
- •Central Nervous System
- •Introduction
- •The Brain
- •The Brain
- •Embryonic Development
- •Embryonic Development
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Development of Neural Tube
- •Primary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Secondary Brain Vesicles
- •Adult Neural Canal Regions
- •Development of Flexures
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Effects of Space Restriction
- •Regions of the Brain
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Gray and White Matter in CNS
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •Ventricles of the Brain
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •The Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Lobes of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Fissures of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Medial Surface of Right Hemisphere
- •Position of Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Hemispheres
- •Cerebral Cortex
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Cerebral Cortex Generalizations
- •Motor Areas
- •Primary Motor Cortex
- •Pyramidal cells
- •Pyramidal Tracts
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Motor
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Premotor Cortex
- •Broca’s area
- •Broca’s area
- •Frontal Eye Field
- •Sensory Areas
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Synaptic Chain
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Motor and Sensory Somatotopy
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somato sensory Cortex
- •Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Somatosensory
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual
- •Primary Visual Cortex
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Association Area
- •Visual Areas
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Primary Auditory Cortex
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Auditory Association Area
- •Gustatory (taste) Cortex
- •Vestibular (equilibrium) Cortex
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Olfactory Area
- •Association Areas
- •Association Areas
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •Prefrontal Cortex
- •General Interpretation Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Language Area
- •Insula
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Lateralization of Cortical Function
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Cerebral White Matter
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •Basal Nuclei
- •The Diencephanlon
- •The Diencephalon
- •The Diencephalon
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •Thalamus
- •The Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Mammillary Bodies
- •Hypothalamus
- •Hypothalamus
- •Autonomic Control Center
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Center for Emotional Response
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Body Temperature Regulation
- •Regulation of Hunger & Thirst
- •Regulation of Water Balance
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Regulation of SleepWake Cycles
- •Control of Endocrine Functioning
- •Formation of Memory
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •Epithalamus
- •The Epithalamus
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Brain Stem
