- •Chemistry
- •Тема 1. «Наука химия. Отрасли химии». Module 1.
- •Some Facts about Chemistry
- •Тема 2. «Периодический закон д. И. Менделеева». «Атом. Атомная модель. Планетарная модель атома» Module 2
- •Mendeleyev's System of the Elements
- •Module 3
- •Some facts about atom
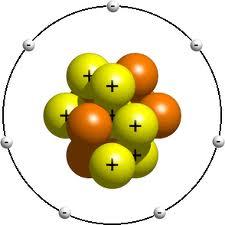
- •The atomic model
- •Тема 3. «Химическая лаборатория. Эксперименты в лаборатории. Правила безопасности в лаборатории». Module 4
- •Laboratory
- •Chemistry Laboratory Safety Rules
- •Тема 4. «Опыты в лаборатории. Пиролиз. Растворы их свойства. Правила безопасности при работе с растворами». Module 5
- •Pyrolysis
- •Module 6
- •Solution
- •Health and safety
- •General precautions
- •Тема 5. «Углерод. Свойства, история открытия. Типы угля. Угли Кузбасса и их использование». Module 7
- •Module 8
- •Types of Coal
- •Тема 6. «Коксование, история процесса и его структура» Module 9
- •Production of coke
- •Тема 7. «Виды коксования и их особенности. Свойства кокса». Module 10
- •History of coke production in the world
- •Coke production
- •Non-Recovery / Heat Recovery Coke Production
- •Module 11
- •Coke Properties
- •Тема 8. «оао «Кокс», структура, история. Продукция». Module 12
- •History and structure of Kemerovo merchant-coke plant
- •Plant flow diagram
- •History of the plant
- •Kemerovo Koks Plant in pictures
- •Coal tar quality, tu 14-7-100-89
- •Тема 9. «оао «Кокс»: инновации, перспективы. Партнеры» Module 13
- •New Automated Covered Coal Warehouse Commissioned at oao “koks”
- •Revise your knowledge and test yourself
- •Appendix List of Chemical elements
Module 3
Task 1. Remember the following words and word combinations:
|
particle – частица copper – медь to come to conclusion – прийти к заключению to summarize – подводить итоги to determine – определять to carry out – проводить contain – содержать charge – заряд |
to exist – существовать to mean – значить, означать to indicate – обозначать to compose – составлять charge – заряд to obtain – получать size – размер relative – относительный concept – понятие |
Task 2. Mind the pronunciation of the following international words. Give Russian equivalents without a dictionary.
atom, extremely, method, molecule, radius, diagram, formula, proton, dioxide, electron, experiment, neutron, regular, quarks, parameters, sulphuric, diameter
Task 3. Translate the following sentences into Russian, paying attention to the passive form of verbs. Rewrite the sentences in the active form.
Model: His work in this field can be relied on.
One can rely on his work in this field.
1. The rate of this reaction can be strongly influenced by high temperature. 2. The changes in these parameters during decomposition were followed by a number of other changes. 3. Common salt was acted upon by sulphuric acid and hydrogen chloride was produced. 4. His work in this field can be relied on. 5. They were told about the new discoveries in oil production. 6. The change in colour was followed by the change of other properties. 7. Fermi is looked upon as an outstanding physicist of our time. 8. The results of their investigation can be referred to. 9. I was asked to attend his lectures on chemistry. 10. Liquid solutions will be dealt with in this chapter. 11. The qualitative examination of these compounds is followed by the quantitative one.
Task 4. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the meaning of the word ''much'':
1. This experiment is much more tedious and time consuming than the first one.
2. That work was much more interesting for us though it was more difficult.
3. The solubility of helium is much less than that of nitrogen.
4. It would be note that as much as 20 per cent of this solvent was used.
5. He worked very much last year and could fulfill as much as 50 per cent of his work.
6. Much attention has been paid to the development of nuclear physics in our country.
7. Much research in the field of atomic structure has been carried out recently.
8. As much as 30 per cent of water was evaporated from this solution upon heating.
9. This new discovery is much spoken about.
Task 5. Read the texts and translate them. Make up a plan, discuss it with other students.
Some facts about atom
Notes on the text
1. X-ray diffraction – дифракция рентгеновским излучением
2. the radius as much as – радиус равен
3. a full stop – точка
4. in the course of – в ходе, в процессе
5. regular arrangement – упорядоченное расположение
An atom may be spoken of as the smallest particle of any substance. If atoms cannot be seen it does not necessarily mean that they do not exist. It indicates that any particles, if present, must be extremely small. There are some methods by means of which the size
|
|
|
of atoms and their arrangement in molecules can be determined. One of these methods uses X-ray diffraction1. The result of a number of investigations show that when atoms are |
in contact with other atoms in molecules, their radius is as much as2 0.1 10–9 m.
Some idea of how small atoms are can be obtained by imagining one million copper atoms (radius = 0.13 10–9 m). If these copper atoms are stacked on top of the other, the pile will be as high as the full stop3 at the end of this sentence.
In the course4 of many investigations, chemists came to a conclusion that the atoms of different elements are all made essentially of three simple types of units, which were referred to as protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are both composed of other particles called quarks and gluons. Protons contain two 'up' quarks and one 'down' quark while neutrons contain one 'up' quark and two 'down' quarks. The gluons are responsible for binding the quarks to one another.
The following diagram shows us the constituents of the atom:
1. Atoms contain the following structural units:
|
Electrons |
Protons |
Neutrons |
|
Charge – 1, very small relative mass |
Charge + 1, relative mass 1 |
Zero charge, relative mass 1 |
2. The numbers of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom of an element can be calculated if the atomic number and relative atomic mass of the element are known:
|
Number of electrons = number of protons = Atomic number of element. |
|
Number of protons + number of neutrons = Relative atomic mass of element. |
It was also found that many elements and compounds are composed of small numbers of atoms which are held together in a regular arrangement5. These groups of atoms are referred to as molecules. The gas hydrogen, for example, is composed of pairs of hydrogen atoms and each pair is called a molecule and its formula is H2.
Another example is the compound carbon dioxide which is composed of molecules, the formula is CO2.