
- •Central Nervous System
- •Introduction
- •The Brain
- •The Brain
- •Embryonic Development
- •Embryonic Development
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Primary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Adult Neural Canal Regions
- •Development of Flexures
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Regions of the Brain
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Fissures of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Medial Surface of Right Hemisphere
- •Position of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Motor Areas
- •Primary Motor Cortex
- •Pyramidal cells
- •Pyramidal Tracts
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Broca’s area
- •Broca’s area
- •Frontal Eye Field
- •Sensory Areas
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Synaptic Chain
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Motor and Sensory Somatotopy
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Areas
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Gustatory (taste) Cortex
- •Vestibular (equilibrium) Cortex
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Association Areas
- •Association Areas
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •General Interpretation Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Insula
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •The Diencephanlon
- •The Diencephalon
- •The Diencephalon
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Mammillary Bodies
- •Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Autonomic Control Center
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Regulation of Hunger & Thirst
- •Regulation of Water Balance
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Control of Endocrine Functioning
- •Formation of Memory
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •Medulla
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Cerebellar Processing 1
- •Cerebellar Processing 2
- •Cerebellar Processing 3
- •Cerebellar Processing 4
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Functional Brain Systems
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic system
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •Protection of the Brain
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Pia Mater
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •The Choroid Plexus
- •CSF Circulation
- •CSF Circulation
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •Homeostatic Imbalances
- •The Brain

Primary Brain Vesicles
Constrictions in the neural tube appear to mark off the three primary brain vesicles
–Prosencephalon
•(forebrain)
–Mesencephalon
•(midbrain)
–Rhombencephalon
•(hindbrain)
The remainder of the neural tube becomes the spinal cord

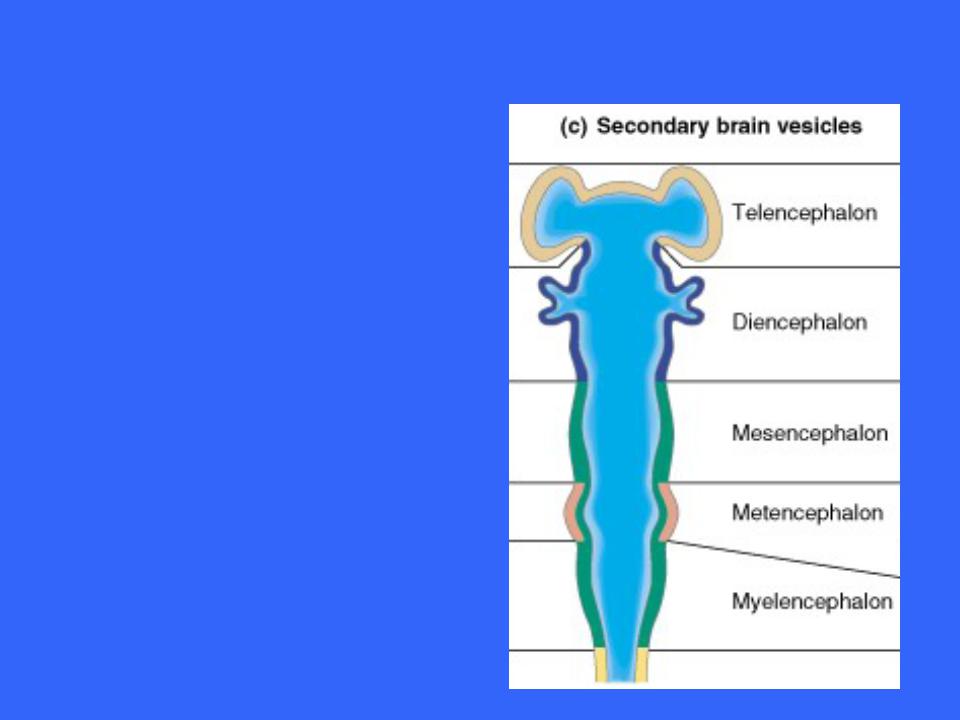
Secondary Brain Vesicles
By the fifth week, the five brain regions of the secondary brain vesicles are evident
The forebrain has divided
–Telencephalon
–Diencephalon
The midbrain remains undivided
The hindbrain has constricted to form
–Metencephalon
–Myelencephalon

Secondary Brain Vesicles
Each of the five secondary brain vesicles develops rapidly to produce the major structures of the adult brain
The greatest change occurs in the telencephalon which sprouts two large swellings which project anteriorly
These paired expansions become the cerebral hemispheres known collectively as the cerebrum
Hemispheres house ventricles

Secondary Brain Vesicles
Various areas of the diencephalon specialize to form
– Hypothalamus
– Thalamus
– Epithalamus

Secondary Brain Vesicles
The mesencephalon develops into
–Midbrain
–Brain stem
Secondary Brain Vesicles
Various areas of the Metencephalon specialize to form
–Brain stem
–Pons
–Cerebellum

Secondary Brain Vesicles
Various areas of the Myelencephalon specialize to form
–Brain stem
–Medulla oblongata
All the midbrain and hindbrain structures, with the exception of the cerebellum, form portions of the brain stem

Adult Neural Canal Regions
The central canal of the neural tube enlarge in four areas to form the fluid filled ventricles
–Telencephalon
•Lateral ventricles
•Superior portion of 3rd
–Diencephalon
•Most of third ventricle
–Mesencephalon
•Cerebral aqueduct
–Metencephalon
•Fourth ventricle
–Myelencephalon
• Fourth ventricle

Development of Flexures
During this period of rapid brain growth change is also occurring in the relative position of its parts
Because the brain’s growth is restricted by the skull, midbrain and cervical flexures develop by the fifth week which bend the forebrain toward the brain stem

Effects of Space Restriction
A second consequence of restricted space is that the cerebral hemispheres are forced to take a horseshoe shaped course posteriorly and laterally
Development of the cerebral hemispheres at 13 weeks
