
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgments
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •1.2 Forehead Augmentation
- •1.2.1 Discussion
- •1.3.1 Discussion
- •1.4 Rhinoplasty
- •1.4.1 Discussion
- •1.5 Lip Augmentation
- •1.5.1 Discussion
- •1.6 Chin and Jaw Augmentation
- •1.6.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Forehead Augmentation
- •Rhinoplasty
- •Lip Augmentation
- •Jaw Augmentation
- •2: Imaging the Postoperative Orbit
- •2.1 Eyelid Weights
- •2.1.1 Discussion
- •2.2 Palpebral Springs
- •2.2.1 Discussion
- •2.3.1 Discussion
- •2.4.1 Discussion
- •2.5.1 Discussion
- •2.6.1 Discussion
- •2.7 Strabismus Surgery
- •2.7.1 Discussion
- •2.8 Glaucoma Surgery
- •2.8.1 Discussion
- •2.9 Scleral Buckles
- •2.9.1 Discussion
- •2.10 Keratoprostheses
- •2.10.1 Discussion
- •2.11 Intraocular Lens Implants
- •2.11.1 Discussion
- •2.12 Surgical Aphakia
- •2.12.1 Discussion
- •2.13 Pneumatic Retinopexy
- •2.13.1 Discussion
- •2.14 Intraocular Silicone Oil
- •2.14.1 Discussion
- •2.15.1 Discussion
- •2.16 Orbital Tissue Expanders
- •2.16.1 Discussion
- •2.17 Orbital Exenteration
- •2.17.1 Discussion
- •2.18.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Eyelid Weights
- •Palpebral Spring
- •Frontalis Suspension Ptosis Repair
- •Strabismus Surgery
- •Glaucoma Surgery
- •Scleral Buckles
- •Keratoprostheses
- •Intraocular Lens Implants
- •Surgical Aphakia
- •Pneumatic Retinopexy
- •Intraocular Silicone Oil
- •Orbital Tissue Expanders
- •Orbital Exenteration
- •3.1.1 Discussion
- •3.2 Septoplasty
- •3.2.1 Discussion
- •3.3.1 Discussion
- •3.4.1 Discussion
- •3.5 Nasal Packing Material
- •3.5.1 Discussion
- •3.6 Rhinectomy
- •3.6.1 Discussion
- •3.7 Sinus Lift Procedure
- •3.7.1 Discussion
- •3.8 Caldwell-Luc Procedure
- •3.8.1 Discussion
- •3.9 External Ethmoidectomy
- •3.9.1 Discussion
- •3.10.1 Discussion
- •3.11 FESS Complications
- •3.11.1 Discussion
- •3.11.2 Discussion
- •3.11.3 Discussion
- •3.11.4 Discussion
- •3.11.5 Discussion
- •3.11.6 Discussion
- •3.11.7 Discussion
- •3.11.8 Discussion
- •3.11.9 Discussion
- •3.11.10 Discussion
- •3.11.11 Discussion
- •3.12 Osteoplastic Flap with Frontal Sinus Obliteration
- •3.12.1 Discussion
- •3.13 Frontal Sinus Cranialization
- •3.13.1 Discussion
- •3.14 Paranasal Sinus Stents
- •3.14.1 Discussion
- •3.15 Frontal Sinus Trephination
- •3.15.1 Discussion
- •3.16.1 Discussion
- •3.17.1 Discussion
- •3.18 Maxillary Swing
- •3.18.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Septoplasty
- •Nasal Septal Button Prosthesis
- •Nasal Packing Material
- •Rhinectomy
- •Sinus Lift
- •Caldwell-Luc Procedure
- •External Ethmoidectomy
- •Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- •FESS Complications
- •Osteoplastic Flap with Frontal Sinus Obliteration
- •Frontal Sinus Cranialization
- •Paranasal Sinus Stents
- •Frontal Sinus Trephination
- •Maxillectomy and Palatectomy
- •Maxillary Swing
- •4.1 Occipital Nerve Stimulator
- •4.1.1 Discussion
- •4.2 Tissue Expander
- •4.2.1 Discussion
- •4.3 Temporal Fossa Implants
- •4.3.1 Discussion
- •4.4.1 Discussion
- •4.5.1 Discussion
- •4.6.1 Discussion
- •4.7 Scalp Tumor Recurrence
- •4.7.1 Discussion
- •4.8 Burr Holes
- •4.8.1 Discussion
- •4.9 Craniotomy
- •4.9.1 Discussion
- •4.10 Cranioplasty
- •4.10.1 Discussion
- •4.11 Autocranioplasty
- •4.11.1 Discussion
- •4.12.1 Discussion
- •4.14.1 Discussion
- •4.15 Box Osteotomy
- •4.16.1 Discussion
- •4.17.1 Discussion
- •4.18.1 Discussion
- •4.19 Subdural Drainage Catheters
- •4.19.1 Discussion
- •4.20.1 Tension Pneumocephalus
- •4.20.5 Pseudomeningoceles
- •4.20.6 Pseudoaneurysm
- •4.20.7 Postoperative Infection
- •4.20.8 Textiloma
- •4.20.9 Sunken Skin Flap Syndrome
- •4.20.10 External Brain Herniation
- •4.20.11 Bone Flap Resorption
- •Further Reading
