
- •Central Nervous System
- •Introduction
- •The Brain
- •The Brain
- •Embryonic Development
- •Embryonic Development
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Primary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Adult Neural Canal Regions
- •Development of Flexures
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Regions of the Brain
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Fissures of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Medial Surface of Right Hemisphere
- •Position of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Motor Areas
- •Primary Motor Cortex
- •Pyramidal cells
- •Pyramidal Tracts
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Broca’s area
- •Broca’s area
- •Frontal Eye Field
- •Sensory Areas
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Synaptic Chain
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Motor and Sensory Somatotopy
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Areas
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Gustatory (taste) Cortex
- •Vestibular (equilibrium) Cortex
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Association Areas
- •Association Areas
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •General Interpretation Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Insula
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •The Diencephanlon
- •The Diencephalon
- •The Diencephalon
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Mammillary Bodies
- •Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Autonomic Control Center
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Regulation of Hunger & Thirst
- •Regulation of Water Balance
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Control of Endocrine Functioning
- •Formation of Memory
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •Medulla
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Cerebellar Processing 1
- •Cerebellar Processing 2
- •Cerebellar Processing 3
- •Cerebellar Processing 4
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Functional Brain Systems
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic system
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •Protection of the Brain
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Pia Mater
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •The Choroid Plexus
