
Antibiotics
.pdf
Measuring Antimicrobial
Sensitivity
A more advanced diffusion method, the E test, enables a lab technician to estimate the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC), the lowest antibiotic concentration that prevents visible bacterial growth. A plastic-coated strip
contains |
a |
gradient |
of |
antibiotic |
concentrations, and the MIC can be read from a scale printed on the strip
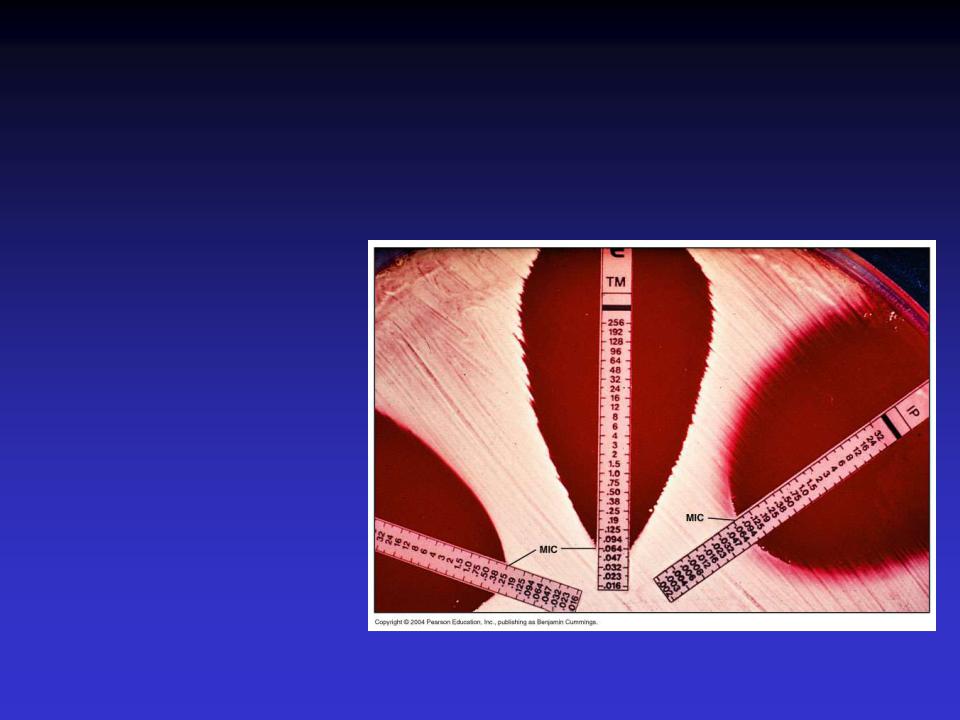
Measuring Antimicrobial
Sensitivity
•E Test
•MIC: Minimal inhibitory concentration

Broth Dilution Tests
A weakness of the diffusion method is that it does not determine whether a drug is bactericidal and not just bacteriostatic. A broth dilution test is often useful in determining the MIC and the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of an antimicrobial drug. The MIC is determined by making a sequence of decreasing concentrations of the drug in a broth, which is then inoculated with the test bacteria

A microdilution, or microtiter, plate used for testing for minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics. Such plates contain as many as 96 shallow wells that contain measured concentrations of antibiotics. They are usually purchased frozen or freeze dried. The test microbe is added simultaneously, with a special dispenser, to all the wells in a row of test antibiotics. A button of growth appears if the antibiotic has no effect on the microbe: the microbe is recorded as not sensitive. If there is no growth in a well, the microbe is sensitive to the antibiotic at that concentration. To ensure that the microbe is capable of growth in the absence of the antibiotic. wells that contain no antibiotic are also inoculated (positive control). To ensure against contamination by unwanted microbes. wells that contain nutrient broth but no antibiotics or inoculum are included (negative control).
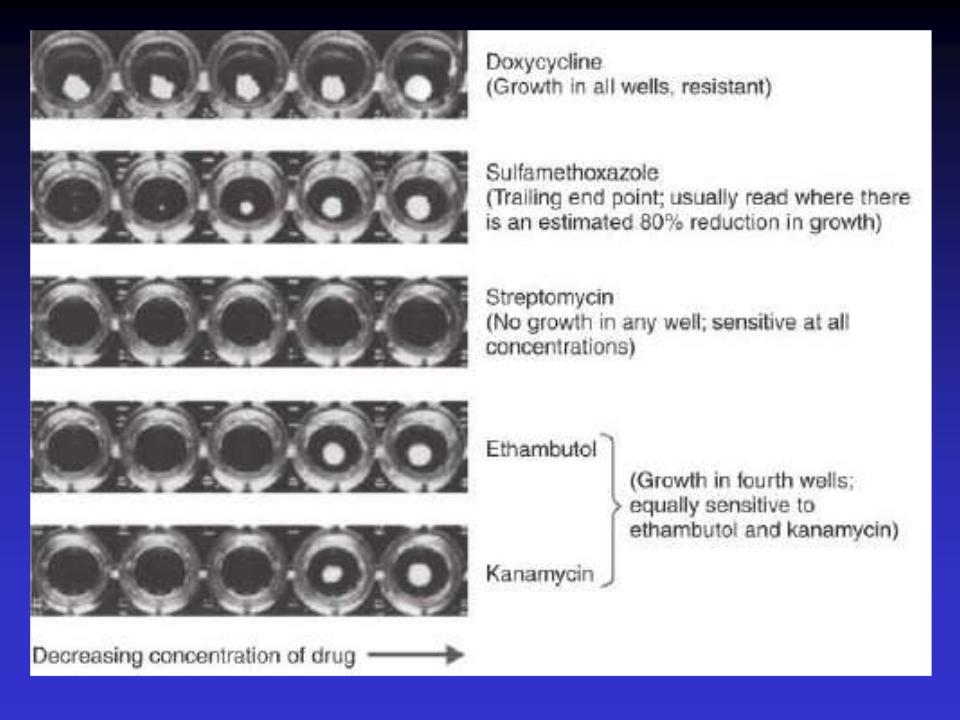
Antibiotic Resistance
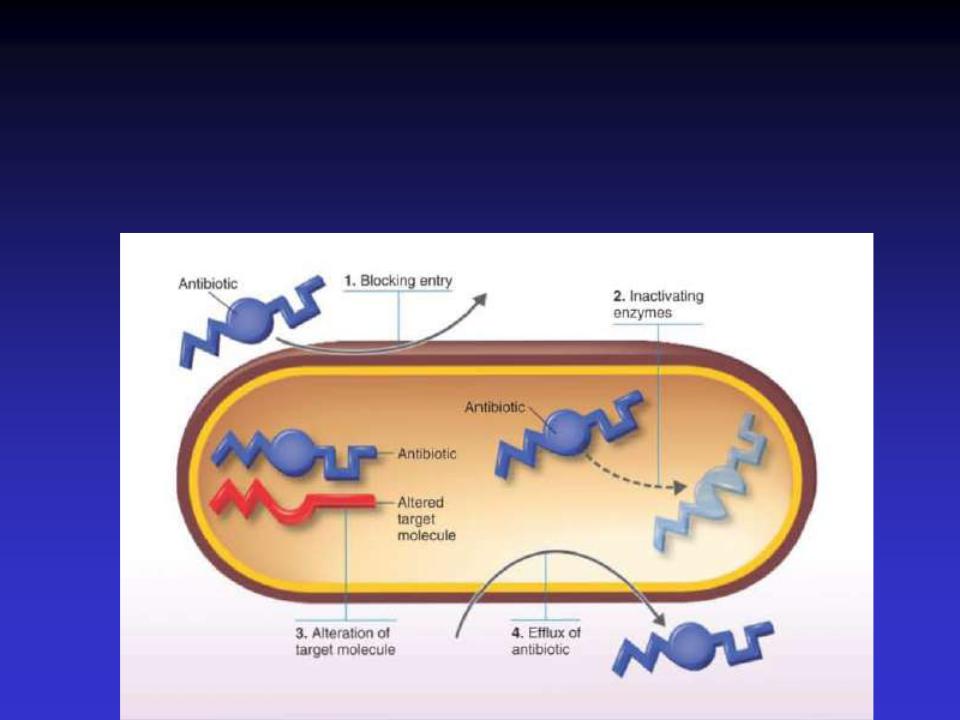
There are only a few major mechanisms by which bacteria become resistant to chemotherapeutic agents.