- •Occipital Nerve Stimulator
- •Tissue Expander
- •Temporal Fossa Implant
- •Scalp Tumor Recurrence
- •Box Osteotomy
- •Absorbable Hemostatic Agents
- •Duraplasty and Sealant Agents
- •Burr Holes
- •Craniotomy
- •Cranioplasty
- •Autocranioplasty
- •Cranial Vault Reconstruction for Craniosynostosis
- •Cranial Vault Encephalocele Repair
- •Subdural Drainage Catheters
- •Intracranial Pressure Monitor
- •Cranial Surgery Complications
- •5.1 Intraoperative MRI
- •5.1.1 Discussion
- •5.2.1 Stereotactic Biopsy
- •5.2.1.1 Discussion
- •5.2.2 Resection Cavities
- •5.2.2.1 Discussion
- •5.2.3 Ommaya Reservoirs
- •5.2.3.1 Discussion
- •5.2.4 Chemotherapy Wafers
- •5.2.4.1 Discussion
- •5.2.5 Brachytherapy Seeds
- •5.2.5.1 Discussion
- •5.2.6.1 Discussion
- •5.3.1 Prefrontal Lobotomy
- •5.3.1.1 Discussion
- •5.3.2 Pallidotomy
- •5.3.2.1 Discussion
- •5.3.3 Cingulotomy
- •5.3.3.1 Discussion
- •5.3.4.1 Discussion
- •5.3.4.2 Thalamotomy
- •5.3.5 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- •5.3.5.1 Discussion
- •5.3.6.1 Discussion
- •5.3.7.1 Discussion
- •5.3.8.1 Discussion
- •5.3.9.1 Discussion
- •5.3.10 Corticectomy
- •5.3.10.1 Discussion
- •5.3.11.1 Discussion
- •5.3.12.1 Discussion
- •5.3.13 Callosotomy
- •5.3.13.1 Discussion
- •5.3.14 Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
- •5.3.14.1 Discussion
- •5.3.15.1 Discussion
- •5.3.16 Hemispherectomy
- •5.3.16.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Intraoperative MRI
- •Brain Tumor Surgery
- •Stereotactic Biopsy
- •Resection Cavities
- •Postoperative Hemorrhagic Lesions
- •Ommaya Reservoirs
- •Chemotherapy Wafers
- •Brachytherapy Seeds
- •GliaSite Radiation Therapy System
- •Prefrontal Lobotomy
- •Pallidotomy
- •Cingulotomy
- •Thalamotomy
- •Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- •Epidural Motor Cortex Stimulator
- •Neural Interface System (BrainGate)
- •Corticectomy
- •Selective Disconnection
- •Callosotomy
- •Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
- •Hemispherectomy
- •6.1 Types of Procedures
- •6.1.1 External Ventricular Drainage
- •6.1.1.1 Discussion
- •6.1.2.1 Discussion
- •6.1.3 Atypical Ventricular Shunts
- •6.1.3.1 Discussion
- •6.1.4 Ventriculosubgaleal Shunts
- •6.1.4.1 Discussion
- •6.1.5.1 Discussion
- •6.1.6.1 Discussion
- •6.1.7 Subdural-Peritoneal Shunts
- •6.1.7.1 Discussion
- •6.1.8.1 Discussion
- •6.1.9.1 Discussion
- •6.1.10 Lumboperitoneal Shunts
- •6.1.10.1 Discussion
- •6.1.11 Third Ventriculocisternostomy
- •6.1.11.1 Discussion
- •6.1.12.1 Discussion
- •6.1.13 Aqueductoplasty
- •6.1.13.1 Discussion
- •6.1.14.1 Discussion
- •6.2.1.1 Discussion
- •6.2.2.1 Discussion
- •6.2.3 Intraventricular Fat Migration
- •6.2.3.1 Discussion
- •6.2.4.1 Discussion
- •6.2.5.1 Discussion
- •6.2.6 Slit Ventricle Syndrome
- •6.2.6.1 Discussion
- •6.2.7.1 Discussion
- •6.2.8 Shunt-Associated Infections
- •6.2.8.1 Discussion
- •6.2.9.1 Discussion
- •6.2.10.1 Discussion
- •6.2.11.1 Discussion
- •6.2.12 Peritoneal Pseudocysts
- •6.2.12.1 Discussion
- •6.2.13.1 Discussion
- •6.2.14 Tumor Seeding
- •6.2.14.1 Discussion
- •6.2.15 Shunt Catheter Calcification
- •6.2.15.1 Discussion
- •6.2.16.1 Discussion
- •6.2.17.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Types of Procedures
- •External Ventricular Drainage
- •Ventriculoperitoneal Shunts
- •Atypical Ventricular Shunts
- •Ventriculosubgaleal Shunts
- •Subdural-Peritoneal Shunts
- •Lumboperitoneal Shunt
- •Third Ventriculostomy
- •Aqueductoplasty
- •Fourth Ventricular Stenting
- •Complications
- •Intraventricular Fat Migration
- •Slit Ventricle Syndrome
- •Shunt-Associated Infections
- •Shunt Malposition and Migration
- •Pseudocysts
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Syndrome
- •Tumor Seeding
- •Shunt Catheter Calcifications
- •7.1.1 Discussion