- •CSF Circulation
- •CSF Circulation
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •Homeostatic Imbalances
- •The Brain
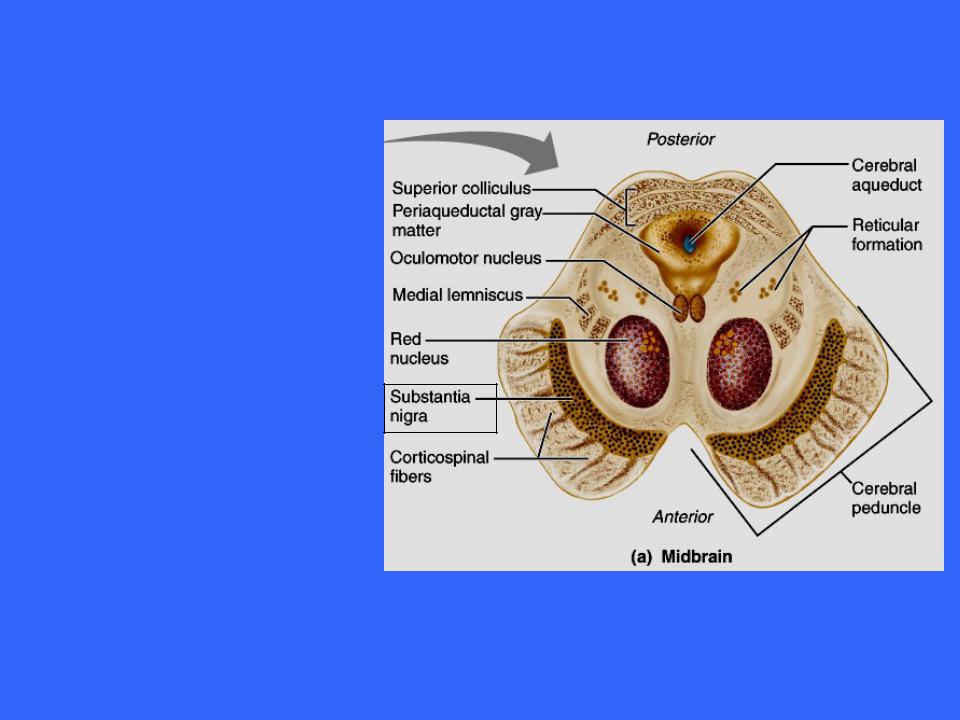
The Midbrain
Also imbedded in the white matter of the midbrain are two pigmented nuclei, the substantia nigra and the red nucleus
The Midbrain
The substantia nigra is a bandlike nucleus located deep to the cerebral peduncle
It is the largest
nuclear mass in the midbrain
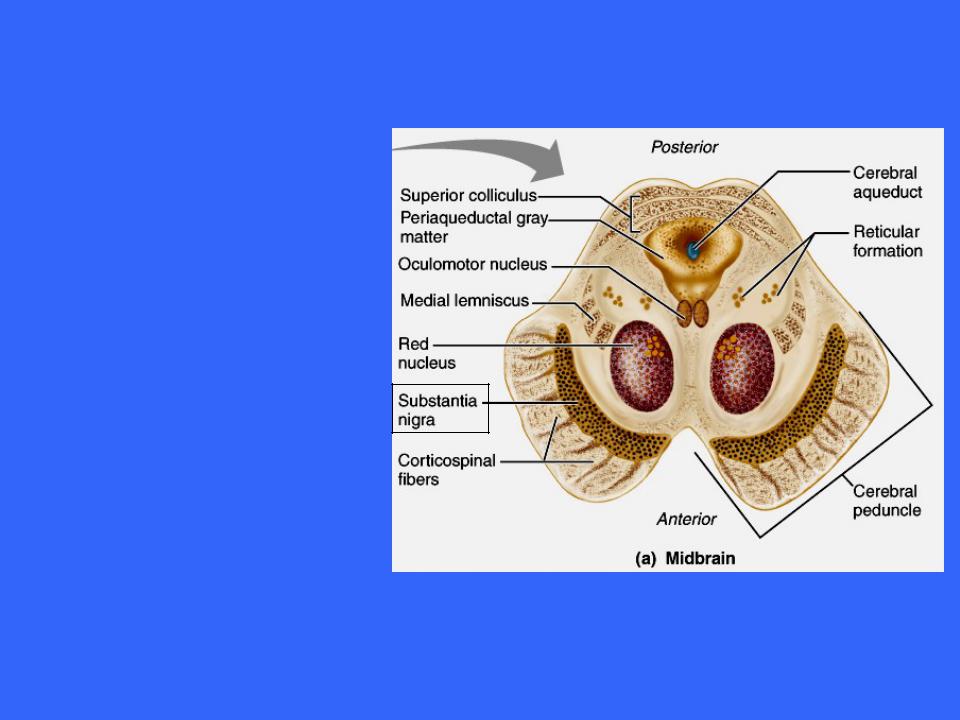
The Midbrain
Its dark color reflects its high content of melanin pigment, a precursor of dopamine a neurotransmitter released by these neurons
The substantia nigra is functionally linked to the basal nuclei of the cerebral hemispheres
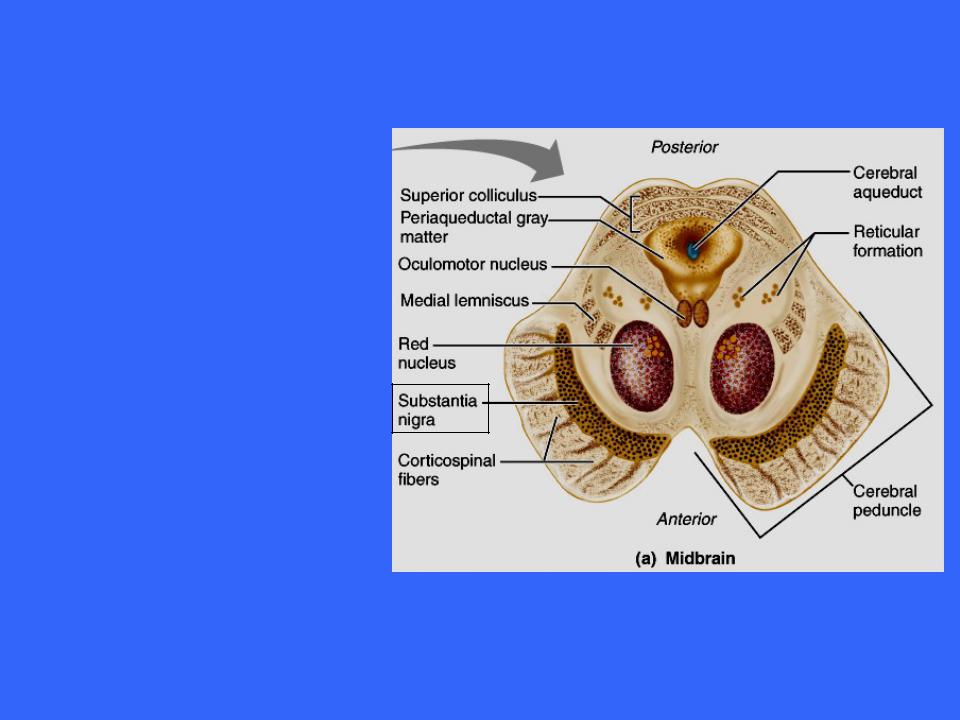
The Midbrain