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Midbrain
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Pons
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •Medulla
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Medulla Oblongata
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Cerebellar Processing 1
- •Cerebellar Processing 2
- •Cerebellar Processing 3
- •Cerebellar Processing 4
- •The Cerebellum
- •The Cerebellum
- •Functional Brain Systems
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic system
- •The Limbic System
- •The Limbic System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •Reticular Formation
- •The Reticular Activating System
- •The Reticular Formation
- •Protection of the Brain
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •Meninges
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Dura Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Arachnoid Mater
- •The Pia Mater
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •Choroid Plexus
- •The Choroid Plexus
- •CSF Circulation
- •CSF Circulation
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •BloodBrain Barrier
- •Homeostatic Imbalances
- •The Brain

Central Nervous System
Chapter 13

Introduction
Analogies; telephone switchboard; computer; miracle
A fantastically complex and flexible biological organ
Cephalization become more apparent in higher order species
Increase in the neurons at the rostral end of the CNS
Highest level of cephalization is found in humans
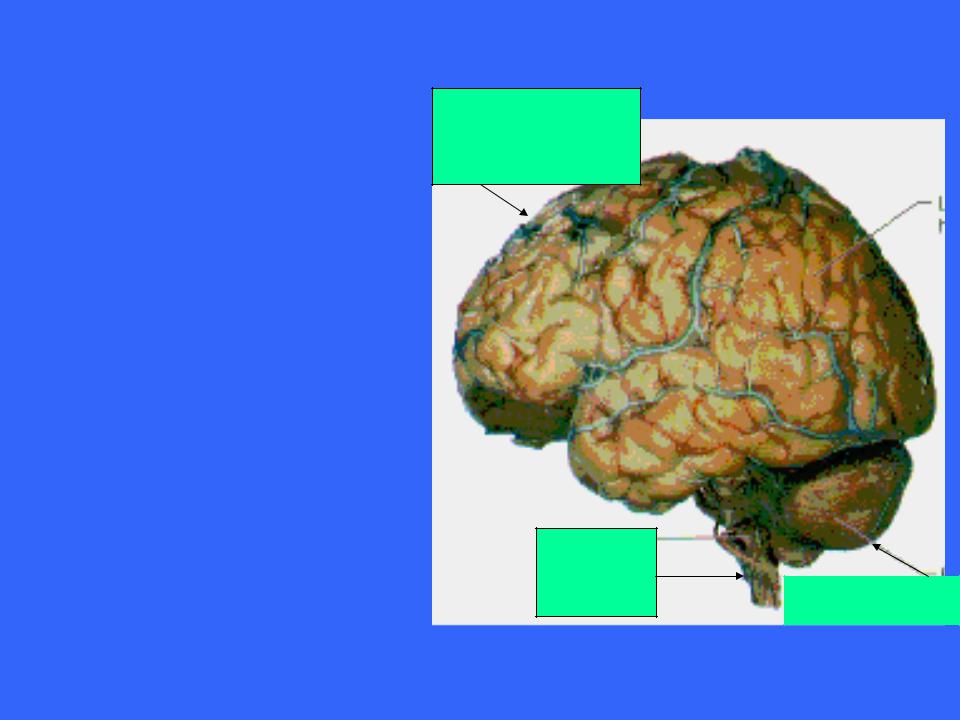
The Brain
The unimpressive appearance of the human brain give few hints of its abilities
It is about two handfuls of delicate pinkish gray tissue