- •7.2.1 Discussion
- •7.3.1 Discussion
- •7.4.1 Discussion
- •7.5.1 Discussion
- •7.6.1 Discussion
- •7.7 Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannomas
- •7.7.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Anterior Craniofacial Resection
- •Transsphenoidal Resection
- •Middle Cranial Fossa Reconstruction
- •Surgical Approaches for Vestibular Schwannoma Resection
- •8.1.1 Discussion
- •8.2 Auriculectomy
- •8.2.1 Discussion
- •8.3 Auricular Reconstruction
- •8.3.1 Discussion
- •8.4.1 Discussion
- •8.5 Atresiaplasty
- •8.5.1 Discussion
- •8.6.1 Discussion
- •8.7.1 Discussion
- •8.8 Ossicular Interposition
- •8.8.1 Discussion
- •8.9.1 Discussion
- •8.10.1 Discussion
- •8.11.1 Discussion
- •8.12 Atticotomy
- •8.12.1 Discussion
- •8.13.1 Discussion
- •8.14.1 Discussion
- •8.15.1 Discussion
- •8.16 Temporal Bone Resection
- •8.16.1 Discussion
- •8.17 Cochlear Implants
- •8.17.1 Discussion
- •8.18.1 Discussion
- •8.19.1 Discussion
- •8.20.1 Discussion
- •8.21.1 Discussion
- •8.22 Labyrinthectomy
- •8.22.1 Discussion
- •8.23 Vestibular Nerve Section
- •8.23.1 Discussion
- •8.24.1 Discussion
- •8.25.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •BAHA Device
- •Auriculectomy
- •Auricular Reconstruction
- •Canaloplasty and Meatoplasty
- •Atresiaplasty
- •Myringoplasty and Tympanoplasty
- •Incus Interposition
- •Ossicular Prosthesis Complications
- •Transcanal Atticotomy
- •Mastoidectomy Complications
- •Lateral Temporal Bone Resection
- •Cochlear Implants
- •Cochlear Implant Complications
- •Auditory Brainstem Stimulator
- •Repair of Perilymphatic Fistula
- •Labyrinthectomy
- •Vestibular Nerve Sectioning
- •Tube Drainage of Cholesterol Cysts
- •9.1 Vertical Ramus Osteotomy
- •9.1.1 Discussion
- •9.2 Sagittal Split Osteotomy
- •9.2.1 Discussion
- •9.3 Genioplasty
- •9.3.1 Discussion
- •9.4.1 Discussion
- •9.5 Mandibular Distraction
- •9.5.1 Discussion
- •9.6 LeFort I Osteotomy
- •9.6.1 Discussion
- •9.7 LeFort III Osteotomy
- •9.7.1 Discussion
- •9.8.1 Discussion
- •9.9 Mandibulotomy
- •9.9.1 Discussion
- •9.10 Enucleation
- •9.10.1 Discussion
- •9.11 Cyst Decompression
- •9.11.1 Discussion
- •9.12 Coronoidectomy
- •9.12.1 Discussion
- •9.13.1 Discussion
- •9.14.1 Discussion
- •9.15.1 Discussion
- •9.16.1 Discussion
- •9.17.1 Discussion
- •9.18.1 Discussion
- •9.19.1 Discussion
- •9.20.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Vertical Ramus Osteotomy
- •Sagittal Split Osteotomy
- •Genioplasty
- •Mandibular Angle Augmentation
- •Mandibular Distraction
- •Lefort I Surgery
- •Lefort III Surgery
- •Fixation of Mandible Fractures
- •Mandibulotomy
- •Enucleation
- •Cyst Decompression
- •Coronoidectomy
- •Eminectomy and Meniscal Plication
- •10: Imaging the Postoperative Neck
- •10.1 Reconstruction Flaps
- •10.1.1 Discussion
- •10.2 Neck Dissection
- •10.2.1 Discussion
- •10.3 Parotidectomy
- •10.3.1 Discussion
- •10.4.1 Discussion
- •10.5 Facial Reanimation
- •10.5.1 Discussion
- •10.6.1 Discussion
- •10.7.1 Discussion
- •10.8 Transoral Robotic Surgery
- •10.8.1 Discussion
- •10.9 Sistrunk Procedure
- •10.9.1 Discussion
- •10.10 Laryngectomy
- •10.10.1 Discussion
- •10.11.1 Discussion
- •10.12 Montgomery T-Tubes
- •10.12.1 Discussion
- •10.13 Salivary Bypass Stent
- •10.13.1 Discussion
- •10.14 Laryngeal Stents
- •10.14.1 Discussion
- •10.15.1 Discussion
- •10.16 Arytenoid Adduction
- •10.16.1 Discussion
- •10.17 Arytenoidectomy
- •10.17.1 Discussion
- •10.18 Laryngeal Cartilage Remodeling
- •10.18.1 Discussion
- •10.19 Tracheotomy
- •10.19.1 Discussion
- •10.20 Thyroidectomy
- •10.20.1 Discussion
- •10.21.1 Discussion
- •10.22 Brachytherapy
- •10.22.1 Discussion
- •10.23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- •10.23.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Reconstruction Flaps