The red nucleus is found between the substantia nigra and the cerebral aqueduct
It reddish hue is due to its vascular supply and the presence of iron pigment in the cell bodies of its neurons
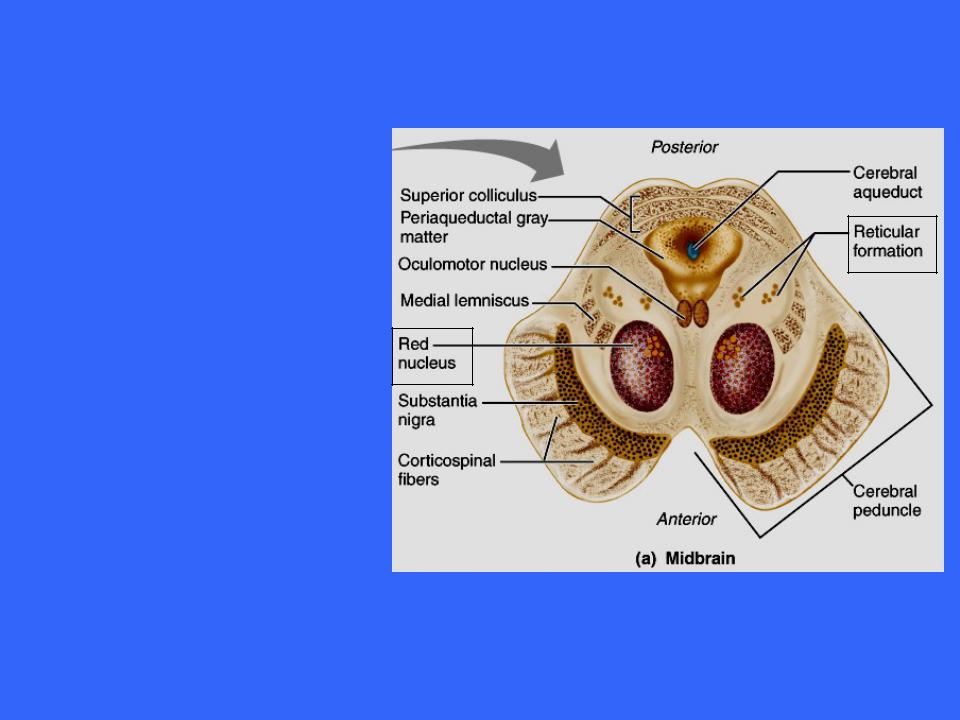
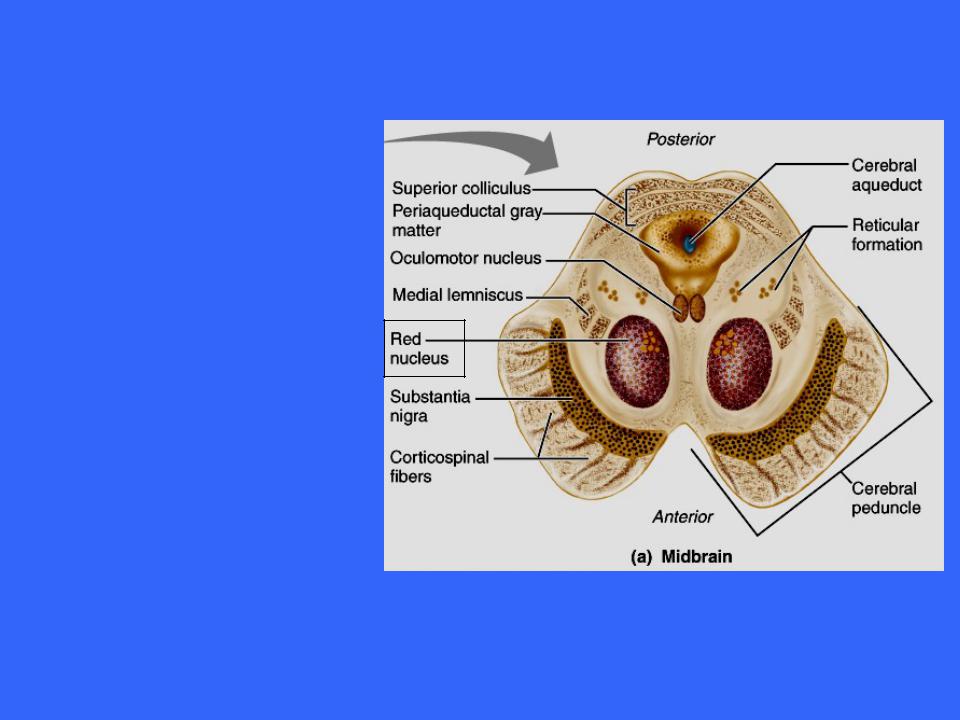
The Midbrain
The red nuclei are relay nuclei in some descending motor pathways that effect limb flexion
The red nuclei is the largest nucleus in the reticular formation, a system of small nuclei scattered through the core of the brain stem
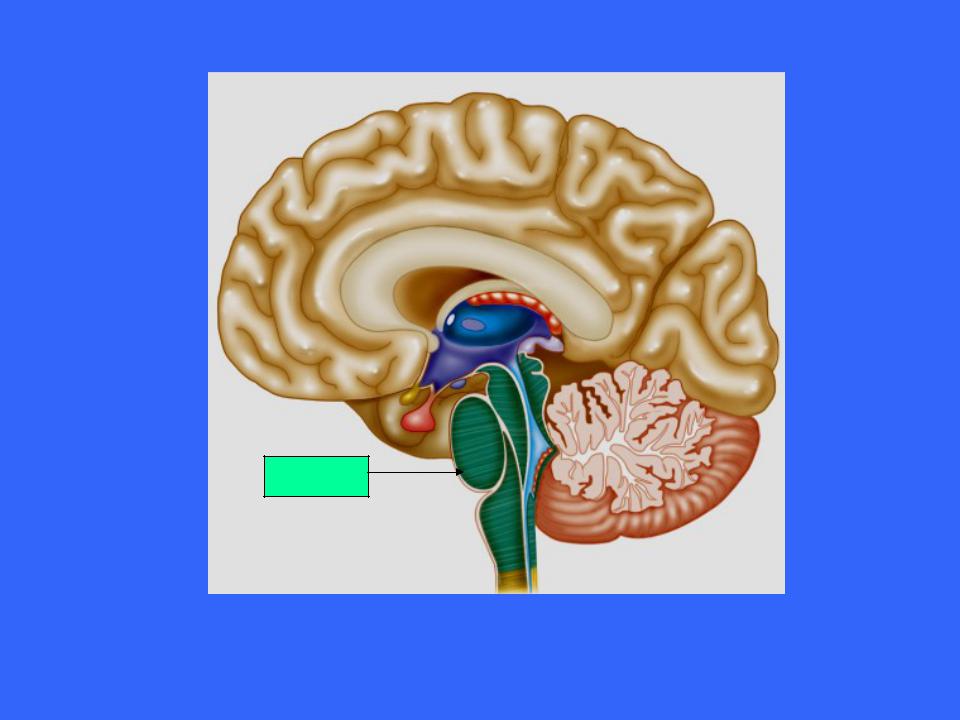
The Pons
Pons
The pons is the bulging brain stem region wedged between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata
The Pons
It forms part of the anterior wall of the fourth ventricle
It is chiefly composed of conduction tracts
The deep projection
fibers run
