
Antibiotics
.pdf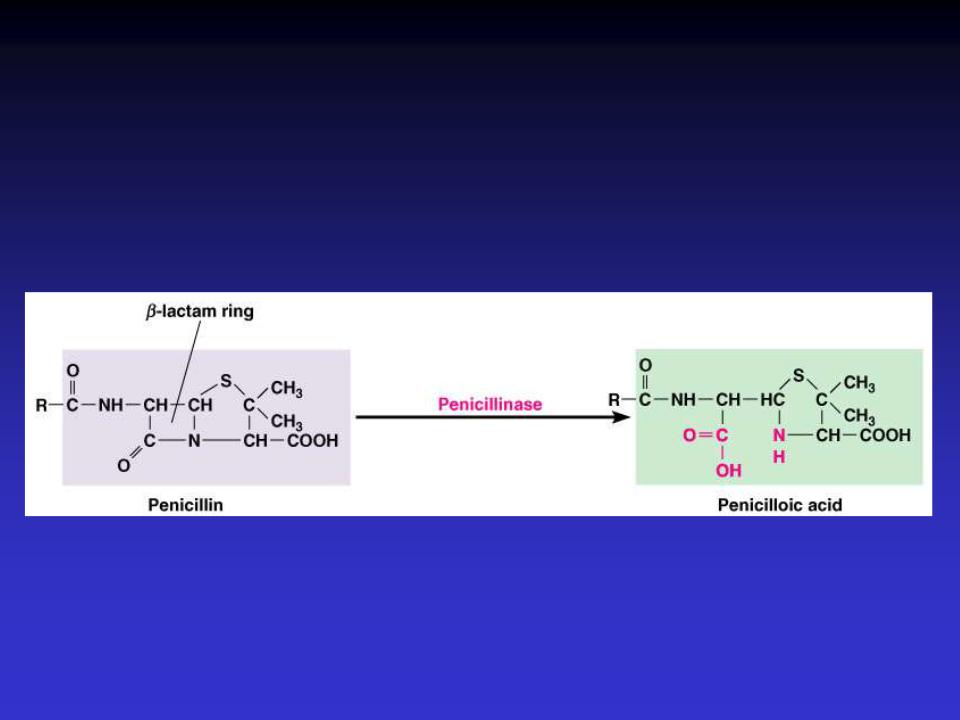
Penicillinase (β Lactamase)
Figure 20.8

Semisynthetic Penicillins
•Penicilinase-resistant penicillins
•Carbapenems: very broad spectrum
•Monobactam: Gram negative
•Extended-spectrum penicillins
•Penicillins + β-lactamase inhibitors

Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall
Synthesis
•Cephalosporins
–2nd, 3rd, and
4th
generations more effective against gramnegatives
Figure 20.9

Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall
Synthesis
•Polypeptide antibiotics
–Bacitracin
•Topical application
•Against gram-positives
–Vancomycin
•Glycopeptide
•Important "last line" against antibiotic resistant S. aureus

Other Inhibitors of Cell Wall
Synthesis
•Antibiotics effective against Mycobacteria: interfere with mycolic acid synthesis or incorporation
–Isoniazid (INH)
–Ethambutol

Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
•Protein synthesis is the end result of two major processes, transcription and translation. An antibiotic that inhibits either of these will inhibit protein synthesis.
•Transcription
•During transcription, the genetic information in DNA is transferred to a complementary sequence of RNA nucleotides by the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
•Antibiotics that either alter the structure of the template DNA or inhibit the RNA polymerase will interfere with the synthesis of RNA, and consequently with protein synthesis.

Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
Actinomycin D binds to guanine in DNA, distorting the DNA, and thus blocking transcription.
Rifampin (Rifampicin or Rifamycin) inhibits protein synthesis by selective inhibiting the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. It does this by binding to the ß subunit in a non-covalent fashion. Antituberculosis
• Quinolones and fluoroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin. Inhibits DNA gyrase Urinary tract infections

Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
Translation
In bacterial cells, the translation of mRNA into protein can be divided into three major phases: initiation, elongation, and termination of the peptide chain.

Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
•Broad spectrum, toxicity problems
•Examples
–Chloramphenicol (bone marrow)
–Aminoglycosides: Streptomycin, neomycin, gentamycin (hearing, kidneys)
–Tetracyclines (Rickettsias & Chlamydia; GI tract)
–Macrolides: Erythromycin (gram +, used in children)

The Cytoplasmic Membrane as the Site
of Antibiotic Action
The cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria is only affected by two clinically-used antibiotics. These are polymyxin B and polymyxin E (colistin). They act by competitively replacing Mg2+ and Ca2+ from negatively charged phosphate groups on membrane lipids. The result is disruption of the membrane.