- •Facial Reanimation
- •Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
- •Transoral Robotic Surgery
- •Neck Dissection
- •Parotidectomy
- •Salivary Duct Stenting
- •Laryngectomy
- •Montgomery T-Tubes
- •Salivary Bypass Stents
- •Laryngeal Stents
- •Arytenoid Adduction
- •Arytenoidectomy
- •Laryngeal Cartilage Remodeling
- •Tracheotomy
- •Thyroidectomy
- •Neck Exploration and Parathyroidectomy
- •Sistrunk Procedure
- •Brachytherapy
- •Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- •11: Imaging of Postoperative Spine
- •11.1 Overview
- •11.2 Spine Decompression
- •11.2.1.1 Discussion
- •11.2.2 Laminectomy
- •11.2.2.1 Discussion
- •11.2.3 Facetectomy
- •11.2.3.1 Discussion
- •11.2.4 Microdiscectomy
- •11.2.4.1 Discussion
- •11.2.5 Laminoplasty
- •11.2.5.1 Discussion
- •11.2.6 Vertebrectomy
- •11.2.6.1 Discussion
- •11.2.7 Cordectomy
- •11.2.7.1 Discussion
- •11.3.1 Halo and Traction Devices
- •11.3.1.1 Discussion
- •11.3.2 Bone Graft Materials
- •11.3.2.1 Discussion
- •11.3.3 Implantable Bone Stimulators
- •11.3.3.1 Discussion
- •11.3.4 Odontoid Screw Fixation
- •11.3.4.1 Discussion
- •11.3.5 Occipitocervical Fusion
- •11.3.5.1 Discussion
- •11.3.6 Anterior Cervical Fusion
- •11.3.6.1 Discussion
- •11.3.7.1 Discussion
- •11.3.8 Posterior Fusion
- •11.3.8.1 Discussion
- •11.3.9 Scoliosis Rods
- •11.3.9.1 Discussion
- •11.3.10 Vertebral Stapling
- •11.3.10.1 Discussion
- •11.3.11 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib (VEPTR)
- •11.3.11.1 Discussion
- •11.3.12 Interbody Fusion
- •11.3.12.1 Discussion
- •11.4.1 Total Disc Replacement
- •11.4.1.1 Discussion
- •11.4.2.1 Discussion
- •11.4.3.1 Discussion
- •11.4.4 Dynamic Facet Replacement
- •11.4.4.1 Discussion
- •11.4.5 Dynamic Rods
- •11.4.5.1 Discussion
- •11.5.1 Overview
- •11.5.2.1 Discussion
- •11.5.3.1 Discussion
- •11.5.4.1 Discussion
- •11.5.5 Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
- •11.5.5.1 Discussion
- •11.5.6.1 Discussion
- •11.5.7 Surgical Site Infections
- •11.5.7.1 Discussion
- •11.5.8 Postoperative Neuritis
- •11.5.8.1 Discussion
- •11.5.9 Arachnoiditis
- •11.5.9.1 Discussion
- •11.5.10.1 Discussion
- •11.5.11 Postoperative Synovial Cyst
- •11.5.11.1 Discussion
- •11.5.12 Residual/Recurrent Tumors
- •11.5.12.1 Discussion
- •11.5.13 Inclusion Cysts
- •11.5.13.1 Discussion
- •11.5.14.1 Discussion
- •11.5.15 Retained Surgical Tools
- •11.5.15.1 Discussion
- •11.5.16 Gossypiboma
- •11.5.16.1 Discussion
- •11.5.17.1 Discussion
- •11.5.18 Postoperative Deformity
- •11.5.18.1 Discussion
- •11.6.1 Discussion
- •11.7 Spinal Cord Stimulators
- •11.7.1 Discussion
- •11.8 Filum Terminale Sectioning
- •11.8.1 Discussion
- •11.9.1 Vertebral Augmentation
- •11.9.1.1 Discussion
- •11.9.2 Kiva Device
- •11.9.2.1 Discussion
- •11.9.3 Sacroplasty
- •11.9.3.1 Discussion
- •11.9.4.1 Discussion
- •11.9.5.1 Discussion
- •11.9.6.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Overview
- •Laminectomy
- •Facetectomy
- •Microdiscectomy
- •Laminoplasty
- •Vertebrectomy
- •Cordectomy
- •Bone Graft Materials
- •Implantable Bone Stimulators
- •Odontoid Screw Fixation
- •Anterior Cervical Fusion
- •Posterior Fusion
- •Occiptiocervical Fusion
- •Scoliosis Rods
- •Vertebral Stapling
- •Interbody Fusion
- •Nucleus Pulposus Replacement
- •Dynamic Facet Replacement
- •Dynamic Rods
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
- •Seromas and Hematomas
- •Postoperative Infection
- •Postoperative Neuritis
- •Arachnoiditis
- •Postoperative Synovial Cyst
- •Residual/Recurrent Tumors
- •Inclusion Cysts
- •Retained Surgical Tools
- •Gossypiboma
- •Postoperative Deformity
- •Intrathecal Spinal Infusion Pump
- •Spinal Cord Stimulators
- •Filum Terminale Sectioning
- •Kiva Device
- •Sacroplasty
- •Percutaneous Spine Fusion
- •CT-Guided Epidural Blood Patch