longitudinally and Pons 
 complete the
complete the
pathway between higher brain centers and spinal cord
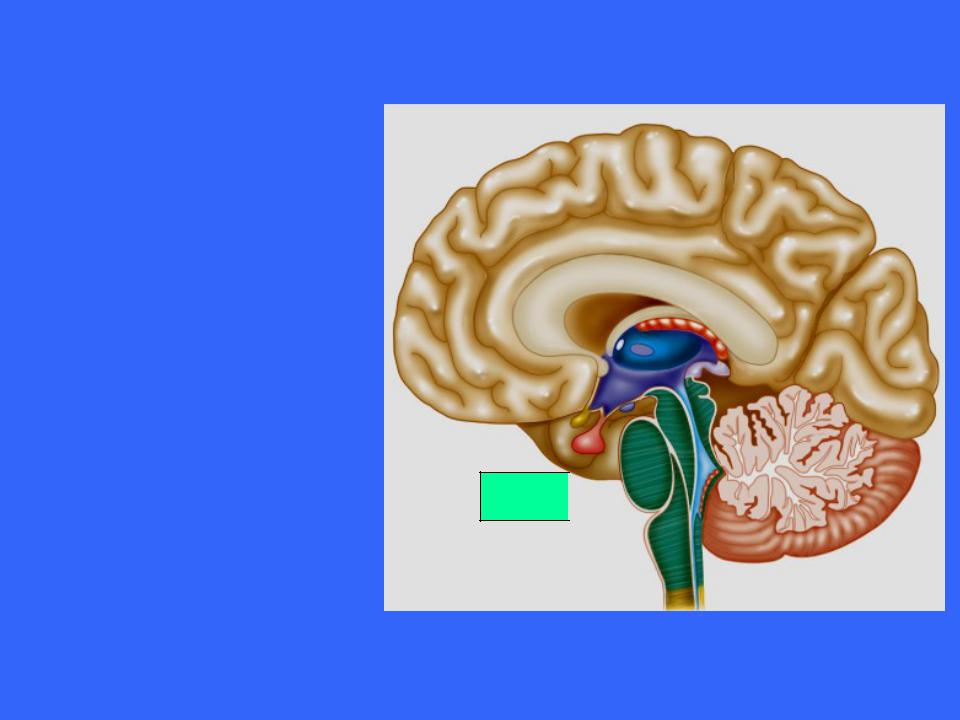
The Pons
The deep projection fibers run longitudinally and complete the superiorinferior pathway between
the higher brain
centers and the 
 Pons spinal cord
Pons spinal cord
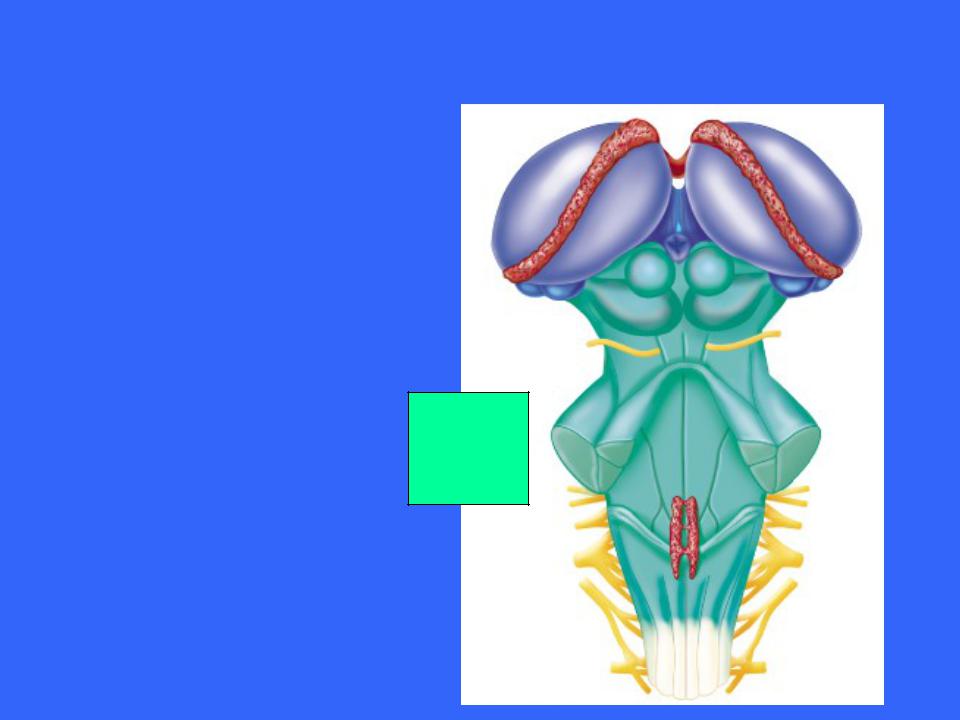
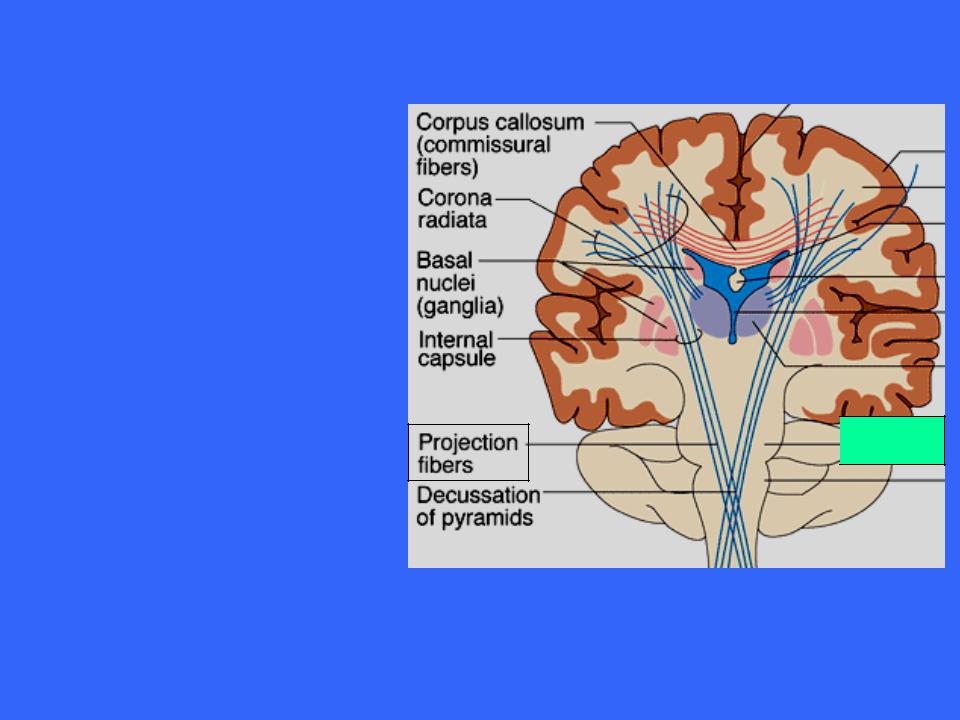
The Pons
The more superficial nuclei are relays for conversations between the motor cortex and the cerebellum
These fibers are orientated dorsally and transversely and connect the pons bilaterally with the cerebellum
Middle Cerebellar  peduncles
peduncles
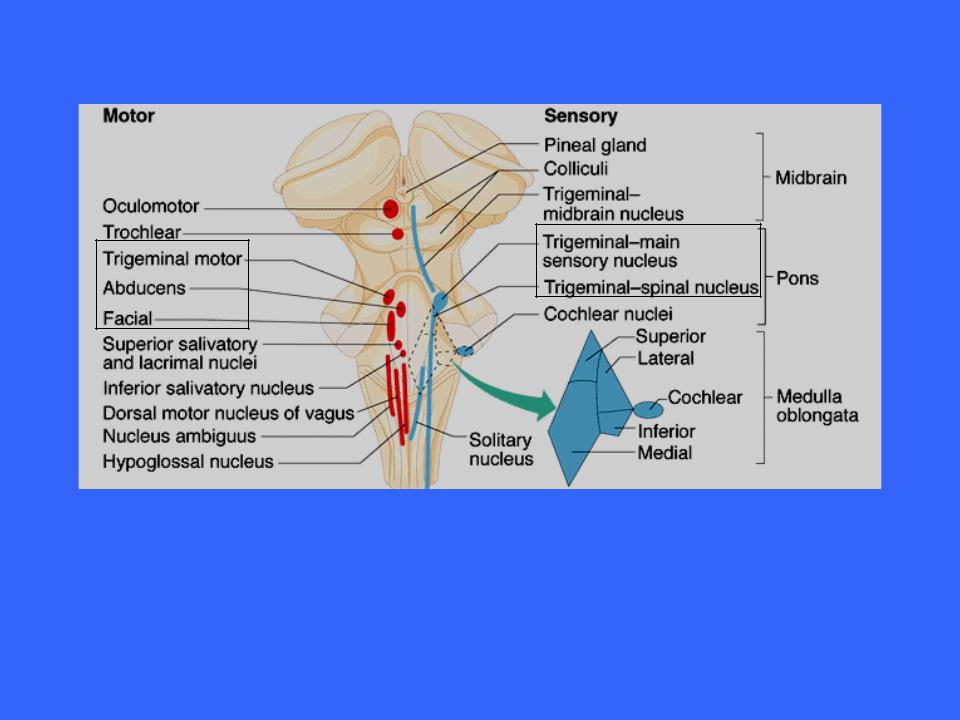
The Pons
Several cranial nerves issue from pons nuclei
–Trigeminal nerve
–Abducens nerve
–Facial nerves