Wrinkled surface
Consistency of cold oatmeal
Cerebral hemisphere
Brain |
|
stem |
Cerebellum |

The Brain
Average adult male’s brain weighs about 1600 g (3.5 pounds)
Average adult female’s brain weighs about 1450 g
Brain size represents a proportional difference in body size
Brain size is not correlated to intelligence but is related to the complexity of the neural connections within the brain
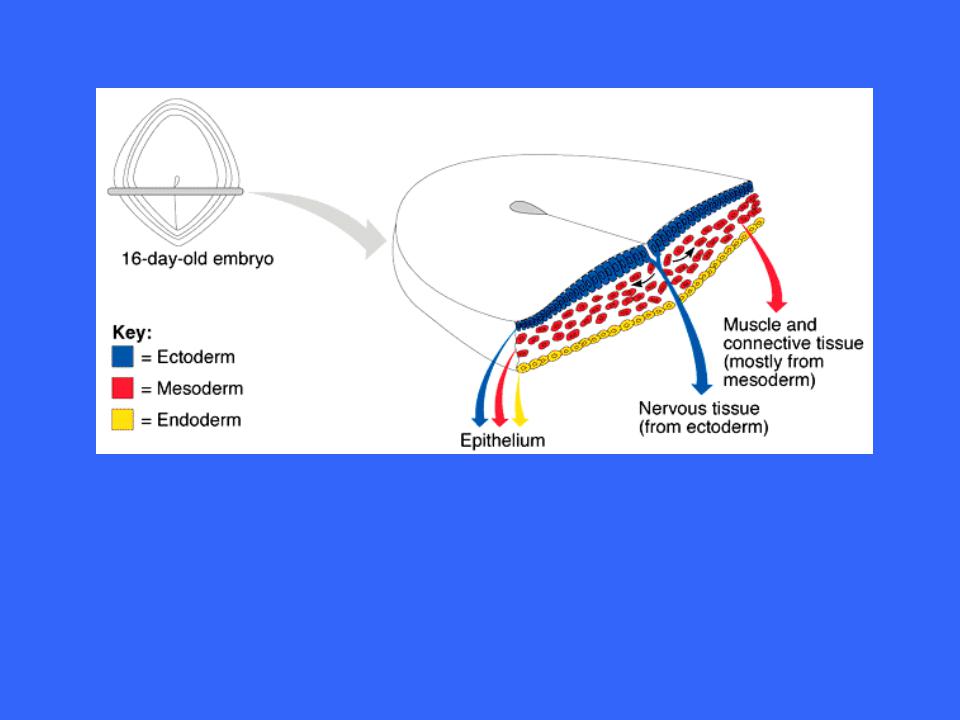
Embryonic Development
Starting in the third week of pregnancy, the ectoderm thickens along the dorsal midline axis of the embryo to form a neural plate
The neural plate eventually gives rise to all neural tissues
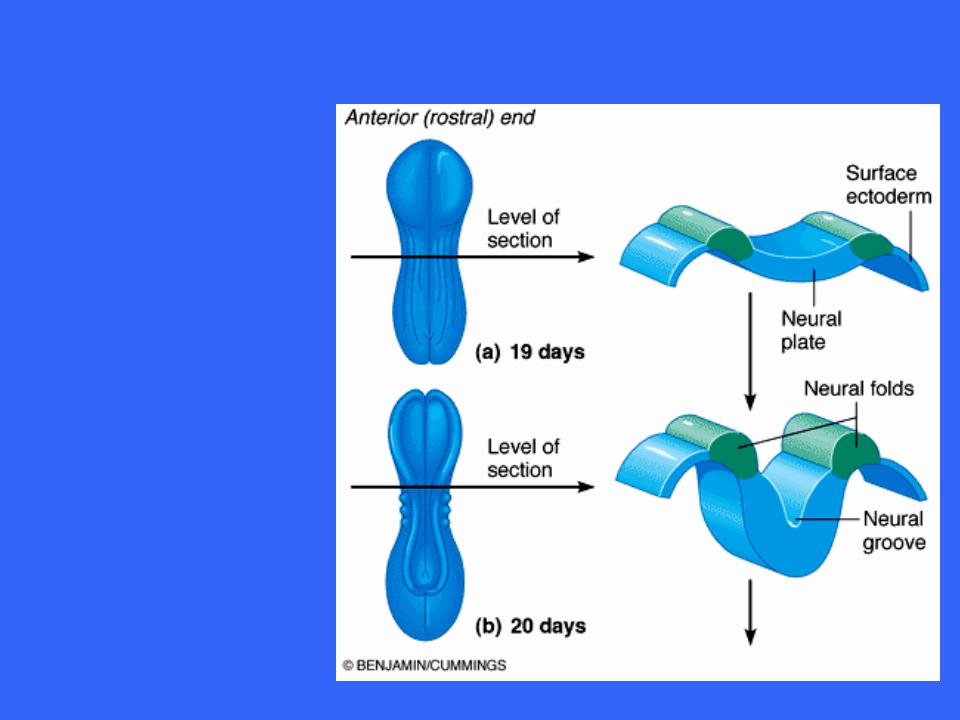
Embryonic Development
The neural plate then invaginates, forming a groove flanked by neural folds
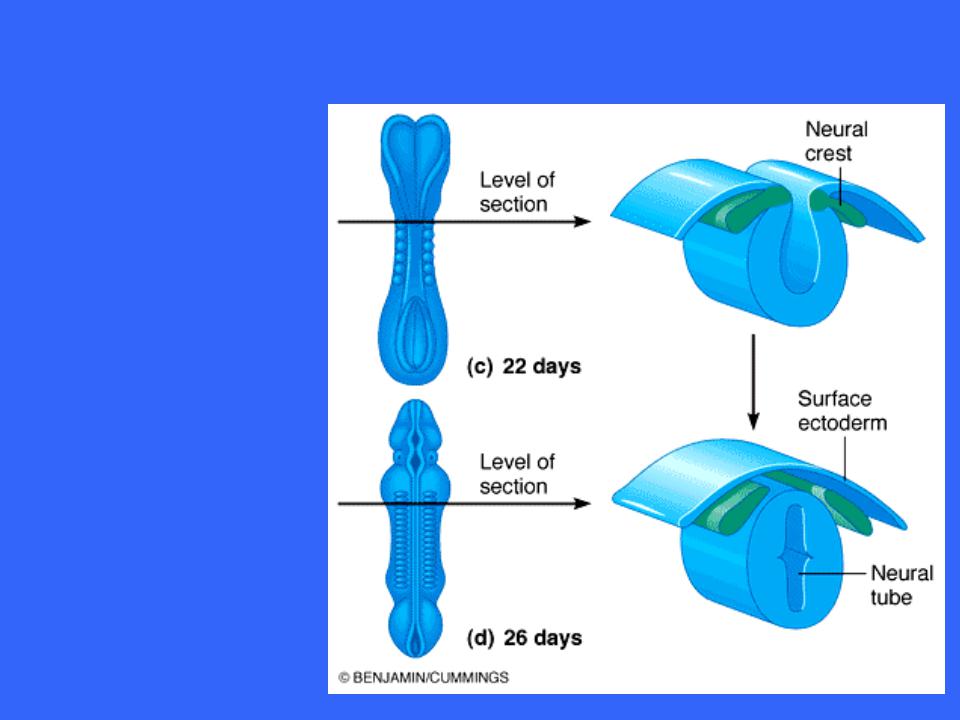
Development of Neural Tube
As the groove deepens the superior edges of the neural folds fuse, forming the neural tube
The tube then detaches from the surface ectoderm and assumes a deeper position in the embryo
Development of Neural Tube
The neural tube is formed by the fourth week of pregnancy and differentiates rapidly into the CNS
The brain forms anteriorly and the spinal cord posteriorly
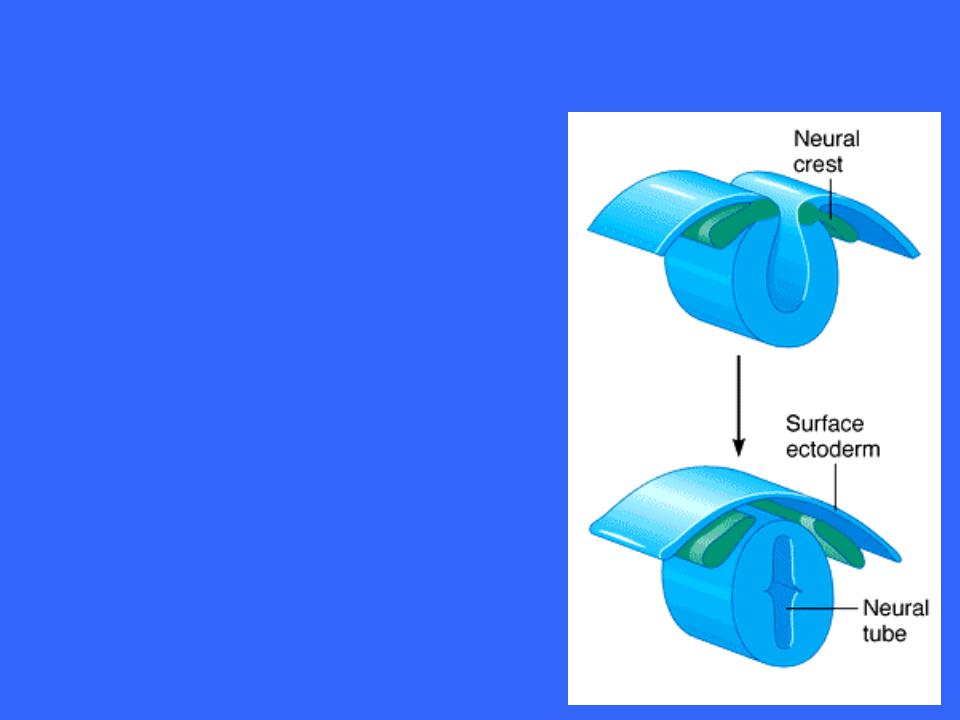
Development of Neural Tube
Small groups of neural fold cells migrate laterally and locate between the surface ectoderm and the neural tube to forming the neural crest
The neural crest gives rise to sensory neurons and some autonomic neurons destined to reside in ganglia

Development of Neural Tube
As soon as the neural tube is formed, its anterior end begins to expand more rapidly than the remaining portion