Mechanisms of Antibiotic
Resistance
•Enzymatic destruction of drug
•Prevention of penetration of drug
•Alteration of drug's target site
•Rapid ejection of the drug

Antibiotic Misuse
Antibiotics have been much misused. A survey in rural Bangladesh, for example, showed that only 8% of antibiotics had been prescribed by a physician. In much of the world, antibiotics are sold to treat headaches and for other inappropriate uses. in the United States, 30% of the antibiotic prescriptions for ear infections, 100% of the prescriptions for the common cold, and 50% of prescriptions for sore throats were unnecessary or inappropriate to treat the problem pathogen. At least half of the more than 100,000 tons of antibiotics consumed in the United States each year are not used to treat disease but are used in animal feeds to promote growth.

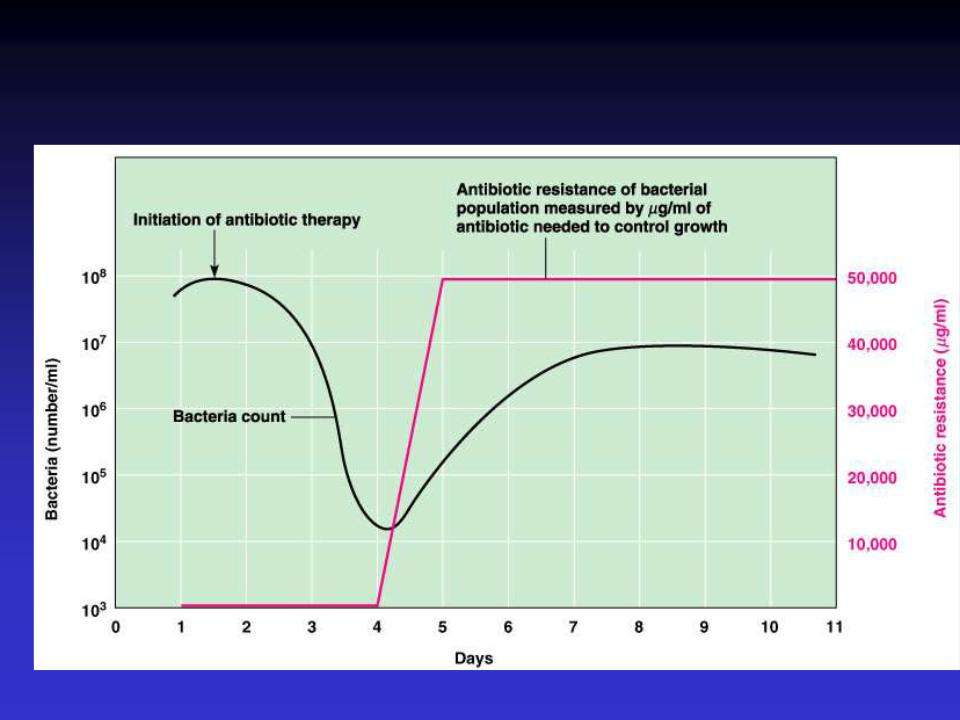
Antibiotic Resistance
Figure 20.20
