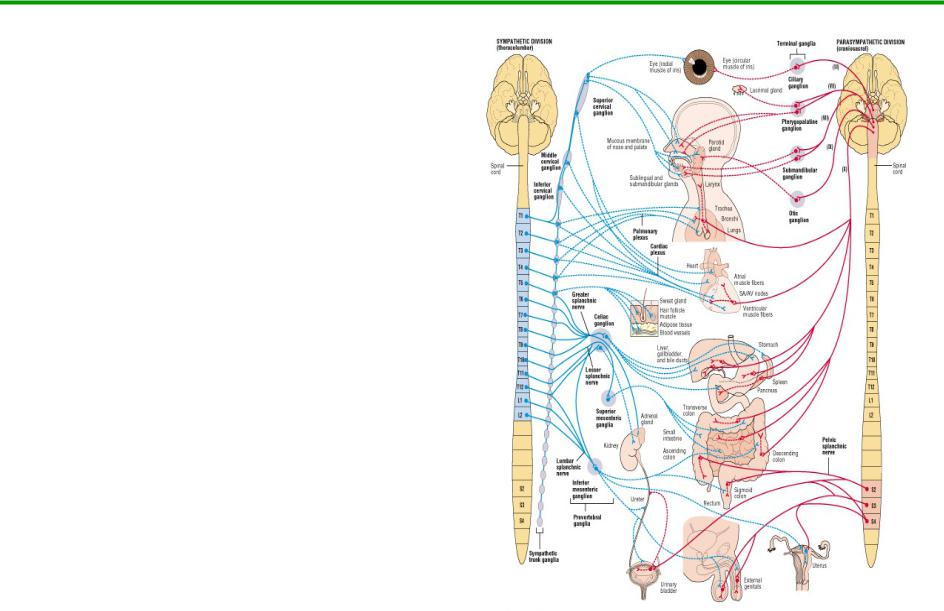
 Sources of Dual Innervation
Sources of Dual Innervation
1.Sympathetic (thoracolumbar) division
preganglionic cell bodies in thoracic and first 2 lumbar segments of spinal cord
2.Parasympathetic (craniosacral) division
preganglionic cell bodies in nuclei of 4
cranial nerves and the |
|
sacral spinal cord |
8 |
|
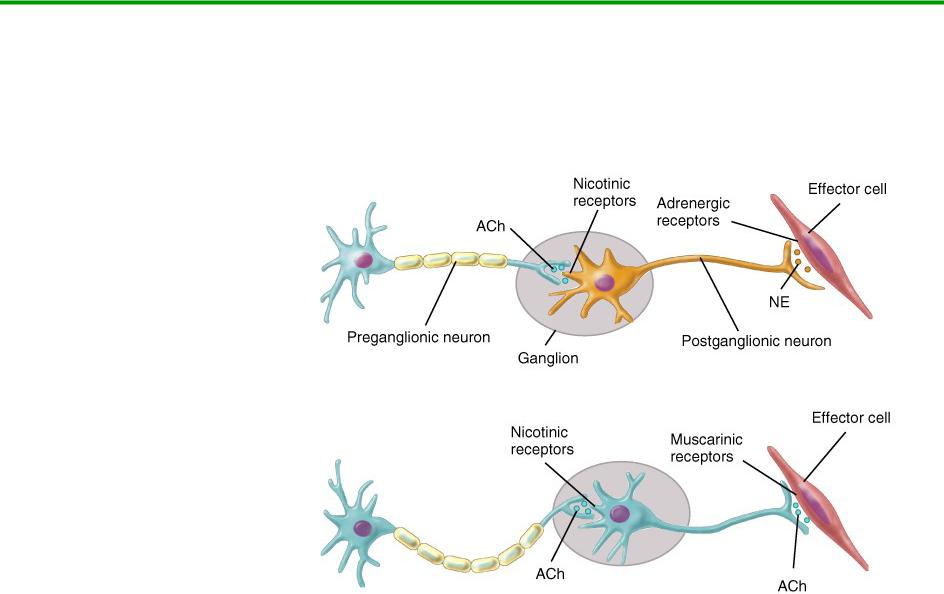
 ANS Neurotransmitters
ANS Neurotransmitters
Classified as either cholinergic or adrenergic neurons based upon the neurotransmitter released
Adrenergic
Cholinergic
19
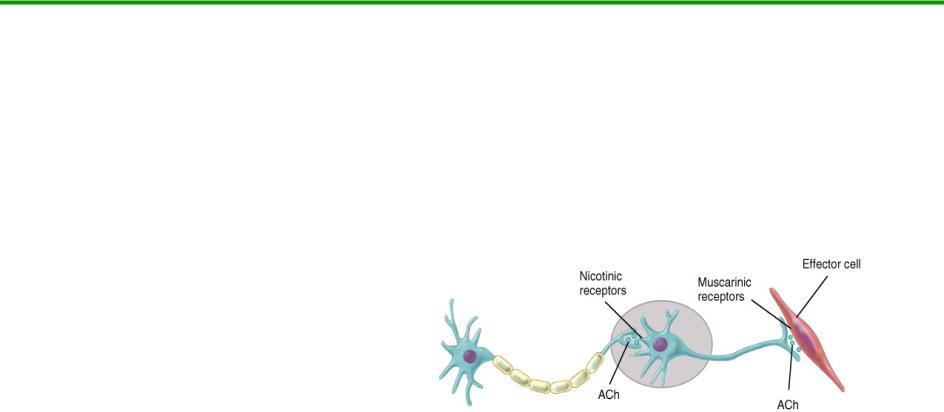
 Parasympathetic
Parasympathetic
Cholinergic neurons release acetylcholine from preganglionic neurons & from parasympathetic postganglionic neurons
Action: Excites or inhibits depending upon receptor type and organ involved
Receptor:
Nicotinic receptors are found on dendrites & cell bodies of autonomic NS cells and at NMJ
Muscarinic receptors are found on plasma membranes of all parasympathetic effectors
20