- •12.1 Vascular Surgery
- •12.1.1.1 Discussion
- •12.1.2.1 Discussion
- •12.1.3.1 Discussion
- •12.1.4.1 Discussion
- •12.1.6.1 Discussion
- •12.1.7 Carotid Endarterectomy
- •12.1.7.1 Discussion
- •12.1.8 Carotid Body Stimulation
- •12.1.8.1 Discussion
- •12.1.9 Adjustable Vascular Clamp
- •12.1.9.1 Discussion
- •12.1.10.1 Discussion
- •12.2 Endovascular Surgery
- •12.2.7 Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Intra-arterial Thrombolysis or Embolectomy
- •12.2.10 Endovascular Stent Reconstructive Treatment for Extracranial Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- •12.2.11 Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Active Extracranial Hemorrhage or Pseudoaneurysm
- •Further Reading
- •Vascular Surgery
- •Aneurysm and Hemostatic Ligation Clips
- •Intracranial Aneurysm Muscle Wrap
- •Vascular Malformation Surgery
- •Carotid Endarterectomy
- •Carotid Body Stimulation
- •Adjustable Vascular Clamp
- •Reconstruction of the Great Vessels
- •Endovascular Surgery
- •General Imaging Considerations Following Endovascular Cerebrovascular Procedures
- •Endovascular Treatment for Aneurysms
- •Endovascular Stent Reconstructive Treatment for Extracranial Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- •Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Active Extracranial Hemorrhage or Pseudoaneurysm
- •Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Venous Stenosis and Occlusion
- •Index

|
|
Jordan DR, St Onge P, Anderson RL, Patrinely JR, Nerad |
|||
|
|
JA (1992) Complications associated with alloplastic |
|||
|
|
implants used in orbital fracture repair. Ophthalmology |
|||
|
|
99(10):1600–1608 |
|
||
|
|
Lelli GJ Jr, Milite J, Maher E (2007) Orbital floor frac- |
|||
Caesar RH, Friebel J, McNab AA (2004) Upper lid load- |
tures: evaluation, indications, approach, and pearls |
||||
ing with gold weights in paralytic lagophthalmos: a |
from an ophthalmologist’s perspective. Facial Plast |
||||
modified technique to maximize the long-term func- |
Surg 23(3):190–199 |
|
|||
tional and cosmetic success. Orbit 23(1):27–32 |
Liss J, Stefko ST, Chung WL (2010) Orbital surgery: state |
||||
Jayashankar N, Morwani KP, Shaan MJ, Bhatia SR, Patil |
of the art. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am |
||||
KT (2008) Customized gold weight eyelid implanta- |
22(1):59–71 |
|
|
||
tion in paralytic lagophthalmos. J Laryngol Otol |
Mauriello JA Jr (1987) Complications of orbital trauma |
||||
122(10):1088–1091 |
|
surgery. Adv Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 7: |
|||
Kartush JM, Linstrom CJ, McCann PM, Graham MD (1990) |
99–115 |
|
|
||
Early gold weight eyelid implantation for facial paralysis. |
|
|
|
||
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 103(6):1016–1023 |
|
|
|
||
Marra S, Leonetti JP, Konior RJ, Raslan W (1995) Effect |
|
|
|
||
of magnetic resonance imaging on implantable eyelid |
Orbital Decompression for |
||||
weights. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104(6):448–452 |
Dysthyroid Orbitopathy |
||||
|
|
||||
Palpebral Spring |
|
Hu WD, Annunziata CC, Chokthaweesak W, Korn BS, |
|||
|
Levi L, Granet DB, Kikkawa DO (2010) Radiographic |
||||
|
|
analysis of extraocular muscle volumetric changes in |
|||
Bergeron CM, Moe KS (2008) The evaluation and treat- |
thyroid-related orbitopathy following orbital decom- |
||||
pression. Ophthal |
Plast Reconstr Surg 26(1): |
||||
ment of upper eyelid paralysis. Facial |
Plast Surg |
||||
1–6 |
|
|
|||
24(2):220–230 |
|
|
|
||
|
Leong SC, White PS (2010) Outcomes following surgical |
||||
Demirci H, Frueh BR (2009) Palpebral spring in the man- |
|||||
decompression |
for |
dysthyroid orbitopathy (Graves’ |
|||
agement of lagophthalmos and exposure keratopathy |
|||||
disease). Curr |
Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg |
||||
secondary to facial nerve palsy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr |
|||||
18(1):37–43 |
|
|
|||
Surg 25(4):270–275 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
Terzis JK, Kyere SA (2008) Experience with the gold weight |
|
|
|
||
and palpebral spring in the management of paralytic lag- |
|
|
|
||
ophthalmos. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(3):806–815 |
Dacryocystorhinostomy and |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
Nasolacrimal Duct Stents |
|||
Frontalis Suspension Ptosis Repair |
|
|
71 |
||
Nakauchi K, Mito H, Mimura O (2013) Frontal suspen- |
|
|
|||
sion for congenital ptosis using an expanded polytetra- |
|
|
|||
fluoroethylene (Gore-Tex(®)) sheet: |
one-year |
|
|
||
follow-up. Clin Ophthalmol 7:131–136 |
|
|
|
||
Kokubo K, Katori N, Hayashi K, Kasai K, Kamisasanuki |
|
|
|||
T, Sueoka K, Maegawa J (2016) Frontalis suspension |
|
|
|||
with an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene sheet for |
|
|
|||
congenital ptosis repair. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg |
|
|
|||
69:673–678 |
|
|
|
||
Orbital Wall Reconstruction and |
|
|
|
||
Augmentation |
|
|
|
||
2 Imaging the Postoperative Orbit |
|
|
|
||
Further Reading |
|
|
|
|
|
Eyelid Weights
Badilla J, Dolman PJ (2007) Cerebrospinal fluid leaks complicating orbital or oculoplastic surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 125(12):1631–1634
72 |
D.T. Ginat et al. |
|
|
Strabismus Surgery
Mehendale RA, Dagi LR, Wu C, Ledoux D, Johnston S, Hunter DG (2012) Superior rectus transposition and medial rectus recession for Duane syndrome and sixth nerve palsy. Arch Ophthalmol 130(2):195–201
Nishida Y, Inatomi A, Aoki Y, Hayashi O, Iwami T, Oda S, Nakamura J, Kani K (2003) A muscle transposition procedure for abducens palsy, in which the halves of the vertical rectus muscle bellies are sutured onto the sclera. Jpn J Ophthalmol 47(3):281–286
Yurdakul NS, Ugurlu S, Maden A (2011) Surgical management of chronic complete sixth nerve palsy. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 42(1):72–77
Glaucoma Surgery
Ceballos EM, Parrish RK 2nd (2002) Plain film imaging of Baerveldt glaucoma drainage implants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23(6):935–937
Dugel PU, Heuer DK, Thach AB, Baerveldt G, Lee PP, Lloyd MA, Minckler DS, Green RL (1997) Annular peripheral choroidal detachment simulating aqueous misdirection after glaucoma surgery. Ophthalmology 104(3):439–444
Freedman J (2010) What is new after 40 years of glaucoma implants. J Glaucoma 19(8):504–508
Jeon TY, Kim HJ, Kim ST, Chung TY, Kee C (2007) MR imaging features of giant reservoir formation in the orbit: an unusual complication of Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(8):1565–1566
Lachkar Y, Hamard P (2002) Nonpenetrating filtering surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 13(2):110–115
Patel S, Pasquale LR (2010) Glaucoma drainage devices: a review of the past, present, and future. Semin Ophthalmol 25(5–6):265–270
Pirouzian A, Scher C, O’Halloran H, Jockin Y (2006) Ahmed glaucoma valve implants in the pediatric population: the use of magnetic resonance imaging findings for surgical approach to reoperation. J AAPOS 10(4):340–344
Scleral Buckles
Bernardino CR, Mihora LD, Fay AM, Rubin PA (2006) Orbital complications of hydrogel scleral buckles. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 22(3):206–208
Bhagat N, Khanna A, Langer PD (2005) Hydrated scleral buckle: a late complication of MAI explants. Br J Ophthalmol 89(10):1380
Lane JI, Randall JG, Campeau NG, Overland PK, McCannel CA, Matsko TA (2001) Imaging of hydro-
