
Fin management materials / 11 P4AFM-Session05_j08
.pdf
SESSION 05 – BASIC INVESTMENT APPRAISAL
Key points
Payback and ARR are commonly used in practice. However neither method informs management of the absolute change in shareholders’ wealth due to a particular project
As well as being able to calculate payback and ARR it is therefore vital that you can also explain why they are not acceptable methods of project appraisal
Discounted cash flow techniques are arguably the most important methods used in financial management.
DCF techniques have two major advantages (i) they focus on cash flow, which is more relevant than the accounting concept of profit (ii) they take into account the time value of money.
NPV must be considered a superior decision-making technique to IRR as it is an absolute measure which tells management the change in shareholders’ wealth expected from a project.
The golden rule – only discount future, incremental, operating cash flows.
Never discount depreciation – it is not a cash flow.
Do not discount finance costs – the cost of finance is measured in the discount rate and is therefore already taken into account.
Exam questions may be in the environment of the UK tax system. Depreciation expense is not a tax allowable deduction in the UK – instead companies can claim Writing Down Allowances/Capital Allowances.
Discounting with inflation is a difficult area. The key here is consistency i.e. if inflation is included in the cash flow forecast then make sure you include it in the discount rate.
Adjusting for changes in working capital is relevant if you are given accruals-based accounting information which needs to be converted to a cash flow basis.
0521

SESSION 05 – BASIC INVESTMENT APPRAISAL
FOCUS
You should now be able to:
¾appraise a project using a variety of profit based and cash flow based methods;
¾understand the benefit and importance of the net present value method;
¾calculate net present values and internal rates of return by identifying relevant cash flows, tax implications and the impact of price level changes.
0522
SESSION 05 – BASIC INVESTMENT APPRAISAL
EXAMPLE SOLUTION
Solution 1
Average annual profit
Total cash flows− Totaldepreciation |
= |
250 −180 |
=17.5 |
|
Noof project years |
4 |
|||
|
|
Average investment
Initial investment+Scrapvalue |
= |
200 + 20 |
=110 |
|
2 |
2 |
|||
|
|
ARR on initial investment 17200.5 ×100 = 8.75%
ARR on average investment 17110.5 ×100 = 15.91%
Solution 2
1 + r = n 1 + R
R = 10% n = 4
1 + r |
= |
4 1.10 |
1 + r |
= |
1.0241 |
3 month interest rate is 2.41%
Discount factor for a cash flow in 3 months time
=1
1.0241
=0.976
0523
SESSION 05 – BASIC INVESTMENT APPRAISAL
Solution 3
Formula
Commentary
The formula always works but take care with + and – signs.
|
|
|
NA |
|
||
IRR ~ A + |
|
(B – A) |
||||
NA −NB |
||||||
|
|
|
71,530 |
|
||
IRR ~ 10 |
+ |
|
|
(15 – 10) |
||
71,530 − 4,370 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||
IRR ~ 10 |
+ 5.325 |
|
|
|||
say 15.4% (rounded up) |
|
|||||
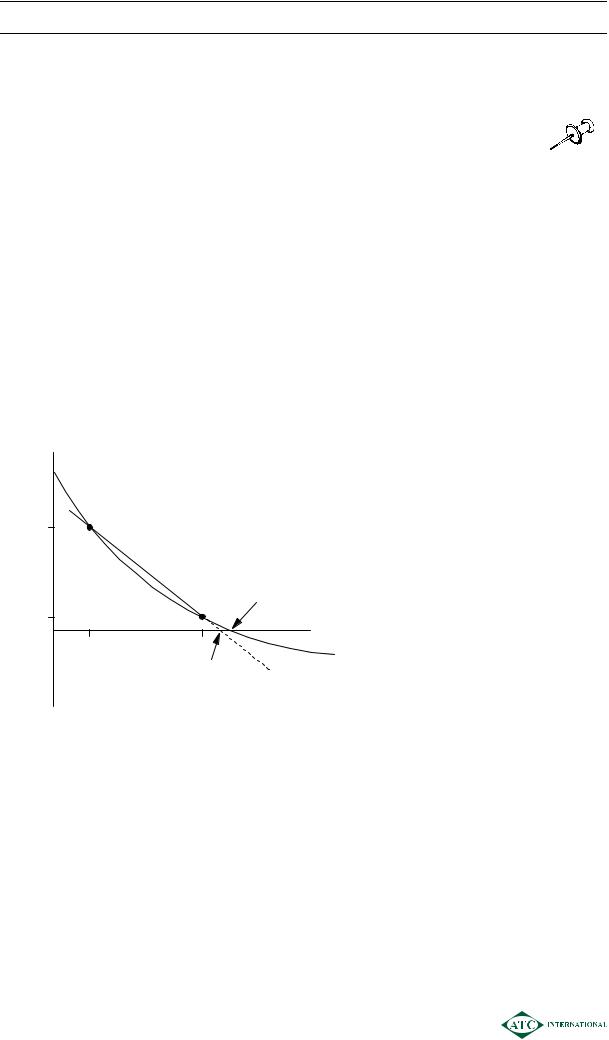
Graphically
NPV
£
Actual
NPV
71,530
Actual
IRR
4,370
10 |
15 |
IRR using formula (extrapolated)
Discount rate
(%)
0524