gel episcleral buckle fragmentation as a late complication after retinal reattachment surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22(6):1199–1202
Lane JI, Watson RE Jr, Witte RJ, McCannel CA (2003) Retinal detachment: imaging of surgical treatments and complications. Radiographics 23(4):983–994
Ginat DT, Singh AD, Moonis G. (2012) Multimodality imaging of hydrogel scleral buckles. Retina. 32:1449–1452
Keratoprostheses
Colby KA, Koo EB (2011) Expanding indications for the Boston keratoimplant. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 22(4):267–273
Garcia JP Jr, de la Cruz J, Rosen RB, Buxton DF (2008) Imaging implanted keratoprostheses with anterior- segment optical coherence tomography and ultrasound biomicroscopy. Cornea 27(2):180–188
Gomaa A, Comyn O, Liu C (2010) Keratoprostheses in clinical practice – a review. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 38(2):211–224
Robert MC, Harissi-Dagher M (2011) Boston type 1 keratoimplant: the CHUM experience. Can J Ophthalmol 46(2):164–168
Intraocular Lens Implants
Aksoy FG, Gomori JM, Halpert M (1999) CT and MR imaging of contact lenses and intraocular lens implants. Comput Med Imaging Graph 23(4):205–208
Bucher PJ, Büchi ER, Daicker BC (1995) Dystrophic calcification of an implanted hydroxyethylmethacrylate intraocular lens. Arch Ophthalmol 113(11):1431–1435 Kuo MD, Hayman LA, Lee AG, Mayo GL, Diaz-Marchan PJ (1998) In vivo CT and MR appearance of prosthetic intra-
ocular lens. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(4):749–753 Rofagha S, Bhisitkul RB (2011) Management of retained
lens fragments in complicated cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 22(2):137–140
Sourdille P (1997) Lensectomy-vitrectomy indications and techniques in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 8(1):56–59
Yong JL, Lertsumitkul S, Killingsworth MC, Filipic M (2004) Calcification of intraocular hydrogel lens: evidence of dystrophic calcification. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 32(5):492–500
Surgical Aphakia
Sourdille P (1997) Lensectomy-vitrectomy indications and techniques in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 8(1):56–59
2 Imaging the Postoperative Orbit |
73 |
|
|
Pneumatic Retinopexy
Berrod JP, Rozot P, Raspiller A, Thiery D (1994–1995) Fluid air exchange in vitreo retinal surgery. Int Ophthalmol 18(4):237–241
Chan CK, Lin SG, Nuthi AS, Salib DM (2008) Pneumatic retinopexy for the repair of retinal detachments: a comprehensive review (1986–2007). Surv Ophthalmol 53(5):443–448
Krzystolik MG, D’Amico DJ (2000) Complications of intraocular tamponade: silicone oil versus intraocular gas. Int Ophthalmol Clin 40(1):187–200
Wirostko WJ, Han DP, Perkins SL (2000) Complications of pneumatic retinopexy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 11(3): 195–200
Intraocular Silicone Oil
Eller AW, Friberg TR, Mah F (2000) Migration of silicone oil into the brain: a complication of intraocular silicone oil for retinal tamponade. Am J Ophthalmol 129: 685–688
Fangtian D, Rongping D, Lin Z, Weihong Y (2005) Migration of intraocular silicone into the cerebral ventricles. Am J Ophthalmol 140:156–158
Herrick RC, Hayinan LA, Maturi RK, Diaz-Marchan PJ, Tang RA, Lambert HM (1998) Optimal imaging protocol after intraocular silicone oil tamponade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:101–108
Lane JI, Watson RE, Witte RJ, McCannel CA (2003) Retinal detachment: imaging of surgical treatments and complications. Radiographics 23:983–994
Mathews VP, Elster AD, Barker PB, Buff BL, Haller JA, Greven CM (1994) Intraocular silicone oil: in vitro and in vivo MR and CT characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:343–347
Evisceration, Enucleation, and Globe
Prostheses
Christmas NJ, Gordon CD, Murray TG, Tse D, Johnson T, Garonzik S, O’Brien JM (1998) Intraorbital implants
after enucleation and their complications: a 10-year review. Arch Ophthalmol 116(9):1199–1203
LeBedis CA, Sakai O (2008) Nontraumatic orbital conditions: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging in the emergent setting. Radiographics 28(6):1741–1753
Orbital Tissue Expanders
Mazzoli RA, Raymond WR 4th, Ainbinder DJ, Hansen EA (2004) Use of self-expanding, hydrophilic osmotic expanders (hydrogel) in the reconstruction of congenital clinical anophthalmos. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 15(5):426–431
Tse DT, Abdulhafez M, Orozco MA, Tse JD, Azab AO, Pinchuk L (2011) Evaluation of an integrated orbital tissue expander in congenital anophthalmos: report of preliminary clinical experience. Am J Ophthalmol 151(3):470–82.e1
Orbital Exenteration
Nassab RS, Thomas SS, Murray D (2007) Orbital exenteration for advanced periorbital skin cancers: 20 years experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60(10): 1103–1109
Tyers AG (2006) Orbital exenteration for invasive skin tumours. Eye (Lond) 20(10):1165–1170
Orbital Radiation Therapy Fiducial
Markers
Ahn YC, Lee KC, Kim DY, Huh SJ, Yeo IH, Lim DH, Kim MK, Shin KH, Park S, Chang SH (2000) Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for extracranial head and neck tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48(2): 501–505
Daftari IK, Aghaian E, O’Brien JM, Dillon W, Phillips TL (2005) 3D MRI-based tumor delineation of ocular melanoma and its comparison with conventional techniques. Med Phys 32(11):3355–3362

Imaging the Paranasal Sinuses |
3 |
and Nasal Cavity |
Daniel Thomas Ginat, Mary Elizabeth Cunnane,
and Robert M. Naclerio
3.1\ Nasal Fracture Reconstruction
(Posttraumatic Rhinoplasty)
3.1.1\ Discussion
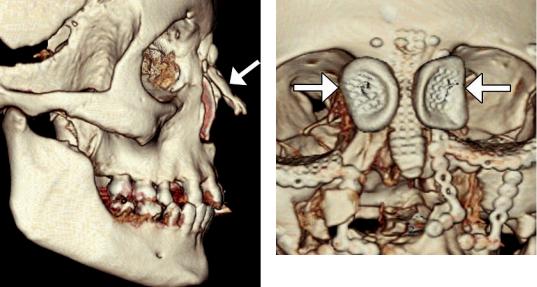
The aim of posttraumatic rhinoplasty surgery is to restore the pretraumatic state and normal function and appearance of the nose. The surgical technique depends on the degree of comminution, associated septal fracture, and presence of other facial fractures. Internal and external fixation approaches can be implemented. Bone grafting can be used to
reconstruct substantial defects (Fig. 3.1). Lowprofile mesh material provides fracture fixation with good cosmetic results (Fig. 3.2). Likewise, temporary external plates and transcutaneous wire can help restore satisfactory alignment. Nasal stents are sometimes inserted to maintain patent nasal passages, while the fracture and associated soft tissue injury heal. CT is generally the imaging modality of choice for postoperative traumatic rhinoplasty assessment. Low-radiation dose techniques are typically adequate. Cosmetic rhinoplasty is otherwise discussed in Chap. 1.
D.T. Ginat, M.D., M.S. (*)
Department of Radiology, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA e-mail: dtg1@uchicago.edu
M.E. Cunnane, M.D.
Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary,
Boston, MA, USA
R.M. Naclerio, M.D.
Section of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA
© Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2017 |
75 |
D.T. Ginat, P.-L.A. Westesson (eds.), Atlas of Postsurgical Neuroradiology,
DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-52341-5_3
76 |
D.T. Ginat et al. |
|
|
Fig. 3.1 Cortical bone reconstruction. 3D CT image shows cortical bone graft positioned along the expected site of the nasal dorsum (arrow) and absence of the native nasal bones and frontal processes of the maxilla
Fig. 3.2 Nasal fracture reconstruction with low-profile mesh. 3D CT image shows a mesh positioned along the nasal dorsum secured via low-profile screws. There are also bilateral molded polyvinyl siloxane plates (arrows) fit over the nasal soft tissue in the medial canthal area and secured via transcutaneous wires
